Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Objectives: Simple Linear Regression
Learning Objectives: Simple Linear Regression
Uploaded by
dat nguyenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Objectives: Simple Linear Regression
Learning Objectives: Simple Linear Regression
Uploaded by
dat nguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12 12-1
Learning Objectives
North Seattle Community College
In this chapter, you learn:
BUS210 ! How to use regression analysis to predict the value of
Business Statistics a dependent variable based on an independent
variable
! The meaning of the regression coefficients b0 and b1
Chapter 12 ! How to evaluate the assumptions of regression
analysis and know what to do if the assumptions are
violated
Simple Linear Regression ! To make inferences about the slope and correlation
coefficient
! To estimate mean values and predict individual values
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 2
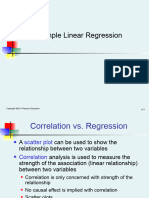
Correlation Regression Analysis
! Correlation analysis… ! Regression analysis is used to…
! is used to measure the association (linear ! predict the value of a dependent variable based on
relationship) between two variables the value of at least one independent variable
! is only concerned with the strength of the relationship ! explain the impact on the dependent variable from
! does not imply cause and effect changes in an independent variable
! can be visualized by the use of a scatter plot to show Dependent variable (Y): the variable we wish to predict or explain
the relationship between two variables
Independent variable (X): the variable used in order to predict or
explain the dependent variable
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 3 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 4
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Simple Linear Regression Types of Relationships
Linear relationships Curvilinear relationships
! Only one independent variable, X
Y Y
! Relationship between X and Y is
described by a linear function
! Assumption:
X X
! Changes in Y are related to changes in X
Y Y
X X
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 5 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 6
NSCC – BUS210 Simple Regression
Chapter 12 12-2
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Strength of Relationships Simple Linear Regression
Strong Weak None For a population:
Y Y Y Independent
Intercept Slope
Variable
Coefficient Coefficient
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Yi = !0 + !1X i + "i
Dependent Linear Random Error
Variable component component
X X X
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 7 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 8
Regression Analysis Simple Linear Regression
Simple Linear Regression Linear Regression Equation
The simple linear regression equation…
Y Random Error • is based on a sample set
Observed
(for this Xi value) Slope (!1) • gives an estimate of the population regression line
Value
of Y for Xi
Estimate of Estimate of
!i the regression the regression
Predicted intercept slope
Value Value of X for
ŷi = b0 + b1x i
of Y for Xi
observation i
Yi = !0 + !1X i
Intercept Estimated
Commonly shown in math
(!0) as y = mx+b (or predicted)
X Y value for
Xi observation i
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 9 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 10
Simple Linear Regression Simple Linear Regression
The Least Squares Method The Least Squares Method
Least Squares Criterion: The sum of the squared differences can be
Minimize the sum of the squared differences minimized when:
between Y and Ŷ !(xi " x )(yi " y )
b1 =
min " (yi !yˆ i ) 2
!(xi " x )2
which equates to
and b0 = y ! b1 x
min " (yi ! (b0 + b1x i )) 2
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 11 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 12
NSCC – BUS210 Simple Regression
Chapter 12 12-3
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Simple Linear Regression Simple Linear Regression
Square House
Feet Price
Example: ($000 s)
! A real estate agent wishes to examine the
x y x!x y! y (x ! x )(y ! y ) (x ! x )2
1400 245 -315 -41.5 13072.5 99225
relationship between the selling price of a home 1600 312 -115 25.5 -2932.5 13225
and its size (measured in square feet) 1700 279 -15 -7.5 112.5 225
1875 308 160 21.5 3440 25600
! A random sample of 10 houses 1100 199 -615 -87.5 53812.5 378225
1550 219 -165 -67.5 11137.5 27225
is selected 2350 405 635 118.5 75247.5 403225
! X = square feet 2450 324 735 37.5 27562.5 540225
1425 319 -290 32.5 -9425 84100
! Y = house price ($000 s) 1700 255 -15 -31.5 472.5 225
Sum 0.0 0.0 172500.0 1571500
Mean 1715 286.5
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 13 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 14
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Simple Linear Regression Scatter Plot
Square House
Feet Price
($000 s) House Price vs. Square Feet
x y x!x y! y (x ! x )(y ! y ) (x ! x )2 450
Sum 0.0 0.0 172500.0 1571500 400
House Price ($1000s)
Mean 1715 286.5 350
300
250
!(xi " x )(yi " y ) 172500 200
b1 = = = 0.11 150
!(xi " x )2 1571500 100
50
0
b0 = y ! b1 x = 286.5 ! (0.11)(1715) = 98.25 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
Square Feet
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 15 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 16
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Using Excel Excel output
Regression Statistics
Multiple R 0.76211 The regression equation is:
R Square 0.58082
Adjusted R Square 0.52842 house price = 98.25 + (0.11)(square feet)
Standard Error 41.33032
Observations 10
ANOVA
df SS MS F Significance F
Regression 1 18934.9348 18934.9348 11.0848 0.01039
Residual 8 13665.5652 1708.1957
Total 9 32600.5000
Coefficients Standard Error t Stat P-value Lower 95% Upper 95%
Intercept 98.24833 58.03348 1.69296 0.12892 -35.57720 232.07386
Square Feet 0.10977 0.03297 3.32938 0.01039 0.03374 0.18580
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 17 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 18
NSCC – BUS210 Simple Regression
Chapter 12 12-4
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Scatter Plot Interpretation of b0
House Price vs. Square Feet house price = 98.25 + 0.11 (square feet)
450
400 ! b0 is….
