Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Probability Sampling - Examples 1
Types of Probability Sampling - Examples 1
Uploaded by
Monaliza NavarroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mutually Exclusive EventsDocument20 pagesMutually Exclusive EventsDeoveon CadoreeNo ratings yet
- SFAS No 117Document70 pagesSFAS No 117abekaforumNo ratings yet
- Book Report On The Pythagorean TheoremDocument7 pagesBook Report On The Pythagorean Theoremwrc089100% (1)
- Stratified Random SamplingDocument19 pagesStratified Random SamplingMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Episode 3 of The Ascent of Money Focuses On The Place Where Shares of Public Listed Companies Are TradedDocument1 pageEpisode 3 of The Ascent of Money Focuses On The Place Where Shares of Public Listed Companies Are Tradeddani qintharaNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Business Combination)Document23 pagesCase Study (Business Combination)Princes S. RoqueNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic AssessmentDocument7 pagesDiagnostic AssessmentChristine JoyceNo ratings yet
- YupDocument52 pagesYupBianca EnglatieraNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2 Math LogicDocument28 pagesMMW Module 2 Math LogicJeanisa FusinganNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Statistics) - AssignmentDocument1 pageProblem Set (Statistics) - Assignmentchelsea kayle licomes fuentes100% (1)
- Time and Motion Studies by TaylorDocument3 pagesTime and Motion Studies by TaylorMansoor MoinNo ratings yet
- Identify and Analyze IT System Components To Be MaintainedDocument12 pagesIdentify and Analyze IT System Components To Be MaintainedAbraha GebrekidanNo ratings yet
- Finals - II. Deductions & ExemptionsDocument13 pagesFinals - II. Deductions & ExemptionsJovince Daño DoceNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply With Surplus and ShortageDocument4 pagesDemand and Supply With Surplus and Shortagemanish KumarNo ratings yet
- Gudsilog Project ProposalDocument2 pagesGudsilog Project ProposalLucas GalingNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Constitution and GovernmentDocument24 pagesLecture Notes On The Constitution and Governmentancaye1962No ratings yet
- Taxation May Board ExamDocument25 pagesTaxation May Board ExamjaysonNo ratings yet
- ISM Finite Ch3-3Document34 pagesISM Finite Ch3-3Ali EzzatNo ratings yet
- Youth UnemploymentDocument6 pagesYouth UnemploymentJames Clarenze VarronNo ratings yet
- Train LawDocument44 pagesTrain LawJuan MiguelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Apportionment: Section 9.1 Basic Concepts of Apportionment and Hamilton's MethodDocument26 pagesChapter 9: Apportionment: Section 9.1 Basic Concepts of Apportionment and Hamilton's MethodJag MasterNo ratings yet
- Module IIDocument76 pagesModule IIAshNo ratings yet
- Flexible BudgetDocument11 pagesFlexible BudgetNic JfNo ratings yet
- Subsistence Theory: Wage Theories Economic Theories of WagesDocument8 pagesSubsistence Theory: Wage Theories Economic Theories of Wagesfelix thadevoosNo ratings yet
- LBOLYTC Quiz No. 1 - T3 2023Document13 pagesLBOLYTC Quiz No. 1 - T3 2023Asdfgh JklNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document21 pagesSheet 2yehyaNo ratings yet
- 3.term PaperDocument14 pages3.term Paperrohitpatil999100% (4)
- Transportation Models (Repaired)Document26 pagesTransportation Models (Repaired)smsmbaNo ratings yet
- PH Credit Corp v. CA, Carlos M FarralesDocument4 pagesPH Credit Corp v. CA, Carlos M FarralesGabby CordovaNo ratings yet
- System Design in POM 1Document11 pagesSystem Design in POM 1John Patrick Lazaro AndresNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation Chapter 1Document5 pagesIncome Taxation Chapter 1Princess Ivy PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Comparative Advantage ExampleDocument3 pagesComparative Advantage ExamplekhushiYNo ratings yet
- Moi Quiz With AnswersDocument6 pagesMoi Quiz With AnswersLorraine TioNo ratings yet
