Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of Iloilo
Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of Iloilo
Uploaded by
Beatrice Maningas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views2 pagesThe nursing care plan is for a patient with chronic confusion and Alzheimer's disease. The short-term goals are for the patient to exhibit minimal confusion and remain safe within 1-2 weeks, and the long-term goals are for the patient to maintain orientation and use support systems within 1-3 months. The nursing interventions include establishing trust, avoiding stressful situations, providing structure, and instructing the family on how to best support and care for the patient.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chronic-Confusion-AD-NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan is for a patient with chronic confusion and Alzheimer's disease. The short-term goals are for the patient to exhibit minimal confusion and remain safe within 1-2 weeks, and the long-term goals are for the patient to maintain orientation and use support systems within 1-3 months. The nursing interventions include establishing trust, avoiding stressful situations, providing structure, and instructing the family on how to best support and care for the patient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Phinma University of Iloilo
Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of Iloilo
Uploaded by
Beatrice ManingasThe nursing care plan is for a patient with chronic confusion and Alzheimer's disease. The short-term goals are for the patient to exhibit minimal confusion and remain safe within 1-2 weeks, and the long-term goals are for the patient to maintain orientation and use support systems within 1-3 months. The nursing interventions include establishing trust, avoiding stressful situations, providing structure, and instructing the family on how to best support and care for the patient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
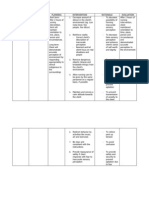
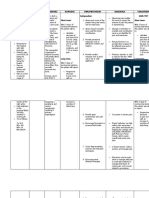
PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF ILOILO
COLLEGE OF ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
Nursing Department
NURSING CARE PLAN
NURSING
ASSESSMENT PLANNING NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective: Chronic Short-term: Independent: Short-term:
“my mom would confusion After 1-2 weeks of nursing Establish rapport with the To build a trusting relationship After 1-2 weeks of nursing
always ask why is related to intervention the client will be patient. between the nurse and the patient. intervention, goal met. The
she in the house Alzheimer’s able to: Assess patient for reversible or Determines type and extent of patient was able to:
and said it’s not her disease as Exhibit minimal or irreversible dementia, causes, dementia to establish a plan of care Exhibited minimal or
house, and she evidenced by reduced confusion, ability to interpret environment, to enhance cognition and emotional reduced confusion,
sometimes doesn’t decrease ability memory loss, and intellectual thought processes, functioning at optimal levels. memory loss, and
know the use of to recognize cognitive disturbances, memory loss, disturbances with cognitive disturbances,
kitchen utensils”, as things and depending upon stage of orientation, behavior, and depending upon stage
stated by the interpret one’s ad. socialization. of ad.
patient’s daughter. environment, Be distracted or use Maintain consistent scheduling Prevents patient agitation, erratic Able to be distracted or
decreased other techniques to with allowances for patient’s behaviors, and combative reactions. used other techniques
capacity for avoid stressful situations specific needs, and avoid Scheduling may need revision to to avoid stressful
Objective: thought, that may cause frustrating situations and show respect for the patient’s sense situations that may
Decrease ability memory aggressive, hostile overstimulation. of worth and to facilitate completion cause aggressive,
to recognize impairment, behaviors or frustration. of tasks. hostile behaviors or
things and disorientation, Remain safe and free Avoid or terminate emotionally Catastrophic emotional response is frustration.
interpret one’s and behavioral from harm. charged situations or prompted by task failure when the Remained safe and
environment. changes. Maintain usual level conversations. Avoid anger and patient feels expected to perform free from harm.