House Price ($1000s)
Intercept 350
Slope
= 98.25 300
= 0.11 ! the estimated mean value of Y
250
200
150
! when the value of X is zero
100
50
Note:
0
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 Because a house cannot have a square footage of zero, b0 has no practical application
Square Feet
house price = 98.25 + (0.11)(square feet)
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 19 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 20
Regression Analysis Regression Analysis
Interpretation of b1 Making Predictions
house price = 98.25 + 0.11 (square feet) Predict the price for a house
with 2000 square feet:
! b1 is….
! the estimated change in the mean value of Y house price = 98.25 + 0.11(sq.ft.)
! when the value of X changes by one unit = 98.25 + 0.11(2000)
! 318
Here, b1 = 0.11 tells us that the mean value of a house
increases by 0.11 x $1000 or about $110, on The predicted price for a house
average, for each additional one square foot of size with 2000 square feet is $318,000
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 21 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 22
Regression Analysis Measures of Variation
Making Predictions Coefficient of Determination
! When using a regression model for prediction,
! Total variation of y is made up of two parts:
only predict within the relevant range of data
Relevant range for
interpolation
!(y
!(yi " y )2 = !( yˆi "i "y )y2 ) + !(yi " yˆi )2
450
Total Sum of Regression
Total Sum
Sum
of Error Sum of
400
Squares of Squares
Squares Squares
House Price ($1000s)
350
300
250
SST = SSR + SSE
200
150 Do not try to
100
extrapolate
50
0
beyond the range
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 of observed X s
BUS210: Business Statistics Square Feet Simple Regression- 23 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 24
NSCC – BUS210 Simple Regression
Chapter 12 12-5
Measures of Variation Measures of Variation
Coefficient of Determination (cont d) Coefficient of Determination (cont d)
y
! SST = total sum of squares (Total Variation)
! The variation of the Yi values around their mean. yi
! SSR = regression sum of squares (Explained Variation) SSE = !(yi " yˆi )2
Variation from the relationship between X and Y SST = !(yi " y )2 ŷi = b0 + b1x i
!
yˆi
! SSE = error sum of squares (Unexplained Variation) SSR = !( yˆi " y )2
! Variation in Y attributable to factors other than X
y
x
xi
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 25 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 26
Measures of Variation Measures of Variation
Coefficient of Determination (cont d) Coefficient of Determination (cont d)
! The coefficient of determination is… Y
! the portion of the total variation in the dependent r2 = 1
variable that is explained by variation in the
independent variable
There is a perfect linear
! also called r-squared and is denoted as r2
relationship between X and Y:
X
regression sum of squares !( yˆi " y )2 SSR r2 = 1
r2 = = = Y 100% of the variation in Y is
total sum of squares !(yi " y )2 SST explained by variation in X
Note: Since r2 is a ratio, then 0 " r2 " 1
X
r2 = 1
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 27 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 28
Measures of Variation Measures of Variation
Coefficient of Determination (cont d) Coefficient of Determination (cont d)
Y
0 < r2 < 1 r2 = 0
Y
As r2 decreases, there is a There is no linear
weaker linear relationship relationship between X and Y:
X
between X and Y:
The value of Y does not
Y X
Some, but not all, of the r2 = 0 depend on X.
variation in Y is explained None of the variation in Y is
by variation in X explained by variation in X.
