Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-84-Đã Chuyển Đổi
Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-84-Đã Chuyển Đổi
Uploaded by
Nguyên Nguyễn Sơn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views1 pageThe document provides examples of calculating angular deflection for electrodynamic instruments. Example 2.13 describes an instrument where the spring constant is given to calculate deflection at full scale current. Example 2.14 gives parameters of an instrument's voltage and current coils to calculate the deflection produced by a given potential difference and current. Example 2.15 provides specifications for a voltmeter to determine the difference between DC and 50Hz AC readings at 50 volts.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides examples of calculating angular deflection for electrodynamic instruments. Example 2.13 describes an instrument where the spring constant is given to calculate deflection at full scale current. Example 2.14 gives parameters of an instrument's voltage and current coils to calculate the deflection produced by a given potential difference and current. Example 2.15 provides specifications for a voltmeter to determine the difference between DC and 50Hz AC readings at 50 volts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views1 pageElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-84-Đã Chuyển Đổi
Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-84-Đã Chuyển Đổi
Uploaded by
Nguyên Nguyễn SơnThe document provides examples of calculating angular deflection for electrodynamic instruments. Example 2.13 describes an instrument where the spring constant is given to calculate deflection at full scale current. Example 2.14 gives parameters of an instrument's voltage and current coils to calculate the deflection produced by a given potential difference and current. Example 2.15 provides specifications for a voltmeter to determine the difference between DC and 50Hz AC readings at 50 volts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Example 2.13 constant is 10-6N-m/radian.
Determine the angular
deflection at full scale.
Now the deflection
Angular deflection at full scale current of I = 25 A is given by:
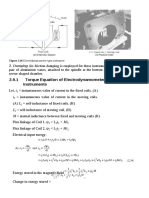
In an electrodynamic instrument the total resistance of the
voltage coil circuit is 8200 Ω and the mutual inductance
changes uniformly from -173 μH at zero deflection to +175
μH at full scale. The angle of full scale being 95°. If a
Example 2.14 potential difference of 100 V is applied across the voltage
circuit and a current of 3 A at a power factor of 0.75 is
passed through the current coil, what will be the deflection.
Spring constant of the instrument is 4.63 × 10-6 N-m/rad.
Solution Change in mutual inductance dM = 175 – (–173) = 348 µH
Deflection θ = 95° = 1.66 rad
Rate of change of mutual inductance
Current through the current coil I1= 3 A
Current through the voltage coil
Power factor cos 6 = 0.75
Deflection
A 50 V range spring-controlled electrodynamic voltmeter
has an initial inductance of 0.25 H, the full scale deflection
torque of 0.4 × 10-4 Nm and full scale deflection current of
Example 2.15
50 mA. Determine the difference between dc and 50 Hz ac
reading at 50 volts if the voltmeter inductance increases
uniformly over the full scale of 90°.
Solution
Full-scale deflection 6 = 90°
You might also like
- PS Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPS Formula SheetBruno Koch SchmittNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFDocument24 pagesGATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- U6 L38 - NumericalsDocument5 pagesU6 L38 - NumericalsRazaq PayapoNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument9 pagesElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Solution:: KVA IpDocument3 pagesSolution:: KVA IpNoor Mohammed100% (1)
- Open-Circuit or No-Load TestDocument13 pagesOpen-Circuit or No-Load TestNANDHAKUMAR ANo ratings yet
- KCL KVL ProblemsDocument5 pagesKCL KVL ProblemsRhemjohn Dave PitongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Magnetic CircuitsDocument49 pagesLecture 6-Magnetic CircuitsMAENYA BRUCE OYONDINo ratings yet
- Sheet 2-Circuit Magnetic PDFDocument14 pagesSheet 2-Circuit Magnetic PDFMarcos Silva MonteloNo ratings yet
- CH-1 - DC Generator Q.bank PDFDocument2 pagesCH-1 - DC Generator Q.bank PDFjaythakar8887No ratings yet
- BEE Question Paper FormatDocument1 pageBEE Question Paper FormatsunilsinghmNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives: Working Principle of Alternator OR Synchronous Generator StatorDocument5 pagesLecture Objectives: Working Principle of Alternator OR Synchronous Generator StatorZ_JahangeerNo ratings yet
- AVG and RMS Values of Periodic Waveforms 2012Document5 pagesAVG and RMS Values of Periodic Waveforms 2012Ang Yu LongNo ratings yet
- CH2Document55 pagesCH2Shantha KumarNo ratings yet
- EE GATE 2000 Question and AnswersDocument8 pagesEE GATE 2000 Question and AnswersUTKAL.45No ratings yet
- Applied Electronics II (Chapter 4)Document34 pagesApplied Electronics II (Chapter 4)Ermias MesfinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - TransformerDocument84 pagesChapter 5 - TransformerZulfikri Zulkifli50% (2)
- Chapter 3 Two Port Netw All in OneDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Two Port Netw All in OneAbdi Jote100% (1)
- Image ImpedanceDocument16 pagesImage ImpedanceErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- 7 Magnetic Circuits: B, and State Their Units A H L ADocument10 pages7 Magnetic Circuits: B, and State Their Units A H L AgebreNo ratings yet
