Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1.1
Assignment 1.1
Uploaded by
Josiah FloresOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 1.1
Assignment 1.1
Uploaded by
Josiah FloresCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT 1.
Calculation of Loads
Note: Use 5 @ 3.5 meters (on the elevation) instead of 5 @ 12’
Problems
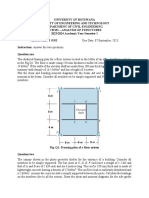
Kindly refer to the figure above for the building layout, Table 204-2 Minimum Design Loads (NSCP 2015) for the uniform
and concentrated loads per occupancy and Section 203.3 (NSCP 2015) for basic load combination. The figure above
provides a plan and elevation of a reinforced concrete building 7 bays long by 4 bays wide. The building has beams
along building lines A through E and one-way slabs spanning between building lines A through E. A central
stairwell/elevator shaft between building lines 5 and 6 provides the lateral support, so only gravity loads need to be
calculated. The bay dimensions, beam dimensions, and occupancy uses are given in the individual problem statements
below. Construction is with normal weight concrete with a density of 23.6 kN/m3 for the purposes of calculating dead
load.
1. The building in the figure is used for general office space. The slab is 20 cm. thick. The beams are 30 cm. wide and
have a total depth of 45 cm., the bay dimensions are 5 meters in the X direction and 6 meters in the Y direction,
and the superimposed service dead load is 0.60 kN/m2.
a. Calculate the slab service load in kN/m2 and the interior beam service load in kN/m.
b. Calculate the factored axial column load transferred to column C3 on the 3rd floor in kN.
c. Calculate the slab factored load in kN/m2 and the beam factored load in kN/m. Comment on your solution
in comparison with your answer in Prob 1.a.
2. The roof on the building has a slab that is 18 cm. thick. The beams are 30 cm. wide and have a total depth of 40
cm., the bay dimensions are 6 m in the X direction and 6.5 m in the Y direction, and the superimposed service
dead load is 0.28 kN/m. Calculate the slab factored load in kN/m2 and the beam factored load in kN/m.
Prepared by:
Engr. Hessa G. Azul
You might also like
- Outline of Topics: Resultant Moments. These Are The Stress Resultants (Also Called Membrane ForcesDocument16 pagesOutline of Topics: Resultant Moments. These Are The Stress Resultants (Also Called Membrane ForcesJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Beef Cattle Housing and EquipmentDocument39 pagesBeef Cattle Housing and EquipmentJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Minimum Design Loads (NSCP 2015)Document22 pagesMinimum Design Loads (NSCP 2015)Josiah Flores50% (2)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sab 4333 Set ADocument8 pagesSab 4333 Set AUsama EL AlaouiNo ratings yet
- Design Example of Six Storey BuildingDocument51 pagesDesign Example of Six Storey BuildingsidhujosephNo ratings yet
- CE 317 - Combined Footing (L3-L4)Document26 pagesCE 317 - Combined Footing (L3-L4)sanjid0002No ratings yet
- Loading and Design of Box Culverts To EurocodesDocument35 pagesLoading and Design of Box Culverts To Eurocodeslnanescu83% (6)
- Design of Stairs 2021 Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesDesign of Stairs 2021 Lecture NotesstevenNo ratings yet
- 1978 Effect of Sequence of Construction in Analysis of Multistoreyed Building - S.C.chakrabarti G. C. Nayak and S.K. AgarwalaDocument6 pages1978 Effect of Sequence of Construction in Analysis of Multistoreyed Building - S.C.chakrabarti G. C. Nayak and S.K. AgarwalaAnonymous UXWnUJqhNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Skew DeckDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Skew Decksolitary_monkNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Box Culvert StressesDocument6 pagesReduction of Box Culvert StressesTakis ApostolidesNo ratings yet
- Two Storayed BuildingDocument5 pagesTwo Storayed BuildingSridhar VasuNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Box Culvert Using Staad Pro - Structville PDFDocument17 pagesAnalysis and Design of Box Culvert Using Staad Pro - Structville PDFMd Ahsanul Kabir100% (1)
- Computational Model and Charts For Cut-and-Cover TunnelsDocument18 pagesComputational Model and Charts For Cut-and-Cover Tunnelskabasy2015No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document14 pagesChapter 10Bhemalee Tono DimalaluanNo ratings yet
- CEB 706 Group Project - QuestionDocument6 pagesCEB 706 Group Project - QuestionKrishan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Balanced Cantilever Prestressed Box Girder Bridge Considering Constructions Stages and Creep RedistributionDocument36 pagesAnalysis and Design of Balanced Cantilever Prestressed Box Girder Bridge Considering Constructions Stages and Creep RedistributionSitthideth Vongchanh100% (1)
