Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System Dysfunctions
Nervous System Dysfunctions
Uploaded by
vea domingoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SinusitisDocument30 pagesSinusitisAbdiqani MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chart NSDocument5 pagesChart NSJilliana Ysabel MiclatNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument6 pagesGen BioNoahNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument2 pagesMultiple SclerosisLuiciaNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument4 pagesNeurophysiologyQUIZANA, Ceazairenee P.No ratings yet
- Bio Assignment Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesBio Assignment Nervous SystemLyra IsraelNo ratings yet
- Neurological DisorderDocument10 pagesNeurological DisordersonyNo ratings yet
- Fop DescriptionDocument3 pagesFop Descriptioncedrictayab2No ratings yet
- Jan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy AtaxiaDocument2 pagesJan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy Ataxia박우진No ratings yet
- Top 5 Nervous System DiseasesDocument4 pagesTop 5 Nervous System DiseasesJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases That Can Affect Our Nervous SystemDocument1 pageCommon Diseases That Can Affect Our Nervous SystemJhe-An PilapilNo ratings yet
- Neurons: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is Called "The Brain of Computer" As ItDocument2 pagesNeurons: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is Called "The Brain of Computer" As ItCedric PilarNo ratings yet
- Joint Receptors 1Document15 pagesJoint Receptors 1Bleslyn Claire LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System GlossaryDocument4 pagesNervous System Glossarywilsonjaramillo51No ratings yet
- Seizure Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsDocument3 pagesSeizure Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsBlessed GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Disease and Disorder of Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesDisease and Disorder of Nervous SystemHannah ۦۦNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument15 pagesBraindiagrodaisy3No ratings yet
- 3 Brain Spinal Cord and Nerve Disorders of DogsDocument18 pages3 Brain Spinal Cord and Nerve Disorders of DogsKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in NeurologyDocument3 pagesCase Studies in NeurologyOnline WriterNo ratings yet
- Psy 03 Biopsychology-Ch. 10 ActivityDocument1 pagePsy 03 Biopsychology-Ch. 10 ActivityMitch Shyrelle BaclaoNo ratings yet
- Untitled Form (Responses)Document28 pagesUntitled Form (Responses)EVELYN EZEKWENo ratings yet
- 7 Ways To Keep Your Circulatory System HealthyDocument3 pages7 Ways To Keep Your Circulatory System HealthyLileth Fabio-oliverioNo ratings yet
- Bilinguismo NeuroDocument6 pagesBilinguismo NeuroNatalia Garcia LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy BDDocument19 pagesAnaphy BDJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemVinDiesel Balag-eyNo ratings yet
- Disorders of NSDocument4 pagesDisorders of NSThe KhanNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- Final Effects of Neurological Diseases in Our Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesFinal Effects of Neurological Diseases in Our Nervous SystemAfesoj BelirNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nerve: Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor & Hod MBBS, MphilDocument26 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve: Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor & Hod MBBS, MphilMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tolfree Product MonographDocument20 pagesTolfree Product MonographbadshahytNo ratings yet
- Draw Ang Label The Major Parts of The Nervous System. (Brain and Spinal Cord)Document9 pagesDraw Ang Label The Major Parts of The Nervous System. (Brain and Spinal Cord)ShainaChescaEvansNo ratings yet
- Nerve AnatomyDocument7 pagesNerve AnatomyvkumaranNo ratings yet
- Degen 1Document21 pagesDegen 1KoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- Gain Booklet Teens NewDocument48 pagesGain Booklet Teens NewMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease Is The Most CommonDocument3 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Is The Most CommonRiham P. MacarambonNo ratings yet
- Disease of Nervous System DRDocument4 pagesDisease of Nervous System DRJaafar AlzuheiriNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Impairment HandoutsDocument2 pagesOrthopedic Impairment HandoutsCaress EusebioNo ratings yet
- Common Ailments of The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCommon Ailments of The Nervous SystemQuennie Coleen ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Seizure Paper For ParentsDocument6 pagesSeizure Paper For ParentsAlexandra DarmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemAlbert SaipNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1 TermsArniie QuilonNo ratings yet
- Neuro Notes #3Document11 pagesNeuro Notes #3Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Seizure - 20240417 - 123136 - 0000Document2 pagesSeizure - 20240417 - 123136 - 0000bspsych.borromeokjpNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy and AlsDocument3 pagesBell's Palsy and AlsTrishia GuillermoNo ratings yet
- PT6 ManilaDocument2 pagesPT6 ManilaAriexia RueNo ratings yet
- Untitled Presentation 1Document14 pagesUntitled Presentation 1api-422807575No ratings yet
- Unit Xi: Neural Regulation (Motor Disturbances) - Upper Motor Neuron DisorderDocument4 pagesUnit Xi: Neural Regulation (Motor Disturbances) - Upper Motor Neuron DisorderCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Yuni CHR D Hekboy Est Unit 6Document16 pagesYuni CHR D Hekboy Est Unit 6IndraNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument7 pagesMultiple SclerosisKyla TongcuaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis ReviewerDocument4 pagesMultiple Sclerosis ReviewerKyla TongcuaNo ratings yet
