Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nature and Concept of Curriculum Infographic
Nature and Concept of Curriculum Infographic
Uploaded by
El DifuntoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nature and Concept of Curriculum Infographic
Nature and Concept of Curriculum Infographic
Uploaded by
El DifuntoCopyright:
Available Formats
CURRICULUM:
What is Curriculum?
Curriculum came from the Latin word "currere" which means "to run" or "to run a course".
A course study which contains a list of subject matter approved for teaching in schools.
Nature of Curriculum
1. The instructional programme as indicated by the course offerings to meet the various requirements of a vast
heterogeneous population.
2. The course of study, embodying outlines of knowledge to be taught.
3. All the experiences provided under the guidance of the school.
Concepts of Curriculum As dynamic as the changes that occur in the society.
Narrow Sense Broad Sense
Viewed merely as a listing of a subject to be taught in Refers to the total learning experiences of individuals not
school. only in schools but in society as well.
Two Points of View of Curriculum
Traditional Points of View Progressive Points of View
Body of subjects or subject matter prepared by the Progressivist believes that written documents or written
teachers for the students to learn. Synonymous to the materials can only be called curriculum if they are actualized
"course of study" and "syllabus". (Bilbao, Lucido, Iringan & by the learners. Hence, curriculum is defined as the total
Javier, 2008) learning experiences of the individual.
Traditional ideas view curriculum as a written document or
a plan of action in accomplishing goals.
Point of View of Curriculum Development
As curriculum is as dynamic as the changes that occur in the society, there is a need to develop and improve
curriculum as learners themselves are changing.
Two Models of Curriculum Development
Ralph Tyler Model: Four Basic Principles Hilda Taba's
(Tyler's Rationale) Grassroots Approach
Formulated four fundamental questions or principles in Improved Tyler's Rationale by making a linear model and seven
examining any curriculum in schools. major steps where teachers have a major input.
1. What educational purpose should the school seek to attain? 1. Diagnosis of learners needs and expectations of the larger
2. What educational experience can be provided that are likely society.
to attain the purpose? 2. Formulation of Learning Objectives.
3. How can these educational experiences be effectively 3. Selection of Learning Content.
organized? 4. Organization of Learning Content.
4. How can we determine whether these purposes are being 5. Selection of Learning Experiences.
attained or not? 6. Organization of Learning Activities.
7. Determination of what to evaluate and the means to doing it.
In summary, the following must be considered in curriculum
development: Sources:
1. Purpose of the School.
https://www.slideshare.net/valarpink/curriculum-its-meaning-nature-and-
2. Educational Experiences. scope#:~:text=Nature%20of%20curriculum%20Curriculum%20is,social%20and%20emot
3. Organization of Experiences. ional)%20and%20simplicity.
https://uomustansiriyah.edu.iq/media/lectures/12/12_2020_03_02!07_22_43_PM.pdf&ved