X
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 29 BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 30
NSCC – BUS210 Simple Regression
Chapter 12 12-6
Coefficient of Determination
Using Excel
Regression Statistics SSR 18934.9348
r2 = = = 0.58082
Multiple R 0.76211
SST 32600.5000
R Square 0.58082
Adjusted R Square 0.52842 58.08% of the variation in
Standard Error 41.33032 house prices is explained
Observations 10 by variation in square feet
ANOVA
df SS MS F Significance F
Regression 1 18934.9348 18934.9348 11.0848 0.01039
Residual 8 13665.5652 1708.1957
Total 9 32600.5000
Coefficients Standard Error t Stat P-value Lower 95% Upper 95%
Intercept 98.24833 58.03348 1.69296 0.12892 -35.57720 232.07386
Square Feet 0.10977 0.03297 3.32938 0.01039 0.03374 0.18580
BUS210: Business Statistics Simple Regression- 31
NSCC – BUS210 Simple Regression
You might also like
- QMM Epgdm 5Document58 pagesQMM Epgdm 5manish guptaNo ratings yet
- Complete Business Statistics: Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationDocument50 pagesComplete Business Statistics: Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationAli ElattarNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS STATISTICS: Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationDocument55 pagesBUSINESS STATISTICS: Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationLaurence Rue AudineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document40 pagesChapter 536. Lê Minh Phương 12A3No ratings yet
- Chap 12Document62 pagesChap 12Krish GujarathiNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Causal Relationships I: Illustration 1Document8 pagesEstimation of Causal Relationships I: Illustration 1Janarthanan Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression ExamplesDocument14 pagesSimple Linear Regression Examplesameera kNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics: A First Course: Simple Linear RegressionDocument65 pagesBusiness Statistics: A First Course: Simple Linear RegressionfredyNo ratings yet
- Basic Business Statistics: 10 EditionDocument77 pagesBasic Business Statistics: 10 EditionUTTAM KOIRALANo ratings yet
- Session 11 - BBS10 - PPT - ch13 - Simple Lin RegDocument78 pagesSession 11 - BBS10 - PPT - ch13 - Simple Lin RegviolettaNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft® Excel 5th Edition: Simple Linear RegressionDocument71 pagesStatistics For Managers Using Microsoft® Excel 5th Edition: Simple Linear Regressionhasan jabrNo ratings yet
- Simple and Multiple Linear RegressionDocument91 pagesSimple and Multiple Linear Regressionkomal kashyapNo ratings yet
- Bda 1Document28 pagesBda 1Ikhsan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document39 pagesChapter 5Afifa SuibNo ratings yet
- 08 Introduction To Correlation and Linear Regression Analysis 2Document5 pages08 Introduction To Correlation and Linear Regression Analysis 2Angela Erish CastroNo ratings yet
- RPI Cover Work For 12D1 FRIDAYDocument40 pagesRPI Cover Work For 12D1 FRIDAYCandy ENo ratings yet
- Kuliah Statistik Inferensial Ke4: Simple Linear RegressionDocument74 pagesKuliah Statistik Inferensial Ke4: Simple Linear Regressionvivian indrioktaNo ratings yet
- Materi 2 - Simple RegressionDocument80 pagesMateri 2 - Simple RegressionThe Sun Will RiseNo ratings yet
- 4 After MidDocument9 pages4 After Midannisa elqairNo ratings yet
- Bivariate Statistical Measures of - 2022100 - 183954Document1 pageBivariate Statistical Measures of - 2022100 - 183954Saku Uchiha100% (1)
- Double Statistics: IntroductionDocument14 pagesDouble Statistics: IntroductionharsmanNo ratings yet
- 2023 Statistics Fin 9Document14 pages2023 Statistics Fin 9TNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Structural Equation Modeling: The Counseling Psychologist September 2006Document34 pagesA Brief Guide To Structural Equation Modeling: The Counseling Psychologist September 2006Norberth Ioan OkrosNo ratings yet
- Stat 222 Lecture 1-1Document71 pagesStat 222 Lecture 1-1MICHAEL TURKSONNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Hoi Qui Don - DT - New - 8.5Document10 pagesLecture - Hoi Qui Don - DT - New - 8.5211124022306No ratings yet
- Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: 6 Global EditionDocument79 pagesStatistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: 6 Global EditionAnita Nida SariNo ratings yet
- KhaterDocument1 pageKhater123456789ra.comNo ratings yet
- Chap010 - Sao ChépDocument50 pagesChap010 - Sao ChépLan PhanNo ratings yet