- 16 Nervous SystemDocument31 pages16 Nervous SystemTouimiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemSamantha FuerteNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy Week 9: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How DiagnosedDocument2 pagesBell's Palsy Week 9: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How DiagnosedshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Disorders For StudentsDocument4 pagesNeurologic Disorders For StudentsElla RoseNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis: Paola Viñé OrtegaDocument21 pagesMultiple Sclerosis: Paola Viñé OrtegaPaola ViñéNo ratings yet
- Brain Function PDFDocument8 pagesBrain Function PDFGenieyung Faranindia Sakanti Topan 10CNo ratings yet
- Perez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Document6 pagesPerez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Jayzyl PerezNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disorders - CUEVODocument1 pageDegenerative Disorders - CUEVOzeeNo ratings yet
- Homeostatic Imbalance 7-10Document4 pagesHomeostatic Imbalance 7-10enewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Venous ThromboembolismDocument49 pagesVenous Thromboembolismadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Music On Auditory Hallucination and Quality of Life in Schizophrenic Patients: A Randomised Controlled TrialDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Music On Auditory Hallucination and Quality of Life in Schizophrenic Patients: A Randomised Controlled Trialyulia22No ratings yet
- COVID-19 Workplace Screening FormDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Workplace Screening FormhumphryNo ratings yet
- Learning Log 3 Style AcademyDocument3 pagesLearning Log 3 Style Academyapi-495193572No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing QuizDocument16 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing QuizJohanna Recca MarinoNo ratings yet
- Progress Exam - Clinical ChemistryDocument87 pagesProgress Exam - Clinical ChemistryAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Association Between Working Memory Impairment and ActivitiesDocument6 pagesAssociation Between Working Memory Impairment and ActivitiesDaniel OrregoNo ratings yet
- Culture Bound SyndromesDocument14 pagesCulture Bound SyndromesLinda MathewNo ratings yet
- Netter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Document19 pagesNetter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Panagiotis SouldatosNo ratings yet
- SOAL UAS XI Ganjil.Document7 pagesSOAL UAS XI Ganjil.Ade RikardoNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 46Document5 pagesOb2 Sas 46????No ratings yet
- RESEARCH Chapter 1Document18 pagesRESEARCH Chapter 1Shadab28No ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument2 pagesTyphoidFatma HasanNo ratings yet
- EPHCG2021Document162 pagesEPHCG2021Ibrahim AbdelaNo ratings yet
- ImpactionDocument475 pagesImpactionHarshitha RajannaNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Infections PreventionDocument34 pagesOpportunistic Infections PreventionEvelyn LimNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hawin - ARDS and Pneomonia in Covid 19Document36 pagesDr. Hawin - ARDS and Pneomonia in Covid 19puannita santosoNo ratings yet
- 2209 148376 Zervoulakos Pierell SignedDocument1 page2209 148376 Zervoulakos Pierell SignedMarevic SanchezNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear Disorders CompiledDocument93 pagesEye and Ear Disorders CompiledJonamae Flor DagumanNo ratings yet
- Biology Project (Edited)Document27 pagesBiology Project (Edited)5cxd7r9nmdNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Title Level Offering Clinical Area of Assignment Date of Exposure No. of HoursDocument9 pagesCourse Code Course Title Level Offering Clinical Area of Assignment Date of Exposure No. of HoursIsaiah RabangNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis20 02 2016 160620141900 PDFDocument20 pagesOsteoporosis20 02 2016 160620141900 PDFenam professorNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus: Some Do'S and Don'Ts: Write The Correct Caption in The BoxDocument2 pagesCoronavirus: Some Do'S and Don'Ts: Write The Correct Caption in The BoxPaul HasasNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Case StudyDocument13 pagesPreeclampsia Case StudyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- 2013 (2) Report Robin Mark TringhamDocument76 pages2013 (2) Report Robin Mark TringhamMarco ViganoNo ratings yet
- 5 Solved-1Document3 pages5 Solved-1Ahtasham AhmedNo ratings yet
- 22.52 Social Determinants of HealthUK and The Local Government - 05 - 0Document26 pages22.52 Social Determinants of HealthUK and The Local Government - 05 - 0lesleyNo ratings yet
- EM Cases Course Pre Course Handbook 2016Document27 pagesEM Cases Course Pre Course Handbook 2016Malik UsmanNo ratings yet
Nervous System Dysfunctions
Nervous System Dysfunctions
Uploaded by
vea domingoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System Dysfunctions
Nervous System Dysfunctions
Uploaded by
vea domingoCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System Dysfunction
Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory
Name: Mallare, Jose Luisito P. Section: NAK
Objective of the task: This activity aims the learner to be familiar with the common nervous
system disorders. Also, for the learners to recognize the pathophysiology of the disease,
identifying what leads to the disorder and which part of the nervous system is affected.
