Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Past Paper Questions: Physics
Past Paper Questions: Physics
Uploaded by
TharushiNethmiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Past Paper Questions: Physics
Past Paper Questions: Physics
Uploaded by
TharushiNethmiCopyright:
Available Formats
G.C.
E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
Unit 8:
Excellent in English Medium
Electromagnetism
Past Paper Physics
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA
Questions
1. The diagram shows an electromagnet with a coil A and a core B. Which combination of the
following would make the magnet stronger?
No. of turns in A the core B
(1) small Soft-iron
(2) small steel
(3) large Soft-iron
(4) large copper
(5) large air
2. Two long straight wires are connected by a circular section that has
a radius R as shown in the diagram. All three wires lie in the same
plane and carry a steady current I. The magnetic flux density at the
center O is,
𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼
(1) (2) (3)
𝑅 2𝑅 4𝑅
𝜇0 𝐼
(4) (5) 0
8𝑅
3. An electron passes through a space with a constant velocity. If E and B represent the magnitude
of the electric field intensity and the magnetic flux density of the electric and magnetic fields
respectively, this region of space may have,
(A) E = 0, B ≠ 0 (B) E ≠ 0, B = 0 (C) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
(1) only (A) is true. (2) only (B) is true
(3) only (C) is true. (4) only (A) and (C) are true.
(5) all (A), (B) and (C) are true
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 1
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
4. Consider the following statements made about magnets.
(A) Most common permanent magnets are made from alloys containing Fe, with Ni or Co.
(B) If a permanent magnet is heated it may lose its magnetism.
(C) If a bar magnet is carefully broken into two equal halves along its axis of magnetization,
each piece will be an equally strong magnet.
Of the above statements
(1) only B is true
(2) only A and B are true
(3) only A and C are true,
(4) only B and C are true
(5) all A, B and C are true.
5. An electron moving horizontally enters a region of space with
uniform magnetic field acting at an angle with the horizontal as
indicated in the figure. Due to the magnetic field the electron
will experiences a force in a direction
(1) perpendicular and into the paper
(2) perpendicular and out of the paper
(3) towards A
(4) towards C
(5) towards D
6. Two circular conducting loops are placed at right angles to each other as shown in the figure.
The radius of the vertical loop is r and it carries a current I. The radius of the horizontal loop is
3r and it carries a current 4I. The magnitude of the magnetic flux density at the common center
O is
𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼
(1) (2)
6𝑅 3𝑅
5𝜇0 𝐼 7𝜇0 𝐼
(3) (4)
6𝑅 6𝑅
25𝜇0 𝐼
(5)
18𝑅
7. Which of the following combinations of units is equivalent to the tesla?
𝑚 𝑁𝑠 𝑁
(1) (2) (3)
𝐶𝑠 𝐶 𝐶𝑚
𝑁𝑠 𝑁𝑠
(4) (5)
𝐶𝑚 𝑚
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 2
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
8. An electron is fired along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid as shown in the figure. It
will strike the florescent screen S at the point
(1) A (2) B (3) C
(4) D (5) E
9. Which of the following current carrying solenoid combinations will produce magnetic field lines
as shown in the figure?
10. A, B and C represent three long straight thin wires placed perpendicular to the plane of paper.
The directions of the currents in A and B are in to the paper while that in C is out of the paper.
The resultant force on B due to current in A and C is
(1) zero
(2) perpendicular to the line joining A, B and C.
(3) in a direction from B to C
(4) in a direction from B to A
(5) in a direction which depends on the magnitudes of the currents.
11. A current I flows in the wire ABCD bent in to the shape as shown in the figure. AB and CD are
straight portions while BC has a shape of an arc of radius R. The magnetic flux density at the
center O is (𝜃 is given in radians)
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 3
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
𝜇0 𝐼𝜃 𝜇0 𝐼𝜃
(1) (2) D
8𝜋𝑅 4𝜋𝑅
𝜇0 𝐼𝜃 𝜇0 𝐼𝜃
(3) (4)
2𝜋𝑅 2𝑅
𝜇0 𝐼𝜃
(5)
𝑅
12. A charged particle having a velocity V enters perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of flux
density B and follows a circular path of radius R as shown in the figure. If the charge on the
particle is q, the mass of the particle is
𝐵𝑞𝑅 𝐵𝑞
(1) (2)
𝑉 𝑅
𝐵𝑞𝑅 𝐵𝑞𝑅 2
(3) (4)
𝑉2 𝑉
𝐵𝑞𝑉 2
(5)
𝑅
13. The variation of magnetic flux density, B, along the axis of a short solenoid, shown in figure
carrying a constant current is best represented by,
14. The loop shown in the figure carries a current I .The magnetic flux density at O is
𝜇0 𝐼 3 1
(1) ( + )
8 𝑅1 𝑅2
𝜇0 𝐼 3 1
(2) ( + )
4 𝑅1 𝑅2
𝜇0 𝐼 1 1
(3) ( + )
8 𝑅1 𝑅2
𝜇0 𝐼
(4)
8(𝑅1 +𝑅2 )
𝜇0 𝐼 2 1
(5) ( + )
2 𝑅1 𝑅2
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 4
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
15. A flat copper plate is placed perpendicular to uniform magnetic field B and a current I is passed
through the plate as shown in the figure. At the steady state
(1) a current will flow from X to Y.