- Glover 10 ExDocument13 pagesGlover 10 ExAseel Bait MaditNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: IES Electrical Engineering Topic Wise QuestionsDocument78 pagesElectrical Machines: IES Electrical Engineering Topic Wise QuestionsahmedNo ratings yet
- BJT Practice Questions PDFDocument5 pagesBJT Practice Questions PDFDustin BentonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document4 pagesAssignment 6Nandhalal100% (1)
- EEE267 Transformer Tests Math Problems PDFDocument3 pagesEEE267 Transformer Tests Math Problems PDFmaakbdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 1Document24 pagesChapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 1temesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-III Question BankDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines-III Question BanksanthiNo ratings yet
- Capítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsDocument49 pagesCapítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsPaulinha BezerraNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - SolutionDocument48 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - SolutionchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNo ratings yet
- Ac QuantitiesDocument7 pagesAc Quantitiessrinivas100% (1)
- Experiment.3. Load Characteristics of D.C Shunt GeneratorDocument2 pagesExperiment.3. Load Characteristics of D.C Shunt Generatorمحمد الحدي100% (1)
- Obective Power SystemDocument22 pagesObective Power Systempoonam yadavNo ratings yet
- Electri Circuits Lab Manual 1Document11 pagesElectri Circuits Lab Manual 1Sri RoNo ratings yet
- Insulator ProblemsDocument16 pagesInsulator Problemssrinimeha@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3Document3 pagesSheet 3Mohab SamehNo ratings yet
- OC and SC Test On Single Phase TransformerDocument5 pagesOC and SC Test On Single Phase TransformerhavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Electrostatic Boundary - Value ProblemsDocument38 pagesChapter 6 - Electrostatic Boundary - Value ProblemsMarc Rivera100% (1)
- DC and AC BridgesDocument55 pagesDC and AC Bridgessaikarthick023100% (1)
- Ch8 DC Machine FundamentalsDocument29 pagesCh8 DC Machine FundamentalsalpizraNo ratings yet
- MCQ of DC Machines Madhuri NewDocument31 pagesMCQ of DC Machines Madhuri NewAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Exercise On DC MachineDocument13 pagesTutorial Exercise On DC MachineTSEGAAB NIGUSSENo ratings yet
- Pe Tutorial 2 PDFDocument10 pagesPe Tutorial 2 PDFkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- EE6604-Design of Electrical Machines - QBDocument16 pagesEE6604-Design of Electrical Machines - QBmadhu balanNo ratings yet
- Example 7 A Voltmeter Having A Sensitivity of 1000 - U03a9 V Reads 100 V On Its 150 V - Course HeroDocument1 pageExample 7 A Voltmeter Having A Sensitivity of 1000 - U03a9 V Reads 100 V On Its 150 V - Course Heroanon_306267635No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 6Document20 pagesDigital Electronics 6Kshitij SalaveNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Set A1880Document16 pagesApgenco Set A1880Srimannarayana NandamNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields Due To Electric CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Fields Due To Electric CurrentHrishikesh GunjalNo ratings yet
- AC TO DC CONVERTERS Paper 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAC TO DC CONVERTERS Paper 1 PDFDonigoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Question Paper MAKAUTDocument8 pagesMechanics Question Paper MAKAUTArka BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits LabDocument64 pagesElectrical Circuits LabraveendrababupNo ratings yet
- 3 - PHASE Solved ProblemsDocument3 pages3 - PHASE Solved ProblemsprabraghuNo ratings yet
- 360 Topic 6 DC MachineDocument33 pages360 Topic 6 DC MachineAchsan ArfandiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering - Electrical MachinesDocument78 pagesElectrical Engineering - Electrical MachinesSangeetha Veera0% (1)
- 1710-EET2166 Three Phase Circuits - SlidesDocument33 pages1710-EET2166 Three Phase Circuits - SlidesLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- Resource Pack - Ac TheoryDocument12 pagesResource Pack - Ac TheoryiirshadNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)Document7 pagesCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)anjanaroy35325No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Part 1Document41 pagesBasic Electronics Part 1Claire RachoNo ratings yet
- Basic Types of Circuit. The Study of Circuits Involves Three Basic Types of Units and Four PossibleDocument13 pagesBasic Types of Circuit. The Study of Circuits Involves Three Basic Types of Units and Four PossibleEduard LauronNo ratings yet
- Ch-07 Alternating Current: Daily Practice Problem 06Document2 pagesCh-07 Alternating Current: Daily Practice Problem 06Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Materials: ContentDocument42 pagesSemiconductor Materials: ContentNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19. TemperatureDocument41 pagesChapter 19. TemperatureNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument9 pagesElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-83-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument1 pageElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-83-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-78-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument2 pagesElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-78-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet