Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Block Diagram of Digital Communication System
Block Diagram of Digital Communication System
Uploaded by
Justine Rain D Querijero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageThe document discusses the process of digital communication from source to destination. An analog signal from the source is converted to digital by an analog-to-digital converter. The digital signal is then encoded, modulated onto a carrier signal, and transmitted through a channel. At the receiver, it is demodulated, decoded, and converted back to analog, restoring the original signal. Error correction coding and decoding helps ensure accurate transmission despite noise in the channel.
Original Description:
Original Title
Block diagram of Digital Communication System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the process of digital communication from source to destination. An analog signal from the source is converted to digital by an analog-to-digital converter. The digital signal is then encoded, modulated onto a carrier signal, and transmitted through a channel. At the receiver, it is demodulated, decoded, and converted back to analog, restoring the original signal. Error correction coding and decoding helps ensure accurate transmission despite noise in the channel.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageBlock Diagram of Digital Communication System
Block Diagram of Digital Communication System
Uploaded by
Justine Rain D QuerijeroThe document discusses the process of digital communication from source to destination. An analog signal from the source is converted to digital by an analog-to-digital converter. The digital signal is then encoded, modulated onto a carrier signal, and transmitted through a channel. At the receiver, it is demodulated, decoded, and converted back to analog, restoring the original signal. Error correction coding and decoding helps ensure accurate transmission despite noise in the channel.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
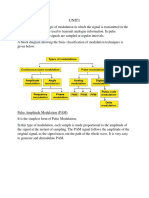
The source can be an analog signal. Example: A Sound signal .
Input Transducer this is a
transducer which takes a physical input and converts it to an electrical signal (Example:
microphone). This block also consists of an analog to digital converter where a digital signal is
needed for further processes. A digital signal is generally represented by a binary sequence. The
source encoder compresses the data into minimum number of bits. This process helps in effective
utilization of the bandwidth. It removes the redundant bits unnecessary excess bits, i.e., zeroes.
The channel encoder, does the coding for error correction. During the transmission of the signal,
due to the noise in the channel, the signal may get altered and hence to avoid this, the channel
encoder adds some redundant bits to the transmitted data. These are the error correcting bits. The
signal to be transmitted is modulated here by a carrier. The signal is also converted to analog
from the digital sequence, in order to make it travel through the channel or medium. The channel
or a medium, allows the analog signal to transmit from the transmitter end to the receiver end.
This is the first step at the receiver end. The received signal is demodulated as well as converted
again from analog to digital. The signal gets reconstructed here. The channel decoder, after
detecting the sequence, does some error corrections. The distortions which might occur during
the transmission, are corrected by adding some redundant bits. This addition of bits helps in the
complete recovery of the original signal. The resultant signal is once again digitized by sampling
and quantizing so that the pure digital output is obtained without the loss of information. The
source decoder recreates the source output. This is the last block which converts the signal into
the original physical form, which was at the input of the transmitter. It converts the electrical
signal into physical output (Example: loud speaker). This is the output which is produced after
the whole process. Example − the sound signal received. This unit has dealt with the
introduction, the digitization of signals, the advantages and the elements of digital
communications. In the coming chapters, we will learn about the concepts of Digital
communications, in detail.