Instructions: The table below enumerates some nervous system disorders. Research on the
definition and pathophysiology of each disorder. Based on your research, complete the table.
Make your answers brief but concise.
Nervous System Disorder Definition Pathophysiology
(make sure that you are able to identify
which part of the nervous system is
affected and to how is it affected)
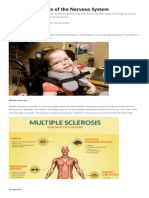
1. Multiple Sclerosis It’s a lifelong It can affect the spinal cord and the
condition that can brain (central nervous system). In MS,
sometimes cause the immune system attacks the
serious disability, protective sheath (myelin) that covers
although it can nerve fibers and causes
occasionally be mild. communication problems between
your brain and the rest of your body.
2. Parkinson’s Disease Parkinson’s disease Parkinson’s disease is a disorder of
affects the nerve cells the central nervous system, which
in the brain that includes the brain and the spinal cord,
produce dopamine. and control everything you do,
Parkinson’s disease including moving. A person with
symptoms include Parkinson’s disease gradually loses
muscle rigidity, the ability to totally control all body
tremors, and changes movements
in speech and gait.
After diagnosis,
treatments can help
relieve symptoms, but
there is no cure.
3. Myasthenia Gravis It’s a chronic Affects the voluntary muscles of the
autoimmune disorder body especially those that controls the
in which antibodies eyes, mouth, throat, and limbs.
destroys the Basically, it affects the Peripheral
communication Nervous System.
between nerves and
muscle, resulting in
weakness of the
skeletal muscle.
4. Amyotrophic Lateral It is
Sclerosis a neurodegenerative
neuromuscular
disease that results in
the progressive loss
of motor neurons that
control voluntary
muscles.
5. Alzheimer’s Disease It is a progressive
neurologic disorder
that causes the brain
to shrink (atrophy)
and brain cells to die.
This type of brain
disorder causes
problems with
memory, thinking and
behavior. This is a
gradually progressive
condition.
6. Bell’s Palsy A condition that
causes temporary
weakness or paralysis
of the muscles in the
face. It causes
paralysis on one side
of the face, drooping
face, headache, loss
of taste, increased
sensitivity to sound,
dry eye and dry mouth
7. Guillain Barre It is a rapid-
Syndrome onset muscle
weakness caused by
the immune
system damaging
the peripheral nervous
system. Typically,
both sides of the body
are involved, and the
initial symptoms are
changes in sensation
or pain often in the
back along with
muscle weakness,
beginning in the feet
and hands, often
spreading to the arms
and upper body.
8. Encephalitis An inflammation of
the brain usually
caused due to viral
infection that causes
flu like symptoms like
headache or fever.
9. Meningitis It is an inflammation
of the fluid and
membranes
(meninges)
surrounding your
brain and spinal
cord. The swelling
from meningitis
typically triggers
signs and symptoms
such as headache,
fever and a stiff neck.
