Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Introduction Guide
Biology Introduction Guide
Uploaded by
Ana Lucia Lozada NoeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Introduction Guide
Biology Introduction Guide
Uploaded by
Ana Lucia Lozada NoeCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology interparcial guide
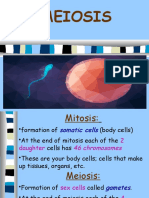
Meosis
Meosis is a form of cell division in which cell gamets produce 4 daughter cell with
haploid (half) number of chromososmes.
The process is also known as gameotosis because sperm and eggs divide by
spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Ha Ha
ploi ploi
d d
()n ()n
Diploid
(2n)
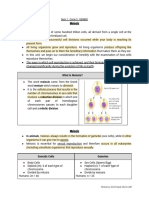
Meosis I
Prophase I { Metaphase I { Anaphase I { Telophase I { Cytokynesis I
Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I
Chromosomes condense and become Homologous Homologous Nucleus is formed around each
visible. chromosomes chromosomes separated chromosome.
Homologous chromosomes (same size) align at the separate and move Spindle fibers disappear.
form pairs called tetrads/ bivalent, process middle equator to opposite poles. Chromosomes decondense cytokinesis
called synapsis, and exchange genetical of the cell begin over.
material, process called crossing over this 1 diploid cell (46) results in 2 haploid
point is chiasma/chiasmata (23).
Spindle fibers are formed they are proteins
that help divide genetic materials by
centrioles.
Nucleus disappears.
Meosis II
Prophase II { Metaphase II { Anaphase II { Telophase II { Cytokynesis II
Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase I Telophase I
Chromosomes condense and become Chromosomes Sister chromatins Nucleus is formed around each
visible. align at the separate and move separated sister chromatin.
Spindle fibers are formed they are proteins middle equator to opposite poles. Spindle fibers disappear.
that help divide genetic materials by of the cell. Chromosomes decondense cytokinesis
centrioles. begin over again.
Nucleus disappears. 2 haploid (23) result in 4 haploid (23).
Importance:o creates genetic diversities, preserves diploid number of chromosomes during
sexual reproduction and leads to evolution.
You might also like
- Biology 30 Student Notes Cells Genetics PopulationDocument47 pagesBiology 30 Student Notes Cells Genetics PopulationuyenNo ratings yet
- The Legal Epistemology of Qur'anic Variants: The Readings of Ibn Mas'ud in Kufan Fiqh and The Hanafi Madhhab - Postprint - Ramon HarveyDocument30 pagesThe Legal Epistemology of Qur'anic Variants: The Readings of Ibn Mas'ud in Kufan Fiqh and The Hanafi Madhhab - Postprint - Ramon Harveyrnharvey100% (1)
- 5.2 Meiosis: 5 People Chapter 5: Cell DivisionDocument4 pages5.2 Meiosis: 5 People Chapter 5: Cell DivisionVivekananda MarieNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument17 pagesMeiosisSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Study Guide PPT AnsDocument12 pagesStudy Guide PPT AnsOleksii SemeniukNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Cellular Basis of HeredityDocument59 pagesChapter I: Cellular Basis of HeredityBnDeRNo ratings yet
- MitosismeiosisDocument44 pagesMitosismeiosisalanamaharaj20No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle&MitosisDocument43 pagesCell Cycle&MitosisPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reduction-Division Genetic RecombinationDocument74 pagesReduction-Division Genetic Recombinationeden loredoNo ratings yet
- 3-Rajesh-Meiosis Class On 12th Feb 2013Document35 pages3-Rajesh-Meiosis Class On 12th Feb 2013Kanishk SinghNo ratings yet
- Handout MeiosisDocument4 pagesHandout MeiosisMoira Regina Lugo QuiogueNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StudentDocument33 pagesMeiosis StudentChernaemiller123No ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- BIOL124 W5 AS Celldivision MeiosisDocument51 pagesBIOL124 W5 AS Celldivision Meiosisadaakyol05No ratings yet
- Meiosis ReductiodivisionDocument55 pagesMeiosis ReductiodivisionJelly Pearl ParzanNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument39 pagesMeiosisGrachiella JanenNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS OnlineDocument42 pagesMEIOSIS OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
- Inheritance, MeiosisDocument7 pagesInheritance, MeiosisTadi MurombaNo ratings yet
- Lab (10) MeiosisDocument6 pagesLab (10) Meiosisjolan.freedomNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument113 pagesMeiosisSubhradeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lecture 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityDocument67 pagesGenetics Lecture 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityKareen Joy ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- BIL250-T1 TermsDocument34 pagesBIL250-T1 TermsClaire IfrahNo ratings yet
- Text Boxes Have Links To Different SlideDocument21 pagesText Boxes Have Links To Different SlideJuana Montoya VenegasNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- BTN222 L4 CellCycle 2019Document51 pagesBTN222 L4 CellCycle 2019rafiya IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Final LectureDocument43 pagesCell Division Final LectureJosielyn Dagondon MachadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Document21 pagesLecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Mohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis. GametogenesisDocument21 pagesMeiosis. GametogenesisRiya PatelNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document37 pagesMeiosis 1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (OrganelleDocument7 pagesMitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (Organelleazzahra adeliaNo ratings yet
- How Do Cells Reproduce?: MeiosisDocument10 pagesHow Do Cells Reproduce?: Meiosismj espanolaNo ratings yet
- (Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisDocument6 pages(Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisFuzieanna BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- 2 MeiosisDocument36 pages2 MeiosisnthabiisengNo ratings yet