You might also like
- Lesson 21: Analog To Digital Conversion: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesLesson 21: Analog To Digital Conversion: Objectivesatif_aman123100% (1)
- UNIT 5 Digital CommunicationDocument14 pagesUNIT 5 Digital CommunicationSunithaNo ratings yet
- block diagramDocument7 pagesblock diagramanitasjadhavNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Communication - Quick GuideDocument70 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication - Quick Guidemahendramahore01No ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Analog To DigitalDocument4 pagesDigital Communication - Analog To DigitalDilip PanchalNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Quick GuideDocument72 pagesDigital Communication - Quick GuideVIKASH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Analof To Digital Conversion-InFO TheoryDocument14 pagesAnalof To Digital Conversion-InFO TheorynanagraphixstudioNo ratings yet
- Dcomms ActDocument3 pagesDcomms ActjjeongdongieeNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 ECE4001 ETH VL2022230102368 Reference Material I 21-07-2022 Module - 1Document20 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 ECE4001 ETH VL2022230102368 Reference Material I 21-07-2022 Module - 1RISHABH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- 1 Lesson2 DigitalCommunicationDocument10 pages1 Lesson2 DigitalCommunicationQhadija JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital AudioDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Digital Audio姚熙No ratings yet
- DC 4Document11 pagesDC 4Shakibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition: An Introduction: Bruxton CorporationDocument5 pagesData Acquisition: An Introduction: Bruxton CorporationkumarcvNo ratings yet
- ADCDocument5 pagesADCnazmulNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition: An Introduction: Bruxton CorporationDocument7 pagesData Acquisition: An Introduction: Bruxton CorporationIvo DimitrovNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument9 pagesPulse Code ModulationDebjyotiNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems (15MT82) : (I) Information SourceDocument10 pagesCommunication Systems (15MT82) : (I) Information Sourcejeremy oswaldNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Quick GuideDocument62 pagesDigital Communication Quick GuideArun avNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DCDocument19 pagesUnit 1 DCANANDHU PILLAINo ratings yet
- ECN 302 NotesDocument16 pagesECN 302 NotesShrey SuriNo ratings yet
- A Level PracticeDocument2 pagesA Level PracticeRakotoarison Louis FrederickNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Group ADocument16 pagesElectronics and Telecommunication Engineering Group AMuhammad AuwalNo ratings yet
- Analogue and Digital Signals-1Document3 pagesAnalogue and Digital Signals-1Tamiranashe Tammie NyunguNo ratings yet
- EI Assignment 1 PDFDocument6 pagesEI Assignment 1 PDFFirozNo ratings yet
- 566.digital Communication - April 2017Document124 pages566.digital Communication - April 2017James kaundaNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio TechniquesDocument8 pagesDigital Audio Techniquesryanphs99No ratings yet
- DC Unit-1Document138 pagesDC Unit-1swethachand7No ratings yet
- Digital ComminicationDocument161 pagesDigital Comminicationmeghaasha6700No ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument3 pagesPulse Code Modulation21ECF031 PONMANIKANDAN PNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document42 pagesCH 08engaydiNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument3 pagesPulse Code ModulationWendell Miles De ArmasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document33 pagesLecture 7Youssef AshrafNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Quick GuideDocument75 pagesDigital Communication - Quick Guidearif8932869039No ratings yet
- AstroDocument41 pagesAstroAhmed Hamed BadrNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Digital CommunicationDocument9 pages2.1 Digital CommunicationMalka WeerasingheNo ratings yet
- PLDT ReportDocument25 pagesPLDT ReportAlfred Joseph ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition SystemDocument14 pagesData Acquisition SystemAditi Saha33% (3)
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) .: Basic Elements of PCMDocument2 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM) .: Basic Elements of PCMPathan MehemudNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication IntroductionDocument69 pagesDigital Communication IntroductionlokeshwarrvrjcNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation: Modulation Is The Process of Varying One or More Parameters of A Carrier Signal inDocument3 pagesPulse Code Modulation: Modulation Is The Process of Varying One or More Parameters of A Carrier Signal inmukulgrd1No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MCDocument63 pagesUnit 1 MCAditi KashetwarNo ratings yet
- S6 Ec Manual October 10thDocument54 pagesS6 Ec Manual October 10thrishikesh tpNo ratings yet
- ICS Unit-1Document10 pagesICS Unit-1Nancy MaanNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 05Document41 pagesData Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 05mr nNo ratings yet
- An Analogue Signal Uses Some Attribute of The Medium To Convey The SignalDocument3 pagesAn Analogue Signal Uses Some Attribute of The Medium To Convey The SignalJoyce BuelaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCDocument4 pagesNama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCRifky Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDocument15 pagesAnalog To Digital ConvertersJuan Angel AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital SystemDocument13 pagesAnalog and Digital SystemBorse RajNo ratings yet
- Data and Digital Communication 1Document6 pagesData and Digital Communication 1Lou Andrei BahoyNo ratings yet
- Wireless AssignmentDocument7 pagesWireless AssignmentJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Sigma Delta Modulator NutshellDocument5 pagesSigma Delta Modulator NutshellZubair MohammedNo ratings yet
- Telephony Expt9Document9 pagesTelephony Expt9Lerry SampangNo ratings yet
- The Analog To Digital Conversion ProcessDocument14 pagesThe Analog To Digital Conversion Processcardi36No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Analog SignalDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Analog SignalMostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document3 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM)Narayana Sai JawaharNo ratings yet
- PCM Lab ManualDocument5 pagesPCM Lab ManualSakshi DewadeNo ratings yet
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)