Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment VI (20×1)
Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment VI (20×1)
Uploaded by
giri ssCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Solution Manual To Chapter 02Document11 pagesSolution Manual To Chapter 02Shreya RameshNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary RealDocument4 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary Realgiri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary RealDocument4 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary Realgiri ssNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Antenna 2020 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAssignment2 Antenna 2020 SolutionsMalathi0% (1)
- Agilent Eesof Eda: Presentation On Adaptive Feedforward Linearization For RF Power Amplifiers - Part 2Document30 pagesAgilent Eesof Eda: Presentation On Adaptive Feedforward Linearization For RF Power Amplifiers - Part 2Bob Laughlin, KWØRLNo ratings yet
- Solid State Devices MCQs-AnswersDocument10 pagesSolid State Devices MCQs-AnswersKimberly TaboraNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ProposalDocument5 pagesMini Project ProposalAwis BeyNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions On Microwave Devices For BSNL and ISRO ExamsDocument29 pagesObjective Questions On Microwave Devices For BSNL and ISRO ExamsRaj Kumar50% (4)
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better UnderstandingDocument5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better Understandinggiri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)giri ss0% (1)
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2teju rajputNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1teju rajputNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution 9 Jan 2020Document5 pagesAssignment Solution 9 Jan 2020VRAJ PATELNo ratings yet
- DSP Important Questions UNIT-3, 4 &5Document3 pagesDSP Important Questions UNIT-3, 4 &5Jagadeesh PenakalapatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution 4 Jan 2020Document5 pagesAssignment Solution 4 Jan 2020VRAJ PATELNo ratings yet
- DL - Assignment 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesDL - Assignment 1 Solutionswathisreejith6No ratings yet
- Optical Communications: Objective QuestionsDocument13 pagesOptical Communications: Objective QuestionsAllanki Sanyasi RaoNo ratings yet
- Unit III - MCQsDocument15 pagesUnit III - MCQsMission Gate2021No ratings yet
- A. Digital Signal ProcessingDocument38 pagesA. Digital Signal ProcessingAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- CS601 700 Solved MCQs by IshfaqDocument79 pagesCS601 700 Solved MCQs by IshfaqJunaid Sajjad100% (3)
- DC Lab QuestionsDocument2 pagesDC Lab QuestionsanittadevadasNo ratings yet
- Antenna McqsDocument7 pagesAntenna McqsTalha Khalid100% (1)
- Choose The Best Answer:: 1. A) B) C) D)Document19 pagesChoose The Best Answer:: 1. A) B) C) D)Basheer NajemNo ratings yet
- Kennedy MCQ in Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument5 pagesKennedy MCQ in Introduction To Communication SystemsDennis ANo ratings yet
- Questions On MOS Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)Document59 pagesQuestions On MOS Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Week 8: Assignment - 8Document5 pagesUnit 9 - Week 8: Assignment - 8xperiaashNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits MCQ PDFDocument24 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits MCQ PDFlovelyosmile253No ratings yet
- Software Defined Radio Assignment 2Document4 pagesSoftware Defined Radio Assignment 2Degala Rajendra50% (2)
- DIP Unit 3 MCQ.Document6 pagesDIP Unit 3 MCQ.Santhosh PaNo ratings yet
- Important Mcq-Digital ElectronicsDocument27 pagesImportant Mcq-Digital ElectronicsarijitlgspNo ratings yet
- Data Communication-By: Basit AliDocument10 pagesData Communication-By: Basit AliRamzan RamzanNo ratings yet
- MCQ-WCN 2 SDocument32 pagesMCQ-WCN 2 SM.Ganesh Kumar mahendrakar100% (1)