- 2.meiosis 1Document36 pages2.meiosis 1taskmask37No ratings yet
- Meiosis PDFDocument22 pagesMeiosis PDFEbook DownloadNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDocument11 pagesCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisJaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument57 pagesMeiosisDrei DeteraNo ratings yet
- Lec 5.3 - Meiosis-BBDocument38 pagesLec 5.3 - Meiosis-BBDuy An VoNo ratings yet
- L4 - Sexual ReproductionDocument58 pagesL4 - Sexual ReproductionTiffany LimNo ratings yet
- Early March, Meiosis - Mitosis Study Guide (3.3)Document9 pagesEarly March, Meiosis - Mitosis Study Guide (3.3)ChanelleNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionsDocument6 pagesCell DivisionsEuniceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisDocument87 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1 MeiosisDocument26 pagesGenetics 1 Meiosisapi-188431847No ratings yet
- 7 MeiosisDocument8 pages7 Meiosisdevanshianand555No ratings yet
- Pembelahan Sel: Langsung Tidak Langsung Mitosis MeiosisDocument68 pagesPembelahan Sel: Langsung Tidak Langsung Mitosis MeiosisPutti AnnisaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 ReviewerDocument2 pages3.3 Reviewerstem.patinosamcharrieNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document6 pagesMeiosis 2Areefa MohamedNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION-MeiosisDocument37 pagesCELL DIVISION-MeiosisAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument9 pagesThe Cell Cyclesalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument6 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamAishley BerdinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes: Biology 4G Chapter 5: Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesLesson Notes: Biology 4G Chapter 5: Cell DivisionBenjamin TeeNo ratings yet
- VC1 - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesVC1 - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAnubhab DasNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Science Chapter 6: Meiosis: BY: Ms Kasthuri JDocument35 pagesFoundation in Science Chapter 6: Meiosis: BY: Ms Kasthuri JKassyKasNo ratings yet
- Cueva - Assignment Mitosis and MeiosisDocument11 pagesCueva - Assignment Mitosis and MeiosisCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- 14-Cell DivisionDocument9 pages14-Cell DivisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- US April'23 PAKET BDocument12 pagesUS April'23 PAKET BProject P2BanjaranNo ratings yet
- Cell Phone Radiation PresentationDocument16 pagesCell Phone Radiation PresentationCeasar CoolNo ratings yet
- Earth As A SphereDocument96 pagesEarth As A SphereMarlina MohamedNo ratings yet
- HLARA ProcessDocument5 pagesHLARA ProcessRanjana SainiNo ratings yet
- A Doll's House - Problem Play and TitleDocument3 pagesA Doll's House - Problem Play and Titlethexgrind683No ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument22 pagesLaplace TransformsAustin JamesNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Spec PDFDocument18 pagesBlockchain Spec PDFblueNo ratings yet
- Ai TS NOTICE FOR CLASS IX XDocument1 pageAi TS NOTICE FOR CLASS IX XVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Angle Closure GlaucomaDocument289 pagesAngle Closure GlaucomaWilson100% (1)
- GR 19 (MND)Document6 pagesGR 19 (MND)arorayash603No ratings yet
- Work in Team Environment Learning ModuleDocument3 pagesWork in Team Environment Learning ModuleNesri YayaNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide To Fit Outs 27-02-20Document8 pagesStep by Step Guide To Fit Outs 27-02-20Kushal kumar.gNo ratings yet
- Travels Booking SystemDocument88 pagesTravels Booking SystemindrajeetNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Review Physics 11 SolutionsDocument8 pagesDynamics Review Physics 11 SolutionsAiswariya Alagu SunderNo ratings yet
- Intercultural and Global Communication ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntercultural and Global Communication ReviewerJESTON AMBUNANNo ratings yet
- How To Mix Colors in Paint ProductionDocument17 pagesHow To Mix Colors in Paint ProductionBachir Ismail100% (1)
- GBD26KS La26r71b GBD32KS La32r71b GBD40KS La40r71b GBD32KS La32r71wDocument177 pagesGBD26KS La26r71b GBD32KS La32r71b GBD40KS La40r71b GBD32KS La32r71wARTMehr Eng. GroupNo ratings yet
- Multi Inverter 4TXM6530A-SUB-1GDocument4 pagesMulti Inverter 4TXM6530A-SUB-1GOmar PiñaNo ratings yet
- Ma2016 Article OverviewOnVerticalAndDirectionDocument31 pagesMa2016 Article OverviewOnVerticalAndDirectionDarryan DhanpatNo ratings yet
- 02 Algorithm AnalysisDocument49 pages02 Algorithm AnalysisĐăng BùiNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Al Ayuni Saudi Arabia: Sponsor Interview On 2Nd Week of June 2019Document3 pagesRequirements For Al Ayuni Saudi Arabia: Sponsor Interview On 2Nd Week of June 2019Tradiyo ForexNo ratings yet
- Seminar PresentationDocument16 pagesSeminar PresentationVinay KurkuriNo ratings yet
- CATIA - Human Builder & SimulationDocument2 pagesCATIA - Human Builder & Simulationguen_betonamuNo ratings yet
- Temporary Sream and Wetland CrossingDocument139 pagesTemporary Sream and Wetland CrossingFranklin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Structure For A Three Point Bending TestDocument13 pagesDesign and Construction of A Structure For A Three Point Bending TestIñigoNo ratings yet
- Inhibition of Methicillin-Resistant StaphylococcusDocument7 pagesInhibition of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcusdaniel_siitompulNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub Numerical and Statistical Methods For Computer Engineering Gujarat Technological University 2017 2nbsped 9789352604852 9352604857Document598 pagesDokumen - Pub Numerical and Statistical Methods For Computer Engineering Gujarat Technological University 2017 2nbsped 9789352604852 9352604857Sasmita NayakNo ratings yet
- CGC1D Assignment 2.1 Fire and Ice ArticlesDocument3 pagesCGC1D Assignment 2.1 Fire and Ice ArticlesMayaNo ratings yet