(2) a current with flow from Y to X.
(3) a negative voltage will develop at X with respect of Y.
(4) a positive voltage will develop at X with respect to Y.
(5) neither a current flow nor a voltage drop will be
resulted across X and Y.
16. Two straight wires, AB and CD carrying equal currents I are placed symmetrically and at right
angles to each other as shown in the figure. AB is infinitely long and CD has a finite length. The
magnetic effect on CD due to AB gives rise to a
(1) resultant force and a clockwise couple.
(2) resultant force and an anti-clockwise couple
(3) zero resultant force and a clockwise couple
(4) zero resultant force and an anti-clockwise couple.
(5) zero resultant force and a zero couple.
17. In vacuum, a beam of electrons is projected into a region of uniform magnetic field B as shown
in the figure. If both electron beam and the magnetic field are in the plain of the paper, then the
path of the electron is,
(1) Not affected by the magnetic field
(2) Bent towards the left
(3) Bent towards the right.
(4) Bent upwards out of the paper.
(5) Bent downwards into the paper.
18. A wire PQ of length 0.15 m and mass 0.015 kg is free to slide
on two smooth vertical wires, as shown in the diagram. If a
magnetic field of flux density 1.0 T is applied into the paper.
The current I required to keep the wire PQ in equilibrium is
(1) 1A (2) 3A (3) 5A
(4) 10A (5) 15A
19. A long straight wire carrying a current is placed in a uniform magnetic field at right angles to
the direction of the field. In a plain perpendicular to the current, the number of points having a
zero resultant magnetic flux density is
(1) Zero (2) 1 (3) 2
(4) 3 (5) 4
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 5
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
20. Consider the following statements made regarding the Hall effect
(A) The sign (positive or negative) of the Hall voltage is independent of the sign(positive or
negative) of the current carriers inside the metal.
(B) A Hall voltage is not generated when the direction of the magnetic field is parallel to the
direction of the current.
(C) The Hall effect is a consequence of the force acting on a moving charge in a magnetic field.
Of the above statements
(1) only (A) is true. (2) only (B) is true
(3) only (B) and (C) are true (4) only (A) and (B) are true
(5) all (A), (B) and (C) are true.
21. A current flows around a closed loop as shown in the figure. The magnetic flux density produced
at the center O is given by
𝜇0 𝐼 1 1 𝜇0 𝐼 1 1
(1) ( + ) (2) ( + )
4 𝑟1 𝑟2 3 𝑟1 𝑟2
𝜇0 𝐼 1 1 𝜇0 𝐼 1 1
(3) ( + ) (4) ( − )
2 𝑟1 𝑟2 2 𝑟1 𝑟2
𝜇0 𝐼 1 1
(5) ( − )
4 𝑟1 𝑟2
22. A compass is placed on top of a wire as shown in the
diagram. When a large current is passed through the wire,
which of the following diagrams best represents the
direction of the compass needle? Neglect the effects due
to the earth’s magnetic field.
23. Two parallel long wires A and B carry identical currents in the same
direction as shown in the diagram. Which of the following diagrams
best represents the magnetic field in a plane perpendicular to the
wires?
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 6
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
24. A horizontal conducting wire of XY of length 20cm and mass 4.5g is suspended by a pair of light
wires in a magnetic field of 0.15 T which is directed into the paper and perpendicular to the wire
as shown in the figure. What magnitude and direction of current in the wire XY are required to
nullify the tension in the light wires?
(1) 0.15 A, X→Y
(2) 0.15 A, Y→X
(3) 1.5 A, X→Y
(4)1.5 A, Y→X
(5) 0
25. A beam of positively charged particles passes through a point A in the upward direction, and an
electron passes through B with a velocity in the downward direction as shown in the figure. The
directions of electrostatic (Fe) and magnetic (Fm) forces on the electron are such that
(1) Fe towards A and Fm away from A.
(2) Fe and Fm both away from A.
(3) Fe and Fm both towards A.
(4) Fe towards A and Fm out of the ⊙ paper.
(5) Fe towards A and Fm into the ⊗ paper.
26. The figure shows three loops A, B and C consist of concentric circular arcs (either half or quarter-
circles of radii r, 2r and 3r). The loops carry the same current I. If the magnetic flux densities
produced at O by each loop is BA,BB and BC respectively, then
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 7
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
(1) BA > BC > BB (2) BA = BB = BC (3) BA > BB > BC
(4) BA < BC < BB (5) BA = BB > BC
27. An object carrying a positive charge slides down a long
inclined rough plane from rest. A uniform magnetic field
is acting as shown in the figure The variation of the
velocity of the object with time t is best represented by
28. The magnitude of the magnetic force acting on a current carrying straight wire in a uniform
magnetic field is determined by
(1) the magnetic flux density, the current, the length of the wire and the angle between the
magnetic field and the wire only.
(2) the magnetic flux density, the current and the length of the wire only
(3) the magnetic flux density, the current and the angle between the magnetic field and the wire
only.