- An-online-news-account-narrates-key-officials-from-both-the-legislative-and-executive-branches-of-the-government-voicing-out-their-concern-on-the-possible-ill-effects-of-too-much-violence-seen-by-children-.docxDocument4 pagesAn-online-news-account-narrates-key-officials-from-both-the-legislative-and-executive-branches-of-the-government-voicing-out-their-concern-on-the-possible-ill-effects-of-too-much-violence-seen-by-children-.docxPeligrino MacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentDocument50 pagesChapter 6 - Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentKenzel lawasNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - Management TrendsDocument7 pagesCourse Syllabus - Management TrendsPat LanugonNo ratings yet
- BTR Functions Draft 6-1-15Document16 pagesBTR Functions Draft 6-1-15Hanna PentiñoNo ratings yet
- What Is The General Accounting Plan of Government Agencies/units?Document2 pagesWhat Is The General Accounting Plan of Government Agencies/units?Che CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Lumban ProbsDocument3 pagesLumban ProbsShinjiNo ratings yet
- Rise and Share Tenancy Act of 1933Document25 pagesRise and Share Tenancy Act of 1933Pamela Ledesma SusonNo ratings yet
- Producer and Consumer SurplusDocument28 pagesProducer and Consumer SurplusSyedNo ratings yet
- DMS NotesDocument45 pagesDMS Notessubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Lesson 1, 2, 3 DiscussionDocument8 pagesLesson 1, 2, 3 DiscussionIrl AlcabazaNo ratings yet
- Income TaxationDocument124 pagesIncome TaxationGWENN JYTSY BAFLORNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesWeek 13 Sampling TechniqueswheezyNo ratings yet
- Business - Talim Bay EcoTourism Facility Improvement-1Document8 pagesBusiness - Talim Bay EcoTourism Facility Improvement-1Geli VNo ratings yet
- S Such That - S Such That - S Such ThatDocument2 pagesS Such That - S Such That - S Such ThatAeron TecsonNo ratings yet
- NSTP FormatDocument3 pagesNSTP FormatJason PanganNo ratings yet
- Assignment: The Rizal LawDocument3 pagesAssignment: The Rizal LawMary ruth DavidNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - General PrinciplesDocument11 pagesModule 1 - General PrinciplesJANE ARVEE ALLYNETTE LEYNES100% (1)
- Pentacapital V MahinayDocument3 pagesPentacapital V MahinayHector Mayel Macapagal0% (1)
- Tesda LawDocument81 pagesTesda LawJOHN QUIROZNo ratings yet
- HOMEWORK 1 Concept of TaxationDocument5 pagesHOMEWORK 1 Concept of Taxationfitz garlitosNo ratings yet
- COA Decision 2010-092 Hazard Pay Exposure To Risk QualificationDocument6 pagesCOA Decision 2010-092 Hazard Pay Exposure To Risk QualificationJasmine MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation01Document7 pagesIncome Taxation01Ailene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Has The Philippines Undergone Demographic Transition? Why or Why Not?Document12 pagesHas The Philippines Undergone Demographic Transition? Why or Why Not?AkoSi Primo0% (1)
- Chap 2 The Business MissionDocument27 pagesChap 2 The Business MissionFarith HanafiNo ratings yet
- Math 15 Module 3 - Exercise 1&2 - GaytaDocument4 pagesMath 15 Module 3 - Exercise 1&2 - GaytaPeter gayta100% (1)
- Module 2 - Research MethodologyDocument18 pagesModule 2 - Research MethodologyPRATHAM MOTWANI100% (1)
- Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail Hypermarket Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail HypermarketFrom EverandCustomers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail Hypermarket Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail HypermarketNo ratings yet
- Government of Tamilnadu: Department of Employment and TrainingDocument155 pagesGovernment of Tamilnadu: Department of Employment and TrainingNijam NagoorNo ratings yet
- Statistical Research ProblemDocument6 pagesStatistical Research ProblemMuslima IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Calculator Technique For Solving Volume Flow Rate Problems in CalculusDocument3 pagesCalculator Technique For Solving Volume Flow Rate Problems in CalculusasapamoreNo ratings yet
- Sequential Encoding of Tamil Kolam PatternsDocument11 pagesSequential Encoding of Tamil Kolam PatternsNITIKA KHATKARNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 4Document80 pagesChapitre 4Chaima BelhediNo ratings yet
