Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2020 06 17 JSA For AC Servicing-Server Room
2020 06 17 JSA For AC Servicing-Server Room
Uploaded by
Darren Oscar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
228 views12 pagesThe document summarizes a job safety analysis for maintenance and service of an AC unit. It identifies 14 steps of the task and potential hazards at each step, such as electric shock, falls, cuts, and muscle strains. Controls are outlined to eliminate or reduce hazards, including use of proper PPE like gloves, safety glasses, coveralls; safe manual handling; first aid access; and taking regular breaks. Tools needed are listed as are required personal protective equipment to complete the task safely.
Original Description:
Original Title
2020 06 17 JSA for AC Servicing-Server Room
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes a job safety analysis for maintenance and service of an AC unit. It identifies 14 steps of the task and potential hazards at each step, such as electric shock, falls, cuts, and muscle strains. Controls are outlined to eliminate or reduce hazards, including use of proper PPE like gloves, safety glasses, coveralls; safe manual handling; first aid access; and taking regular breaks. Tools needed are listed as are required personal protective equipment to complete the task safely.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
228 views12 pages2020 06 17 JSA For AC Servicing-Server Room
2020 06 17 JSA For AC Servicing-Server Room
Uploaded by
Darren OscarThe document summarizes a job safety analysis for maintenance and service of an AC unit. It identifies 14 steps of the task and potential hazards at each step, such as electric shock, falls, cuts, and muscle strains. Controls are outlined to eliminate or reduce hazards, including use of proper PPE like gloves, safety glasses, coveralls; safe manual handling; first aid access; and taking regular breaks. Tools needed are listed as are required personal protective equipment to complete the task safely.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
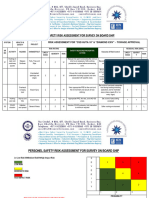
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS Reference No: UNOC-FAC-HAV-OO3
Date: 17/06/2020
Task (Describe task): Team (Enter names of team members): Reviewed by (Reviewing Manager):
Maintenance /Service of AC Unit in the Paul Mbaga, David Nsibuka and Charles
Main Server room/UPS Room on 2nd Floor Byakagaba
of the Main Office Building- Plot 15 Yusuf
Lule Road-Kampala
Simultaneous Operations: (List any operation in the area that is happening at the same time and can impact the safety of task):
Normal Office Operations
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
Predictable accidents (Which have happened or could have happened):
Electric shock, Electric burn, pinch points, muscle strains, cuts and falling from height.
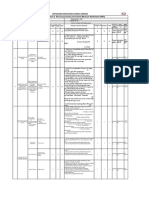
STEPS (Break task into steps in order of HAZARDS (Identify hazards for each CONTROLS (List actions to eliminate or
sequence) step) control all identified hazards)
STANDARD CONTROLS: Full PPE, proper
manual handling, Access to First Aid, enough
drinking water, have Transport available on site in
case of emergency, taking regular breaks,.
1. Tool box Talk Miscommunication. Ensure all personnel doing the task
Inadequate information. understood it properly by asking them
Language barrier. questions regarding the task.
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
Carry out enough research on the task
before executing it.
Use of common language or
interpreters for those who do not
understand the language being used.
Demonstrate the task if necessary.
2. Inspection of the work tools in order to Cuts and bruises from sharp objects. Wear your full PPE when checking
isolate and report defective tool. Failure to notice defects. tools e.g. safety glasses, gloves and
Choice of wrong tools for the task. coveralls
Use competent inspectors to minimize
chances of not noticing the defects.
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
Choose tools appropriate for the task at
hand.