(4) the magnetic flux density and the length of the wire only.
(5) the magnetic flux density and the current only.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 8
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
29. Two long, parallel, thin wires placed at a distance D apart as shown in
the figure, carry equal currents I in the same direction. Variation of the
magnitude of the resultant magnetic flux density B along the line PQ
from P to Q, is best represented by
30. XY is a long vertical wire carrying a current I in the upward direction as shown in figure (a).
ABCD is a horizontal plane perpendicular to the wire. The directions of the magnet of a compass
kept at positions P1 P2 , P 3 , P 4 and P 5 on the plane ABCD near the wire are shown in figure
(b). The figure the position at which the direction indicated by the magnet of the compass is the
same as the direction of the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is
(1) P1 (2) P2 (3) P3
(4) P4 (5) P5
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 9
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
31. A beam of electrons enters the region between two charged parallel plates with speed 106 ms -1
as shown in the figure. The potential difference across the plates is 200 V. Magnetic field
required to keep the beam along the y direction is
(1) 2.0 x 10-4 T, along the direction of the beam.
(2) 2.0 x 10-4 T, into the paper.
(3) 2.0 x 10-2T, along the direction of the beam.
(4) 2.0 x 10-2 T, into the paper.
(5) 2.0 x 10-2 T, out of the paper.
32. A thin uniform wire PQ carrying a current I could be held without any mechanical support above
an infinitely long horizontal wire RS carrying the same current I. If the mass per unit length of
the wire PQ is m, the equilibrium height h of PQ above RS is given by
𝜇0 𝐼 2 𝜇0 𝐼 2 𝜇0 𝐼 2
(1) ℎ = (2) ℎ = (3) ℎ =
𝑚𝑔 2𝑚𝑔 2𝜋𝑚𝑔
𝜇0 𝐼 2 𝜇0 𝐼 2
(4) ℎ = (5) ℎ =
𝜋𝑚𝑔 𝜋2 𝑚𝑔
33. A long insulated wire carrying a current I is bent to form a flat circular coil of N turns and radius
r. The two straight ends of the wire extend to a large distance as shown. The magnitude of the
magnetic flux density at the center C of the coil is
(1) 0
𝑁𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼
(2) +
2𝜋𝑟 2𝑟
𝑁𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼
(3) −
2𝑟 2𝜋𝑟
𝑁𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼
(4) +
2𝑟 2𝜋𝑟
𝑁𝜇0 𝐼 𝜇0 𝐼
(5) −
2𝑟 2𝑟
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 10
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
34. A particle with charge q and mass m travels perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field along a
circular path of radius R with frequency f. The magnitude of the magnetic flux density is given
by
𝑚𝑓 2𝜋𝑚𝑓 𝑚
(1) (2) (3)
𝑞 𝑞 2𝜋𝑓𝑞
𝑚 𝑞𝑓
(4) (5)
𝑞𝑅 2𝜋𝑅
35. Diagrams below show situations where two charges +q and –q moving with a uniform velocity
(v) and separately entering five regions having a uniform electric field (E) and a uniform
magnetic field (B). Vectors E and B are always perpendicular to each other, and the vector v can
be either perpendicular to E and B or parallel to E. Which of the following configurations may
provide a possibility for charges to move across the region without changing their directions?
36. A magnet with magnetic flux density of 1.0 T between the poles is placed on an electronic
balance. A rectangular wire loop of resistance 10Ω, which is connected to a 40V battery with
zero internal resistance, is placed in between the poles of the magnet so that the side AB of the
loop is completely inside the magnetic field and the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the
magnetic field , as shown in the figure. The loop firmly fixed to avoid any movement. When the
switch S1 is closed, the reading of the electronic balance
(1) will decrease by 200grams.
(2) will decrease by 20 grams.
(3) will increase by 200 grams
(4) will increase by 20grams.
(5) will not change.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 11
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
37. When a person performs a certain task a weak current of 10µA is
produced along a conducting path between brain cells. The figure
shows such a small path of length 1 mm. The magnitude of the
magnetic flux density produced by this current element at a point P
at a distance of 2 cm from it is (µ0 = 4π x 10-7 T m A-1)
(1) 2.5 x 10-10 T (2) 1.0 x 10-10 T (3) 2.5 x 10-11 T
(4) 1.0 x 10-11 T (5) 2.5 x 10-12 T
38. Four long, parallel, straight wires run normal to the plane of the
paper through vertices of a square as shown in the figure. If
currents of equal magnitude are set up in the wires along the
directions (⊙ 𝑜𝑟 ⊗ ) shown, and if the wires are free to move,
the arrows in which of the following diagrams correctly represent
the directions that the wires will tend to move?
