Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculator Using Generic Delegate and Event: Laboratory Exercise
Calculator Using Generic Delegate and Event: Laboratory Exercise
Uploaded by
Ruq BaldemorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculator Using Generic Delegate and Event: Laboratory Exercise
Calculator Using Generic Delegate and Event: Laboratory Exercise
Uploaded by
Ruq BaldemorCopyright:
Available Formats
IT1811
Laboratory Exercise
Calculator Using Generic Delegate and Event
Objectives:
At the end of the exercise, the students should be able to:
Declare, instantiate, and invoke delegates;
Use generic delegate data types in a program; and
Declare events and use event accessors.
Software Requirement:
Visual Studio IDE 2015 or higher
Procedures:
Instructions:
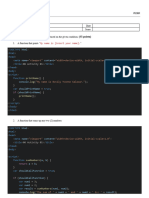
1. Create a simple calculator for a Windows application. Name the project as CalculatorApplication and
the form as FrmCalculator.
2. Follow the design for the FrmCalculator using the screenshot below. Refer to the table for the
properties for each control.
Windows Forms Controls Properties
Name: txtBoxInput1
TextBox
Font Size: 12
Name: cbOperator
ComboBox Font Name: Consolas
Font Size: 12
Name: txtBoxInput2
TextBox
Font Size: 12
Label Name: lblDisplayTotal
Name: btnEqual
Button Font Name: Consolas
Font Size: 14
01 Laboratory Exercise 2 *Property of STI
Page 1 of 3
IT1811
3. In the ComboBox, add the following arithmetic operators:
Arithmetic Operators
+
-
*
/
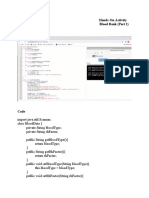
4. Create a class named CalculatorClass and declare a generic delegate named Formula above the
name of the class. See sample code below.
public delegate T Information<T>(T arg1);
5. Inside the class, declare the generic delegate's variable and set its data type to double. See sample
code below.
public Information<string> info;
6. After declaring the variable for the generic delegate, create two (2) methods that return the sum and
difference based on the following table:
Method Name Data Type
GetSum Double
GetDifference Double
7. Add an event accessor named CalculateEvent with two (2) methods add and remove. Set a message
in the console just to confirm if the delegate is added or removed.
Example: Console.WriteLine("Added the Delegate");
8. In the frmCalculator class, declare the variable for the CalculatorClass named cal. After declaring,
instantiate it inside the constructor of frmCalculator.
9. Set the two (2) variables where the data types are double with a variable named num1 and num2.
10. Double click the button to create the method for button event automatically.
11. Get the value of txtBoxInput1 for num1 and txtBoxInput2 for num2.
Note: You may encounter an error that says, "Cannot implicitly convert type string to double." If this happen
use Convert.ToDouble() to convert the value in the TextBox.
01 Laboratory Exercise 2 *Property of STI
Page 2 of 3
IT1811
Challenge Exercise:
12. In CalculatorClass, add two (2) return type methods named GetProduct for multiplication and
GetQuotient for division.
13. In the frmCalculator class, write a condition that validates the selected arithmetic operator in the
ComboBox. It should call the event and display the answer in a label.
Example:
cal.CalculateEvent += new Formula<double>(cal.GetSum);
lblDisplayTotal.Text = cal.GetSum(num1,num2).ToString();
cal.CalculateEvent -= new Formula<double>(cal.GetSum);
