Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foxamax and Iboprofen Drug Study
Foxamax and Iboprofen Drug Study
Uploaded by
aaron taberna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views4 pages1) Alendronate is a bisphosphonate prescribed to treat and prevent osteoporosis. It works by inhibiting osteoclasts and reducing bone resorption.
2) Common side effects include constipation, heartburn, and diarrhea. It is important to take it with a full glass of water in the upright position.
3) Nurses should monitor calcium levels, ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, and report fever or severe pain to the prescriber. Proper administration is key to minimize side effects.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Alendronate is a bisphosphonate prescribed to treat and prevent osteoporosis. It works by inhibiting osteoclasts and reducing bone resorption.
2) Common side effects include constipation, heartburn, and diarrhea. It is important to take it with a full glass of water in the upright position.
3) Nurses should monitor calcium levels, ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, and report fever or severe pain to the prescriber. Proper administration is key to minimize side effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views4 pagesFoxamax and Iboprofen Drug Study
Foxamax and Iboprofen Drug Study
Uploaded by
aaron taberna1) Alendronate is a bisphosphonate prescribed to treat and prevent osteoporosis. It works by inhibiting osteoclasts and reducing bone resorption.
2) Common side effects include constipation, heartburn, and diarrhea. It is important to take it with a full glass of water in the upright position.
3) Nurses should monitor calcium levels, ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, and report fever or severe pain to the prescriber. Proper administration is key to minimize side effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
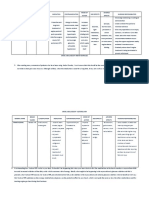
NAME OF DOSAGE/RO MECHANISM INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE NURSING
DRUG UTE/ OF ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITY
FREQUENCY Geriatric patients may be at
Alendronate Alendronate is Treatment and increased risk for the Common WARNING: Give in AM
sodium 10 mg qd a second- prevention of development of adverse GI side with full glass of water at
(Fosamax) PO generation osteoporosis in reactions during alendronate effects of least 30 min before the
bisphosphonate postmenopausal therapy Fosamax first beverage, food, or
Drug that binds to women Hypocalcemia, vitamin D include medication of the day.
Classification: bone Treatment of deficiency constipation Patient must stay upright
Bisphosphonat hydroxyapatite men with , for 30 min.
e and specifically osteoporosis Preexistent hypocalcemia heartburn, Monitor serum calcium
inhibits the Treatment must be corrected before diarrhea, levels before, during, and
activity of of glucocorticoid- initiating alendronate therapy. bloating, after therapy.
osteoclasts, the induced Similarly, vitamin D deficiency nausea, Ensure 6-mo rest period
bone-resorbing osteoporosis must also be corrected. vomiting, after treatment
cells. Treatment Adequate intake of calcium stomach for Paget’s disease
Alendronate of Paget’s diseas and vitamin D during treatment pain, if retreatment is required.
reduces bone e of bone in are essential. This is most joint pain or Ensure adequate vitamin
resorption with patients with important for patients with swelling, D and calcium intake.
no direct effect alkaline phospha Paget's disease who are to swelling in Provide comfort
on bone tase at least two receive alendronate. your hands measures if bone pain
formation, times upper limit Alendronate can decrease or feet, returns
although the of normal, those serum calcium and phosphate dizziness,
latter process is who are in these patients, who may headache, Report fever, especially
ultimately symptomatic, have a higher rate of bone eye pain, when accompanied by
reduced those at risk for turnover. back pain, arthralgia and myalgia.
because bone future Sunlight (UV) exposure or Do not breast feed while
resorption and complications Alendronate may cause a rash weakness. taking this drug.
formation are that is worsened by sunlight
coupled during (UV) exposure. However, erious side
bone turnover. patients should be advised that effects of
inadequate sunlight exposure Fosamax
can increase the risk of vitamin include
D insufficiency. severe pain
(joints,
Cardiac disease, heart bone,
failure, hypertension, muscle,
sodium restriction jaw, back or
Each alendronate effervescent heartburn),
tablet contains 650 mg of chest pain,
sodium, which is equivalent to difficulty
approximately 1650 mg of salt swallowing,
(NaCl). When possible, use of bloody
the effervescent tablet stools,
formulation should be avoided eye pain,
in patients that require sodium skin blisters
restriction, including patients , and
with heart failure, swelling of
hypertension, and other the face,
cardiac disease. tongue, or
throat.