Decreased orientation. expectation of patient to beyond ability and becomes Maintained usual level
capacity for remember or follow instructions. frustrated and angry. Responding orientation.
thought Long-term: Do not expect more than the calmly to the patient validates
Memory After 1-3 months of nursing patient is capable of doing. feeling and causes less stress. Long-term:
impairment intervention the client will be Provide time for reminiscing if Allows for memory of past pleasant After 1-3 months of nursing
Disorientation able to: patient so desires. events. Patient may be reliving intervention, goal met. The
Behavioral Maintain usual level of events in the past and the caregiver patient was able to:
changes orientation should identify this behavior and Maintained usual level
Use appropriate support respect it. of orientation
systems. Limit sensory stimuli and Decreases frustration and Used appropriate
Remains safe and harm independent decision-making. distractions from environment. support systems.
free. Decreasing stress of making a Remained safe and
Maintain minimal or choice helps to promote security. harm free.
reduce confusion, Assist with establishing cues and Assists patients with early AD to Maintained minimal or
memory loss, and reminders for patient’s remember location of articles and reduce confusion,
cognitive disturbances if assistance. facilitates some orientation. memory loss, and
not improved. Identify family members and/or Helps to determine appropriate cognitive disturbances
support systems for the patient. person to notify for changes, to if not improved.
assist with care, and someone
familiar to patient to help deal with
his confusion.
Ask family members about their Identifies family’s need for
ability to provide care for patient. assistance.
Instruct family and provide them Patient may require ongoing skilled
with information regarding nursing care that the patient’s family
community services and long- is unable or unwilling to provide.
term health care facilities.
Instruct family regarding Patient may have delusions and
avoidance of arguing with patient hallucinations, that are real to the
about what he thinks, sees, or patient, and no amount of
hears. persuasion will convince him or her
otherwise. The patient may become
agitated or violent if contradicted.
Instruct family to consider if what Sometimes portions of
patient believes has some basis conversations can be heard and
in reality. misinterpreted by the patient.
Instruct family to avoid having Patient cannot make distinction of
patient watch violent TV shows. reality from fiction, and witnessing
violent acts on the screen may be
frightening to the patient.
Instruct family to utilize Distraction may be effective to calm
distraction techniques, such as patient if stressful situations occur.
soothing music, going for a walk,
or looking at picture albums if
patient has delusions.
Dependent:
Assist in treating contributing The patient may have an underlying
conditions. condition that can contribute
to/exacerbate confusion, discomfort
and agitation.
Administer medications, as To managed symptoms of
ordered. psychosis, depression, or
aggressive behavior.
Collaborative:
Identify appropriate To provide patient with support and
community resources. assist with problem-solving.
Provide appropriate To promote wellness and to provide
referrals. appropriate assistance for the
patient.
PREPARED BY: BEATRICE MANINGAS, UICN-SN
You might also like
- ACT Case Formulation Template v2.0Document3 pagesACT Case Formulation Template v2.0Sandy MagedNo ratings yet
- Impaired MemoryDocument1 pageImpaired MemoryHarmony Grace0% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderDocument2 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Care Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderChelsea Williams100% (1)
- Main Solomon 1990 Procedures For Identifying Infants As Disorganized Disoriented During The Ainsworth Strange SituationDocument44 pagesMain Solomon 1990 Procedures For Identifying Infants As Disorganized Disoriented During The Ainsworth Strange SituationKevin McInnes100% (3)
- Ineffective Role Perf Romance FinalDocument1 pageIneffective Role Perf Romance Finalasymptomaticcrisis0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationJulvica HeuwNo ratings yet
- NCP Self EsteemDocument4 pagesNCP Self Esteemeinghel_24100% (2)
- Dialectical Dilemma TherapistDocument3 pagesDialectical Dilemma TherapistRosalie Lotspeich100% (1)
- Example of Nursing Care Plan: Dr. Evelyn M Del MundoDocument20 pagesExample of Nursing Care Plan: Dr. Evelyn M Del MundoteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanJewelyn Bronda100% (2)
- Anxiety Related To Stress HspitaiztionDocument1 pageAnxiety Related To Stress HspitaiztionEunice Lan Sandoval Ardiente100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralRomzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Assessment ToolDocument53 pagesPsychiatric Assessment ToolLori100% (5)