- Steel Deck 101Document3 pagesSteel Deck 101arnoldistunoNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Civil Engineering and ArchitectureDocument1 pageUniversity of Bahrain Department of Civil Engineering and Architectureali mustafaNo ratings yet
- Cut and Covers TunnelsDocument18 pagesCut and Covers TunnelsRene RoblesNo ratings yet
- Assignment20 SolutionDocument10 pagesAssignment20 SolutionMohamed ElsaneeNo ratings yet
- Brick NomogramDocument5 pagesBrick NomogramJeffrey ThomasNo ratings yet
- Combined FootingDocument24 pagesCombined FootingMd. Naimul Islam SanyNo ratings yet
- DP7 04/03/18 CEE 6527 Spring 2018 Team: - Due: (ONE SOLUTION PER TEAM) at The Beginning of Class, Tuesday, April 17Document3 pagesDP7 04/03/18 CEE 6527 Spring 2018 Team: - Due: (ONE SOLUTION PER TEAM) at The Beginning of Class, Tuesday, April 17Amrith NairNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Load-Carrying Capacity of Concrete Tunnel LiningDocument10 pagesExperimental Investigation On Load-Carrying Capacity of Concrete Tunnel LiningHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- Time Saving-Two Way2Document9 pagesTime Saving-Two Way2Wanda Beasley100% (1)
- 560.325 Homework Assignment 2Document1 page560.325 Homework Assignment 2BELAL ALSUBARINo ratings yet
- Homework2 Confined RC Section AnalysisDocument13 pagesHomework2 Confined RC Section AnalysisQingzhi Liu100% (1)
- Design of 6 Storey Building in EtabsDocument51 pagesDesign of 6 Storey Building in EtabsMisqal A Iqbal100% (2)
- One Way SlabsDocument16 pagesOne Way Slabsbemd_ali6990No ratings yet
- Explanation of One Way and Two Way Slab ActionDocument17 pagesExplanation of One Way and Two Way Slab Actionxckwzr100% (4)
- Lecture 4 Frame Analysis Shear Walls HKUSTDocument9 pagesLecture 4 Frame Analysis Shear Walls HKUSTApril Ingram100% (1)
- A Modified Tube Concept For Tall BuildingsDocument5 pagesA Modified Tube Concept For Tall BuildingsBill HuttonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structures - Assignment1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Structures - Assignment1Bright MvaloNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of Asymmetrical Infilled Concrete Frames: T. MahdiDocument7 pagesPushover Analysis of Asymmetrical Infilled Concrete Frames: T. MahdiGabriela EsmalibethNo ratings yet
- Analysis Assignment 2 - 2021Document8 pagesAnalysis Assignment 2 - 2021kameshNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Practical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemFrom EverandPractical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsFrom EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsNo ratings yet
- Some Mooted Questions in Reinforced Concrete Design American Society of Civil Engineers, Transactions, Paper No. 1169, Volume LXX, Dec. 1910From EverandSome Mooted Questions in Reinforced Concrete Design American Society of Civil Engineers, Transactions, Paper No. 1169, Volume LXX, Dec. 1910No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173No ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Structures: Shukhov's Lattice Towers - Forerunners of Modern Lightweight ConstructionFrom EverandHyperbolic Structures: Shukhov's Lattice Towers - Forerunners of Modern Lightweight ConstructionNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeFrom EverandA Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Locomotive Performance On Grades Of Various Lengths, Paper No. 1172From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Locomotive Performance On Grades Of Various Lengths, Paper No. 1172No ratings yet
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- Strength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionFrom EverandStrength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer The Following Question. Show Your SolutionDocument4 pagesInstruction: Answer The Following Question. Show Your SolutionJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Travel Demand Forecastin Part 2Document14 pagesTravel Demand Forecastin Part 2Josiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Engr'ng Economy Report - Aguilar, A.MDocument27 pagesEngr'ng Economy Report - Aguilar, A.MJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Part 3Document13 pagesEngineering Economy Part 3Josiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument11 pagesTravel Demand ForecastingJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Travel Distribution Method ContnDocument7 pagesTravel Distribution Method ContnJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Table 1 Properties of Common Plane SectionsDocument1 pageTable 1 Properties of Common Plane SectionsJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Reinforced Concrete DesignJosiah Flores100% (1)
- Course Name: Civil Engineering Laws, Contracts, and Specifications Course DescriptionDocument3 pagesCourse Name: Civil Engineering Laws, Contracts, and Specifications Course DescriptionJosiah Flores100% (1)