39. Two particles having charges +Q and –Q revolve in opposite directions with the same angular
velocity ω along two circular paths of radius r, which are very close to each other as shown in
the figure. Magnetic flux density at the center of the circular path is
𝜇0 𝑄𝜔 𝜇0 𝑄𝜔
(1) zero (2) (3)
4𝜋𝑟 2𝜋𝑟
𝜇0 𝑄𝜔 𝜇0 𝑄𝜔
(4) (5)
2𝜋2 𝑟 4𝑟
40. Two long parallel wires placed normal to the plane of the paper carry equal currents in opposite
directions as shown in the figure. The variation of the component of the magnetic flux density
in y direction (B) along the x axis is best represented by
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 12
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
41. The diagram shows two thin smooth strips of aluminium of length l pasted on a flat smooth
horizontal wooden surface S, Strips are connected to a battery at one end. A uniform upward
magnetic field is setup, perpendicular to the surface, throughout the region between the
aluminium strips. When a steel rod is placed on the two aluminium strips as shown, the rod starts
to move. The variation of the velocity (v) of the rod with distance along the x axis is best
represented by
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 13
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
42. Four infinitely long wires are arranged as shown in the accompanying figure end–on view. All
four wires are perpendicular to the plane of the page and have the same magnitude of current I.
The conventional current in the wire in the upper right–hand corner is directed into the plane of
the page. The other conventional currents are out of the plan of the page. Point P is a distance
a from all four wires. What is the total magnetic field at point P?
o I
(1) toward the upper left hand corner
2 a
o I
(2) toward the lower left hand corner
2 a
I
(3) 2 o toward the upper left hand corner
2 a
I
(4) 2 o toward the lower left hand corner
2 a
(5) 0
43. A rectangular coil of length 0.10 m and breadth 0.04 m consists 500 turns and is placed in a
uniform magnetic field of flux density 0.10 T. If the coil carries a current of 10-2A,the maximum
possible torque on the coil is,
(1) 10-3 N m (2) 2×10-3 N m (3) 3×10-3 N m
(4) 4×10-3 N m (5) 5×10-3 Nm
44. Five pieces of wires are bent as shown in the diagrams and are made to move with a constant
velocity V, maintaining their planes perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. Which of the
wires will develop the largest induced e.m.f. across its ends?
45. Two conducting coils X and Y are placed close to each
other with their axes in the same line as shown in the
figure. The current, ix in coil X is varied with tune t, as
shown. Which of the following graphs best represents the
variation of the induced current iy, through the resistor R
with t ? (Consider the direction of the current through R to
the left to be positive.)
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 14
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
46. Three conducting loops A, B and C made of thin wire are
placed in the vicinity of a long straight wire which carries a
changing current. The planes of A and B are perpendicular to
the wire and plane of C and wire lie in the same plane. In which
loop/loops shown in the figure, an e.m.f. is/are developed?
(1) A only (2) B only (3) C only
(4) A and B only (5) A and C only
47. The following three methods have been suggested by a student as possible ways to obtaining a
steady voltage of 3 V using a single 1 V cell.
(A) By connecting the cell to a set-up transformer having primary to secondary turns ratio
of 1:3.
(B) By taking the voltage across a series connection of three 1 Ω resistors after connecting
the cell across any one of the resistors.
(C) By charging three identical capacitors to 1 V separately using the cell, then connecting
them in series and taking the voltage across the combination.
Of the above methods
(1) only (A) can generate 3 V. (2) only (C) can generate 3 V.
(3) only (A) and (C) can generate 3 V. (4) all can generate 3V.
(5) none can generate 3V.
48. A piece of metal wire XY bent in to the form
shown in the figure and moving at a constant
velocity V in the direction shown, enters a
region with an uniform magnetic field, at time
t = 0 . The potential (Vx) induced at the end X
with respect to the end Y with time (t) can be
best represented by
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 15
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
49. During a power cut, person tried to use twenty 12 V car batteries to power some domestic electric
appliances. Which of the following appliances will not work?
(1) an iron (2) A filament bulb (3) A ceiling fan
(4) A hot plate (5) all A, B and C are true
50. A circular conducting loop S passes through a
region of uniform magnetic field with a constant
velocity as shown in the figure. Which of the
following graphs best represents the variation of
the induced current (I) in the loop with time (t)?
51. The primary winding of an ideal transformer has 200 turns and its secondary winding has 50
turns. If the current in the secondary is 40 A, the current in the primary is
(1) 5 A (2) 10 A (3) 80 A
(4) 120 A (5) 160 A
52. Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between voltage(V) and time (t)
for the output from a power supply consisting of an alternating current generator and a full wave
rectifier without smoothing?
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 16
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
53. A small square loop of a wire having a negligible mass is moved at
a constant velocity V across a uniform magnetic field as shown in
the figure. The variation of the external force F that has to be
applied to maintain its constant velocity V with time (t) is best
represented by
54. A long bar magnet is held vertically and made to move with a constant
velocity V, in the direction shown so that its north pole is very close to a
horizontal conducting sheet.
Which of the following diagrams best represents the eddy currents induced
in the sheet?