- Rmbi1020 Lec05 RegressionDocument47 pagesRmbi1020 Lec05 RegressionLaw Po YiNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument56 pagesLinear RegressionRanz CruzNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression and CorrelationDocument52 pagesLinear Regression and CorrelationAkiraNo ratings yet
- Stat 302 Lec 12Document59 pagesStat 302 Lec 12Rehman BukhariNo ratings yet
- CH-2 - PPT-Simple Linear Regression AnalysisDocument105 pagesCH-2 - PPT-Simple Linear Regression AnalysisMUSA KEDIRONo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Correlation, Regression Factor AnalysisDocument76 pagesTopic 8 - Correlation, Regression Factor AnalysisNe NeNo ratings yet
- Simple Regression Analysis Report1Document45 pagesSimple Regression Analysis Report1stillwinmsNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Simple RegressionDocument68 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Simple RegressionMd. Rezwan Hossain Sakib 1711977630No ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression and Logistic Regression: Vybhav - 20M226 Ashok - 20M236Document17 pagesSimple Linear Regression and Logistic Regression: Vybhav - 20M226 Ashok - 20M23620M130 - MUKUNTH A GNo ratings yet
- Unit 17Document33 pagesUnit 17Bhumika BhallaNo ratings yet
- Sessions 18 19 - Regression - SLR MLRDocument70 pagesSessions 18 19 - Regression - SLR MLRjeevanboda.738No ratings yet
- 2023 Statistics Fin 10Document14 pages2023 Statistics Fin 10TNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Causal Relationships I: Illustration 1Document11 pagesEstimation of Causal Relationships I: Illustration 1Dharshini RajkumarNo ratings yet
- LP-III Lab ManualDocument49 pagesLP-III Lab ManualNihal GujarNo ratings yet
- Regression Including The Interaction Between Quantitative VariablesDocument8 pagesRegression Including The Interaction Between Quantitative Variablesajax_telamonioNo ratings yet
- Online 7 RegressionDocument36 pagesOnline 7 RegressionSenthilNo ratings yet
- Stats1 Chapter 4::: CorrelationDocument13 pagesStats1 Chapter 4::: Correlationiminathi ndlovuNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear RegressionDocument195 pagesSimple Linear Regressionsarvesh.bagad25No ratings yet
- Levine Bsfc7ge ch12Document84 pagesLevine Bsfc7ge ch12Chih Chou ChiuNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression PDFDocument7 pagesSimple Linear Regression PDFLanceee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Correlation and Linear RegressionDocument51 pagesChapter 13 - Correlation and Linear RegressionBrenda TandayuNo ratings yet
- Cream and Brown Simple Modern Creative Mind Map BrainstormDocument1 pageCream and Brown Simple Modern Creative Mind Map BrainstormKaren tovarNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression: Statistics For Economics 1Document72 pagesCorrelation and Regression: Statistics For Economics 1Benyamin DimasNo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document64 pagesChap 11huynhnguyet1601No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Quantitative AnalysisDocument244 pagesChapter 2 - Quantitative AnalysisCHAN StephenieNo ratings yet
- WEEK7 - Data Analysis - Correlation and SRDocument20 pagesWEEK7 - Data Analysis - Correlation and SRAnh Tú BùiNo ratings yet
- Correlation Analysis: Concept of Univariate, Bivariate DataDocument48 pagesCorrelation Analysis: Concept of Univariate, Bivariate DataPanma PatelNo ratings yet
- Simple Correlation and Regression AnalysisDocument14 pagesSimple Correlation and Regression AnalysisBibhush MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument17 pagesLinear RegressionLuka SavićNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression: Chapter 12, Slide 1Document45 pagesSimple Linear Regression: Chapter 12, Slide 1yNo ratings yet
- 8-Correlation and Regression AnalysisDocument4 pages8-Correlation and Regression Analysischobiipiggy26No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document26 pagesChapter 11dat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Bus210 Ch10bDocument4 pagesBus210 Ch10bdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9a 9a-1: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesChapter 9a 9a-1: Learning Objectivesdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Two-Sample Tests Two-Sample TestsDocument6 pagesTwo-Sample Tests Two-Sample Testsdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9b 9b-1: of The MeanDocument6 pagesChapter 9b 9b-1: of The Meandat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Describing