- Multitheoretical Psychotherapy For Depression Integrating Strategies Fro...Document15 pagesMultitheoretical Psychotherapy For Depression Integrating Strategies Fro...Semenova MorattoNo ratings yet
- Crisis Intervention: Psychiatric Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesCrisis Intervention: Psychiatric Nursing Nursing Care PlanKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico Laud100% (4)
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- NCP Violence - OtherDocument2 pagesNCP Violence - OtherRosean Venus SilangNo ratings yet
- ND - Risk For SuicideDocument3 pagesND - Risk For SuicideHu Dawi100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. PiñeroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPCharles Mallari Valdez100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 pagesND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiNo ratings yet
- NCP PowerlessnessDocument6 pagesNCP PowerlessnessopxNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 pagesDisturbed Thought ProcessJessieRamosAnicetoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralRomzy Basañes100% (2)
- Cues Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: StoDocument3 pagesCues Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: StoSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- NCP StressDocument2 pagesNCP StressWaqas Javed100% (7)
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPTrixia Diaz67% (3)
- Xi. Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesXi. Nursing Care PlansNic Ji100% (1)
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Panic Attack Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesPanic Attack Nursing Care PlanSamVelasco100% (2)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceRheegell Ellar-Fuertes50% (2)
- Social IsolationDocument2 pagesSocial IsolationFlos Carmeli MontanaNo ratings yet
- NCP Self EsteemDocument3 pagesNCP Self EsteemAlfadz AsakilNo ratings yet
- Nursing CARE PLAN PsychDocument7 pagesNursing CARE PLAN Psychtiptopyo100% (1)
- NCP Social InteractionDocument3 pagesNCP Social InteractionJohn Cruz0% (1)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Anticipatory GrievingDocument2 pagesAnticipatory GrievingKM100% (5)
- Self Cre DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Cre DeficitSteph_Toinkz_240No ratings yet
- NCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor ActivityDocument3 pagesNCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor Activitydana75% (4)
- PSYCH - Defensive CopingDocument3 pagesPSYCH - Defensive CopingRoch Oconer100% (1)
- Alzheimer S Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesAlzheimer S Disease Nursing Care Planmp1757No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJay Villasoto100% (1)
- Altered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 pagesAltered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessRosecinie Torrente100% (2)
- Cva NCP AnxietyDocument1 pageCva NCP AnxietyQueenElsaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie Rosalejos100% (1)
- NCP - Self-Care Deficit Related To Weakness Due To Chemotherapy and Side Effects of Other MedicationsDocument3 pagesNCP - Self-Care Deficit Related To Weakness Due To Chemotherapy and Side Effects of Other MedicationsKian Herrera100% (1)
- NCP Risk For FallDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For FallHero Tauro0% (2)
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPChrisTine M. MoralesNo ratings yet
- Additional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaDocument26 pagesAdditional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob100% (5)
- Dementia Symptoms and CareDocument32 pagesDementia Symptoms and CareKiran Mini Ravi100% (1)
- DocumentDocument10 pagesDocumentNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought Process Related CNS Infection by HIVDocument5 pagesDisturbed Thought Process Related CNS Infection by HIVNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Individual CopingDocument1 pageNCP Inffective Individual CopingNatalie DulawanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Inference Nursing Goal Nursing Interventions EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Inference Nursing Goal Nursing Interventions EvaluationtrishxianieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management For A Patient With Schizophrenia and Generalized AnxietyDocument23 pagesNursing Care Management For A Patient With Schizophrenia and Generalized AnxietyKimberly Ann Boricano100% (1)
- 188 - BULAN - Task For Week 1Document5 pages188 - BULAN - Task For Week 1Cyril BulanNo ratings yet
