Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
JackRolunaBernalesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mini VET GuideDocument186 pagesMini VET GuideemitibiNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document4 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan N V DDocument28 pagesNursing Care Plan N V DDr-Sanjay Singhania75% (4)
- Vitamins Chemistry Project Report (ST Josephs HSS Trivandrum, Year 2009-2010)Document25 pagesVitamins Chemistry Project Report (ST Josephs HSS Trivandrum, Year 2009-2010)kidilamvivek88% (26)
- NcpFatigue Related To Decreased Hemoglobin and Diminished Oxygen-Carrying Capacity of The Blood.Document3 pagesNcpFatigue Related To Decreased Hemoglobin and Diminished Oxygen-Carrying Capacity of The Blood.The Right WayNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Priority No. 3Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Priority No. 3Pantaleon PacisNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- Body WeaknessDocument1 pageBody Weaknessnymphaaugustus100% (3)
- NCP Severe HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesNCP Severe HypocalcemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in SwallowingDocument1 pageDifficulty in SwallowingmawelNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDocument12 pagesBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- NCP Template ObDocument7 pagesNCP Template ObMae CeaesarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanMiguelito Galagar GultianoNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocument1 pageOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Classifications and LanguagesDocument12 pagesNursing Classifications and LanguagesGiselle Chloe Baluya ico0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationRheeanne Mae Amilasan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument2 pagesDisturbed Sleep PatternROxanne S. RendonNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJaney Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- NCP Pot Riskforinjury EncephalitisDocument3 pagesNCP Pot Riskforinjury Encephalitisaila angNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina Aubrey0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan - Activity IntoleranceChezka Orton Swift Bolintiam100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- NCP Arra AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP Arra AnemiaShin GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument4 pagesDrug Namecheanne003No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- NCP GoiterDocument1 pageNCP GoiterDavid Calalo67% (3)
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NCP Group 3 Fatigue ..Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan NCP Group 3 Fatigue ..Aerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPmimingdot33No ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument6 pagesNCP AnemiaJudeLax100% (1)
- Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesNursing Responsibilityايام اول الشحيNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanRaphael Reyes Enriquez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- NCP AnemiaDocument3 pagesNCP AnemiaJadeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Long Term: Long TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Long Term: Long TermAriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AnemiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AnemiaMyrshaida Ibrahim0% (1)
- NCP AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP AnemiaAriaNo ratings yet
- Recommendation RenalDocument3 pagesRecommendation RenalJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Recommendation AnemiaDocument3 pagesRecommendation AnemiaJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Week7 BERNALESDocument2 pagesWeek7 BERNALESJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Recommendation BurnDocument3 pagesRecommendation BurnJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Burn Injury: RecommendationDocument3 pagesBurn Injury: RecommendationJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- GeriaDocument2 pagesGeriaJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Aluminum and The Prevalence of Anemia in Communities in Barcarena Pará, BrazilDocument7 pagesExposure To Aluminum and The Prevalence of Anemia in Communities in Barcarena Pará, BrazilIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Tariq PresentationDocument24 pagesTariq PresentationHasnain AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Nutrition and Nutraceuticals: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesChapter 7. Nutrition and Nutraceuticals: Multiple ChoicericharegbeNo ratings yet