- NMOS 2014 Preliminary RoundDocument11 pagesNMOS 2014 Preliminary Roundyijie liNo ratings yet
- Incremental Calculation of Weighted Mean and VarianceDocument8 pagesIncremental Calculation of Weighted Mean and VarianceScott TreloarNo ratings yet
- Real NumbersDocument4 pagesReal NumbersDumbNo ratings yet
- The Canonical Partition FunctionDocument15 pagesThe Canonical Partition FunctionWellington ZorzettiNo ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated Motion (One Dimension)Document12 pagesUniformly Accelerated Motion (One Dimension)Ma Kristina Cassandra LunorNo ratings yet
- Proofs Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesProofs Cheat SheethamzaNo ratings yet
- DSD Lectures 13 14Document13 pagesDSD Lectures 13 14ammar abbasNo ratings yet
- Queueing ModelDocument54 pagesQueueing ModelBikram KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2Yordanos AbebawNo ratings yet
- Standard Eight: No Plastic PleaseDocument132 pagesStandard Eight: No Plastic PleaseVinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- Timetable For Upper Class LatestDocument2 pagesTimetable For Upper Class LatestPersona DelailaNo ratings yet
- GATE - CSE Made Easy 342 392Document51 pagesGATE - CSE Made Easy 342 392Stuti Gupta100% (1)
- Introduction To Data SturctureDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Data SturcturebahugunaharishNo ratings yet
- Adarsh Front PagesDocument8 pagesAdarsh Front Pagesravi singhNo ratings yet
- Sma 2270 Calculus IiiDocument50 pagesSma 2270 Calculus IiiCamilla IrunguNo ratings yet
- Scientific Work PlaceDocument551 pagesScientific Work Placepeloton10No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 More About PolynomialsDocument15 pagesChapter 7 More About Polynomialsapi-3704862No ratings yet
- J. Mozo - P.Fernandez - H. NeciosupDocument14 pagesJ. Mozo - P.Fernandez - H. NeciosupJimmy Támara AlbinoNo ratings yet
- ve#Multi!Step%Inequalities: NotesDocument4 pagesve#Multi!Step%Inequalities: Notesapi-327561261No ratings yet
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Slope Intercept FormDocument13 pagesG8 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Slope Intercept FormWenilyn MananganNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression WRK CH 1Document3 pagesLinear Regression WRK CH 1Katie DuncanNo ratings yet
- Mid Point & Section FormulaDocument3 pagesMid Point & Section FormulaAanjaneya JindalNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification - First GradingDocument1 pageTable of Specification - First GradingWellaCelestinoNo ratings yet
- Master of Science Naresuan UniversityDocument29 pagesMaster of Science Naresuan UniversityHira DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Cs Fall 21 Seq Sheet TransferDocument1 pageCs Fall 21 Seq Sheet Transferapi-547823268No ratings yet
Types of Probability Sampling - Examples 1
Types of Probability Sampling - Examples 1
Uploaded by
Monaliza NavarroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Probability Sampling - Examples 1
Types of Probability Sampling - Examples 1
Uploaded by
Monaliza NavarroCopyright:
Available Formats
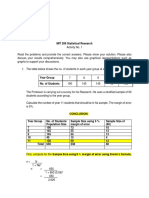
Direction:
Create examples for each of the types of probability sampling discussed in Lecture 2.
Probability Sampling and its example:
1. Simple Random Sampling
- A group of researchers wants to know the daily allowance of a student from BS
Mathematics- Applied Statistics. There are a total of 526 students on the list from the
office under the said program. Now, the researchers have decided to randomly pick
100 students from the said list that will serve as their sample. The 100 students were
randomly selected and has the equal chance to get picked among the 526 students,
therefore, it was a simple random sampling.
2. Stratified Random Sampling
- Ella, a nursing student wants to know the cholesterol of her block mates that ranges to
18-25 years old. There are 50 students in her block and she assumed that a number of
10 people would suffice as her sample to represent the total number of her block
mates. To get the sample size, she divided the assumed entire sample size by the total
number of her block mates and multiplied it to the number of each stratum.