3. Clear working space by removing Hand injuries Wear gloves
everything that is not work related or Slip, trip and fall Take extra care
that may obstruct work smooth
progress such the computers
4. Turn off rotary isolator to A.Cs, lock Wrong isolator identification. Done by competent personnel.
out and tag out. Measure to ensure Electric shock. Measure on a known circuit prior to
that the circuit is dead. Faulty multimeter use
Measure the circuit to be worked on
to confirm that its dead
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
5. Condon off working area to prevent Slip and fall. Take extra care while moving
people from in/ out Eliminate all the trip hazards from
working environment
6. Remove all electrical panel covers. Falls from platform or height Put working platform in right
Check all internal wirings for correct Exposure to sharp objects positions
routing and look out any signs of Flying particles into eyes Use buddy system
overheating. By using the step Use safety gloves
platform or ladder Use safety glasses
Ensure there is second person to
hold the ladder
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
7. Opening of the indoor and outdoor unit Fall from height and Put working platform in right
to remove the air filters wash it in the Hand injuries and cuts positions
bucket and pressure washer, after Equipment damage. Use safety gloves
replace. Sharp object contact Use buddy system
Use safety glasses
Ensure there is second person to
hold the ladder
8. Visibly check the evaporator and out Hand injuries. Wearing gloves.
let vents wash it with pressure where . Use safety glasses.
necessary.
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
9. Check the condition of the fan blades. Hand injuries. Wearing gloves
Clean were necessary. Take extra care
Use safety glasses
10. Blowing out of lake flies by use of a Electric shock Ensure cable/connection of the
high pressure washer. From outside Flying objects into eyes equipment is not wet in water-
the container Inhalation of dust place it at a safe distance.
Pressure hazard Use dust musk
Use safety glasses
Do not aim the nozzle at someone
during the operation.
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
11. Re-assemble of indoor and outdoor Finger injuries. Wearing gloves.
unit panels. Falling off height Use helper to hold the ladder
12. Remove isolation tags, test run unit Electric shock. Wearing gloves.
and monitor its operating condition Work to be done by a competent
person
13. Check for the gas pressure level using Cold burns Use gloves
a manifold gauge Use safety glasses
Attached is the MSDS for Freon
r22 gas
14. Doing the necessary housekeeping Slips, falls, pinch points. Safety shoes must be ensured, use
of gloves
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
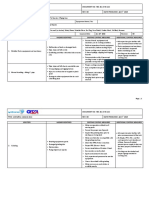
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT TO BE USED:
Assorted hand tools, High pressure washer, extension cable, bucket, rags, platform, spanners, gas r22, multimeter and ladders
REQUIRED PPE:
Long sleeved coveralls, safety goggles, Gloves, Safety Shoes, hard hat and dust musk
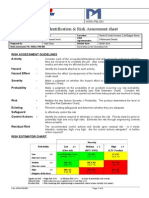
What is Job Safety Analysis (JSA)? 01 Electricity 08 Depths 17 Surfaces
JSA is the process which analyzes the tasks to identify the associated hazards and define control 02 Chemicals 09 Confined Spaces 18 Tools / Equipment
measures so that the accidents can be prevented. 03 Rotating Equipment 10 Vibration 19 Human Factors
04 Vehicles 11 Moving Objects 20 Insect/Animal Bites
05 Muscular Stress 12 Weather 21 Pressure
Why Use a JSA? 06 Mental Stress 13 Hot / Cold Objects 22 Lifting Machinery
To identify hazards and their controls 07 Heights 14 Noise 23 Illumination levels
To prevent potential accidents 15 Radiation 24 Other (Specify)
To identify most efficient and safest way of performing a task 16 Hydrocarbon/gas release
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
To demonstrate duty of care for workforce and 3rd parties
Format Step-3 Break Down the Job into Steps in Order of Sequence
JSA sheet should have at least the following three columns. More columns can be added as Break down the job to be done into sequential steps
required, but make sure it does not get complicated for the users: Use definite action words for each step e.g. Open, Stop, Check, Remove, Fix, Close etc.
1. Steps of the task Make sure the sequence is maintained
2. Potential hazards Make sure the person directly related with the job is involved while breaking the steps
3. Control measures or procedures Make observation of the job while it is being done to catch all the steps
Producing JSA Step-4 Identify Potential Hazards Associated with Each Step
Involves five basic steps In conjunction with the “Identified Hazards List” of Step 2, use the following to describe the hazard:
1. Select the job to be done
2. Identify and document all associated hazards
3. Break down the job into steps in order of sequence
4. Identify potential hazards associated with each step MARK THE HAZARDS IN THE NEXT TABLE:
5. Develop control measures for hazards so that the job can be done safely
Step-1 Selecting The Job to be Done 1. Striking against 12. Overexertion/Fatigue by lifting, pulling carrying,
Jobs to be analyzed are: 2. Struck by pushing etc.