- Multi Vibrators MCQDocument11 pagesMulti Vibrators MCQRAJNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Multirate Digital Signal ProcesingDocument7 pagesQuestions & Answers On Multirate Digital Signal Procesingkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs On Analog Modulation (Am FM) Am Radio Limits The Upper Modulating Frequency To 5 Khz. This Results in ADocument18 pagesMcqs On Analog Modulation (Am FM) Am Radio Limits The Upper Modulating Frequency To 5 Khz. This Results in AZynNo ratings yet
- Introduction To High Frequency Hybrid Pi or Giacoletto Model of BJTDocument2 pagesIntroduction To High Frequency Hybrid Pi or Giacoletto Model of BJTSai Sadiq100% (1)
- MCQ Questions Analog Circuits (EC-405)Document15 pagesMCQ Questions Analog Circuits (EC-405)Ankit Kapoor0% (1)
- Digital Image Processing Assignment-Week 1: NPTEL Online Certification Courses Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument10 pagesDigital Image Processing Assignment-Week 1: NPTEL Online Certification Courses Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurPandu KNo ratings yet
- Adc MCQDocument9 pagesAdc MCQTrojanNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Antennas and Wave Propagation Multiple Choice Questions Unit-1 - Antenna Basics - Ravi Kumar - Academia - EduDocument19 pages(PDF) Antennas and Wave Propagation Multiple Choice Questions Unit-1 - Antenna Basics - Ravi Kumar - Academia - EduRAJESH0% (1)
- Logic Families MCQs SimpleDocument8 pagesLogic Families MCQs SimplebijukumargNo ratings yet
- AWP Assignments NptelDocument26 pagesAWP Assignments NptelkolisettyvsureshNo ratings yet
- MCQ 3,4Document18 pagesMCQ 3,4vijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ's PDFDocument13 pagesDSP MCQ's PDFMUSHTAREEN HARLAPURNo ratings yet
- Lab Exam MCQsDocument12 pagesLab Exam MCQsShivansh LaadNo ratings yet
- Transistors McqsDocument12 pagesTransistors McqsKrishnaveni DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Assignment SolutionsDocument5 pagesWeek 12 Assignment SolutionsDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Digital Communication - PRANSHI - VERMADocument74 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Digital Communication - PRANSHI - VERMAMd Siraj UddinNo ratings yet
- Full-Unit-3 - Baseband Shaping For Data TransmissionDocument93 pagesFull-Unit-3 - Baseband Shaping For Data Transmissionsaswati paramita100% (1)
- Bpe MCQDocument80 pagesBpe MCQSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Electronic SwitchingDocument55 pagesElectronic SwitchingSunny Tyagi VatsNo ratings yet
- Na Unit1c Zeal MCQDocument20 pagesNa Unit1c Zeal MCQPankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemDocument21 pagesMcqs in Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemLovielyn Poquiz De VeraNo ratings yet
- AC 1&2 Objective PDFDocument5 pagesAC 1&2 Objective PDFsameer nayakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 UM AnswersDocument10 pagesAssignment 1 UM AnswersMaheswaran UmaiyorupaganNo ratings yet
- EC6801 Unit 1 MCQDocument17 pagesEC6801 Unit 1 MCQVanitha R100% (1)
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Microwave EngineeringDocument51 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Microwave EngineeringSuman Bhardwaj100% (3)
- Analog Electronics (0500625) SET 3Document8 pagesAnalog Electronics (0500625) SET 3Avinash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Analog Guide RajaReddyDocument30 pagesAnalog Guide RajaReddyKirti Susan VargheseNo ratings yet
- Quiz AICDDocument2 pagesQuiz AICDAnil RawatNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better UnderstandingDocument5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better Understandinggiri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)giri ss0% (1)
- 10week 1 Assignment SolutionDocument3 pages10week 1 Assignment Solutiongiri ssNo ratings yet
- Digital Ic TesterDocument28 pagesDigital Ic TesterChris ManojNo ratings yet