14. Run the program to check the output.
15. Inform your instructor once you’re done as this will be recorded.
Grading Rubric:
CRITERIA PERFORMANCE INDICATORS POINTS
Correctness The code produces the expected result. 30
Logic The code meets the specifications of the problem. 30
Efficiency The code is concise without sacrificing correctness and logic. 20
Syntax The code adheres to the rules of the programming language. 20
TOTAL 100
01 Laboratory Exercise 2 *Property of STI
Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Account Registration: Laboratory ExerciseDocument3 pagesAccount Registration: Laboratory ExerciseRuq BaldemorNo ratings yet
- Task 3Document51 pagesTask 3Alisher ShokhanovNo ratings yet
- CHAKRA FOR SEX - Harnessing The Sexual EnergyDocument36 pagesCHAKRA FOR SEX - Harnessing The Sexual EnergyDamir67% (3)
- SQLTRANSACTIONSDocument2 pagesSQLTRANSACTIONSSTEVE JHONSON LepasanaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Risk Management NewDocument42 pagesModule 8 - Risk Management NewEmmie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 03 Activity 3 - ARGDocument4 pages03 Activity 3 - ARGstapaNo ratings yet
- GplistDocument10 pagesGplistDean Fanning50% (2)
- 02 Laboratory Exercise 1Document2 pages02 Laboratory Exercise 1Ryan LumpasNo ratings yet
- Lab Exer 9Document1 pageLab Exer 9AnonymousNo ratings yet
- 02 TaskPerformance 1 ITSMDocument1 page02 TaskPerformance 1 ITSMRuq BaldemorNo ratings yet
- CodesDocument3 pagesCodesAshley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 07 Hands-On Activity 1 - ARG (TANTAY)Document5 pages07 Hands-On Activity 1 - ARG (TANTAY)Christian Luzon TantayNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1-ISSDocument1 page01 Laboratory Exercise 1-ISSPrincess AletreNo ratings yet
- 05 Laboratory Exercise 1Document4 pages05 Laboratory Exercise 1PJ FloresNo ratings yet
- 1.0 What Is Operating System?: Four Components of Computer SystemDocument8 pages1.0 What Is Operating System?: Four Components of Computer SystemPaolo Yao ElloNo ratings yet
- 02 Laboratory Exercise 1 PDFDocument1 page02 Laboratory Exercise 1 PDFAeirra Mae Mislang ReyesNo ratings yet
- Tourism Characteristics of Camiguin IslandDocument28 pagesTourism Characteristics of Camiguin IslandLanie HampacNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE VIIDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in TLE VIIJose Nilo Pastorall70% (10)
- Offshore Engineer-February 2015Document84 pagesOffshore Engineer-February 2015ilkerkozturk100% (2)
- Survey Questionnaire - 21st Century SkillsDocument2 pagesSurvey Questionnaire - 21st Century SkillsJhun Lerry Manalo Tayan100% (3)
- Operators and Array: 06 Laboratory Exercise 1Document3 pagesOperators and Array: 06 Laboratory Exercise 1PJ FloresNo ratings yet
- 08 Laboratory Exercise 1Document3 pages08 Laboratory Exercise 1PJ FloresNo ratings yet
- 02 Hands-On Activity 1Document4 pages02 Hands-On Activity 1Ericka JanelleNo ratings yet
- 03 - Quiz - 1 - Dela CernaDocument2 pages03 - Quiz - 1 - Dela CernaNerren Ann Caseñas EspinaNo ratings yet
- Task Performance ProcessesDocument3 pagesTask Performance ProcessesGosenNo ratings yet
- 06 Activity 1Document3 pages06 Activity 1yvonnekim1432No ratings yet
- 05 Laboratory Exercise Join ClausesDocument5 pages05 Laboratory Exercise Join ClausesGhefelyn Medina0% (1)
- 07 Hands-On Activity 1Document1 page07 Hands-On Activity 1DARA0% (2)
- Run Savings AccountDocument2 pagesRun Savings Accountjolo magtutoNo ratings yet
- 02 Task Performance 1 ARG PlatForm LorejoDocument3 pages02 Task Performance 1 ARG PlatForm LorejoJimboy LorejoNo ratings yet
- Labexer 7 ADocument8 pagesLabexer 7 AAnonymousNo ratings yet
