Professional Documents
Culture Documents
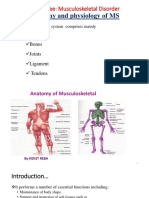
Muscular System
Muscular System
Uploaded by
Lean Divine CoyocaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Coco Fitness Glute GuideDocument15 pagesCoco Fitness Glute GuideDenise Lomax100% (2)
- Unit 10 11 Present Perfect Continuous and SimpleDocument5 pagesUnit 10 11 Present Perfect Continuous and SimpleDanil Pechorin100% (1)
- AnatomyDocument63 pagesAnatomyjayamohanNo ratings yet
- MUSCLESDocument6 pagesMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Self Myofascial ReleaseDocument22 pagesSelf Myofascial ReleaseMuhammad Fahmy100% (1)
- Pair Activity: B. Concept MasteryDocument3 pagesPair Activity: B. Concept MasteryNichole DequitoNo ratings yet
- Muscles - Workbook PDFDocument71 pagesMuscles - Workbook PDFakash100% (1)
- Muscles WorkbookDocument35 pagesMuscles WorkbookProdosh ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Muscle Fiber: Muscles Tissues Properties Four Properties of Muscle TissuesDocument3 pagesKinds of Muscle Fiber: Muscles Tissues Properties Four Properties of Muscle Tissuestupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Voluntary, Striated, MultinucleatedDocument4 pagesMuscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Voluntary, Striated, MultinucleatedElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HTDocument65 pagesChapter 3 HTtesfamichael mengistuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 18 Sept MuscleDocument3 pagesAnatomy 18 Sept MuscleShreeraj BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatDocument4 pagesAssignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatKassandra Shayne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument6 pagesMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Diseases: Presented by Group 5Document175 pagesMusculoskeletal Diseases: Presented by Group 5Niko Agustin BalilihanNo ratings yet
- Physio Lab 1-3Document6 pagesPhysio Lab 1-3Allison Eunice Servando100% (1)
- PJK Folio: Name: X Class: X Topic: Muscles and Tendons Teacher: Mr. LowDocument21 pagesPJK Folio: Name: X Class: X Topic: Muscles and Tendons Teacher: Mr. LowHo Qing JunNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesMuscular SystemJonalyn ChewacheoNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYDocument38 pagesGeneral Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYneanna100% (1)
- Muscular 1Document67 pagesMuscular 1Cherub ChuaNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module 3Document25 pagesPe 1 Module 3Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Mus Culo SkeletalDocument26 pagesMus Culo SkeletalCristy Ellain EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDocument46 pagesLecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- 2-Muscular System HandoutDocument4 pages2-Muscular System Handoutapi-302873465No ratings yet
- Injuries Main BookDocument9 pagesInjuries Main Bookomar alaa kaiokenNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNo ratings yet
- Ap Muscular System 1Document11 pagesAp Muscular System 1SALAZAR, John Vincent C.No ratings yet
- 1.2 TheMuscularSystemDocument60 pages1.2 TheMuscularSystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Muscular System of The Frog - NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Zoology Muscular System of The Frog - NotesMarian CordanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chapter 10 & 11 OutlineDocument8 pagesPhysiology Chapter 10 & 11 OutlineArtinDaryabariNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Ankles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingDocument18 pagesAnkles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingJess Zausa MasulaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesMuscular SystemMyat NyanNo ratings yet
- Describe The Stages of A Muscle TwitchDocument17 pagesDescribe The Stages of A Muscle TwitchshaiksardarnagulmeeraNo ratings yet
- 6 Human Anatomy - Muscular SystemDocument34 pages6 Human Anatomy - Muscular SystemDivya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cyriax HandoutDocument43 pagesCyriax HandoutMeenakshiputraeashwarprasad MacherlaNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesMuscular SystemJules ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Musclular SystemDocument69 pagesMusclular SystemYahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- Refined Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesRefined Muscular SystemogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Midterms RevDocument26 pagesAnatomy Midterms RevErnest VincentNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesActivity 4 Critical ThinkingDenisse Angelie CastroNo ratings yet
- T1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoDocument6 pagesT1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoMartín Benítez del HoyoNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM - ELOI BestDocument109 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM - ELOI BestEloisa Beltran AbquinaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 (Muscles)Document5 pagesCHAPTER 11 (Muscles)eumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Bones and MusclesDocument8 pagesBones and MusclesMarc Justine Gamiao GoNo ratings yet
- Lec 9active & Passive InsufficiencyDocument32 pagesLec 9active & Passive InsufficiencySajida Bibi Noonari75% (4)