- FET - Inverter12v - IRF740Document9 pagesFET - Inverter12v - IRF740Macuco CamNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot RTWP IssueDocument11 pagesTroubleshoot RTWP IssueWasim Iqbal100% (1)
- Simply Be Mobile.: 2-SEITER - S35 (E) 14.12.2006 11:36 Uhr Seite 1Document2 pagesSimply Be Mobile.: 2-SEITER - S35 (E) 14.12.2006 11:36 Uhr Seite 1api-3738523No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Manual A5E34279422ADocument76 pagesManual A5E34279422AEngenheiro Controle e AutomaçãoNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1: School of Electronics Engineering ECE4009-Wireless and Mobile CommunicationsDocument2 pagesAssignment: 1: School of Electronics Engineering ECE4009-Wireless and Mobile CommunicationsAYUSH GURTU 17BEC0185No ratings yet
- Single Band - Colinear Omni Antenna - V-Pol - 360° - 7.8 DbiDocument1 pageSingle Band - Colinear Omni Antenna - V-Pol - 360° - 7.8 DbiThomas NoelNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Model 1080arcDocument15 pagesUser Manual: Model 1080arcelyuyaNo ratings yet
- ACS880-1604LC DC/DC Converter Modules: Hardware ManualDocument298 pagesACS880-1604LC DC/DC Converter Modules: Hardware Manualemmanuel nolascoNo ratings yet
- WireGuidance MM PDSS-0051Document57 pagesWireGuidance MM PDSS-0051angelbendito34No ratings yet
- Electronic FuzeDocument14 pagesElectronic FuzehyderabadunniNo ratings yet
- 1 Simatic: User InformationDocument138 pages1 Simatic: User InformationSihamaSihamNo ratings yet
- 14 Ram&romDocument40 pages14 Ram&romvenikiranNo ratings yet
- Platform Technology Midterm ReviewerDocument16 pagesPlatform Technology Midterm ReviewerlernzsarabiaNo ratings yet
- CX-BK1 Componente AIWADocument93 pagesCX-BK1 Componente AIWApata salada100% (3)
- 12V AC-DC Switching Regulated Power Supply: SpecificationsDocument1 page12V AC-DC Switching Regulated Power Supply: SpecificationsAbhijeet ChavanNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument7 pagesTransistorsDan Jeric Arcega RustiaNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Automatic Energy MeterDocument80 pagesGSM Based Automatic Energy MeterKhalid BenaribaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor System-Ii (8086) Practical File: SemesterDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor System-Ii (8086) Practical File: SemesterpolarizadmaxNo ratings yet
- 91212Document9 pages91212Krista TranNo ratings yet
- EM24DINDSDocument14 pagesEM24DINDSJavaprima Dinamika AbadiNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Wallace Tree Multiplier With Kogge Stone Adder Using 15-4 CompressorDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of Wallace Tree Multiplier With Kogge Stone Adder Using 15-4 Compressoranil kumarNo ratings yet
- Ieee p1687 Internal Jtag Taps Embedded Instrumentation White PaperDocument12 pagesIeee p1687 Internal Jtag Taps Embedded Instrumentation White PaperShrestha GowdaNo ratings yet
- 1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EDocument3 pages1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EthomvalensiNo ratings yet
- Module Level Rapid Shutdown: Made Easy by Yaskawa Solectria Solar & TigoDocument2 pagesModule Level Rapid Shutdown: Made Easy by Yaskawa Solectria Solar & TigoBaggi NNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Combiner 4:4 698 - 2690 MHZ 4 X 150 W: Technical Data Type No. 78210534Document2 pagesHybrid Combiner 4:4 698 - 2690 MHZ 4 X 150 W: Technical Data Type No. 78210534Radu BarbuNo ratings yet
- Regulator TL431 WorksDocument4 pagesRegulator TL431 WorksDemóstenes Moraes OlintoNo ratings yet
- KS7D CL29Z40MQDocument84 pagesKS7D CL29Z40MQChris RedfieldNo ratings yet
Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment VI (20×1)
Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment VI (20×1)
Uploaded by
giri ssOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment VI (20×1)
Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment VI (20×1)
Uploaded by
giri ssCopyright:
Available Formats
Millimeter-Wave Technology
Assignment VI (20×1)
Choose the most appropriate answer.
All symbols have their usual meaning.