- Transfusion MCQs and SAQsDocument3 pagesTransfusion MCQs and SAQsSaima IramNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia 170119201048Document33 pagesPancytopenia 170119201048Dabogski FranceNo ratings yet
- Anemia - PPT PresentationDocument23 pagesAnemia - PPT PresentationRommel Montero RicioNo ratings yet
- English Course: Instructor'S Contact Info Ahmad Ridho Rojabi, S.PD, M.PDDocument62 pagesEnglish Course: Instructor'S Contact Info Ahmad Ridho Rojabi, S.PD, M.PDeliahapsaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Bone Marrow Aspiration in Hematological DisorderDocument4 pagesInterpretation of Bone Marrow Aspiration in Hematological Disordervanessa wijayaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 305 Sgd'sDocument9 pagesPharmacology 305 Sgd'sanojanNo ratings yet
- Complete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineDocument8 pagesComplete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anaemia Armando HasudunganDocument1 pageIron Deficiency Anaemia Armando HasudunganhiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianDocument54 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianFlavia PolodeanuNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument92 pagesAnemiasangeetachatterjee100% (1)
- RBC PathologyDocument7 pagesRBC PathologyKent CruzNo ratings yet
- Higlighted For FNCPSDocument55 pagesHiglighted For FNCPSCarey Jamille YadanNo ratings yet
- Morning Report Pediatric DepartmentDocument18 pagesMorning Report Pediatric DepartmentMedina MarwanNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With AnemiaDocument37 pagesApproach To The Patient With AnemiaSumeet PratapNo ratings yet
- CompleteBloodCounts NORMAL VALUEDocument4 pagesCompleteBloodCounts NORMAL VALUEWoro Hapsari Wahyuningrum100% (1)
- Lina's THESISDocument40 pagesLina's THESISlina.o.mintNo ratings yet
- To Study The Prevalence of Anaemia in Indoor Patients of Tertiary Care CentreDocument3 pagesTo Study The Prevalence of Anaemia in Indoor Patients of Tertiary Care CentreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Document2 pagesVitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Ghubaya CopNo ratings yet
- Header Halaman Google Penelusuran: Hasil WebDocument5 pagesHeader Halaman Google Penelusuran: Hasil WebmuniraliiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Drug NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Drug NameCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument32 pagesVitaminmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Blood MCQDocument10 pagesBlood MCQTennyson MachiwenyikaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis - UpToDateDocument76 pagesHereditary Spherocytosis - UpToDateHuỳnh Thị Khả DuyNo ratings yet
- Transfusion and Apheresis Science: SciencedirectDocument4 pagesTransfusion and Apheresis Science: SciencedirectMarini TaslimaNo ratings yet
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
JackRolunaBernales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesOriginal Title
FATIGUE-NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
JackRolunaBernalesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
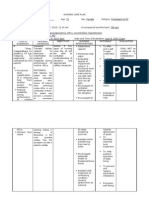
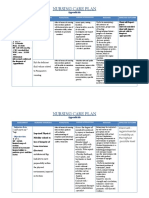
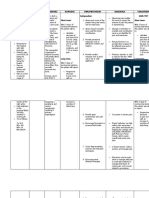
ASSESSMENT NURSING BACKGROUND PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS KNOWLEDGE
Medical Fatigue Short Term: Assess the The specific
Diagnosis: related to At the end of specific cause cause of fatigue
Decreased interventions, of fatigue. is due to tissue
Anemia hemoglobin the client will hypoxia from
and be able to normocytic
Subjective: diminished verbalize anemia; Other
Pt complaint of oxygen- reduction of related medical
feeling tired carrying fatigue, as problems can
capacity of evidenced by also
Objective: the blood. reports of compromise
Hgb: 8.1 g/dL as evidenced increased activity
Oxygen by feeling energy and tolerance.
Saturation 94% tired. ability to
on 2 L/minute perform
desired Assess the Fatigue can
Medical activities. client’s ability limit the client’s
History: to perform ability to
(+) CHF Long Term: activities of participate
(+) COPD At the end of daily living in self-care and
(+) the (ADLs), and perform his or
Osteoarthritis interventions, the demands her role
client will of daily responsibilities
verbalize living. in family and
understanding society, such as
on the use of working outside
energy the home.
conservation
principles. Assist the This will allow
client in the client to
planning and maximize
prioritizing his/her time for
activities of accomplishing
daily living important
(ADL). activities. Not
all self-care and
hygiene
activities need
to be completed
i the morning.
Likewise, not all
housework
needs to be
completed in
one day.