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Muscle Re-Education by Venkata RamaiahDocument8 pagesMuscle Re-Education by Venkata Ramaiahvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument2 pagesIndexprice32447No ratings yet
- SAKUNADocument19 pagesSAKUNAErika Lee ToretaNo ratings yet
- DR - Irfan - Phisiologi of MuscleDocument20 pagesDR - Irfan - Phisiologi of MuscleilhamaminsyaputraNo ratings yet
- Muscular Strength and Endurance:: WEEK 2 (Final Term)Document6 pagesMuscular Strength and Endurance:: WEEK 2 (Final Term)Hey itsJamNo ratings yet
- CH-7 Class 12Document54 pagesCH-7 Class 12Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- 4 - Muscular SystemDocument39 pages4 - Muscular SystemMaryam ElammaryNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics LectureDocument3 pagesBiomechanics LectureOmar OsamaNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Natural SciencesDocument4 pagesSchool of Health and Natural SciencesHa GiyoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)
- The Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesThe Muscular SystemLesly Oquiño BetuinNo ratings yet
- Pathfit2 M1Document7 pagesPathfit2 M1corpuzjohnnilyn716No ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Muscular Systemvincealgarme09No ratings yet
- The Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainFrom EverandThe Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio de WH Questions in Simple Present TenseDocument1 pageEjercicio de WH Questions in Simple Present TenseYOMIRA MURILLONo ratings yet
- HimlDocument1 pageHimlKarabelo KhethengNo ratings yet
- Hope 4 G12 Q3 TQDocument7 pagesHope 4 G12 Q3 TQPaulo MoralesNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 PeDocument2 pagesWEEK 3 PeRye FelimonNo ratings yet
- Test Batteries Assessing Physical Fitness in School-Aged Children in The Czech Republic: A Brief ReviewDocument8 pagesTest Batteries Assessing Physical Fitness in School-Aged Children in The Czech Republic: A Brief ReviewFateen IrwahandNo ratings yet
- HongKong Sport Edu Part6 - enDocument33 pagesHongKong Sport Edu Part6 - enjlemmon1979No ratings yet
- Summative Exam Pe and HealthDocument2 pagesSummative Exam Pe and HealthLezette Escario0% (1)
- PE 10 1st Quarter - Lifestyle and Weight Management (Part I)Document10 pagesPE 10 1st Quarter - Lifestyle and Weight Management (Part I)Gicale, Jess Mathieu100% (1)
- Example Pa LogDocument13 pagesExample Pa LogTereseAnchetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Comparative Chart Group 2Document2 pagesUnit 6 Comparative Chart Group 2Arlene Culagbang GuitguitinNo ratings yet
- PE Health PDFDocument12 pagesPE Health PDFJuvelyn TorresNo ratings yet
- Let Review Part 2 Movement EdDocument42 pagesLet Review Part 2 Movement EdVan Errl Nicolai SantosNo ratings yet
- Bodypump Senior Chair Exercise Cardio Kickbox Groove CyclingDocument2 pagesBodypump Senior Chair Exercise Cardio Kickbox Groove CyclingmetroatlantaymcaNo ratings yet
- 5 6332511923094946274Document2 pages5 6332511923094946274Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Pe2 - Yoga ExercisesDocument31 pagesPe2 - Yoga Exercisesgarry reyesNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub The Progressive Calisthenics Program For Everyone 9798583191628 D 3786208Document48 pagesDokumen - Pub The Progressive Calisthenics Program For Everyone 9798583191628 D 3786208CrykNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Physical Education: Melvin Reyes Pascual IinstructorDocument16 pagesThe Nature of Physical Education: Melvin Reyes Pascual IinstructorDiane BolongaitaNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 L1Document33 pagesPathfit 1 L1Camilo LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Silenciador RectangularDocument2 pagesSilenciador RectangularelstrowNo ratings yet
- Q4 PE 8 - Module 2 PDFDocument12 pagesQ4 PE 8 - Module 2 PDFkateNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Transferring Between Bed and Chair (NCM 103-SL) Done Not DoneDocument2 pagesProcedure Checklist Transferring Between Bed and Chair (NCM 103-SL) Done Not DoneJiya JheNo ratings yet
- PE VI Third QuarterDocument2 pagesPE VI Third QuarterRonel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- A Level Pe Coursework RugbyDocument8 pagesA Level Pe Coursework Rugbyafjwdfmkapgipn100% (2)
- Body by Rings Training Log Phase #3 Session Letter Exercise Intensity SetsDocument12 pagesBody by Rings Training Log Phase #3 Session Letter Exercise Intensity SetsskyonNo ratings yet
- Consider Four Basic Food GroupsDocument3 pagesConsider Four Basic Food GroupsPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Body MechanicsDocument18 pagesBody MechanicsMelody LandichoNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Chapter-4 Summer 2014Document20 pagesPhysical Fitness Chapter-4 Summer 2014Kid-an KibrieNo ratings yet
- Every Witch Way - Ellen Dugan, Tess WhitehurstDocument220 pagesEvery Witch Way - Ellen Dugan, Tess WhitehurstJullia Romano100% (1)
Muscular System
Muscular System
Uploaded by
Lean Divine CoyocaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Muscular System
Muscular System
Uploaded by
Lean Divine CoyocaCopyright:
Available Formats
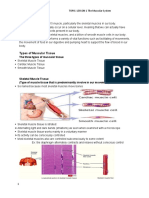
Muscular system
1. Briefly discuss the 4 types of muscular contraction
Isometric: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle does not change.