10. Huntington’s Disease It is a rare, inherited
disease that causes
the progressive
breakdown
(degeneration) of
nerve cells in the
brain. Huntington's
disease has a broad
impact on a person's
functional abilities
and usually results in
movement, thinking
(cognitive) and
psychiatric disorders
You might also like
- SinusitisDocument30 pagesSinusitisAbdiqani MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chart NSDocument5 pagesChart NSJilliana Ysabel MiclatNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument6 pagesGen BioNoahNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument2 pagesMultiple SclerosisLuiciaNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument4 pagesNeurophysiologyQUIZANA, Ceazairenee P.No ratings yet
- Bio Assignment Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesBio Assignment Nervous SystemLyra IsraelNo ratings yet
- Neurological DisorderDocument10 pagesNeurological DisordersonyNo ratings yet
- Fop DescriptionDocument3 pagesFop Descriptioncedrictayab2No ratings yet
- Jan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy AtaxiaDocument2 pagesJan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy Ataxia박우진No ratings yet
- Top 5 Nervous System DiseasesDocument4 pagesTop 5 Nervous System DiseasesJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases That Can Affect Our Nervous SystemDocument1 pageCommon Diseases That Can Affect Our Nervous SystemJhe-An PilapilNo ratings yet
- Neurons: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is Called "The Brain of Computer" As ItDocument2 pagesNeurons: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is Called "The Brain of Computer" As ItCedric PilarNo ratings yet
- Joint Receptors 1Document15 pagesJoint Receptors 1Bleslyn Claire LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System GlossaryDocument4 pagesNervous System Glossarywilsonjaramillo51No ratings yet
- Seizure Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsDocument3 pagesSeizure Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsBlessed GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Disease and Disorder of Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesDisease and Disorder of Nervous SystemHannah ۦۦNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument15 pagesBraindiagrodaisy3No ratings yet
- 3 Brain Spinal Cord and Nerve Disorders of DogsDocument18 pages3 Brain Spinal Cord and Nerve Disorders of DogsKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in NeurologyDocument3 pagesCase Studies in NeurologyOnline WriterNo ratings yet
- Psy 03 Biopsychology-Ch. 10 ActivityDocument1 pagePsy 03 Biopsychology-Ch. 10 ActivityMitch Shyrelle BaclaoNo ratings yet
- Untitled Form (Responses)Document28 pagesUntitled Form (Responses)EVELYN EZEKWENo ratings yet
- 7 Ways To Keep Your Circulatory System HealthyDocument3 pages7 Ways To Keep Your Circulatory System HealthyLileth Fabio-oliverioNo ratings yet
- Bilinguismo NeuroDocument6 pagesBilinguismo NeuroNatalia Garcia LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy BDDocument19 pagesAnaphy BDJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemVinDiesel Balag-eyNo ratings yet
- Disorders of NSDocument4 pagesDisorders of NSThe KhanNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- Final Effects of Neurological Diseases in Our Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesFinal Effects of Neurological Diseases in Our Nervous SystemAfesoj BelirNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nerve: Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor & Hod MBBS, MphilDocument26 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve: Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor & Hod MBBS, MphilMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tolfree Product MonographDocument20 pagesTolfree Product MonographbadshahytNo ratings yet
- Draw Ang Label The Major Parts of The Nervous System. (Brain and Spinal Cord)Document9 pagesDraw Ang Label The Major Parts of The Nervous System. (Brain and Spinal Cord)ShainaChescaEvansNo ratings yet
- Nerve AnatomyDocument7 pagesNerve AnatomyvkumaranNo ratings yet
- Degen 1Document21 pagesDegen 1KoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- Gain Booklet Teens NewDocument48 pagesGain Booklet Teens NewMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease Is The Most CommonDocument3 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Is The Most CommonRiham P. MacarambonNo ratings yet
- Disease of Nervous System DRDocument4 pagesDisease of Nervous System DRJaafar AlzuheiriNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Impairment HandoutsDocument2 pagesOrthopedic Impairment HandoutsCaress EusebioNo ratings yet
- Common Ailments of The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCommon Ailments of The Nervous SystemQuennie Coleen ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Seizure Paper For ParentsDocument6 pagesSeizure Paper For ParentsAlexandra DarmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemAlbert SaipNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1 TermsArniie QuilonNo ratings yet
- Neuro Notes #3Document11 pagesNeuro Notes #3Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Seizure - 20240417 - 123136 - 0000Document2 pagesSeizure - 20240417 - 123136 - 0000bspsych.borromeokjpNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy and AlsDocument3 pagesBell's Palsy and AlsTrishia GuillermoNo ratings yet
- PT6 ManilaDocument2 pagesPT6 ManilaAriexia RueNo ratings yet