Assist the Energy reserves
client in may be depleted
developing unless the client
a schedule for respects the
daily activity body’s need for
and increased rest. A
rest. Stress th plan that
e importance balances periods
of frequent of activity with
rest periods. periods of rest
can help the
client complete
desired activities
without adding
levels to fatigue.
Monitor Decreased RBC
hemoglobin, indexes are
hematocrit, associated with
RBC counts, decreased
and oxygen-carrying
reticulocyte capacity of the
counts. blood. It is
critical to
compare serial
laboratory
values to
evaluate
progression or
deterioration in
the client and to
identify changes
before they
become
potentially life-
threatening.
Educate Clients and
energy- caregivers may
conservation need to learn
techniques. skills for
delegating task
to others, setting
priorities, and
clustering care
to use available
energy to
complete
desired
activities.
Organization
and time
management can
help the client
conserve energy
and reduce
fatigue.
Instruct the Recombinant
client about human
medications erythropoietin, a
that may hematological
stimulate growth factor,
RBC increases
production in hemoglobin and
the bone decreases the
marrow. need for RBC
transfusions.
Provide Oxygen
supplemental saturation
oxygen should be kept
therapy, as at 90% or
needed. greater.
Anticipate the Packed RBCs
need for the increase
transfusion of oxygen-carrying
packed RBCs. capacity of the
blood.
Refer the The
client and occupational
family to an therapist can
occupational teach the client
therapist. about using
assistive
devices. The
therapist also
can help the
client and
family evaluate
the need for
additional
energy-
conservation
measures in the
home setting.
REFERENCES:
Martin, P. B. (2021, August 30). 5 Anemia Nursing Care Plans. Nurseslabs. https://nurseslabs.com/anemia-nursing-care-plans/
R. (2019, March 28). Iron Deficiency Anemia Nursing Care Plan & Management. RNpedia. https://www.rnpedia.com/nursing-
notes/maternal-and-child-nursing-notes/iron-deficiency-anemia-nursing-care-plan-management/
You might also like
- Mini VET GuideDocument186 pagesMini VET GuideemitibiNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document4 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan N V DDocument28 pagesNursing Care Plan N V DDr-Sanjay Singhania75% (4)
- Vitamins Chemistry Project Report (ST Josephs HSS Trivandrum, Year 2009-2010)Document25 pagesVitamins Chemistry Project Report (ST Josephs HSS Trivandrum, Year 2009-2010)kidilamvivek88% (26)
- NcpFatigue Related To Decreased Hemoglobin and Diminished Oxygen-Carrying Capacity of The Blood.Document3 pagesNcpFatigue Related To Decreased Hemoglobin and Diminished Oxygen-Carrying Capacity of The Blood.The Right WayNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Priority No. 3Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Priority No. 3Pantaleon PacisNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- Body WeaknessDocument1 pageBody Weaknessnymphaaugustus100% (3)
- NCP Severe HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesNCP Severe HypocalcemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in SwallowingDocument1 pageDifficulty in SwallowingmawelNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDocument12 pagesBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- NCP Template ObDocument7 pagesNCP Template ObMae CeaesarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanMiguelito Galagar GultianoNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocument1 pageOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Classifications and LanguagesDocument12 pagesNursing Classifications and LanguagesGiselle Chloe Baluya ico0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationRheeanne Mae Amilasan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument2 pagesDisturbed Sleep PatternROxanne S. RendonNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJaney Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- NCP Pot Riskforinjury EncephalitisDocument3 pagesNCP Pot Riskforinjury Encephalitisaila angNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina Aubrey0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan - Activity IntoleranceChezka Orton Swift Bolintiam100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- NCP Arra AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP Arra AnemiaShin GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument4 pagesDrug Namecheanne003No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- NCP GoiterDocument1 pageNCP GoiterDavid Calalo67% (3)
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NCP Group 3 Fatigue ..Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan NCP Group 3 Fatigue ..Aerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPmimingdot33No ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument6 pagesNCP AnemiaJudeLax100% (1)
- Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesNursing Responsibilityايام اول الشحيNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanRaphael Reyes Enriquez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- NCP AnemiaDocument3 pagesNCP AnemiaJadeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Long Term: Long TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Long Term: Long TermAriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AnemiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AnemiaMyrshaida Ibrahim0% (1)
- NCP AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP AnemiaAriaNo ratings yet
- Recommendation RenalDocument3 pagesRecommendation RenalJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Recommendation AnemiaDocument3 pagesRecommendation AnemiaJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Week7 BERNALESDocument2 pagesWeek7 BERNALESJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Recommendation BurnDocument3 pagesRecommendation BurnJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Burn Injury: RecommendationDocument3 pagesBurn Injury: RecommendationJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- GeriaDocument2 pagesGeriaJackRolunaBernalesNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Aluminum and The Prevalence of Anemia in Communities in Barcarena Pará, BrazilDocument7 pagesExposure To Aluminum and The Prevalence of Anemia in Communities in Barcarena Pará, BrazilIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Tariq PresentationDocument24 pagesTariq PresentationHasnain AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Nutrition and Nutraceuticals: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesChapter 7. Nutrition and Nutraceuticals: Multiple ChoicericharegbeNo ratings yet
- Transfusion MCQs and SAQsDocument3 pagesTransfusion MCQs and SAQsSaima IramNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia 170119201048Document33 pagesPancytopenia 170119201048Dabogski FranceNo ratings yet
- Anemia - PPT PresentationDocument23 pagesAnemia - PPT PresentationRommel Montero RicioNo ratings yet
- English Course: Instructor'S Contact Info Ahmad Ridho Rojabi, S.PD, M.PDDocument62 pagesEnglish Course: Instructor'S Contact Info Ahmad Ridho Rojabi, S.PD, M.PDeliahapsaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Bone Marrow Aspiration in Hematological DisorderDocument4 pagesInterpretation of Bone Marrow Aspiration in Hematological Disordervanessa wijayaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 305 Sgd'sDocument9 pagesPharmacology 305 Sgd'sanojanNo ratings yet
- Complete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineDocument8 pagesComplete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anaemia Armando HasudunganDocument1 pageIron Deficiency Anaemia Armando HasudunganhiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianDocument54 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianFlavia PolodeanuNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument92 pagesAnemiasangeetachatterjee100% (1)
- RBC PathologyDocument7 pagesRBC PathologyKent CruzNo ratings yet
- Higlighted For FNCPSDocument55 pagesHiglighted For FNCPSCarey Jamille YadanNo ratings yet
- Morning Report Pediatric DepartmentDocument18 pagesMorning Report Pediatric DepartmentMedina MarwanNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With AnemiaDocument37 pagesApproach To The Patient With AnemiaSumeet PratapNo ratings yet
- CompleteBloodCounts NORMAL VALUEDocument4 pagesCompleteBloodCounts NORMAL VALUEWoro Hapsari Wahyuningrum100% (1)
- Lina's THESISDocument40 pagesLina's THESISlina.o.mintNo ratings yet
- To Study The Prevalence of Anaemia in Indoor Patients of Tertiary Care CentreDocument3 pagesTo Study The Prevalence of Anaemia in Indoor Patients of Tertiary Care CentreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Document2 pagesVitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Ghubaya CopNo ratings yet
- Header Halaman Google Penelusuran: Hasil WebDocument5 pagesHeader Halaman Google Penelusuran: Hasil WebmuniraliiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Drug NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Drug NameCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument32 pagesVitaminmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Blood MCQDocument10 pagesBlood MCQTennyson MachiwenyikaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis - UpToDateDocument76 pagesHereditary Spherocytosis - UpToDateHuỳnh Thị Khả DuyNo ratings yet
- Transfusion and Apheresis Science: SciencedirectDocument4 pagesTransfusion and Apheresis Science: SciencedirectMarini TaslimaNo ratings yet