- 03 Laboratory Exercise 1Document5 pages03 Laboratory Exercise 1Vincent Lorenton BiñasNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 FajardoMDocument12 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 1 FajardoMMurielle FajardoNo ratings yet
- 04 Task Performance 1 - ARGDocument2 pages04 Task Performance 1 - ARGNedelyn PayaoNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming 2 - 09 Hands-On Activity 2Document3 pagesComputer Programming 2 - 09 Hands-On Activity 2AnimeZing ChannelNo ratings yet
- 02 Task Performance 1Document2 pages02 Task Performance 1Ed Gierson PascualNo ratings yet
- JawaaaaDocument1 pageJawaaaaFrancis jade SolomonNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGDocument1 page01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGChesang Mond Jib100% (1)
- 02 Activity 1Document1 page02 Activity 1Ralier CalalangNo ratings yet
- 05 Laboratory Exercise 1 Mariano Winston - Docx 1Document5 pages05 Laboratory Exercise 1 Mariano Winston - Docx 1jhonnel umandalNo ratings yet
- Decimals ExamplesDocument2 pagesDecimals ExamplesKazel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 06TaskPerformance1 GrijaldoDocument5 pages06TaskPerformance1 GrijaldoDoctor Edward KenwayNo ratings yet
- Garamond (12) : Ge180401Task Performance 1 Property of Stipage 1of 2Document2 pagesGaramond (12) : Ge180401Task Performance 1 Property of Stipage 1of 2Nes MendozaNo ratings yet
- 08 Task PerformanceDocument5 pages08 Task Performancecyrelle josueaNo ratings yet
- 1502 F17 Assignment 4 - Payroll System v2Document4 pages1502 F17 Assignment 4 - Payroll System v2Rehan BariNo ratings yet
- 06 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGDocument2 pages06 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGUnknown PeterosNo ratings yet
- 06 PTintroDocument2 pages06 PTintroKamote Que100% (1)
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 15Document3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 15Ruq BaldemorNo ratings yet
- 06 HandsDocument2 pages06 HandsAnonNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise (Programming)Document1 pageLab Exercise (Programming)Ashley AquinoNo ratings yet
- 08activity1 DataStructures&Algorithms MoralesDocument1 page08activity1 DataStructures&Algorithms MoralesHazzel GilveroNo ratings yet
- 08 Laboratory Exercise 1Document1 page08 Laboratory Exercise 1Cj AdonisNo ratings yet
- Midterm Practical Exam (OOP)Document3 pagesMidterm Practical Exam (OOP)Alden DadesNo ratings yet
- Overloading Examples JavaDocument5 pagesOverloading Examples JavaaasxdasNo ratings yet
- 11 Seatwork 2Document1 page11 Seatwork 2Adrian AndalNo ratings yet
- 07 Task Performance 1 - ARGDocument1 page07 Task Performance 1 - ARGkring kringNo ratings yet
- 03 Task Performance 1 1Document2 pages03 Task Performance 1 1Jash FranceNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: Introduction To Turbo Assembler 2.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityDocument9 pagesActivity 2: Introduction To Turbo Assembler 2.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityKimCanillasVincereNo ratings yet
- SALVADOR - 05 Hands On Activity 1 ARGDocument2 pagesSALVADOR - 05 Hands On Activity 1 ARGJanah Rose MedinaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 1: Know The UserDocument4 pagesLaboratory Exercise 1: Know The Usertami cruzNo ratings yet
- CLI Basics: Laboratory ExerciseDocument5 pagesCLI Basics: Laboratory ExerciseJhalen Shaq CarrascoNo ratings yet
- 04 Task Performance 1 - ARGDocument2 pages04 Task Performance 1 - ARGLacorte Jr MeranoNo ratings yet
- 02 Task Performance 1 Data and Digital Comms (Javier)Document1 page02 Task Performance 1 Data and Digital Comms (Javier)Vinz Dominic JavierNo ratings yet
- VALMONTEDocument3 pagesVALMONTEXijhyve ManganaNo ratings yet