Age Total number Number of her block mates per stratum
≤ 20 29
( 1050 ) ×29
=5.8 or simply 6
≥ 21 21 10
( )
50
×21
=4.2 or simply 4
Total 50 6+ 4=10
Now, she was able to compute the right sample per ages for her sample size.
Everyone was available that time so she decided to let her phone application- spin the
wheel to set the 4 students who less than equal to 20 and 6 students who are greater
than equal to 21.
3. Cluster sampling
- A company wants to know the spending cycle of population in Meycauayan. There
are 10 barangays that has 20,100 people. Due to lack of work force, the company has
decided to take 500 people to be the sample size. Now they estimated the average
number of populations per barangay dividing the total population to the number of
barangays.
No. of Barangays Population Average no. of population
30 20,100 20,100
=670
30
people per barangay.
Now divide the sample size to the average people per barangay
500
=0.746 or 0.75 or 75% of the population in one barangay
670
To check, multiply the value above to average population per barangay
0.746 ×670=499.82∨500 participants
Use Simple Random Sampling to get 500 participants out of 670 people.
4. Systematic Random Sampling
- A kindergarten teacher wants 10 students from 50 students to participate in a dance
program. No one wants to join so she decided to let her students count 1-5 and all
those who said number 2 will be the one to represent her class in the said program.
She finalized the list getting all the 2 nd position per 5 students in the counting in a
systematic yet everyone has the chance to be selected.
You might also like
- Mutually Exclusive EventsDocument20 pagesMutually Exclusive EventsDeoveon CadoreeNo ratings yet
- SFAS No 117Document70 pagesSFAS No 117abekaforumNo ratings yet
- Book Report On The Pythagorean TheoremDocument7 pagesBook Report On The Pythagorean Theoremwrc089100% (1)
- Stratified Random SamplingDocument19 pagesStratified Random SamplingMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Episode 3 of The Ascent of Money Focuses On The Place Where Shares of Public Listed Companies Are TradedDocument1 pageEpisode 3 of The Ascent of Money Focuses On The Place Where Shares of Public Listed Companies Are Tradeddani qintharaNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Business Combination)Document23 pagesCase Study (Business Combination)Princes S. RoqueNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic AssessmentDocument7 pagesDiagnostic AssessmentChristine JoyceNo ratings yet
- YupDocument52 pagesYupBianca EnglatieraNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2 Math LogicDocument28 pagesMMW Module 2 Math LogicJeanisa FusinganNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Statistics) - AssignmentDocument1 pageProblem Set (Statistics) - Assignmentchelsea kayle licomes fuentes100% (1)
- Time and Motion Studies by TaylorDocument3 pagesTime and Motion Studies by TaylorMansoor MoinNo ratings yet
- Identify and Analyze IT System Components To Be MaintainedDocument12 pagesIdentify and Analyze IT System Components To Be MaintainedAbraha GebrekidanNo ratings yet
- Finals - II. Deductions & ExemptionsDocument13 pagesFinals - II. Deductions & ExemptionsJovince Daño DoceNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply With Surplus and ShortageDocument4 pagesDemand and Supply With Surplus and Shortagemanish KumarNo ratings yet
- Gudsilog Project ProposalDocument2 pagesGudsilog Project ProposalLucas GalingNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Constitution and GovernmentDocument24 pagesLecture Notes On The Constitution and Governmentancaye1962No ratings yet
- Taxation May Board ExamDocument25 pagesTaxation May Board ExamjaysonNo ratings yet
- ISM Finite Ch3-3Document34 pagesISM Finite Ch3-3Ali EzzatNo ratings yet
- Youth UnemploymentDocument6 pagesYouth UnemploymentJames Clarenze VarronNo ratings yet
- Train LawDocument44 pagesTrain LawJuan MiguelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Apportionment: Section 9.1 Basic Concepts of Apportionment and Hamilton's MethodDocument26 pagesChapter 9: Apportionment: Section 9.1 Basic Concepts of Apportionment and Hamilton's MethodJag MasterNo ratings yet