4. Evaluation of the Experiences.
=2ahUKEwjhrN3v5bzyAhVHAIgKHfb6CHwQFnoECB0QAQ&usg=AOvVaw2KPocE2XQkPDe
N7AxZsg_n
You might also like
- Reading Comprehension Using Story GrammarDocument4 pagesReading Comprehension Using Story GrammarSharlene Williams100% (1)
- Berlitz Self Teacher FrenchDocument294 pagesBerlitz Self Teacher FrenchFredy Guerrero Poma100% (10)
- The Fisher King WoundDocument6 pagesThe Fisher King WoundEdward L Hester100% (2)
- Smart Time Special Edition Grade 12 Teachers Book Web1Document307 pagesSmart Time Special Edition Grade 12 Teachers Book Web1Thùy Linh PhùngNo ratings yet
- Viva Pancho - Works of Pancho GuedesDocument33 pagesViva Pancho - Works of Pancho GuedesDogancan DemirNo ratings yet
- Outcomes, Indicators, Benchmarks, NormsDocument67 pagesOutcomes, Indicators, Benchmarks, NormsGellirose S. BantayanNo ratings yet
- Co 1 Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesCo 1 Lesson PlanRhym M. PagandahanNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Congson, Fatima Grace CDocument2 pagesTask 1 Congson, Fatima Grace CFatima Grace CongsonNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 12 JessaDocument3 pagesProf Ed 12 JessaClarizza Mae Abejo100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Module 4Document19 pagesChapter 3 Module 4sofeia delambacaNo ratings yet
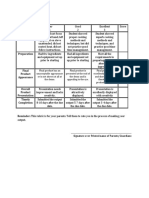
- Cookery 10 - RubricDocument1 pageCookery 10 - RubricDiofhelkenneth GjcNo ratings yet
- Done SUB-TED Prelim-Module EDUC 302Document26 pagesDone SUB-TED Prelim-Module EDUC 302Pepito ManuawanNo ratings yet
- PPST Based Evaluation Sheet For Pre Service TeachersDocument1 pagePPST Based Evaluation Sheet For Pre Service TeachersRochelle Anne Perez Reario100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6hasimhkalil227No ratings yet
- ALEJANDRO-Enhanced Teacher Education Curriculum Anchored On OBEDocument26 pagesALEJANDRO-Enhanced Teacher Education Curriculum Anchored On OBEAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Ronan D. Avenilla BSED ENGLISH 1Document3 pagesRonan D. Avenilla BSED ENGLISH 1Ryan LaspiñasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in EPPDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in EPPJobeth BalicogNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2: Participation and Teaching Assistantship: Page - 1Document29 pagesField Study 2: Participation and Teaching Assistantship: Page - 1Michelle BecodoNo ratings yet
- Types of Portfolio and Stages in Implementing Portfolio AssessmentDocument5 pagesTypes of Portfolio and Stages in Implementing Portfolio AssessmentJohn Carlo Mora CampoNo ratings yet
- Prelim ExaminationDocument4 pagesPrelim ExaminationGhie RardNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Challenges Encountered by The Teachers in Implementing Modular Distance Learning: Impact On Students' Academic PerformanceDocument10 pagesStrategies and Challenges Encountered by The Teachers in Implementing Modular Distance Learning: Impact On Students' Academic PerformancePsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Principles and Strategies (Lesson Planning)Document10 pagesModule 5 - Principles and Strategies (Lesson Planning)Jesryl Remerata OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Problems Encountered by Teachers in The Teaching-Learning Process: A Basis of An Action PlanDocument20 pagesProblems Encountered by Teachers in The Teaching-Learning Process: A Basis of An Action PlanERIKA O. FADEROGAONo ratings yet
- Quizizz Workshop Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesQuizizz Workshop Lesson Planapi-290870308No ratings yet
- 21st Century Assessments & CharacteristicsDocument2 pages21st Century Assessments & CharacteristicsJhay-Ar Espeleta PalarisNo ratings yet
- Module 3-Curriculum Design: 1 Semester 2021-2022 FHRLDocument6 pagesModule 3-Curriculum Design: 1 Semester 2021-2022 FHRLAsuna SanNo ratings yet
- Developing THE Scoring RubricDocument43 pagesDeveloping THE Scoring RubricRona BuhatNo ratings yet
- Ma Angela Kristine Valencia - Activity On Affective AssessmentDocument6 pagesMa Angela Kristine Valencia - Activity On Affective AssessmentMa. Angela Kristine ValenciaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Table of Specifications 2Document4 pagesWhat Is A Table of Specifications 2CherryLee AnnNo ratings yet