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
1. Jobs that have a history of incident 3. Caught in, on, under, between, against 13. Repetitive motion
2. Jobs that should always be done in the same way 4. Falling from height 14. Awkward position/Static Posture
3. Jobs in which the sequence of doing the task is important for risk management 5. Exposure to high noise 15. Exposure to high speed
4. New jobs or jobs for which the procedure is changed
6. Exposure to high or low temperature 16. Bitten by
7. Exposure to chemicals 17. Exposure to infectious agent
8. Contacting electric current 18. Behavioral issues e.g. taking shortcuts, improper use
9. Slip, trip and fall from height of equipment etc.
10. Slip trip and fall at same level 19. Improper tools for the job
11. Uncontrolled containment (Spill) 20. Simultaneous Operations
21. Others (Specify)
Step-2 Identify Potential Hazards for the job Step-5 Device Controls and Safe Working Procedures
Definition: A hazard is something which by itself or by interacting with other When determining risk reduction measures, use a Hierarchy of Controls, in descending order of preference:
variables can result in: 1. Elimination / Substitution and/or Process Modification
Physical injury or death 2. Engineering Controls
3. Isolation
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
Damage to assets or the environment 4. Administrative Controls
Production loss or increased liability 5. PPE
Prior to identifying potential incidents & hazardous conditions, identify the Final Check
hazards associated with the works as per the below mentioned hazards list : 1. Make sure the Hazard list is marked
2. Make sure the Supervisors has signed the sheet
MARK THE IDENTIFIED HAZARDS IN NEXT TABLE: 3. Make sure the person filling the sheet is trained for the job
UNOC-CPL-SF-190012-Rev: 00, March 2019
You might also like
- The 9 Centers Human DesignDocument14 pagesThe 9 Centers Human Designmonicabors100% (11)
- Fiber Optic Cable Laying JHADocument9 pagesFiber Optic Cable Laying JHAmortadha husainNo ratings yet
- Lumber Case ModelDocument6 pagesLumber Case ModeltheonlypaulNo ratings yet
- Wifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Document10 pagesWifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Sathwik YadalamNo ratings yet
- JSA - Suface Preparationand Brush PaintingDocument5 pagesJSA - Suface Preparationand Brush PaintingAzad pravesh khanNo ratings yet
- LG 55ea9800Document102 pagesLG 55ea9800CadwillNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Axial Piston Eaton Vickers PVB Pump: - Basic CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesHydraulic Axial Piston Eaton Vickers PVB Pump: - Basic Characteristicsjose alberto olvera gomezNo ratings yet
- Case Study Julies BakeshopDocument3 pagesCase Study Julies BakeshopKristel Anne AquinoNo ratings yet
- Aj Infratech: Job Hazard AnalysisDocument5 pagesAj Infratech: Job Hazard AnalysisDwitikrushna RoutNo ratings yet
- Safe Work Method Statement: One World Place Manila, 32nd ST, Taguig, Metro ManilaDocument6 pagesSafe Work Method Statement: One World Place Manila, 32nd ST, Taguig, Metro Manilanani ferrerNo ratings yet
- JHA - Excavation, Pile Hacking and Construction of Lean ConcreteDocument13 pagesJHA - Excavation, Pile Hacking and Construction of Lean ConcreteJansen SungaNo ratings yet
- Jsa Fan Coil Unites MaintenanceDocument5 pagesJsa Fan Coil Unites MaintenanceASLAM MULANINo ratings yet
- JHA Lifting-Moving Heavy ObjectsDocument5 pagesJHA Lifting-Moving Heavy ObjectsOgunwa EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- PTW JHA Prayer Garment Hanging Rack InstallationDocument2 pagesPTW JHA Prayer Garment Hanging Rack InstallationPHH9834No ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Painting DateDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Painting DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Chemical Ware HouseDocument4 pagesJsa For Chemical Ware Housesalauddin0mohammedNo ratings yet