DRUG NAME DOSAGE AND ADVERSE NURSING
ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION
ROUTE EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITY
Ibuprofen Unknown. May Ibuprofen contains the CNS Contraindicated in Tell patient to take with
300 to 800 mg P.O. inhibit active ingredient Headache, patients hypersensitive to meals or milk to reduce
Apo-Ibuprofen t.i.d. or q.i.d. prostaglandin ibuprofen, which dizziness, drug and in those with adverse GI reactions.
Maximum daily synthesis, to belongs to a group of nervousness, angioedema, syndrome of Note: Drug is available
dose is 3.2 g. produce anti- medicines called non- aseptic nasal polyps, or at OTC. Instruct patient
inflammatory, steroidal anti- meningitis. bronchospastic reaction to not to exceed 1.2 g
analgesic, and inflammatory drugs CV aspirin or other NSAIDs. daily, not to give to
antipyretic (NSAIDs). Peripheral Contraindicated in chidren younger than
effects. It works by blocking edema, fluid pregnant women. age 12, and not to take
the action of a retention, edema. Use cautiously in patients for extended periods
substance in the body EENT with GI disorders, history ( longer than 3 days for
called cyclo-oxygenase. Tinnitus of peptic ulcer disease, fever or longer than 10
Cyclo-oxygenase is GI cardiac decompensation, days for pain) without
involved in the Epigastric hypertension, asthma, or consulting presciber.
production of various distress, nausea, intrinsic coagulation Tell patient that full
chemicals in the body, occult blood defects. therapeutic effect for
some of which are loss, peptic arthritis may be
known as ulceration, delayed for 2 to 4
prostaglandins. diarrhea, weeks. Although pain
Prostaglandins are constipation, relief occurs at low
produced in response to abdominal pain, dosage levels,
injury or certain bloating, GI inflammation doesn’t
diseases and would fullness, improve at dosages less
otherwise go on to dyspepsia, than 400 mg q.i.d.
cause pain, swelling flatulence, Teach patient to watch
and inflammation. heartburn, for and report to
Ibuprofen is therefore decreased prescriber immediately
used to relieve pain and appetite. signs and symptoms of
inflammation. GU GI bleeding, including
All the medicines in Acute renal blood in vomit, urine,
this group (NSAIDs) failure, azotemia, or stool or coffee
reduce inflammation cystitis, ground vomit, and
caused by the body's hematuria. black, tarry stool.
own immune system, HEMATOLOGIC Warn patient to avoid
and are effective pain Plonged bleeding hazardous activities
killers. Ibuprofen can time, anemia, that require mental
be used to relieve pain neutropenia, alertness until effects
such as muscular pancytopenia, on CNS are known.
aches and pains, period thrombocytopeni Advise patient to wear
pains, headache, a, aplastic sunscreen to avoid
backache, rheumatic anemia, hypersensitivity to
pain, dental pain and leucopenia, sunlight.
neuralgia. It can also agranulocystocis.
reduce feverishness and METABOLIC
the symptoms of colds Hypoglycemia,
and flu. hyperkalemia.
RESPIRATORY:
Bronchospasm
SKIN
Pruritus, rash,
urticaria, stevens
Johnson
syndrome.