55. A metal rod AB of length 2R moving with a constant velocity
V is passing over a uniform magnetic field confined to a circular
region of radius R, as shown in the figure. The variation of the
e.m.f.(E) induced across the rod with time (t) is best represented
by
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 17
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
56. A long wire ABC is bent to form a 600 angle and kept in a plane perpendicular to a uniform
magnetic field, as shown in the figure. Another long straight wire PQ made of the same material
with the same cross-sectional area is pulled with a constant velocity on the wire ABC, so that the
triangle RBS is always equilateral. The induced current (I) in the triangle RBS varies with time
(t) as
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 18
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
57. An ideal transformer has 100 windings in the primary and 200 windings in the secondary. The
primary is connected to an A.C. supply of 120V at 10A.Then the ‘voltage/current’ in the
secondary is
(1) 240 V/5A (2) 240V/10A (3) 240V/2.5A
(4) 120 V/ 5A (5) 120V/2.5A
58. A bar magnet is dropped with its axis vertical, and it accelerates through a
coil as shown in the figure. Which of the following graphs best represents
the variation of the induced e.m.f. (E) of the coil with time (t)?
59. Of the elements given bellow, power (VI) can be amplified only with
(1) resistors (2) diodes (3) capacitors
(4) transformers (5) transistors
60. A circular conduction loop moves at a constant
velocity through two regions consisting of magnetic
fields. The magnetic fields in the two regions are
uniform and have the same magnitude but acting
opposite directions as shown in the figure. The
induced e.m.f. (E) in the loop varies with time(t) as
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 19
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
61. A closed rectangular wire loop (W) falls vertically through two
uniform magnetic field regions of flux density B as shown in the
figure. If viscous and up thrust forces on the loop are negligible,
the velocity (v) – time (t) graph of the loop is best represented
by
62. A semicircular conductor PQR having a uniform cross-
sectional area is placed vertically in a horizontal
uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure. A
conducting rod OA pivoted at the center O of the
semicircular conductor rotates with a constant angular
speed about a horizontal axis passing through O parallel
to the magnetic field. PQR and OA are made of a
material with the same resistivity. An ammeter is
connected to the two ends O and R. If the end A touches
PQR, the variations of the e.m.f. E induced across OA
and the current I through the ammeter with time t are
best represented by the pair of graphs.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 20
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
63. The transformer shown in the figure has N1 turns in the primary and N2 turns in the secondary.
Root mean square voltages across primary and secondary are V1 and V2 respectively. The correct
statement regarding the trans-former is
(1) V1 N1 = V2 N2
(2) if the A.C. source is replaced by a battery with the same voltage, V2 will remain the same.
(3) when the secondary is connected to a load, the current in the secondary will not depend on
the load.
(4) the only reason why the core becomes warm after sometime is the heat generated due to the
resistance of the coils.
(5) if the core is removed, V2 will decrease.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 21
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
64. Consider the following statements made regarding a transformer.
(A) The core of a transformer is usually made of soft iron in order to maintain a better flux
linkage.
(B) The wire diameter of the secondary coil of a step-down transformer is usually larger
than that of the primary coil.
(C) When winding transformers, wires without insulated coating must be used.
Of the above statements,
(1) only (A) is true (2) only (B) is true (3) only (C) is true
(4) only (A) and (B) are true. (5) all (A), (B) and (C) are true
65. The circuit shown is placed in a uniform magnetic field
that is acting into the page. This magnetic field is
decreasing in magnitude at a rate of 150 T s-1 The reading
of the ammeter is
(1) 0.15 A
(2) 0.35 A
(3) 0.50 A
(4) 0.65 A
(5) 0.80 A
66. An e.m.f. is induced across the length of a wire when it is moving in a uniform magnetic field.
This e.m.f. does not depend on
(1) velocity of the wire
(2) radius of the wire
(3) length of the wire
(4) flux density of the magnetic wire
(5) the angle that the wire makes with the magnetic field
67. Three identical circular wire loops are placed perpendicularly to uniform magnetic fields of flux
density B. The extents of the magnetic fields are different from one another in situations P, Q
and R as shown in figures. The extents of the magnetic field in Q is equal to the area of the loop.
When the flux density B varies with time at the same constant rate, the induced e.m.f.s of the
respective wire loops are Ep , EQ and ER ?
(1) Ep = 0, EQ = ER
(2) Ep = 0, ER > EQ
(3) Ep = EQ = 0, ER ≠ 0
(4) Ep < EQ , EQ= ER
(5) Ep < EQ < ER
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 22
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
68. A rectangular wire frame made from a smooth resistive wire is connected to a battery of e.m.f.
E with negligible internal resistance as shown in the figure. XY is a piece cut from the same wire,
which can slide along the wire frame .A non-conducting liquid film of surface tension T is formed
in the region CDXY, and the entire structure is placed in a uniform magnetic field of flux density
B acting in the direction shown. If XY =XD = CD =CY, and the current through AX is I, then the
wire XY will tend to move to the right when
8𝑇 4𝑇 8𝑇
(1) B > (2) B > (3) B <
3𝐼 𝐼 3𝐼
4𝑇 4𝑇
(4) B > (5) B <
3𝐼 3𝐼
69. A transformer having which of the following characteristics is suitable to reduce a 220V ac
voltage to 20 V ac?