Q1. Which of the following is a Cross field tube device?
a) Klystron
b) Magnetron
c) Vacuum Triodes
d) Pentodes
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 2 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q2. Which of the following is not a type of Solid state device?
a) BJT
b) FET
c) HEMT
d) Pentodes
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 2 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q3) Which of the following do you think creates a problem for the MOSFET at the millimeter-
wave (MMW) frequencies?
a) significant gate to source parasitic capacitance
b) significant gate to source parasitic inductance
c) significant gate-source and gate-drain parasitic capacitances
d) significant parasitic inductances at the all terminals
Please go through week 6 presentation slides 49˗50 and related lecture/ discussions
for better understanding
Q4) The device for which the thickness of the depletion region under reverse bias is varied
for capacitance variation is
a) Light emitting diode
b) Varactor diode
c) Thermistor
d) IMPATT diode
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 7 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q5) One of the major application of Impatt diode is
a) Transmitter Amplifier
b) Tuning
c) Phase Shifter
d) Modulator
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 7 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q6) Which of the following is not the way to make a BJT-
a) Diffusion
b) Ion Implantation
c) Electrostatic fusion
d) Molecular Beam Epitaxy
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 11 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q7) The transistor for which two different barrier height is created for its two pn junctions is
a) HEMT (High electron mobility transistor)
b) HBT (Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor)
c) Thyristor
d) MESFET (metal-semiconductor FET)
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 16 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q8) Typical forward voltage drop of Schottky diode is between
a) 0.7˗1 V
b) 0.7˗1.7 V
c) 0.4˗0.7 V
d) 0.1˗0.4 V
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 20 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q9) Transferred Electron Devices have
a) 1 PN junction
b) 2 PN junction
c) 3 PN Junction
d) No PN Junction
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 28 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q10) Avalanche transit time devices rely on
a) Voltage breakdown across reverse biased pn junction
b) Current breakdown across reverse biased pn junction
c) Voltage breakdown across forward biased pn junction
d) None of the above
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 39 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q11) The efficiency in TRAPATT mode of operation is typically
a) 20-60%
b) 5-10%
c) 70-90%
d) 25-40%
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 39 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q12) In the following device, only one type of charge carriers are involved in current flow.
a) HEMT (High electron mobility transistor)
b) HBT (Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor)
c) PIN diode
d) Varactor diode
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 44 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q13) FET is
a) Voltage controlled as it depends on VGS
b) Current controlled as it depends on ID
c) Voltage controlled as it depends on VTH
d) All of the above
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 44 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q14) When a MESFET is used as an amplifier, the drain current ID is given by
a) ID = IDSS (1-(VP/VGS))2
b) ID = IDSS (1-(|VGS|/VP))2
c) ID = IDSS (1+(|VGS|/VP))2
d) ID = IDSS (1-(VGS/VP))
Please go through week 6 presentation slide 45 and related lecture/ discussions for
better understanding
Q15) When the gate to source voltage of a depletion type RF n-MOSFET is less than the
pinch off voltage, drain current is of the order of
a) 100 mA
b) 0
c) 1 mA
d) 10 mA
When the gate to source voltage is less than pinch off, both of the junctions will be
reverse biased and channel is not formed. Hence, no current flows.
Q16) MOSFET behaves as a voltage-controlled resistor in the following region.
a) cutoff
b) triode
c) saturation
d) both b and c
Please look at the slope of output characteristics in slide 44.
Q17) The device that improves mobility by avoiding scattering from the doping agent by
using highly doped n-channel to create 2D electron gas is
a) HBT
b) MESFET
c) HEMT
d) SCR
Please look at slide 51.
Q18) The following device utilizes the property of negative resistance for amplification.
a) GUNN diode
b) IMPATT diode
c) BARITT diode
d) All of the above
Please look at slide 28 and 39.
Q19) Among the following C-MOS technological nodes that would provide the best device
performance at 60 GHz is
a) A 180 nm node n-MOS
b) A 180 nm node p-MOS
c) A 65 nm node n-MOS
d) A 65 nm node p-MOS
The dimensions are the smallest gate width that can be fabricated in that
fabrication process. Now, transit time must be small as the frequency increases.
Therefore, lower node provide higher unity gain frequency fT. Further, electron
mobility is higher than the hole mobility.