- Math10 q1Document8 pagesMath10 q1Jasmin Move-RamirezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/Ies: Code: S10Mt-Iva-B21Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/Ies: Code: S10Mt-Iva-B21Ritz Anton LimNo ratings yet
- Finalppt For Oral Defense 2Document24 pagesFinalppt For Oral Defense 2Donna LagongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Operations With Whole Numbers: Concept / Topic To Teach: Adding and Subtracting IntegersDocument6 pagesLesson Plan On Operations With Whole Numbers: Concept / Topic To Teach: Adding and Subtracting IntegersLady Jane EstrivelloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. What Is Project-Based Multimedia Learning?Document7 pagesChapter 1. What Is Project-Based Multimedia Learning?Romeo Balingao100% (1)
- Group 1 ReportDocument26 pagesGroup 1 ReportAvergonzado Roquez AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Assessment - EportfolioDocument4 pagesAlternative Assessment - EportfolioFrancis Oso PantinoNo ratings yet
- CPE108 A6 (Curricula 3)Document3 pagesCPE108 A6 (Curricula 3)CORINNE FAITH BASLOTNo ratings yet
- in Inquiry Based LearningDocument29 pagesin Inquiry Based LearningRonnelNo ratings yet
- SEPTEMBER 12, 2023 Day 2-Tuesday Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle/Epp - Home Economics Grade 6Document3 pagesSEPTEMBER 12, 2023 Day 2-Tuesday Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle/Epp - Home Economics Grade 6karen rose maximoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Implementation HandoutsDocument3 pagesCurriculum Implementation HandoutsChristine Joy PerionNo ratings yet
- Ecological Literacy and Arts and Creative Literacy: (Grab Your Reader'S Attention With A GreatDocument11 pagesEcological Literacy and Arts and Creative Literacy: (Grab Your Reader'S Attention With A GreatChristine LumbreNo ratings yet
- FS 3 Episode 3Document7 pagesFS 3 Episode 3Mark Anthony Nieva RafalloNo ratings yet
- Internship Reflection JournalDocument12 pagesInternship Reflection Journalapi-357369904No ratings yet
- Example of ASSURE Model - Understanding GeometryDocument4 pagesExample of ASSURE Model - Understanding GeometryhasimharunNo ratings yet
- School Campus and Community VisitDocument3 pagesSchool Campus and Community VisitdweezillNo ratings yet
- Methods of Curriculum IntegrationDocument3 pagesMethods of Curriculum IntegrationApril Rose BaratoNo ratings yet
- Outcomes Based Education: ThesisDocument17 pagesOutcomes Based Education: ThesisLin Coloma Viernes WagayenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Test 2Document7 pagesMultiple Choice Test 2Yshin Mejos MicarandayoNo ratings yet
- Profed7 Cm1 Engaged: Classroom Visitor 7. Field Trip and Service Learning 8. Context Curriculum 9. Impact InvestigationDocument9 pagesProfed7 Cm1 Engaged: Classroom Visitor 7. Field Trip and Service Learning 8. Context Curriculum 9. Impact InvestigationAndrea Mae DelimaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 109 Rosario Mark John Rey R. Module 8Document2 pagesProf Ed 109 Rosario Mark John Rey R. Module 8JayacinthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TTTSCDocument19 pagesChapter 1 TTTSCJackaii Waniwan IINo ratings yet
- Grade 7 ''POLYGON''Document9 pagesGrade 7 ''POLYGON''Niño Lemuel Lazatin ConcinaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 PPT Ta vs. Aa 15 July 2017Document11 pagesGroup 1 PPT Ta vs. Aa 15 July 2017Yhervin Lucero SaysonNo ratings yet
- RRL NewDocument8 pagesRRL NewJhay-ar FernandezNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Understanding CLSDocument41 pagesWEEK 3 Understanding CLSPrimaNo ratings yet
- TefaniaDocument8 pagesTefaniaTeph BalagaNo ratings yet
- Science DLPDocument2 pagesScience DLPJesusa Gregory HabigNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Year & Section Subject:: ST NDDocument2 pagesName: Date: Year & Section Subject:: ST NDFaizal MaligaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Development of Assessment ToolsDocument12 pages4.1 Development of Assessment ToolsChano MorenoNo ratings yet