Transformer type 𝑵𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒎𝒔 𝒊𝒏 𝒔𝒆𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒅𝒂𝒓𝒚 𝒄𝒐𝒊𝒍
𝑵𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒎𝒆𝒔 𝒊𝒏 𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒎𝒂𝒓𝒚 𝒄𝒐𝒊𝒍
(1) Step-down 1
22
(2) Step-down 1
11
(3) Step-down 11
(4) Step-up 1
11
(5) Step-up 11
70. Figure shows the path of an electron traveling along an arc of a circle
of radius R with a speed v in a uniform magnetic field. The magnitude
(B) of the magnetic flux density is given by ( m – mass of an electron;
e = charge of an electron)
𝑚𝑣 𝑚𝑣 2
(1) B =√ (2) B = ( )
𝑒𝑅 𝑒𝑅
𝑚𝑣 𝑚𝑣
(3) B = (4) B=
2𝑒𝑅 𝑒𝑅
𝑚𝑣
(5) B=
2𝑒𝑅
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 23
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
71. A part of a conducting square wire loop of side 2m
is placed in a uniform magnetic field as shown in
the figure. If the magnitude of the magnetic flux
density decreases at a constant rate of 0.8 T s-1, the
net e.m.f. in the circuit would be
(1) 0.4 V
(2) 1.2V
(3) 2.8 V
(4) 3.6 V
(5) 5.2V
72. The figure shows two transformers A and B connected to power lines. The primary coil of A is
connected to a voltage of 33000 V ac and the secondary coil of B provides a voltage of 230V ac
for domestic use. Transformer A has N1 and N2 turns in its primary and secondary respectively.
Transformer B has N3 and N4 turns in its primary and secondary respectively.
If the power losses in the system are neglected, which of the following is true?
𝑁1 33000
(1) =
𝑁4 230
𝑁4 33000
(2) =
𝑁1 230
𝑁1 𝑁3 33000
(3) =
𝑁2 𝑁4 230
𝑁2 𝑁4 33000
(4) =
𝑁1 𝑁3 230
𝑁1 𝑁4 33000
(5) =
𝑁2 𝑁3 230
73. The graph shows the variation of a magnetic flux (ϕ) through a
coil with time (t).
The variation of the corresponding induced e.m.f. (E) with time
(t) is best represented by
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 24
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
74.
75.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 25
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
76.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 26
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
77.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 27
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
78.
79.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 28
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
80.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 29
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
81.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 30
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
82.
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 31
G.C.E Advanced level 2021 PHYSICS – English Medium
SUDHEERA JAYAMANNA Electromagnetism IV 32
You might also like
- Historinha Clima G5Document28 pagesHistorinha Clima G5Miss HelenNo ratings yet
- Weavetech Case (HR)Document5 pagesWeavetech Case (HR)K.Akshay Pai0% (3)
- List of Pestel Characteristics: PoliticalDocument8 pagesList of Pestel Characteristics: PoliticalFiz Arman100% (1)
- City Test 03 - Test PaperDocument18 pagesCity Test 03 - Test Paperneet20242526No ratings yet
- SR NEET STAR SUPER CHAINA (XII Syllabus GT-6) Q.P EX - DT. 15.03.2024Document24 pagesSR NEET STAR SUPER CHAINA (XII Syllabus GT-6) Q.P EX - DT. 15.03.2024divya202230014No ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics 12th., Set-2, 2022-23Document7 pagesSample Paper Physics 12th., Set-2, 2022-23Task MastersNo ratings yet
- 658fb48bff7e470018bd5e5b - ## - Magnetic Effects of Current Practice SheetDocument6 pages658fb48bff7e470018bd5e5b - ## - Magnetic Effects of Current Practice Sheetshilpkarjatil77No ratings yet
- Test Paper 7Document10 pagesTest Paper 7ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Set A PDFDocument10 pagesClass Xii Physics Set A PDFJ NNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Pre Board Xii Phy 2023-24Document11 pagesPractice Paper Pre Board Xii Phy 2023-24Buvaneswari SriniNo ratings yet
- JEE Main - 2020 9 January 2020 (Morning Shift) : General InstructionsDocument12 pagesJEE Main - 2020 9 January 2020 (Morning Shift) : General InstructionsRaghav MadanNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument7 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsSankar Kumarasamy100% (1)
- Bhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1Document9 pagesBhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1niladriputatunda1No ratings yet
- CST 1Document20 pagesCST 1aryaadarshsinghNo ratings yet
- Allen: Final Jee-Main Examination - March, 2021Document5 pagesAllen: Final Jee-Main Examination - March, 2021Again MishraNo ratings yet
- Physics ExamDocument13 pagesPhysics ExamAndrew EwersNo ratings yet
- James Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsDocument13 pagesJames Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsLisWeiNo ratings yet