- Untitled Presentation 1Document14 pagesUntitled Presentation 1api-422807575No ratings yet
- Unit Xi: Neural Regulation (Motor Disturbances) - Upper Motor Neuron DisorderDocument4 pagesUnit Xi: Neural Regulation (Motor Disturbances) - Upper Motor Neuron DisorderCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Yuni CHR D Hekboy Est Unit 6Document16 pagesYuni CHR D Hekboy Est Unit 6IndraNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument7 pagesMultiple SclerosisKyla TongcuaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis ReviewerDocument4 pagesMultiple Sclerosis ReviewerKyla TongcuaNo ratings yet
- 16 Nervous SystemDocument31 pages16 Nervous SystemTouimiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemSamantha FuerteNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy Week 9: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How DiagnosedDocument2 pagesBell's Palsy Week 9: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How DiagnosedshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Disorders For StudentsDocument4 pagesNeurologic Disorders For StudentsElla RoseNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis: Paola Viñé OrtegaDocument21 pagesMultiple Sclerosis: Paola Viñé OrtegaPaola ViñéNo ratings yet
- Brain Function PDFDocument8 pagesBrain Function PDFGenieyung Faranindia Sakanti Topan 10CNo ratings yet
- Perez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Document6 pagesPerez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Jayzyl PerezNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disorders - CUEVODocument1 pageDegenerative Disorders - CUEVOzeeNo ratings yet
- Homeostatic Imbalance 7-10Document4 pagesHomeostatic Imbalance 7-10enewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Venous ThromboembolismDocument49 pagesVenous Thromboembolismadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Music On Auditory Hallucination and Quality of Life in Schizophrenic Patients: A Randomised Controlled TrialDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Music On Auditory Hallucination and Quality of Life in Schizophrenic Patients: A Randomised Controlled Trialyulia22No ratings yet
- COVID-19 Workplace Screening FormDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Workplace Screening FormhumphryNo ratings yet
- Learning Log 3 Style AcademyDocument3 pagesLearning Log 3 Style Academyapi-495193572No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing QuizDocument16 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing QuizJohanna Recca MarinoNo ratings yet
- Progress Exam - Clinical ChemistryDocument87 pagesProgress Exam - Clinical ChemistryAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Association Between Working Memory Impairment and ActivitiesDocument6 pagesAssociation Between Working Memory Impairment and ActivitiesDaniel OrregoNo ratings yet
- Culture Bound SyndromesDocument14 pagesCulture Bound SyndromesLinda MathewNo ratings yet
- Netter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Document19 pagesNetter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Panagiotis SouldatosNo ratings yet
- SOAL UAS XI Ganjil.Document7 pagesSOAL UAS XI Ganjil.Ade RikardoNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 46Document5 pagesOb2 Sas 46????No ratings yet
- RESEARCH Chapter 1Document18 pagesRESEARCH Chapter 1Shadab28No ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument2 pagesTyphoidFatma HasanNo ratings yet
- EPHCG2021Document162 pagesEPHCG2021Ibrahim AbdelaNo ratings yet
- ImpactionDocument475 pagesImpactionHarshitha RajannaNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Infections PreventionDocument34 pagesOpportunistic Infections PreventionEvelyn LimNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hawin - ARDS and Pneomonia in Covid 19Document36 pagesDr. Hawin - ARDS and Pneomonia in Covid 19puannita santosoNo ratings yet
- 2209 148376 Zervoulakos Pierell SignedDocument1 page2209 148376 Zervoulakos Pierell SignedMarevic SanchezNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear Disorders CompiledDocument93 pagesEye and Ear Disorders CompiledJonamae Flor DagumanNo ratings yet
- Biology Project (Edited)Document27 pagesBiology Project (Edited)5cxd7r9nmdNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Title Level Offering Clinical Area of Assignment Date of Exposure No. of HoursDocument9 pagesCourse Code Course Title Level Offering Clinical Area of Assignment Date of Exposure No. of HoursIsaiah RabangNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis20 02 2016 160620141900 PDFDocument20 pagesOsteoporosis20 02 2016 160620141900 PDFenam professorNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus: Some Do'S and Don'Ts: Write The Correct Caption in The BoxDocument2 pagesCoronavirus: Some Do'S and Don'Ts: Write The Correct Caption in The BoxPaul HasasNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Case StudyDocument13 pagesPreeclampsia Case StudyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- 2013 (2) Report Robin Mark TringhamDocument76 pages2013 (2) Report Robin Mark TringhamMarco ViganoNo ratings yet
- 5 Solved-1Document3 pages5 Solved-1Ahtasham AhmedNo ratings yet
- 22.52 Social Determinants of HealthUK and The Local Government - 05 - 0Document26 pages22.52 Social Determinants of HealthUK and The Local Government - 05 - 0lesleyNo ratings yet
- EM Cases Course Pre Course Handbook 2016Document27 pagesEM Cases Course Pre Course Handbook 2016Malik UsmanNo ratings yet