- Module IIDocument76 pagesModule IIAshNo ratings yet
- Flexible BudgetDocument11 pagesFlexible BudgetNic JfNo ratings yet
- Subsistence Theory: Wage Theories Economic Theories of WagesDocument8 pagesSubsistence Theory: Wage Theories Economic Theories of Wagesfelix thadevoosNo ratings yet
- LBOLYTC Quiz No. 1 - T3 2023Document13 pagesLBOLYTC Quiz No. 1 - T3 2023Asdfgh JklNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document21 pagesSheet 2yehyaNo ratings yet
- 3.term PaperDocument14 pages3.term Paperrohitpatil999100% (4)
- Transportation Models (Repaired)Document26 pagesTransportation Models (Repaired)smsmbaNo ratings yet
- PH Credit Corp v. CA, Carlos M FarralesDocument4 pagesPH Credit Corp v. CA, Carlos M FarralesGabby CordovaNo ratings yet
- System Design in POM 1Document11 pagesSystem Design in POM 1John Patrick Lazaro AndresNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation Chapter 1Document5 pagesIncome Taxation Chapter 1Princess Ivy PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Comparative Advantage ExampleDocument3 pagesComparative Advantage ExamplekhushiYNo ratings yet
- Moi Quiz With AnswersDocument6 pagesMoi Quiz With AnswersLorraine TioNo ratings yet
- An-online-news-account-narrates-key-officials-from-both-the-legislative-and-executive-branches-of-the-government-voicing-out-their-concern-on-the-possible-ill-effects-of-too-much-violence-seen-by-children-.docxDocument4 pagesAn-online-news-account-narrates-key-officials-from-both-the-legislative-and-executive-branches-of-the-government-voicing-out-their-concern-on-the-possible-ill-effects-of-too-much-violence-seen-by-children-.docxPeligrino MacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentDocument50 pagesChapter 6 - Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentKenzel lawasNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - Management TrendsDocument7 pagesCourse Syllabus - Management TrendsPat LanugonNo ratings yet
- BTR Functions Draft 6-1-15Document16 pagesBTR Functions Draft 6-1-15Hanna PentiñoNo ratings yet
- What Is The General Accounting Plan of Government Agencies/units?Document2 pagesWhat Is The General Accounting Plan of Government Agencies/units?Che CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Lumban ProbsDocument3 pagesLumban ProbsShinjiNo ratings yet
- Rise and Share Tenancy Act of 1933Document25 pagesRise and Share Tenancy Act of 1933Pamela Ledesma SusonNo ratings yet
- Producer and Consumer SurplusDocument28 pagesProducer and Consumer SurplusSyedNo ratings yet
- DMS NotesDocument45 pagesDMS Notessubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Lesson 1, 2, 3 DiscussionDocument8 pagesLesson 1, 2, 3 DiscussionIrl AlcabazaNo ratings yet
- Income TaxationDocument124 pagesIncome TaxationGWENN JYTSY BAFLORNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesWeek 13 Sampling TechniqueswheezyNo ratings yet
- Business - Talim Bay EcoTourism Facility Improvement-1Document8 pagesBusiness - Talim Bay EcoTourism Facility Improvement-1Geli VNo ratings yet
- S Such That - S Such That - S Such ThatDocument2 pagesS Such That - S Such That - S Such ThatAeron TecsonNo ratings yet
- NSTP FormatDocument3 pagesNSTP FormatJason PanganNo ratings yet
- Assignment: The Rizal LawDocument3 pagesAssignment: The Rizal LawMary ruth DavidNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - General PrinciplesDocument11 pagesModule 1 - General PrinciplesJANE ARVEE ALLYNETTE LEYNES100% (1)
- Pentacapital V MahinayDocument3 pagesPentacapital V MahinayHector Mayel Macapagal0% (1)
- Tesda LawDocument81 pagesTesda LawJOHN QUIROZNo ratings yet
- HOMEWORK 1 Concept of TaxationDocument5 pagesHOMEWORK 1 Concept of Taxationfitz garlitosNo ratings yet
- COA Decision 2010-092 Hazard Pay Exposure To Risk QualificationDocument6 pagesCOA Decision 2010-092 Hazard Pay Exposure To Risk QualificationJasmine MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation01Document7 pagesIncome Taxation01Ailene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Has The Philippines Undergone Demographic Transition? Why or Why Not?Document12 pagesHas The Philippines Undergone Demographic Transition? Why or Why Not?AkoSi Primo0% (1)