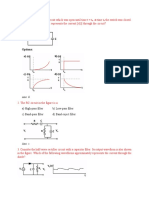
Q20) The output characteristics of a MOSFET with low values of Vds, the value of the on-
state resistance is
a) Vds/Id
b) 0
c) Vds/Ig
d) Infinity
The o/p characteristics is a plot of Id verses Vds, which for low values of Vds is almost
constant. Hence, the on-state resistance is constant & the slop is its constant value.
Please look at the slope of output characteristics in slide 44.
You might also like
- Solution Manual To Chapter 02Document11 pagesSolution Manual To Chapter 02Shreya RameshNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary RealDocument4 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary Realgiri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary RealDocument4 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment II (10×1 + 5×2) : Imaginary Realgiri ssNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Antenna 2020 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAssignment2 Antenna 2020 SolutionsMalathi0% (1)
- Agilent Eesof Eda: Presentation On Adaptive Feedforward Linearization For RF Power Amplifiers - Part 2Document30 pagesAgilent Eesof Eda: Presentation On Adaptive Feedforward Linearization For RF Power Amplifiers - Part 2Bob Laughlin, KWØRLNo ratings yet
- Solid State Devices MCQs-AnswersDocument10 pagesSolid State Devices MCQs-AnswersKimberly TaboraNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ProposalDocument5 pagesMini Project ProposalAwis BeyNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions On Microwave Devices For BSNL and ISRO ExamsDocument29 pagesObjective Questions On Microwave Devices For BSNL and ISRO ExamsRaj Kumar50% (4)
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better UnderstandingDocument5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better Understandinggiri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)giri ss0% (1)
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2teju rajputNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1teju rajputNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution 9 Jan 2020Document5 pagesAssignment Solution 9 Jan 2020VRAJ PATELNo ratings yet
- DSP Important Questions UNIT-3, 4 &5Document3 pagesDSP Important Questions UNIT-3, 4 &5Jagadeesh PenakalapatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution 4 Jan 2020Document5 pagesAssignment Solution 4 Jan 2020VRAJ PATELNo ratings yet
- DL - Assignment 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesDL - Assignment 1 Solutionswathisreejith6No ratings yet
- Optical Communications: Objective QuestionsDocument13 pagesOptical Communications: Objective QuestionsAllanki Sanyasi RaoNo ratings yet
- Unit III - MCQsDocument15 pagesUnit III - MCQsMission Gate2021No ratings yet
- A. Digital Signal ProcessingDocument38 pagesA. Digital Signal ProcessingAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- CS601 700 Solved MCQs by IshfaqDocument79 pagesCS601 700 Solved MCQs by IshfaqJunaid Sajjad100% (3)
- DC Lab QuestionsDocument2 pagesDC Lab QuestionsanittadevadasNo ratings yet
- Antenna McqsDocument7 pagesAntenna McqsTalha Khalid100% (1)
- Choose The Best Answer:: 1. A) B) C) D)Document19 pagesChoose The Best Answer:: 1. A) B) C) D)Basheer NajemNo ratings yet
- Kennedy MCQ in Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument5 pagesKennedy MCQ in Introduction To Communication SystemsDennis ANo ratings yet
- Questions On MOS Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)Document59 pagesQuestions On MOS Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Week 8: Assignment - 8Document5 pagesUnit 9 - Week 8: Assignment - 8xperiaashNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits MCQ PDFDocument24 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits MCQ PDFlovelyosmile253No ratings yet
- Software Defined Radio Assignment 2Document4 pagesSoftware Defined Radio Assignment 2Degala Rajendra50% (2)
- DIP Unit 3 MCQ.Document6 pagesDIP Unit 3 MCQ.Santhosh PaNo ratings yet
- Important Mcq-Digital ElectronicsDocument27 pagesImportant Mcq-Digital ElectronicsarijitlgspNo ratings yet