You might also like
- United States Patent Application Publication No .: US 2021/0082583 A1Document53 pagesUnited States Patent Application Publication No .: US 2021/0082583 A1Tim Brown100% (7)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlansAngelie Sanchez86% (14)
- Module 1-Ergonomics and Facilities PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 1-Ergonomics and Facilities Planninglei melendrez100% (6)
- NCM 116 - Ortho Midterm Exam MidyearDocument21 pagesNCM 116 - Ortho Midterm Exam Midyearaaron taberna100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Patients May Common Side Effects of Fosamax IncludeDocument6 pagesGeriatric Patients May Common Side Effects of Fosamax IncludeDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia Metabolic Bone Disease Joint DisorderDocument11 pagesHypocalcemia Metabolic Bone Disease Joint DisorderLlewelyn AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Bone. OsteoporosisDocument4 pagesBone. OsteoporosisFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- 70 MG Once Weekly For Mrs. CordovaDocument2 pages70 MG Once Weekly For Mrs. CordovaSherrie Ann Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Pagets Disease: Osteoporosis Decrease in The Density of Bone, Decreasing ItsDocument4 pagesPagets Disease: Osteoporosis Decrease in The Density of Bone, Decreasing ItsRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Zinc Sulfate (Drug Study)Document5 pagesZinc Sulfate (Drug Study)shielani100% (1)
- Aclasta Drug PresentationDocument23 pagesAclasta Drug Presentationphp_czarina04421No ratings yet
- MusculoSensory - TCA #3 - Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis DDDDocument8 pagesMusculoSensory - TCA #3 - Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis DDDapi-3822433No ratings yet
- Ibandro 150mg Tab. - Dawaai - Uses, Side Effect, Price in PakistanDocument1 pageIbandro 150mg Tab. - Dawaai - Uses, Side Effect, Price in Pakistanmamajan601No ratings yet
- Drug Ana Gin Amoxicillin DiclofenacDocument2 pagesDrug Ana Gin Amoxicillin DiclofenacmarohunkNo ratings yet
- Zoledronic AcidDocument7 pagesZoledronic AcidbabiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting On Osteoporosis: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, Pharmd International Medical UniversityDocument25 pagesDrugs Effecting On Osteoporosis: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, Pharmd International Medical UniversityRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Michael Brian Umali 3A:G6 Classification & BDocument3 pagesMichael Brian Umali 3A:G6 Classification & Bexcel21121No ratings yet
- Festin - Drug Study 3Document22 pagesFestin - Drug Study 3Hazel Mae FestinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPsalms Aubrey Domingo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Osteoporosis: Submitted To: Dr. Divya Vohra Submitted By: Sharique Raza M.pharm Jamia HamdardDocument38 pagesPresentation On Osteoporosis: Submitted To: Dr. Divya Vohra Submitted By: Sharique Raza M.pharm Jamia Hamdardsri susantiiNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationDocument4 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationAnalyn Sarmiento100% (1)
- CH 32 - Bone Mineral HomeostasisDocument4 pagesCH 32 - Bone Mineral HomeostasisNiki NourNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyanelyukiNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument3 pagesName of DrugLYRA GUEVARRANo ratings yet
- Case Study About: OsteoporosisDocument15 pagesCase Study About: OsteoporosisAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Bone Disorders CompleteDocument18 pagesDrugs For Bone Disorders CompleteOmar AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal ReviewerDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal ReviewerLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- ClopidogrelDocument4 pagesClopidogrelRachelNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Bone MetabolismDocument15 pagesDrugs For Bone MetabolismkwennybiangNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Trade Name Uses Adverse Reactions Dosage RangesDocument5 pagesGeneric Name Trade Name Uses Adverse Reactions Dosage Rangessticksam203No ratings yet
- Osam D Tab Leaflet Pakistan PDFDocument1 pageOsam D Tab Leaflet Pakistan PDFpharmacist PUCPNo ratings yet
- OSTEOMALACIADocument16 pagesOSTEOMALACIAlibrian_pallavi39420% (1)
- Drug Study - Anti-AnemiaDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Anti-AnemiaChelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- IbandronatedrugscomDocument25 pagesIbandronatedrugscomroyNo ratings yet