Data Visually: Applied Statistics in Business & EconomicsDocument8 pagesDescribing Data Visually: Applied Statistics in Business & Economicsdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesChapter 05 - Sampling and Sampling Distributiondat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics: 4 Edition David P. Doane and Lori E. SewardDocument9 pagesDescriptive Statistics: 4 Edition David P. Doane and Lori E. Sewarddat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics in Business & EconomicsDocument6 pagesApplied Statistics in Business & Economicsdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Probability: Applied Statistics in Business & EconomicsDocument9 pagesProbability: Applied Statistics in Business & Economicsdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Random VariablesDocument14 pagesChapter 03 - Random Variablesdat nguyenNo ratings yet
- Resilient Marketing Ebook FDocument20 pagesResilient Marketing Ebook Fmaneesh mittalNo ratings yet
- Dealer Price List 14.06.2016 EnkiDocument6 pagesDealer Price List 14.06.2016 EnkiNicolae IsacNo ratings yet
- Bollard Pull CalculationsDocument16 pagesBollard Pull CalculationsLuis Sierra100% (1)
- M.SC Math PDFDocument42 pagesM.SC Math PDFgollakotiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 BIO Learn - ExcretionDocument22 pagesWeek 1 BIO Learn - ExcretionEseel AlsammarraieNo ratings yet
- Draft OperatingProcedures NR 2019-20Document67 pagesDraft OperatingProcedures NR 2019-20Xen Operation DPHNo ratings yet
- Significant Figure Rules For LogsDocument2 pagesSignificant Figure Rules For Logsmooningearth2No ratings yet
- Advanced Electronics Ee 407 Year: Fourth Theoretical: 2 Hrs/Week Tutorial: - Hrs/weekDocument1 pageAdvanced Electronics Ee 407 Year: Fourth Theoretical: 2 Hrs/Week Tutorial: - Hrs/weekcarmo-netoNo ratings yet
- Muet Speaking Past Year QuestionsDocument6 pagesMuet Speaking Past Year Questionsaina sorfina100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Fundamentals of CrystallographyDocument51 pagesChapter 3: Fundamentals of CrystallographyAli ZbayelNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 68 - 4th - Quarter - Science - 4. Role of Sun in The Water CycleDocument3 pagesLesson - 68 - 4th - Quarter - Science - 4. Role of Sun in The Water CycleVenus Cureg100% (4)
- 17-619 Introduction To Real-Time Software and Systems: Carnegie MellonDocument7 pages17-619 Introduction To Real-Time Software and Systems: Carnegie Mellonbkit_n_haiNo ratings yet
- General 2Document6 pagesGeneral 2skynyrd75No ratings yet
- Testing TOPIC 3. Kinds of TestsDocument17 pagesTesting TOPIC 3. Kinds of TestsHung Thuyen PhamNo ratings yet
- IB DP English B (Practice Test)Document2 pagesIB DP English B (Practice Test)Menon Hari100% (1)
- 1967 - McLuhan - Invisible - Environment NewDocument7 pages1967 - McLuhan - Invisible - Environment NewJeanNo ratings yet
- Earth Pressure TheoryDocument30 pagesEarth Pressure TheoryDhananjay ShahNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Ulf 600 Pro2Document3 pagesData Sheet Ulf 600 Pro2Salman ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Permeability of Granular Soils (Constant Head) : Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesPermeability of Granular Soils (Constant Head) : Standard Test Method ForEdwardNo ratings yet
- Solution Class 12 ChemistryDocument3 pagesSolution Class 12 Chemistryom prakashNo ratings yet
- Carrefour 4kDocument13 pagesCarrefour 4kmona asgharNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanPrincess Kylah Chua TorresNo ratings yet
- JSG Decoration Brochure-S3000 - 1Document3 pagesJSG Decoration Brochure-S3000 - 1HuyenNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Algorithms Mock TestDocument6 pagesData Structures Algorithms Mock Testnehal nasimNo ratings yet
- Em TechDocument18 pagesEm TechFrederick Bautista AboboNo ratings yet
- Personality DeterminantsDocument13 pagesPersonality DeterminantsPranay KarnikNo ratings yet
- TMA03Document6 pagesTMA03Elena Elisa BotezatuNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Assist SystemDocument2 pagesHydraulic Assist SystemengfaridmalkNo ratings yet
- Course Details: Course Details:: Course Coordinator: Email: Office LocationDocument12 pagesCourse Details: Course Details:: Course Coordinator: Email: Office LocationHephzibah EniloloboNo ratings yet
- Digital Astrophotography A Guide To Capturing The Cosmos (PDFDrive)Document236 pagesDigital Astrophotography A Guide To Capturing The Cosmos (PDFDrive)Paolo Fasselli100% (1)