Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes (Intro To Conic Sections)
Notes (Intro To Conic Sections)
Uploaded by
Not MeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes (Intro To Conic Sections)
Notes (Intro To Conic Sections)
Uploaded by
Not MeCopyright:
Available Formats
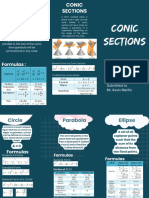
INTRODUCTION TO CONIC SECTIONS
Objective/s:
• Illustrate the different types of conic sections: circles, parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas and degenerated
cases.
Definition of Terms: →
Double Right Circular Cone → formed when a straight line intersects a vertical line at fixed point and
rotates about that fixed point
→ consists of two cones joined at a fixed point and has a circular base
Vertex → fixed point joining the two cones of the double right circular cone
Generator → the line that rotates the vertical line
Axis → the fixed/vertical line where the generator rotates and perpendicular to
the circular base
Directrix → the perimeter of the circular base
Nappe → the lateral surface of the right circular cone
→ the double right circular cone is composed of two nappes:
upper nappe (above the vertex) and lower nappe (below the vertex)
Vertex Angle → the angle between the generator and the axis
CONIC SECTIONS – the two dimensional curves formed when the plane intersects
a double right circular cone (depending on the angle made by
plane with the axis of the cone)
a. Ellipse → (closed curve) when the plane intersects to one nappe of the double right circular cone and
the angle formed between the plane and the axis is greater than the vertex angle
b. Circle → (closed curve and special type of ellipse) when the plane is perpendicular to the axis
c. Parabola → (open curve) when the plane intersects to one nappe of the double right circular cone and the
angle formed between the plane and the axis is exactly equal to the vertex angle
d. Hyperbola → (two disjoint open curves) when the plane intersects both the nappes of the double right
circular cone and the angle formed between the plane and the axis is less than the vertex angle
e. Degenerate Conics → Point (Ellipse) - when the plane intersects the vertex of the cone the angle formed
between the plane and the axis is greater than the vertex angle
→ Line (Parabola) - when the plane intersects the vertex of the cone the angle formed
between the plane and the axis is exactly equal to the vertex angle
→ Two Intersecting Line (Hyperbola) - when the plane intersects the vertex of the cone
the angle formed between the plane and the axis is less than the vertex angle
Reference:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HO2zAU3Eppo
You might also like
- 8 CW 5-2Document2 pages8 CW 5-2Kayla IkumaNo ratings yet
- Conics 1 Cut ConeDocument11 pagesConics 1 Cut ConeMarc LambertNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11Document5 pagesCONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- Synch1-How Conic Sections Are FormedDocument49 pagesSynch1-How Conic Sections Are FormedAlkirsten GalvezNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument10 pagesConic SectionsJunna Mae GimongalaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Prepared By: Ms. Daina Rose CacaitDocument20 pagesConic Sections: Prepared By: Ms. Daina Rose Cacait11 STEM 4-Petilona Vincent C.No ratings yet
- L1 Intro To Conic SectionDocument36 pagesL1 Intro To Conic Sectionjinnie kimNo ratings yet
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) Conic Section 3D Animation (DownSub - Com)Document3 pages(English (Auto-Generated) ) Conic Section 3D Animation (DownSub - Com)cale suarezNo ratings yet
- In This Module, You Have Learnt: X: Vertex Angle, The Hyperbola Is FormedDocument1 pageIn This Module, You Have Learnt: X: Vertex Angle, The Hyperbola Is Formedshad bostonNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS and Circles Grade 11Document7 pagesCONIC SECTIONS and Circles Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - An Overview of Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - An Overview of Conic SectionsIresh Gail DoriaNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument14 pagesConic SectionsjbdliganNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Conic SectionsDocument4 pagesConcepts of Conic SectionsMario AnacletoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Mendoza, Jillea RDocument4 pagesAssignment - Mendoza, Jillea Rjillea mendozaNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Maths Project PDFDocument13 pagesConic Section Maths Project PDFSiva Kumar75% (4)