isotonic: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle changes.
eccentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle lengthens.
concentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle shortens.
2. Differentiate origin of muscle insertion
The origin is the attachment site that doesn't move during contraction, while
the insertion is the attachment site that does move when the muscle contracts.
The insertion is usually distal, or further away, while the origin is proximal, or closer to
the body, relative to the insertion.
3. Define the following terms:
a. Muscle fatigue
Muscle fatigue is a symptom that decreases your muscles’ ability to perform over
time. It can be associated with a state of exhaustion, often following strenuous activity or
exercise. When you experience fatigue, the force behind your muscles’ movements
decrease, causing you to feel weaker.
b. Muscle tone
Muscle TONE is defined as the tension in a muscle at rest. It is
the muscle's response to an outside force, such as a stretch or change in direction.
Appropriate muscle tone enables our bodies to quickly respond to a stretch.
c. Muscle twitch
A muscle twitch is an involuntary contraction of the fibers that make up a muscle.
Nerves control muscle fibers. When something stimulates or damages a nerve, it causes
the muscle fibers to contract, resulting in a twitch. A person can often see or feel
these twitches below the skin
d. rigor
a sudden feeling of cold with shivering accompanied by a rise in temperature,
often with copious sweating, especially at the onset or height of a fever
e. Physical contracture
A contracture occurs when your muscles, tendons, joints, or other tissues tighten
or shorten causing a deformity. Contracture symptoms include pain and loss of
movement in the joint. If this occurs, you should seek treatment right away. Doctors can
treat contractures with medicine, casts, and physical therapy.
4. What is an aponeurosis?
Aponeurosis, a flat sheet or ribbon of tendonlike material that anchors a muscle
or connects it with the part that the muscle moves. The aponeurosis is composed of
dense fibrous connective tissue containing fibroblasts (collagen-secreting spindle-
shaped cells) and bundles of collagenous fibres in ordered arrays.
5. Enumerate the following muscles by regions of the following animals (superficial
and deep muscles)
a. Cattle
The superficial muscles of a Cattle Occipito-Frontalis, Orbicularis Palpaebrarum,
Masseter, Sterno-cleido-Mastoid, Trapezius, Latissimus Dorsi, Pectoralis, External
and Internal oblique muscles, Opening of the mammary artery and vein (milk vein),
Gluteii, Rectus Femoris muscle.