- LarideDocument3 pagesLaridelouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Scizophrenia NCP2Document12 pagesScizophrenia NCP2Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinNo ratings yet
- NCP For Obsessions in NCM 117 (Anxiety)Document2 pagesNCP For Obsessions in NCM 117 (Anxiety)unkown userNo ratings yet
- MS2 Rle Sas 18Document3 pagesMS2 Rle Sas 18Beatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Transcultural NSG SAS 19Document4 pagesTranscultural NSG SAS 19Beatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Supervision/Nursing: 1. Unom4a Nonsl StmcneDocument3 pagesLesson Title: Supervision/Nursing: 1. Unom4a Nonsl StmcneBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Memantine AD Drug StudyDocument1 pageMemantine AD Drug StudyBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Dextroamphetamine ADHD Drug StudyDocument1 pageDextroamphetamine ADHD Drug StudyBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Decisional Role Ofa Health Manager: Presentation By: Beatrice V. ManingasDocument17 pagesDecisional Role Ofa Health Manager: Presentation By: Beatrice V. ManingasBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- 10 Herbal Medicines Approved by DOHDocument10 pages10 Herbal Medicines Approved by DOHBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Summary Differences Between Dementia and DeliriumDocument4 pagesSummary Differences Between Dementia and Deliriumtheglobalnursing100% (1)
- Concept PaperDocument11 pagesConcept PaperSun ShineNo ratings yet
- DSM 5 Intellectual Disability Fact SheetDocument2 pagesDSM 5 Intellectual Disability Fact Sheetapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Thérapie Cognitive Et Comportemental Du PerfectionnismeDocument11 pagesThérapie Cognitive Et Comportemental Du PerfectionnismeOmar HaouiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Dr. Saelan - Kelompok 7 - PJJ Jwa Periode 26 April-1 Mei 2021Document83 pagesTugas Dr. Saelan - Kelompok 7 - PJJ Jwa Periode 26 April-1 Mei 2021michael palitNo ratings yet
- Notes On PsychologyDocument14 pagesNotes On PsychologybinduannNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Empirical Perspectives On Secrets and Lies in PsychotherapyDocument32 pagesClinical and Empirical Perspectives On Secrets and Lies in Psychotherapybia shampooNo ratings yet
- Manohar Scholastic BackwardnessDocument5 pagesManohar Scholastic Backwardnessapi-228136529No ratings yet
- From Hypnotic Suggestion To Free Association: Freud As A Psychotherapist, Circa 1892-1893Document18 pagesFrom Hypnotic Suggestion To Free Association: Freud As A Psychotherapist, Circa 1892-1893adamNo ratings yet
- Pelaksanaan Teknik Mengontrol Halusinasi: Kemampuan Klien Skizofrenia Mengontrol Halusinasi Umam, RelianiDocument6 pagesPelaksanaan Teknik Mengontrol Halusinasi: Kemampuan Klien Skizofrenia Mengontrol Halusinasi Umam, RelianierinaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Child Abuse TotDocument7 pagesEffects of Child Abuse Totapi-253999496No ratings yet
- Teacher Resource Levels Combined yDocument186 pagesTeacher Resource Levels Combined yapi-263662188No ratings yet
- Burnout Among NursesDocument6 pagesBurnout Among NursesYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- John Sadler - Descriptions and Prescriptions - Values, Mental Disorders, and The DSMsDocument419 pagesJohn Sadler - Descriptions and Prescriptions - Values, Mental Disorders, and The DSMsBrunoMoriPorrecaNo ratings yet
- Only Human: Mental Health Difficulties Among Clinical, Counseling, and School Psychology Faculty and TraineesDocument49 pagesOnly Human: Mental Health Difficulties Among Clinical, Counseling, and School Psychology Faculty and TraineescrisolarisNo ratings yet
- Drug Addict ReportDocument13 pagesDrug Addict ReportZumer HashmiNo ratings yet
- A Case StudyDocument12 pagesA Case StudyericNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisordersDocument2 pagesSomatoform DisordersZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology: Session 3: Diagnosis of Mental DisordersDocument38 pagesAbnormal Psychology: Session 3: Diagnosis of Mental DisordersHumanist English ManNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Depression ScaleDocument3 pagesGeriatric Depression ScalevkNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines For Anxiety Disorders Maximising The Benefits and Minimising The RisksDocument9 pagesBenzodiazepines For Anxiety Disorders Maximising The Benefits and Minimising The RisksJordanNo ratings yet
- Habituation CEDARDocument24 pagesHabituation CEDARSven HartleyNo ratings yet
- The 12 Core Concepts - Concepts For Understanding Traumatic Stress Responses in Children and FamiliesDocument5 pagesThe 12 Core Concepts - Concepts For Understanding Traumatic Stress Responses in Children and FamiliesAlguémNo ratings yet
- 40 People vs. Rafanan, Jr.Document10 pages40 People vs. Rafanan, Jr.Simeon TutaanNo ratings yet