- Conic Section True or FalseDocument1 pageConic Section True or FalseFlorence T. CaceresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 An Overview of Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesLesson 1 An Overview of Conic SectionsIresh Gail DoriaNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument11 pagesConic SectionsSamantha Marie DiabocoNo ratings yet
- Precal M1Document1 pagePrecal M1Eme RoseNo ratings yet
- PRECAL - Lesson 1 - Introduction To Conic SectionDocument23 pagesPRECAL - Lesson 1 - Introduction To Conic SectionmanansalastarringNo ratings yet
- Blue White Geometric Modern Sea Travel BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue White Geometric Modern Sea Travel Brochurenightmarehappy142No ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Parts of ConicsDocument16 pagesConic Sections: Parts of ConicsSophia AbendanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic SectionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Conic SectionEJ ARREZANo ratings yet
- Thea Pre-Cal IntroDocument1 pageThea Pre-Cal IntrotheaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1ruth torzarNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument38 pagesHyperbolaMarineth MonsantoNo ratings yet
- The Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesThe Conic SectionsDominic RagoNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Discussion RoughDocument8 pagesConic Section Discussion RoughSamantha BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- To Conic Sections: Prepared By: Miss Carizza BatacDocument24 pagesTo Conic Sections: Prepared By: Miss Carizza BatacBruceNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument26 pagesConic SectionRyōsei TanakaNo ratings yet
- PC Reviewer Q1Document4 pagesPC Reviewer Q1Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document22 pagesPresentation 1Amit YadavNo ratings yet
- ELECTIVE-MATHEMATICS-10-Module-5 Degeneration of ConicsDocument13 pagesELECTIVE-MATHEMATICS-10-Module-5 Degeneration of ConicsFVERON, JESSICA FABELLORENo ratings yet
- Conic Section - CircleDocument8 pagesConic Section - CircleAPngnbnNo ratings yet
- From The Article That You Have Read, List The 4 Conic Sections and Describe Each. Draw Each Conic Section and Label The PartsDocument2 pagesFrom The Article That You Have Read, List The 4 Conic Sections and Describe Each. Draw Each Conic Section and Label The PartsRafael CunetaNo ratings yet
- Precal 1Document43 pagesPrecal 1Xzy BuenafeNo ratings yet
- 11 ConicsDocument9 pages11 Conicsshubhamdalal.anmNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Conics or Conic Sections Were Studied by Greek Mathematicians, With ApolloniusDocument18 pagesConic Sections: Conics or Conic Sections Were Studied by Greek Mathematicians, With ApolloniusS P ECIALISENo ratings yet
- Lect-1 Introduction To Conics and EllipseDocument23 pagesLect-1 Introduction To Conics and EllipseSachin SawantNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument5 pagesPre CalCristina Astrero BisqueraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic Sections: Lesson 1Document3 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sections: Lesson 1Jan RobertsNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Conic Sections: DefinitionDocument2 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Conic Sections: DefinitionAdrian DiazNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument6 pagesPre CalPaul Mikko MolonNo ratings yet
- q1 Precal Notes (In Progress)Document20 pagesq1 Precal Notes (In Progress)saturosjuliaclarisseNo ratings yet
- Defining Conic SectionsDocument5 pagesDefining Conic SectionsMylaRoseMacadangdangAcobaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus First SemesterDocument2 pagesPre Calculus First SemesterNursaeda MusaiyaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesConic Sections WPS OfficeJeanny Mae PesebreNo ratings yet
- Parabola: Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument10 pagesParabola: Introduction To Conic SectionsGURUMARUTHI KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1 Semester: Cag - Edu.Gt/11Th-Grade-Precalculus/ - /RSRC/ 1413568039105/config/ Customlogo - Gif?Revision 24Document12 pages1 Semester: Cag - Edu.Gt/11Th-Grade-Precalculus/ - /RSRC/ 1413568039105/config/ Customlogo - Gif?Revision 24Coulline DamoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal Reviewer Conic Sections (Conics) Properties of A CircleDocument3 pagesPre-Cal Reviewer Conic Sections (Conics) Properties of A CircleHSeuji LspONo ratings yet
- Outline: Engineering Curves Ellipse Parabola HyperbolaDocument16 pagesOutline: Engineering Curves Ellipse Parabola HyperbolaPrem SaiNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Angles in Circles - MathBitsNotebook (Geo - CCSS Math)Document4 pagesFormulas For Angles in Circles - MathBitsNotebook (Geo - CCSS Math)Ashwin KumarNo ratings yet
- Transformation and Circle TheoremDocument10 pagesTransformation and Circle TheoremLisha CampbellNo ratings yet
- Toddle PresentationDocument7 pagesToddle Presentationamogh vorugantiNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument9 pagesHyperbolanathanalocilloNo ratings yet
- Notes - Lines and AnglesDocument6 pagesNotes - Lines and Anglesarunimafunnygirl12No ratings yet
- Answer The Following: 1. What Are The Different Types of Conic Sections?Document1 pageAnswer The Following: 1. What Are The Different Types of Conic Sections?Melvin Juden MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.introduction To Conic SectionsDocument11 pages1.1.introduction To Conic Sectionscharlene quiambaoNo ratings yet
- E) Geometric ConstructionDocument3 pagesE) Geometric ConstructionalmorsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Conic Sections PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Conic Sections PDFceca.mizuNo ratings yet
- Curves I: Curvature and TorsionDocument7 pagesCurves I: Curvature and TorsionAbdur Rauf AlamNo ratings yet
- Quadric SurfacesDocument5 pagesQuadric SurfacesIsabellaNo ratings yet
- A-SMA 103 I.B Anatycal GeometryDocument2 pagesA-SMA 103 I.B Anatycal GeometryJob OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Superficies RegularesDocument21 pagesSuperficies RegularesFabio ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Complex Number Practice Sheet Varsity 23Document8 pagesComplex Number Practice Sheet Varsity 23ivan hossainNo ratings yet
- On Implicit Surfaces and Their Intersection Curves in EuclideanDocument13 pagesOn Implicit Surfaces and Their Intersection Curves in EuclideanAmbrish SinghNo ratings yet
- Ellipse - Mind Maps - Prayas JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesEllipse - Mind Maps - Prayas JEE 2.0 2024hrupam34No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 The CircleDocument26 pagesLesson 1.1 The CircleManuel Anthony ContridasNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola ProblemsDocument16 pagesHyperbola ProblemsblacknaitNo ratings yet
- Sumit Raj PPT Surface Area and VolumeDocument25 pagesSumit Raj PPT Surface Area and VolumeSumit Raj 9A100% (3)
- Riemann Sphere: Complex Plane, The Complex Plane Plus A Point at Infinity. ThisDocument6 pagesRiemann Sphere: Complex Plane, The Complex Plane Plus A Point at Infinity. ThisoscarNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinateDocument37 pagesCo OrdinateVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Differential Geomet: Mathematics (H) 39Document1 pageDifferential Geomet: Mathematics (H) 39Satyaki GhosalNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus: Jean B. Corpuz, LPT InstructorDocument31 pagesPre-Calculus: Jean B. Corpuz, LPT InstructorJean CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Epicycloid ConstructionDocument2 pages1.3 Epicycloid ConstructionMartin De Boras Pragash100% (1)
- Section 6.4: Arc Length and Surface AreaDocument9 pagesSection 6.4: Arc Length and Surface AreaHiepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Notescreative mughalsNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Part 4 of 8Document24 pagesConic Section Part 4 of 8majji satishNo ratings yet
- Angular Momentum and Rotations: Classical Mechanics HomeworkDocument2 pagesAngular Momentum and Rotations: Classical Mechanics HomeworkplfratarNo ratings yet
- Hermite Curve HandoutDocument2 pagesHermite Curve HandoutRicardo DíazNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFalgohrythmNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Dynamical Systems and Differentiation of Genus 4 Hyperelliptic FunctionsDocument17 pagesPolynomial Dynamical Systems and Differentiation of Genus 4 Hyperelliptic Functionsim.marzaNo ratings yet
- Precal 1Document43 pagesPrecal 1Xzy BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Scale-& Curves in Engineering GraphicsDocument55 pagesScale-& Curves in Engineering GraphicsUDDALAKNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument81 pagesAnalytic GeometryJohn Rofer CabantingNo ratings yet
- Mte-05 EngDocument45 pagesMte-05 EngSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Article 31Document16 pagesArticle 31TamathNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Part 1Document90 pagesEngineering Drawing Part 1Shiva Sankar BeharaNo ratings yet