- The Oliva ModelDocument2 pagesThe Oliva ModelPrincess Kaye RicioNo ratings yet
- School of Liberal Arts and Teacher Education: University of Cagayan ValleyDocument3 pagesSchool of Liberal Arts and Teacher Education: University of Cagayan ValleyFerliza Cudiamat PacionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Module 2 Lesson 2 Approaches About School CurriculumDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Module 2 Lesson 2 Approaches About School CurriculumHazim Gomer Dognap100% (2)
- Questions:: Name of FS Student Course, Year and Section Name of FS Mentor DateDocument8 pagesQuestions:: Name of FS Student Course, Year and Section Name of FS Mentor DateJeniva MalicdemNo ratings yet
- TTSCMT4Document6 pagesTTSCMT4RENIEL PAORNo ratings yet
- Shaping the College Curriculum: Academic Plans in ContextFrom EverandShaping the College Curriculum: Academic Plans in ContextRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Materi To TOEFL 01 NovemberDocument73 pagesMateri To TOEFL 01 Novembernamira ammarinNo ratings yet
- GM608-Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice-Course Outline-2020-21Document2 pagesGM608-Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice-Course Outline-2020-21rajani mahapatraNo ratings yet
- MUMONKAN - All 48 Koans With CommentariesDocument22 pagesMUMONKAN - All 48 Koans With CommentariesAhmad AlhourNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making in Foreign Policy PDFDocument10 pagesDecision-Making in Foreign Policy PDFvishal rajput100% (1)
- Strategic Mindset - Action GuideDocument19 pagesStrategic Mindset - Action GuideTinki DewanganNo ratings yet
- Cip Ques PaperDocument10 pagesCip Ques Paperapi-3721660100% (2)
- V R Siddhartha Engineering College:: Vijayawada 17EC3701A: Antennas and Wave Propagation Questions Bank UNIT: I & II A.Y 2021-22Document2 pagesV R Siddhartha Engineering College:: Vijayawada 17EC3701A: Antennas and Wave Propagation Questions Bank UNIT: I & II A.Y 2021-22Narasimhareddy MmkNo ratings yet
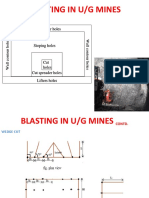
- Blasting in U/G Mines: Roof Contour Holes Roof Contour HolesDocument10 pagesBlasting in U/G Mines: Roof Contour Holes Roof Contour HolesSiddharth MukhillaNo ratings yet
- PrgadDocument3 pagesPrgadJohn James AquinoNo ratings yet
- (Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - SolutionsDocument6 pages(Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- Kissinger The Secret SideDocument98 pagesKissinger The Secret Sidekaf_kingNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistrySayantanNo ratings yet
- Green BeanDocument8 pagesGreen BeanHà Anh Lê VũNo ratings yet
- Rooms DivisionDocument19 pagesRooms Divisionনিয়াজ মাহমুদNo ratings yet
- National Certificate Ii - Optional Skill Module - Bread and Pastry Production PDFDocument116 pagesNational Certificate Ii - Optional Skill Module - Bread and Pastry Production PDFMicol Villaflor ÜNo ratings yet
- The Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelyDocument11 pagesThe Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelypriyankaNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Cutting Force Model For High-Speed Milling of Titanium AlloysDocument4 pagesA Hybrid Cutting Force Model For High-Speed Milling of Titanium Alloysabdsu75No ratings yet
- I TalmudicHermeneuticsDocument6 pagesI TalmudicHermeneuticsrefugioaguiasNo ratings yet
- RUDS Presents FAMEDocument12 pagesRUDS Presents FAMERUDSdrama0% (1)
- Financial Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making 7th Edition Kimmel Test BankDocument36 pagesFinancial Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making 7th Edition Kimmel Test Bankhopehigginslup31100% (25)
- The Important of English in EducationDocument5 pagesThe Important of English in EducationSaya SyazrulNo ratings yet
- Vinuya vs. RomuloDocument2 pagesVinuya vs. RomuloLajilaNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Text MessagesDocument7 pagesGood Morning Text MessagesStephan MilesNo ratings yet
- SDN PCo 03Document23 pagesSDN PCo 03UwedaNo ratings yet
- NAV 2015 Install Guide PDFDocument17 pagesNAV 2015 Install Guide PDFJacob Joseph OchiengNo ratings yet