- Data Communication-By: Basit AliDocument10 pagesData Communication-By: Basit AliRamzan RamzanNo ratings yet
- MCQ-WCN 2 SDocument32 pagesMCQ-WCN 2 SM.Ganesh Kumar mahendrakar100% (1)
- Multi Vibrators MCQDocument11 pagesMulti Vibrators MCQRAJNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Multirate Digital Signal ProcesingDocument7 pagesQuestions & Answers On Multirate Digital Signal Procesingkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs On Analog Modulation (Am FM) Am Radio Limits The Upper Modulating Frequency To 5 Khz. This Results in ADocument18 pagesMcqs On Analog Modulation (Am FM) Am Radio Limits The Upper Modulating Frequency To 5 Khz. This Results in AZynNo ratings yet
- Introduction To High Frequency Hybrid Pi or Giacoletto Model of BJTDocument2 pagesIntroduction To High Frequency Hybrid Pi or Giacoletto Model of BJTSai Sadiq100% (1)
- MCQ Questions Analog Circuits (EC-405)Document15 pagesMCQ Questions Analog Circuits (EC-405)Ankit Kapoor0% (1)
- Digital Image Processing Assignment-Week 1: NPTEL Online Certification Courses Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument10 pagesDigital Image Processing Assignment-Week 1: NPTEL Online Certification Courses Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurPandu KNo ratings yet
- Adc MCQDocument9 pagesAdc MCQTrojanNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Antennas and Wave Propagation Multiple Choice Questions Unit-1 - Antenna Basics - Ravi Kumar - Academia - EduDocument19 pages(PDF) Antennas and Wave Propagation Multiple Choice Questions Unit-1 - Antenna Basics - Ravi Kumar - Academia - EduRAJESH0% (1)
- Logic Families MCQs SimpleDocument8 pagesLogic Families MCQs SimplebijukumargNo ratings yet
- AWP Assignments NptelDocument26 pagesAWP Assignments NptelkolisettyvsureshNo ratings yet
- MCQ 3,4Document18 pagesMCQ 3,4vijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ's PDFDocument13 pagesDSP MCQ's PDFMUSHTAREEN HARLAPURNo ratings yet
- Lab Exam MCQsDocument12 pagesLab Exam MCQsShivansh LaadNo ratings yet
- Transistors McqsDocument12 pagesTransistors McqsKrishnaveni DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Assignment SolutionsDocument5 pagesWeek 12 Assignment SolutionsDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Digital Communication - PRANSHI - VERMADocument74 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Digital Communication - PRANSHI - VERMAMd Siraj UddinNo ratings yet
- Full-Unit-3 - Baseband Shaping For Data TransmissionDocument93 pagesFull-Unit-3 - Baseband Shaping For Data Transmissionsaswati paramita100% (1)
- Bpe MCQDocument80 pagesBpe MCQSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Electronic SwitchingDocument55 pagesElectronic SwitchingSunny Tyagi VatsNo ratings yet
- Na Unit1c Zeal MCQDocument20 pagesNa Unit1c Zeal MCQPankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemDocument21 pagesMcqs in Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemLovielyn Poquiz De VeraNo ratings yet
- AC 1&2 Objective PDFDocument5 pagesAC 1&2 Objective PDFsameer nayakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 UM AnswersDocument10 pagesAssignment 1 UM AnswersMaheswaran UmaiyorupaganNo ratings yet
- EC6801 Unit 1 MCQDocument17 pagesEC6801 Unit 1 MCQVanitha R100% (1)
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Microwave EngineeringDocument51 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Microwave EngineeringSuman Bhardwaj100% (3)
- Analog Electronics (0500625) SET 3Document8 pagesAnalog Electronics (0500625) SET 3Avinash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Analog Guide RajaReddyDocument30 pagesAnalog Guide RajaReddyKirti Susan VargheseNo ratings yet
- Quiz AICDDocument2 pagesQuiz AICDAnil RawatNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment III (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment IV (20×1)giri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better UnderstandingDocument5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment V (20×1) : Please Go Through Week 5 Slide 5 For Better Understandinggiri ssNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)Document5 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology Assignment I (20×1)giri ss0% (1)