- JSA Gate Installation - 1 ProjectDocument4 pagesJSA Gate Installation - 1 ProjectMuhammad Umar GondalNo ratings yet
- PCC & ConcDocument4 pagesPCC & Concprasanna okNo ratings yet
- SWMS - HVAC ShiftingDocument6 pagesSWMS - HVAC ShiftingParas100% (1)
- ISLA JHA Removal of BarricadeDocument3 pagesISLA JHA Removal of Barricadeaasafety06No ratings yet
- Jsa 07 (G) # Steel Structure Erection & Miscellaneous Steel-Ptj - S-007Document30 pagesJsa 07 (G) # Steel Structure Erection & Miscellaneous Steel-Ptj - S-007elmsm14No ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis - Granite Surface PlateDocument2 pagesJob Hazard Analysis - Granite Surface PlateRaziellia Nor SaafriNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Roof Plumbing - Working On Roofs Construction & RepairDocument14 pagesJob Safety Analysis Roof Plumbing - Working On Roofs Construction & RepairLokesh AravindanNo ratings yet
- Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesJob Safety AnalysiscitraNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: Required References Jsa ReviewDocument5 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Required References Jsa ReviewMoaatazz Nouisri100% (1)
- Panipat Refinery & Petrochemical Complex Job Safety AnalysisDocument6 pagesPanipat Refinery & Petrochemical Complex Job Safety AnalysisSaiyad RiyazaliNo ratings yet
- 23 JSA For Block WorkDocument2 pages23 JSA For Block WorkWakil AhmadNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) : Description Hazard ControlDocument3 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) : Description Hazard ControlRidha BennasrNo ratings yet
- Hira Gi SheetDocument1 pageHira Gi SheetChandresh SinghNo ratings yet
- PM 01 Hira For Excavation of Boiler FoundationDocument3 pagesPM 01 Hira For Excavation of Boiler FoundationSyed Shariq Hassan100% (1)
- 0 JsaDocument54 pages0 JsaRavi AmarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis - Cone ErectionDocument7 pagesJob Safety Analysis - Cone ErectionMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- JSA - Electrical IsolationDocument1 pageJSA - Electrical IsolationRaju KhalifaNo ratings yet
- JSA For EXCAVATION AND BACKFILLING ARAMCO PROJECTDocument6 pagesJSA For EXCAVATION AND BACKFILLING ARAMCO PROJECTshaibaz chafekar100% (1)
- Risk Assessment:: Corresponding Permit To Work NoDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment:: Corresponding Permit To Work NoNaseemandson TeamNo ratings yet
- JSA-Replacement of GD, FD & MCP - Rev.00Document7 pagesJSA-Replacement of GD, FD & MCP - Rev.00Muhammad Umar GondalNo ratings yet
- 31.HIRA - Boom Placer OperationDocument3 pages31.HIRA - Boom Placer OperationMMRDACA07 SAFETYNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesRisk AssessmentJo PaNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis FOR Precast Concrete WorksDocument3 pagesJob Safety Analysis FOR Precast Concrete Worksprabu lingamNo ratings yet
- Height Pass FormatDocument1 pageHeight Pass Formatamit kumarNo ratings yet
- JSA For Work at HeightDocument3 pagesJSA For Work at Heightbagas prakoso100% (1)
- CamScanner 03-22-2023 07.44Document2 pagesCamScanner 03-22-2023 07.44Umar AliNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan FormatDocument2 pagesLifting Plan FormatmdmuzafferazamNo ratings yet
- Rock Breaker Self ChecklistDocument1 pageRock Breaker Self ChecklistNair R RakeshNo ratings yet
- JSA For HILTIDocument3 pagesJSA For HILTIMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- Jsa CompressorDocument9 pagesJsa CompressorRavi thokalNo ratings yet
- Jsa Bitumen Heating, Lying at DahejDocument6 pagesJsa Bitumen Heating, Lying at DahejJayavant LoharNo ratings yet
- JHA For Work PermitDocument1 pageJHA For Work PermitShahid RazaNo ratings yet
- JSA For Bobcat OperationDocument2 pagesJSA For Bobcat Operationwahyu nugrohoNo ratings yet
- Hira RCC Cement MillDocument2 pagesHira RCC Cement MillRaju100% (1)
