Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2
Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2
Uploaded by
Rj AndayaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2
Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2
Uploaded by
Rj AndayaCopyright:
Available Formats
RJ Andaya General Biology
STEM 111-08
Activity No. 2: General Biology
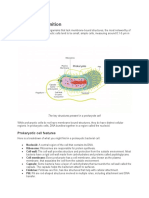
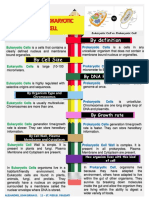
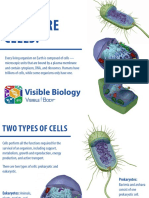
A. Directions: Now that you are equipped with the knowledge of the differences between prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells, differences between plants and animal cells. In a clean sheet of paper, list down the
characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. ( 10pts.)
PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL
Prokaryotes are exclusively Eukaryotic cells are larger
unicellular organisms. than prokaryotic cells and
have a “true” nucleus,
membrane-bound
organelles, and rod-shaped
chromosomes.
Most prokaryotes are A cell wall is the outermost
extremophiles. layer of the eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotes do not have Having complex cells in
membrane bound organelles. which the genetic material
is organized into
membrane-bound nuclei.
Prokaryotes have circular DNA. All eukaryotic cells have a
surrounding plasma
membrane, which is also
known as the cell
membrane.
Prokaryotes do not have a true The cell has mitochondria.
nucleus, instead, their DNA
occupies an irregularly-shaped
area (nucleoid)
The cell size ranges from 0.1 to Flagella and cilia are the
5.0 micrometre in size. locomotory organs in a
eukaryotic cell.
Chloroplasts are absent. The nucleus houses the
cell’s DNA and directs the
synthesis of proteins and
ribosomes.
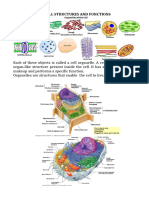
B. Direction: Do you think there is any differences between the plant and animal cells? And how does they
differ in structure. In an essay form, explain your answer on the space provided. (5pts.)
Yes, since animal cells lack a cell wall, although plant cells do, which is a significant
distinction, and animal cells lack chloroplasts, but plant cells do not lack
chloroplasts. Photosynthesis is carried out by chloroplasts, which allows plants to
manufacture food. Plant cells frequently have one or more large vacuoles, in
which animal cells have tiny vacuoles, if any at all.
You might also like
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument58 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- GN 1.2 - Classify CellsDocument2 pagesGN 1.2 - Classify CellsJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument24 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatNo ratings yet
- List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesList All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Flagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesDocument18 pagesFlagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Cell Structure and OrganellesDocument48 pagesChapter 1 - Cell Structure and OrganellesNatalie GraceNo ratings yet
- Lecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument16 pagesLecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesCell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaapi-3714451100% (2)
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureIrvin Jacob AquinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- WK 2-Bacterial CellDocument2 pagesWK 2-Bacterial Cellalmirarepollo015No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument9 pagesCell BiologyMick HardyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIODocument25 pages1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIOedensatire21No ratings yet
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- 4.06__Eukaryotic_Cells_-_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_CellsDocument2 pages4.06__Eukaryotic_Cells_-_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_CellsMae ann CumpletoNo ratings yet
- Science & TechnologyDocument115 pagesScience & TechnologyvinayNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesGamu GamuNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesChool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell Notes FinalDocument2 pagesBiology Cell Notes FinalDark hunter Gaming zoneNo ratings yet
- Bio1 11 - 12 Q1 0201 PF FDDocument37 pagesBio1 11 - 12 Q1 0201 PF FDsamsungboyles127No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1Document15 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1porchypepita37No ratings yet
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Prokalytic Vs EurokalyticDocument1 pageProkalytic Vs EurokalyticJessielyn DangananNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Document3 pagesProkaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Anime KpopNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells NotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells NotesMischi Jeda ElumbaNo ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- Biochem - LecDocument29 pagesBiochem - LecBEA FRANCINE DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesEukaryotic CellsLolaNo ratings yet
- Your Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesYour Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsVisca El BarcaNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral Biologyjohnraymercado2No ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Mrsa 4Document10 pagesMrsa 4Ach Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Bacterial Growth and Culture MediaDocument26 pagesBacterial Growth and Culture MediaMuhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Microscope REVIEWERDocument6 pagesMicroscope REVIEWERkjdobdin23No ratings yet
- An Examination of Handwritten Signatures Forged Using Photosensitive Signature StampDocument16 pagesAn Examination of Handwritten Signatures Forged Using Photosensitive Signature Stampshuchim guptaNo ratings yet
- Making Wet Mount SlideDocument6 pagesMaking Wet Mount SlideCarolina SantanderNo ratings yet
- Equipment BrochureDocument60 pagesEquipment BrochureAmar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Gotu Kola Centella AsiatDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Gotu Kola Centella Asiatnik nikkitNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 2Document5 pagesLaboratory Activity 2Sabrina MascardoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document12 pagesGen Bio 2Ma.Dulce ManalastasNo ratings yet
- How It Works?: Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA)Document9 pagesHow It Works?: Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA)dragusriyadi01No ratings yet
- Microscope 2015 NOTES 2Document20 pagesMicroscope 2015 NOTES 2Rdh MnbNo ratings yet
- Sydney-Mae Low - Lab Report 1Document13 pagesSydney-Mae Low - Lab Report 1Sydney-Mae LowNo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument30 pagesSpecial StainsNatalia HaikaliNo ratings yet
- Micro (Volume 1)Document67 pagesMicro (Volume 1)Dr. noor taherNo ratings yet
- Asbestos Guidance Apr09Document30 pagesAsbestos Guidance Apr09RTRMuizerNo ratings yet
- BACTE (Quizlet)Document4 pagesBACTE (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Histology LDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Human Histology LAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument16 pagesCell TypesyvetteNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 MCQDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class 9 MCQEnter NameNo ratings yet
- Agricultural MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesAgricultural MicrobiologyManjunath RamannaNo ratings yet
- Dimension Edge Atomic Force Microscope - B074-RevC1Document8 pagesDimension Edge Atomic Force Microscope - B074-RevC1Ivan Hernádez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety Rules and Gram StainingDocument4 pagesLab Safety Rules and Gram StainingAsad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 7 Methods of Studying BacteriaDocument21 pages7 Methods of Studying BacteriaAngel Marie JamilaNo ratings yet
- Oil Immersion PDFDocument3 pagesOil Immersion PDFeqmedNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument27 pagesCytoskeletonserenity limNo ratings yet
- Dip-Pen NanolithographyDocument21 pagesDip-Pen NanolithographySenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- E Optic3 Chap 4Document30 pagesE Optic3 Chap 4dejavu77No ratings yet
- SOP For Microbial Staining Procedures - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesSOP For Microbial Staining Procedures - Pharmaceutical GuidelinessatishNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Alina VoinescuDocument197 pagesDissertation Alina Voinescurollo100% (2)
- Ultrasonic Imaging Inspection of Projection Welds: 5th Pan American Conference For NDTDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Imaging Inspection of Projection Welds: 5th Pan American Conference For NDTAsif HameedNo ratings yet