- 10week 1 Assignment SolutionDocument3 pages10week 1 Assignment Solutiongiri ssNo ratings yet
- Digital Ic TesterDocument28 pagesDigital Ic TesterChris ManojNo ratings yet
- FET - Inverter12v - IRF740Document9 pagesFET - Inverter12v - IRF740Macuco CamNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot RTWP IssueDocument11 pagesTroubleshoot RTWP IssueWasim Iqbal100% (1)
- Simply Be Mobile.: 2-SEITER - S35 (E) 14.12.2006 11:36 Uhr Seite 1Document2 pagesSimply Be Mobile.: 2-SEITER - S35 (E) 14.12.2006 11:36 Uhr Seite 1api-3738523No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Manual A5E34279422ADocument76 pagesManual A5E34279422AEngenheiro Controle e AutomaçãoNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1: School of Electronics Engineering ECE4009-Wireless and Mobile CommunicationsDocument2 pagesAssignment: 1: School of Electronics Engineering ECE4009-Wireless and Mobile CommunicationsAYUSH GURTU 17BEC0185No ratings yet
- Single Band - Colinear Omni Antenna - V-Pol - 360° - 7.8 DbiDocument1 pageSingle Band - Colinear Omni Antenna - V-Pol - 360° - 7.8 DbiThomas NoelNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Model 1080arcDocument15 pagesUser Manual: Model 1080arcelyuyaNo ratings yet
- ACS880-1604LC DC/DC Converter Modules: Hardware ManualDocument298 pagesACS880-1604LC DC/DC Converter Modules: Hardware Manualemmanuel nolascoNo ratings yet
- WireGuidance MM PDSS-0051Document57 pagesWireGuidance MM PDSS-0051angelbendito34No ratings yet
- Electronic FuzeDocument14 pagesElectronic FuzehyderabadunniNo ratings yet
- 1 Simatic: User InformationDocument138 pages1 Simatic: User InformationSihamaSihamNo ratings yet
- 14 Ram&romDocument40 pages14 Ram&romvenikiranNo ratings yet
- Platform Technology Midterm ReviewerDocument16 pagesPlatform Technology Midterm ReviewerlernzsarabiaNo ratings yet
- CX-BK1 Componente AIWADocument93 pagesCX-BK1 Componente AIWApata salada100% (3)
- 12V AC-DC Switching Regulated Power Supply: SpecificationsDocument1 page12V AC-DC Switching Regulated Power Supply: SpecificationsAbhijeet ChavanNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument7 pagesTransistorsDan Jeric Arcega RustiaNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Automatic Energy MeterDocument80 pagesGSM Based Automatic Energy MeterKhalid BenaribaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor System-Ii (8086) Practical File: SemesterDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor System-Ii (8086) Practical File: SemesterpolarizadmaxNo ratings yet
- 91212Document9 pages91212Krista TranNo ratings yet
- EM24DINDSDocument14 pagesEM24DINDSJavaprima Dinamika AbadiNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Wallace Tree Multiplier With Kogge Stone Adder Using 15-4 CompressorDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of Wallace Tree Multiplier With Kogge Stone Adder Using 15-4 Compressoranil kumarNo ratings yet
- Ieee p1687 Internal Jtag Taps Embedded Instrumentation White PaperDocument12 pagesIeee p1687 Internal Jtag Taps Embedded Instrumentation White PaperShrestha GowdaNo ratings yet
- 1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EDocument3 pages1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EthomvalensiNo ratings yet
- Module Level Rapid Shutdown: Made Easy by Yaskawa Solectria Solar & TigoDocument2 pagesModule Level Rapid Shutdown: Made Easy by Yaskawa Solectria Solar & TigoBaggi NNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Combiner 4:4 698 - 2690 MHZ 4 X 150 W: Technical Data Type No. 78210534Document2 pagesHybrid Combiner 4:4 698 - 2690 MHZ 4 X 150 W: Technical Data Type No. 78210534Radu BarbuNo ratings yet
- Regulator TL431 WorksDocument4 pagesRegulator TL431 WorksDemóstenes Moraes OlintoNo ratings yet
- KS7D CL29Z40MQDocument84 pagesKS7D CL29Z40MQChris RedfieldNo ratings yet