b. Horse
superficial muscles
*
c. Sheep/goat
d. Swine
e. Chicken
6. Draw and label clearly the superficial muscle of the following animals
a. Cattle
b. Horse
c. Sheep/goat
d. Swine
e. Chicken
7. Draw a schematic representation of skeletal muscle and its fibers.
You might also like
- Coco Fitness Glute GuideDocument15 pagesCoco Fitness Glute GuideDenise Lomax100% (2)
- Unit 10 11 Present Perfect Continuous and SimpleDocument5 pagesUnit 10 11 Present Perfect Continuous and SimpleDanil Pechorin100% (1)
- AnatomyDocument63 pagesAnatomyjayamohanNo ratings yet
- MUSCLESDocument6 pagesMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Self Myofascial ReleaseDocument22 pagesSelf Myofascial ReleaseMuhammad Fahmy100% (1)
- Pair Activity: B. Concept MasteryDocument3 pagesPair Activity: B. Concept MasteryNichole DequitoNo ratings yet
- Muscles - Workbook PDFDocument71 pagesMuscles - Workbook PDFakash100% (1)
- Muscles WorkbookDocument35 pagesMuscles WorkbookProdosh ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Muscle Fiber: Muscles Tissues Properties Four Properties of Muscle TissuesDocument3 pagesKinds of Muscle Fiber: Muscles Tissues Properties Four Properties of Muscle Tissuestupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Voluntary, Striated, MultinucleatedDocument4 pagesMuscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Voluntary, Striated, MultinucleatedElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HTDocument65 pagesChapter 3 HTtesfamichael mengistuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 18 Sept MuscleDocument3 pagesAnatomy 18 Sept MuscleShreeraj BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatDocument4 pagesAssignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatKassandra Shayne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument6 pagesMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Diseases: Presented by Group 5Document175 pagesMusculoskeletal Diseases: Presented by Group 5Niko Agustin BalilihanNo ratings yet
- Physio Lab 1-3Document6 pagesPhysio Lab 1-3Allison Eunice Servando100% (1)
- PJK Folio: Name: X Class: X Topic: Muscles and Tendons Teacher: Mr. LowDocument21 pagesPJK Folio: Name: X Class: X Topic: Muscles and Tendons Teacher: Mr. LowHo Qing JunNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesMuscular SystemJonalyn ChewacheoNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYDocument38 pagesGeneral Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYneanna100% (1)
- Muscular 1Document67 pagesMuscular 1Cherub ChuaNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module 3Document25 pagesPe 1 Module 3Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Mus Culo SkeletalDocument26 pagesMus Culo SkeletalCristy Ellain EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDocument46 pagesLecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- 2-Muscular System HandoutDocument4 pages2-Muscular System Handoutapi-302873465No ratings yet
- Injuries Main BookDocument9 pagesInjuries Main Bookomar alaa kaiokenNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNo ratings yet
- Ap Muscular System 1Document11 pagesAp Muscular System 1SALAZAR, John Vincent C.No ratings yet
- 1.2 TheMuscularSystemDocument60 pages1.2 TheMuscularSystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Muscular System of The Frog - NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Zoology Muscular System of The Frog - NotesMarian CordanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chapter 10 & 11 OutlineDocument8 pagesPhysiology Chapter 10 & 11 OutlineArtinDaryabariNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Ankles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingDocument18 pagesAnkles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingJess Zausa MasulaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesMuscular SystemMyat NyanNo ratings yet
- Describe The Stages of A Muscle TwitchDocument17 pagesDescribe The Stages of A Muscle TwitchshaiksardarnagulmeeraNo ratings yet
- 6 Human Anatomy - Muscular SystemDocument34 pages6 Human Anatomy - Muscular SystemDivya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cyriax HandoutDocument43 pagesCyriax HandoutMeenakshiputraeashwarprasad MacherlaNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesMuscular SystemJules ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Musclular SystemDocument69 pagesMusclular SystemYahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- Refined Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesRefined Muscular SystemogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Midterms RevDocument26 pagesAnatomy Midterms RevErnest VincentNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesActivity 4 Critical ThinkingDenisse Angelie CastroNo ratings yet
- T1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoDocument6 pagesT1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoMartín Benítez del HoyoNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM - ELOI BestDocument109 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM - ELOI BestEloisa Beltran AbquinaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 (Muscles)Document5 pagesCHAPTER 11 (Muscles)eumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Bones and MusclesDocument8 pagesBones and MusclesMarc Justine Gamiao GoNo ratings yet
- Lec 9active & Passive InsufficiencyDocument32 pagesLec 9active & Passive InsufficiencySajida Bibi Noonari75% (4)
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Muscle Re-Education by Venkata RamaiahDocument8 pagesMuscle Re-Education by Venkata Ramaiahvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument2 pagesIndexprice32447No ratings yet
- SAKUNADocument19 pagesSAKUNAErika Lee ToretaNo ratings yet
- DR - Irfan - Phisiologi of MuscleDocument20 pagesDR - Irfan - Phisiologi of MuscleilhamaminsyaputraNo ratings yet
- Muscular Strength and Endurance:: WEEK 2 (Final Term)Document6 pagesMuscular Strength and Endurance:: WEEK 2 (Final Term)Hey itsJamNo ratings yet
- CH-7 Class 12Document54 pagesCH-7 Class 12Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- 4 - Muscular SystemDocument39 pages4 - Muscular SystemMaryam ElammaryNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics LectureDocument3 pagesBiomechanics LectureOmar OsamaNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Natural SciencesDocument4 pagesSchool of Health and Natural SciencesHa GiyoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)
- The Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesThe Muscular SystemLesly Oquiño BetuinNo ratings yet
- Pathfit2 M1Document7 pagesPathfit2 M1corpuzjohnnilyn716No ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Muscular Systemvincealgarme09No ratings yet
- The Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainFrom EverandThe Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio de WH Questions in Simple Present TenseDocument1 pageEjercicio de WH Questions in Simple Present TenseYOMIRA MURILLONo ratings yet
- HimlDocument1 pageHimlKarabelo KhethengNo ratings yet
- Hope 4 G12 Q3 TQDocument7 pagesHope 4 G12 Q3 TQPaulo MoralesNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 PeDocument2 pagesWEEK 3 PeRye FelimonNo ratings yet
- Test Batteries Assessing Physical Fitness in School-Aged Children in The Czech Republic: A Brief ReviewDocument8 pagesTest Batteries Assessing Physical Fitness in School-Aged Children in The Czech Republic: A Brief ReviewFateen IrwahandNo ratings yet
- HongKong Sport Edu Part6 - enDocument33 pagesHongKong Sport Edu Part6 - enjlemmon1979No ratings yet
- Summative Exam Pe and HealthDocument2 pagesSummative Exam Pe and HealthLezette Escario0% (1)
- PE 10 1st Quarter - Lifestyle and Weight Management (Part I)Document10 pagesPE 10 1st Quarter - Lifestyle and Weight Management (Part I)Gicale, Jess Mathieu100% (1)
- Example Pa LogDocument13 pagesExample Pa LogTereseAnchetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Comparative Chart Group 2Document2 pagesUnit 6 Comparative Chart Group 2Arlene Culagbang GuitguitinNo ratings yet
- PE Health PDFDocument12 pagesPE Health PDFJuvelyn TorresNo ratings yet
- Let Review Part 2 Movement EdDocument42 pagesLet Review Part 2 Movement EdVan Errl Nicolai SantosNo ratings yet
- Bodypump Senior Chair Exercise Cardio Kickbox Groove CyclingDocument2 pagesBodypump Senior Chair Exercise Cardio Kickbox Groove CyclingmetroatlantaymcaNo ratings yet
- 5 6332511923094946274Document2 pages5 6332511923094946274Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Pe2 - Yoga ExercisesDocument31 pagesPe2 - Yoga Exercisesgarry reyesNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub The Progressive Calisthenics Program For Everyone 9798583191628 D 3786208Document48 pagesDokumen - Pub The Progressive Calisthenics Program For Everyone 9798583191628 D 3786208CrykNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Physical Education: Melvin Reyes Pascual IinstructorDocument16 pagesThe Nature of Physical Education: Melvin Reyes Pascual IinstructorDiane BolongaitaNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 L1Document33 pagesPathfit 1 L1Camilo LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Silenciador RectangularDocument2 pagesSilenciador RectangularelstrowNo ratings yet
- Q4 PE 8 - Module 2 PDFDocument12 pagesQ4 PE 8 - Module 2 PDFkateNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Transferring Between Bed and Chair (NCM 103-SL) Done Not DoneDocument2 pagesProcedure Checklist Transferring Between Bed and Chair (NCM 103-SL) Done Not DoneJiya JheNo ratings yet
- PE VI Third QuarterDocument2 pagesPE VI Third QuarterRonel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- A Level Pe Coursework RugbyDocument8 pagesA Level Pe Coursework Rugbyafjwdfmkapgipn100% (2)
- Body by Rings Training Log Phase #3 Session Letter Exercise Intensity SetsDocument12 pagesBody by Rings Training Log Phase #3 Session Letter Exercise Intensity SetsskyonNo ratings yet
- Consider Four Basic Food GroupsDocument3 pagesConsider Four Basic Food GroupsPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Body MechanicsDocument18 pagesBody MechanicsMelody LandichoNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Chapter-4 Summer 2014Document20 pagesPhysical Fitness Chapter-4 Summer 2014Kid-an KibrieNo ratings yet
- Every Witch Way - Ellen Dugan, Tess WhitehurstDocument220 pagesEvery Witch Way - Ellen Dugan, Tess WhitehurstJullia Romano100% (1)