- DS (Alendronate)Document5 pagesDS (Alendronate)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PrescriptionDocument5 pagesArthritis PrescriptionWania ZaibNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyOlivia Solomon100% (1)
- Eye Optic Nerve: Glaucoma or Increased Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Is The Result of InadequateDocument5 pagesEye Optic Nerve: Glaucoma or Increased Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Is The Result of InadequateTeresa ReitzNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaroneedemNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Drugs 2020Document34 pagesMusculoskeletal Drugs 2020Anna Lin YeeNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument2 pagesPharmapreciousmargot100% (1)
- NCMB316 OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesNCMB316 Osteoporosis3-B-4 NAVIA, Kyle Bless V.No ratings yet
- OP ملونة كاملةDocument27 pagesOP ملونة كاملةArcangela QuaintrelleNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Pharma Agasbsn2-ADocument4 pagesAssignment in Pharma Agasbsn2-AMahdiyah AgasNo ratings yet
- Agents That Affect Bone Mineral Homeostasis PDFDocument4 pagesAgents That Affect Bone Mineral Homeostasis PDFCas BuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesDrug Study Magnesium SulfateSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGICAL AIDS - MergedDocument7 pagesPHARMACOLOGICAL AIDS - MergedCynthia WilsonNo ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument2 pagesCelecoxibAxseal ANo ratings yet
- OtcDocument3 pagesOtcMaria Erica Jan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Alendronate SodiumDocument3 pagesAlendronate SodiumGLen Caniedo100% (1)
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Review Treatment With Vitamin D3 And/or Vitamin K2Document4 pagesReview Treatment With Vitamin D3 And/or Vitamin K2fpm5948No ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument2 pagesOsteoporosisAseel AlsheeshNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis y OsteopeniaDocument2 pagesOsteoporosis y Osteopenia7uiz RiveraNo ratings yet
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitiesangel cenaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Grp4 Case Analysis Case 2Document4 pagesGrp4 Case Analysis Case 2aaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- PRE MS N2016 Ans KeyDocument33 pagesPRE MS N2016 Ans Keyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Cavite State University Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, CaviteDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Cavite State University Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, Caviteaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDocument19 pages5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care Plansaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ranitidine TramadolDocument11 pagesDrug Study Ranitidine Tramadolaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- VALDEZ, JUDY ANN B. Journal Reading 1Document3 pagesVALDEZ, JUDY ANN B. Journal Reading 1aaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Process Recording Taberna Catherine TDocument15 pagesProcess Recording Taberna Catherine Taaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Grp4 Act1 Disaster Nursing LabDocument5 pagesGrp4 Act1 Disaster Nursing Labaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Soft Copy - Osteo g2 Undone1Document13 pagesSoft Copy - Osteo g2 Undone1aaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- TABERNA - Choosing A Delivery Care Model and Staffing PatternDocument2 pagesTABERNA - Choosing A Delivery Care Model and Staffing Patternaaron taberna0% (1)
- Case Study Tension Pneumothorax BSN 4 2 1Document57 pagesCase Study Tension Pneumothorax BSN 4 2 1aaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing HistoryDocument12 pagesQuestions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing Historyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Leaderhsip and Management-TabernaDocument4 pagesNursing Leaderhsip and Management-Tabernaaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Song Theraphy - TabernaDocument2 pagesSong Theraphy - Tabernaaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Taberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTDocument17 pagesTaberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectiveaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Staffing Taberna Catherine TDocument7 pagesStaffing Taberna Catherine Taaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper TabernaDocument2 pagesReaction Paper Tabernaaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- ,mental Status Examination No. 1 Date: 11-19-21 Day: 1 1. General DescriptionDocument5 pages,mental Status Examination No. 1 Date: 11-19-21 Day: 1 1. General Descriptionaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Pathopysiology Book BasedtanginaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument2 pagesPathopysiology Book Basedtanginaaaaaaaaaaaaaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Complicated Iais: As Described Previously, Ciais Extend Beyond TheDocument3 pagesComplicated Iais: As Described Previously, Ciais Extend Beyond Theaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Activity TABERNADocument2 pagesReflection Activity TABERNAaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- RV. Based On Clinical Findings, Including Chest Pain, Shortness of Breath, HypoxiaDocument2 pagesRV. Based On Clinical Findings, Including Chest Pain, Shortness of Breath, Hypoxiaaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Sicksinussyndrome: Roberto de Ponti,, Jacopo Marazzato,, Giuseppe Bagliani,, Fabio M. Leonelli,, Luigi PadelettiDocument13 pagesSicksinussyndrome: Roberto de Ponti,, Jacopo Marazzato,, Giuseppe Bagliani,, Fabio M. Leonelli,, Luigi Padelettijose noel garcia perezNo ratings yet
- Bullets: "Victory Belongs To Those Who Are Most Persevering. Ad Majorem Dei Gloriam."Document15 pagesBullets: "Victory Belongs To Those Who Are Most Persevering. Ad Majorem Dei Gloriam."Jhaylord mendozaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument13 pagesHirschsprung Diseaseganesh reddyNo ratings yet
- Mesha (Aries) Lagna Characteristics: Physical AppearanceDocument3 pagesMesha (Aries) Lagna Characteristics: Physical AppearanceSuryaadeviKhatriNo ratings yet
- Dua Kasus Multipel Sklerosis Dengan Tipe Yang Berbeda Di Rsup M. Djamil, PadangDocument7 pagesDua Kasus Multipel Sklerosis Dengan Tipe Yang Berbeda Di Rsup M. Djamil, PadangNurul Fitriana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Living ThingsDocument23 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Living ThingsclarisseNo ratings yet
- Surgery in Elderly 2Document41 pagesSurgery in Elderly 2Zeba NaveedNo ratings yet
- 11 Tips To Treat InsomniaDocument7 pages11 Tips To Treat Insomniashivaniikumarii7889No ratings yet
- NCM 112 Eval ExamDocument11 pagesNCM 112 Eval ExamMartin T Manuel100% (1)
- Preeclampsia 2022Document16 pagesPreeclampsia 2022Jose DuranNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic and Nutritional Disorders 3b Aug 2023Document52 pagesAlcoholic and Nutritional Disorders 3b Aug 2023Vanshika KashyapNo ratings yet
- Tubulointerstitial Nephritis - 161269200418Document12 pagesTubulointerstitial Nephritis - 161269200418ተሣለነ ወልድNo ratings yet
- Yu Han, MM, Jianguang Sun, MM, Chenghan Luo, MM, Shilei Huang, MM, Liren Li, MM, Xiang Ji, MM, Xiaozong Duan, MM, Zhenqing Wang, MM, and Guofu Pi, MMDocument7 pagesYu Han, MM, Jianguang Sun, MM, Chenghan Luo, MM, Shilei Huang, MM, Liren Li, MM, Xiang Ji, MM, Xiaozong Duan, MM, Zhenqing Wang, MM, and Guofu Pi, MManjingbasah 24No ratings yet
- Disorders of The Umbilicus: Normal EmbryologyDocument12 pagesDisorders of The Umbilicus: Normal EmbryologyJulio LealNo ratings yet
- Manual of Antimicrobial Stewardship (1st Edition)Document49 pagesManual of Antimicrobial Stewardship (1st Edition)Socrates AbroadNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Cystic FibrosisDocument2 pagesChap 1 Cystic FibrosisSabina MoolyeNo ratings yet
- HASS R-ToolDocument6 pagesHASS R-ToolSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- 2019 Physical Therapy in Adult Inflammmatory Myopathy Patients A Systematic ReviewDocument13 pages2019 Physical Therapy in Adult Inflammmatory Myopathy Patients A Systematic ReviewAngelica OvandoNo ratings yet
- Fatty Liver InformationDocument2 pagesFatty Liver Informationohayo3590No ratings yet
- ITEC Facial & Skincare Scheme of Work (Syllabus)Document21 pagesITEC Facial & Skincare Scheme of Work (Syllabus)Genie KenNo ratings yet
- Add-Adhd EssayDocument13 pagesAdd-Adhd Essayapi-578080741No ratings yet
- Urology Written EssaysDocument12 pagesUrology Written EssaysTien Dung NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Talmudic Perspective On The Old TestamDocument388 pagesA Talmudic Perspective On The Old TestamOhad MagoriNo ratings yet
- Sumit SIP REPORT 18-20Document53 pagesSumit SIP REPORT 18-20Nikhil KharodeNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda at KaivalyadhamaDocument8 pagesAyurveda at KaivalyadhamaAnshumaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology Review 2023Document2 pagesGrade 11 Biology Review 2023Gur DayalNo ratings yet
- Ledderhose Disease: Pathophysiology Diagnosis and ManagementDocument3 pagesLedderhose Disease: Pathophysiology Diagnosis and ManagementLeandro PolancoNo ratings yet
- OSCE Review: by KP FerrarisDocument86 pagesOSCE Review: by KP Ferrarismahmoud azmyNo ratings yet