- T.Me/Agexpr MEC: I 2 - 4 R I 2 4 R I 2 2 R I 2 - 2 RDocument14 pagesT.Me/Agexpr MEC: I 2 - 4 R I 2 4 R I 2 2 R I 2 - 2 RHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aakash Intensive CST 01-A (@neet - Nikalo1)Document39 pagesAakash Intensive CST 01-A (@neet - Nikalo1)all India TamilNo ratings yet
- 12TH PhysicsDocument17 pages12TH PhysicsAkshatNo ratings yet
- Ii Pre Board Class XiiDocument14 pagesIi Pre Board Class XiiPrithibiNo ratings yet
- Physics SQPDocument14 pagesPhysics SQPUNDERWORLD MAFIANo ratings yet
- Cbse SQP Xii Physics Sqp-1Document16 pagesCbse SQP Xii Physics Sqp-1virdishivaliNo ratings yet
- 658bdb00f2827e0018f81d34 - ## - ROI Pre-Board Exam Paper - Physics Dated 27-Dec-2023 - Question PaperDocument6 pages658bdb00f2827e0018f81d34 - ## - ROI Pre-Board Exam Paper - Physics Dated 27-Dec-2023 - Question PaperMishra Ji PionoNo ratings yet
- M1 TestDocument3 pagesM1 Testsehajpahwa0009No ratings yet
- Physics SQP - 05 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEDocument27 pagesPhysics SQP - 05 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEmr mindNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 3Document22 pagesRevision Test 3ASHWANI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 2 2022-23 BoardDocument10 pagesPhysics Set 2 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument13 pages12 PhysicsSaaraNo ratings yet
- Physics PQ2Document7 pagesPhysics PQ2David BamNo ratings yet
- Mslive: Part - I: Only One Option Correct TypeDocument50 pagesMslive: Part - I: Only One Option Correct TypeTaheera KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics2023 24PaperWisdomClassesDocument11 pagesPhysics2023 24PaperWisdomClassesMj Chemistry FacultyNo ratings yet
- PH Sample Paper 3 UnsolvedDocument9 pagesPH Sample Paper 3 UnsolvedApSWgxmwNo ratings yet
- NEET UG 2021 Physics Part 1Document3 pagesNEET UG 2021 Physics Part 1Girish NaikNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics SQPDocument125 pagesClass Xii Physics SQPbrutalrx3310No ratings yet
- Eee701-Fields and WavesDocument6 pagesEee701-Fields and WavesLendry NormanNo ratings yet
- 2.physics Qp-XiiDocument6 pages2.physics Qp-XiiEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 98 - Model 2019Document10 pagesPractice Test 98 - Model 2019HimayaNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Paper SolutionDocument55 pagesNEET 2024 Paper SolutionKrishna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH - 04Document5 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH - 04Arunima SinghNo ratings yet
- 27 Jan Shift-1 Mains 2024Document12 pages27 Jan Shift-1 Mains 2024raiutkarsh057No ratings yet
- Allen Talent Ex 2018 Paper 3012Document14 pagesAllen Talent Ex 2018 Paper 3012Kundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Poll-18: PHYSICS (P-18)Document4 pagesPoll-18: PHYSICS (P-18)Abhimanyu BhasinNo ratings yet
- R-NET (2021) : (Reliable National Entrance Test)Document8 pagesR-NET (2021) : (Reliable National Entrance Test)aditi singhNo ratings yet
- Intensive CST-01 (Code-A) 09-06-2022 SolDocument23 pagesIntensive CST-01 (Code-A) 09-06-2022 SolThe BoNg FOOD recipesNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics PDFDocument4 pagesElectrodynamics PDFcherinet SNo ratings yet
- SB-AITS Test 12 (Full Length 08)Document39 pagesSB-AITS Test 12 (Full Length 08)yourcompanionforjeeandneetNo ratings yet
- Anthe Senior Sample Paper 2012Document14 pagesAnthe Senior Sample Paper 2012Janaki KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Exam Papers 2023Document19 pagesExam Papers 2023supbolte12No ratings yet
- MT AprilDocument2 pagesMT AprilAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter - Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Chapterwise Practise Problems (CPP) For NEETDocument12 pagesPhysics: Chapter - Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Chapterwise Practise Problems (CPP) For NEETsoyel afridiNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre BoardDocument10 pagesPhysics Pre Boardizumigamer69No ratings yet
- Ncert Booster Test Series: 24/02/2021 Coe-XiiDocument16 pagesNcert Booster Test Series: 24/02/2021 Coe-XiiEr SirNo ratings yet
- 14 SQPDocument8 pages14 SQPdipanshu76612No ratings yet
- PHYSICS Burdwan University Question PaperDocument2 pagesPHYSICS Burdwan University Question Paperb718535740No ratings yet
- Class - Xii Terminal Test - 01: Sri Krish International School SchoolDocument10 pagesClass - Xii Terminal Test - 01: Sri Krish International School SchoolKamranNo ratings yet
- Physics XII - Set 3Document6 pagesPhysics XII - Set 3ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Board Pattern Sample Paper 02 - PHYSICSDocument4 pagesBoard Pattern Sample Paper 02 - PHYSICSsoumyadiptaseal09No ratings yet
- Test Paper 8 (Answers)Document17 pagesTest Paper 8 (Answers)ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Aakash: TobyjusDocument3 pagesAakash: Tobyjussaicharandimpu2007No ratings yet
- 12phy SQP10Document15 pages12phy SQP10annutom1234No ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sri Lanka Examinations Prices JUNE 2018Document17 pagesSri Lanka Examinations Prices JUNE 2018TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Prototype PapersDocument212 pages2019 Prototype PapersTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- Microneedling For The Skin - Before Your Visit: How To PrepareDocument2 pagesMicroneedling For The Skin - Before Your Visit: How To PrepareTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
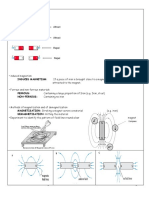
- Magnetism For Physics Grade 12Document15 pagesMagnetism For Physics Grade 12TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- Aadhila Nasir-800: Random Essay Question - 20Document1 pageAadhila Nasir-800: Random Essay Question - 20TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Physics Bahuwarana WiwaranayaDocument7 pages2015 Physics Bahuwarana WiwaranayaTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- 2017 AL Chemistry Past Paper - English MediumDocument23 pages2017 AL Chemistry Past Paper - English MediumTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- 2017 AL Chemistry Past Paper - English MediumDocument23 pages2017 AL Chemistry Past Paper - English MediumTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- Aadhila Nasir-800: Random Essay Question - 20Document1 pageAadhila Nasir-800: Random Essay Question - 20TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- L 2021 Model Paper - 45Document10 pagesL 2021 Model Paper - 45TharushiNethmi100% (1)
- Assignment No: 07Document4 pagesAssignment No: 07TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- EGr13OM Physical Chemistry-Part 2Document279 pagesEGr13OM Physical Chemistry-Part 2TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 01-06-2021 12.31Document28 pagesCamScanner 01-06-2021 12.31TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- Gene Mutations-Essay 69Document2 pagesGene Mutations-Essay 69TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 09-25-2020 16.18.31Document24 pagesCamScanner 09-25-2020 16.18.31TharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- Wallbox Supernova BrochureDocument8 pagesWallbox Supernova BrochuresaraNo ratings yet
- Full Download Understanding Pathophysiology 4th Edition Huether Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Understanding Pathophysiology 4th Edition Huether Test Bankkuhsegrady100% (32)
- Esip 2021-2024 LinabuisDocument107 pagesEsip 2021-2024 LinabuisJheryl Malapad Fortun-Guibelondo50% (2)
- Higher Modern Languages: What Is New?Document28 pagesHigher Modern Languages: What Is New?bleinNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaMaulinaNo ratings yet
- SEL Lesson Plan: Family LoveDocument5 pagesSEL Lesson Plan: Family LoveNur Ain Mohd Amin100% (3)
- Dear Sirs and Madams Cover LetterDocument4 pagesDear Sirs and Madams Cover Letterc2yyr2c3100% (1)
- 3RD Quarter Week 6 MusicDocument3 pages3RD Quarter Week 6 MusicMichaella Liongco AmanteNo ratings yet
- Zener Tester: by MedhatkoDocument6 pagesZener Tester: by Medhatkosaran gulNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Post TestDocument2 pagesMath 7 Post TestDonabel Carios100% (3)
- Singala SuttaDocument8 pagesSingala SuttaAshin Sucitta PkNo ratings yet
- Solar - UttarakhandDocument13 pagesSolar - Uttarakhandvin0dNo ratings yet
- Statement of The ProblemDocument7 pagesStatement of The ProblemJhona Mae ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain.Document53 pagesChest Pain.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Y3 Numeracy ETZ FreeDocument16 pagesY3 Numeracy ETZ FreeenggmohanNo ratings yet
- Oracle Rac Pratice On Virtual BoxDocument94 pagesOracle Rac Pratice On Virtual BoxpandsinNo ratings yet
- The Emergence Of Bangladesh Interdisciplinary Perspectives Habibul Khondker full chapter pdf docxDocument69 pagesThe Emergence Of Bangladesh Interdisciplinary Perspectives Habibul Khondker full chapter pdf docxgucsonfeie100% (2)
- Risma, Mary Grace U. BEED 2-A (Module 5, Lesson 1 Application)Document4 pagesRisma, Mary Grace U. BEED 2-A (Module 5, Lesson 1 Application)Scherasid VillejoNo ratings yet
- Blackrock Us Factor Outlook July 2017 en UsDocument6 pagesBlackrock Us Factor Outlook July 2017 en UsAugusto Peña ChavezNo ratings yet
- Frederick - Nietzsche Nietzsche S Best 8 Books PDFDocument1,344 pagesFrederick - Nietzsche Nietzsche S Best 8 Books PDFNicolae PînzaruNo ratings yet
- Su 80 GPDocument3 pagesSu 80 GPKurtis SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Cables: June 2015Document27 pagesCables: June 2015Gaurav NeermulNo ratings yet
- ToC - Industrial Motor Market - Fact - MRDocument16 pagesToC - Industrial Motor Market - Fact - MRLiora Vanessa DopacioNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet - ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet - ThermodynamicsDivyaprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit3 OBDocument57 pagesUnit3 OBsiddhi vermaNo ratings yet
- Gertrud Rosshalde Ultima Vara A Lui Klingsor Romanian Edition by Hermann Hesse 6066096141Document5 pagesGertrud Rosshalde Ultima Vara A Lui Klingsor Romanian Edition by Hermann Hesse 6066096141Zaiu DaiuNo ratings yet
- Maltego CEDocument4 pagesMaltego CEArief PrihantoroNo ratings yet