- 2 PointsDocument5 pages2 PointsJoel ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Alvarado 04 TP Concurrency DeadlocksDocument2 pagesAlvarado 04 TP Concurrency DeadlocksXeb VlogsNo ratings yet
- 05 Demonstration PDFDocument3 pages05 Demonstration PDFMook HyangNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 15Document3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 15Ruq BaldemorNo ratings yet
- New Regular Passport Application (Adult)Document2 pagesNew Regular Passport Application (Adult)Ruq BaldemorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 and 4 GuideDocument7 pagesChapter 3 and 4 GuideRuq BaldemorNo ratings yet
- Shezan Project Marketing 2009Document16 pagesShezan Project Marketing 2009Humayun100% (3)
- How To Perfect A LienDocument7 pagesHow To Perfect A LienKonan Snowden83% (6)
- Dance Like A ManDocument4 pagesDance Like A ManShubhadip aichNo ratings yet
- How Do Homes Provide Safe ShelterDocument10 pagesHow Do Homes Provide Safe ShelterInda KusumawatiNo ratings yet
- Oikonomou Mpegetis S 2014 PHD ThesisDocument352 pagesOikonomou Mpegetis S 2014 PHD ThesisCsillag JanosNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency (Essential Competency) : Let's Recall (Review)Document6 pagesLearning Competency (Essential Competency) : Let's Recall (Review)Heidee BasasNo ratings yet
- Installing Wonderware InTouch 2014 R2 DevelopmentDocument12 pagesInstalling Wonderware InTouch 2014 R2 DevelopmentARMANDO GALENONo ratings yet
- Time Clauses - That Vs Which-Relative ClausesDocument8 pagesTime Clauses - That Vs Which-Relative ClausesZuza AlexandrinaNo ratings yet
- 13 3friedman PDFDocument20 pages13 3friedman PDFfreedownloads1No ratings yet
- Презентация smartwatchesDocument10 pagesПрезентация smartwatchesZiyoda AbdulloevaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Health Systems and PolicyDocument81 pagesEthiopian Health Systems and PolicyFami Mohammed100% (2)
- Marketable Avenues: 14,15,16 April 2023Document31 pagesMarketable Avenues: 14,15,16 April 2023Avaneesh Natraj GujranNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 NotesDocument5 pagesGRADE 8 NotesIya Sicat PatanoNo ratings yet
- HRM Project On Engro FoodsDocument20 pagesHRM Project On Engro FoodsSaad MughalNo ratings yet
- MUSIC10 Q2 (Latin American Music, Jazz and Pop Music) Week 2 - CardelDocument5 pagesMUSIC10 Q2 (Latin American Music, Jazz and Pop Music) Week 2 - CardelJeff Nieva CardelNo ratings yet
- REPLY in Opposition To Barry MargolisDocument9 pagesREPLY in Opposition To Barry MargolisSLAVEFATHERNo ratings yet
- The Role of The School Psychologist in The Inclusive EducationDocument20 pagesThe Role of The School Psychologist in The Inclusive EducationCortés PameliNo ratings yet
- Nod 321Document12 pagesNod 321PabloAyreCondoriNo ratings yet
- Global Guidelines For The Prevention of Surgical Site Infection: An IntroductionDocument8 pagesGlobal Guidelines For The Prevention of Surgical Site Infection: An IntroductionJNUHospital NABHNo ratings yet
- HW On Receivables CDocument5 pagesHW On Receivables CAmjad Rian MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - TR-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesActivity 4 - TR-WPS OfficeJed JaquecaNo ratings yet
- Graded Lab Lab - 7 Introduction To Computing: Topics: If - Else Conditions, While LoopDocument5 pagesGraded Lab Lab - 7 Introduction To Computing: Topics: If - Else Conditions, While LoopqwertyNo ratings yet
- Word Form KeyDocument2 pagesWord Form KeyHoang Quynh AnhNo ratings yet
- EnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 12BDocument1 pageEnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 12BB Mc0% (1)
- General Electrical SystemDocument136 pagesGeneral Electrical SystemSales AydinkayaNo ratings yet