- Chap 2 The Business MissionDocument27 pagesChap 2 The Business MissionFarith HanafiNo ratings yet
- Math 15 Module 3 - Exercise 1&2 - GaytaDocument4 pagesMath 15 Module 3 - Exercise 1&2 - GaytaPeter gayta100% (1)
- Module 2 - Research MethodologyDocument18 pagesModule 2 - Research MethodologyPRATHAM MOTWANI100% (1)
- Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail Hypermarket Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail HypermarketFrom EverandCustomers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail Hypermarket Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Customers Switching Intentions Behavior in Retail HypermarketNo ratings yet
- Government of Tamilnadu: Department of Employment and TrainingDocument155 pagesGovernment of Tamilnadu: Department of Employment and TrainingNijam NagoorNo ratings yet
- Statistical Research ProblemDocument6 pagesStatistical Research ProblemMuslima IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Calculator Technique For Solving Volume Flow Rate Problems in CalculusDocument3 pagesCalculator Technique For Solving Volume Flow Rate Problems in CalculusasapamoreNo ratings yet
- Sequential Encoding of Tamil Kolam PatternsDocument11 pagesSequential Encoding of Tamil Kolam PatternsNITIKA KHATKARNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 4Document80 pagesChapitre 4Chaima BelhediNo ratings yet
- NMOS 2014 Preliminary RoundDocument11 pagesNMOS 2014 Preliminary Roundyijie liNo ratings yet
- Incremental Calculation of Weighted Mean and VarianceDocument8 pagesIncremental Calculation of Weighted Mean and VarianceScott TreloarNo ratings yet
- Real NumbersDocument4 pagesReal NumbersDumbNo ratings yet
- The Canonical Partition FunctionDocument15 pagesThe Canonical Partition FunctionWellington ZorzettiNo ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated Motion (One Dimension)Document12 pagesUniformly Accelerated Motion (One Dimension)Ma Kristina Cassandra LunorNo ratings yet
- Proofs Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesProofs Cheat SheethamzaNo ratings yet
- DSD Lectures 13 14Document13 pagesDSD Lectures 13 14ammar abbasNo ratings yet
- Queueing ModelDocument54 pagesQueueing ModelBikram KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2Yordanos AbebawNo ratings yet
- Standard Eight: No Plastic PleaseDocument132 pagesStandard Eight: No Plastic PleaseVinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- Timetable For Upper Class LatestDocument2 pagesTimetable For Upper Class LatestPersona DelailaNo ratings yet
- GATE - CSE Made Easy 342 392Document51 pagesGATE - CSE Made Easy 342 392Stuti Gupta100% (1)
- Introduction To Data SturctureDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Data SturcturebahugunaharishNo ratings yet
- Adarsh Front PagesDocument8 pagesAdarsh Front Pagesravi singhNo ratings yet
- Sma 2270 Calculus IiiDocument50 pagesSma 2270 Calculus IiiCamilla IrunguNo ratings yet
- Scientific Work PlaceDocument551 pagesScientific Work Placepeloton10No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 More About PolynomialsDocument15 pagesChapter 7 More About Polynomialsapi-3704862No ratings yet
- J. Mozo - P.Fernandez - H. NeciosupDocument14 pagesJ. Mozo - P.Fernandez - H. NeciosupJimmy Támara AlbinoNo ratings yet
- ve#Multi!Step%Inequalities: NotesDocument4 pagesve#Multi!Step%Inequalities: Notesapi-327561261No ratings yet
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Slope Intercept FormDocument13 pagesG8 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Slope Intercept FormWenilyn MananganNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression WRK CH 1Document3 pagesLinear Regression WRK CH 1Katie DuncanNo ratings yet
- Mid Point & Section FormulaDocument3 pagesMid Point & Section FormulaAanjaneya JindalNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification - First GradingDocument1 pageTable of Specification - First GradingWellaCelestinoNo ratings yet
- Master of Science Naresuan UniversityDocument29 pagesMaster of Science Naresuan UniversityHira DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Cs Fall 21 Seq Sheet TransferDocument1 pageCs Fall 21 Seq Sheet Transferapi-547823268No ratings yet