- JSA Formet New Hot WorkDocument6 pagesJSA Formet New Hot Worksakthi venkat100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis - Tbl-Jsa: STEP 4: Hazard Risk AssessmentDocument6 pagesJob Safety Analysis - Tbl-Jsa: STEP 4: Hazard Risk AssessmentMoaatazz Nouisri100% (1)
- JSA For Scaffolding Erection Removal Around AT-911Document1 pageJSA For Scaffolding Erection Removal Around AT-911Equipment Materials100% (1)
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocument4 pagesJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDsoubhagyaNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - CONCRETE WORKS - DateDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - CONCRETE WORKS - Datenabeel100% (1)
- JSA - CivilDocument5 pagesJSA - CivilRajuNo ratings yet
- JSA For Removal of Broken Bolts and Installation of Switch Pannel On Compressor at Process AraeDocument4 pagesJSA For Removal of Broken Bolts and Installation of Switch Pannel On Compressor at Process AraeMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- JSA of Materila Handling ApproviedDocument2 pagesJSA of Materila Handling Approviedsakthi venkatNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis - Overhead Power LinesDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis - Overhead Power Linesrenee100% (2)
- HIRA No. 05 Erecation WorkDocument4 pagesHIRA No. 05 Erecation WorkAttaullah AnsariNo ratings yet
- 142 Jsa Modify To 2 Inch MPW-2 To Reactor 2 Piping LineDocument6 pages142 Jsa Modify To 2 Inch MPW-2 To Reactor 2 Piping LineMohd KhaidirNo ratings yet
- Jsa ConcretingDocument4 pagesJsa ConcretingRavi thokalNo ratings yet
- Environmental, Health and Safety Risks AnalysisDocument2 pagesEnvironmental, Health and Safety Risks AnalysisKrishna Patil100% (1)
- Jsa Ground Grid MocksvilleDocument2 pagesJsa Ground Grid MocksvilleChristopher NewbyNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Hazard Assessment PDF Master HireDocument6 pagesDiesel Generator Hazard Assessment PDF Master HireMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- 2020 06 17 JSA For Installation of The AC Unit in The Server RoomDocument11 pages2020 06 17 JSA For Installation of The AC Unit in The Server RoomDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- Arch WeldingDocument16 pagesArch WeldingDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- Floodlight Switch RelocationDocument2 pagesFloodlight Switch RelocationDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- JSA Form - Installation of ATS atDocument4 pagesJSA Form - Installation of ATS atDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- Cold Room ServiceDocument2 pagesCold Room ServiceDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- 2020 06 17 JSA For Installation of The AC Unit in The Server RoomDocument11 pages2020 06 17 JSA For Installation of The AC Unit in The Server RoomDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- 250KVA Gen No1 Mantrac ServiceDocument3 pages250KVA Gen No1 Mantrac ServiceDarren OscarNo ratings yet
- S100X220YAJ Panduit Datasheet 5314981Document2 pagesS100X220YAJ Panduit Datasheet 5314981Ilham MaurizaNo ratings yet
- Benzene - It'S Characteristics and Safety in Handling, Storing & TransportationDocument6 pagesBenzene - It'S Characteristics and Safety in Handling, Storing & TransportationEhab SaadNo ratings yet
- An International Cohort Study of Cancer in Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument10 pagesAn International Cohort Study of Cancer in Systemic Lupus ErythematosusCristina TudorNo ratings yet
- UO Mixing Liquid PhaseDocument2 pagesUO Mixing Liquid PhaseKumara Haekal Hafidz AmrullahNo ratings yet
- IdealStandard 120m-Frame R0094Document2 pagesIdealStandard 120m-Frame R0094nasser mhannaNo ratings yet
- b4 EngDocument2 pagesb4 EngAdrian LopezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 2021-2022Document19 pagesChemistry Project 2021-2022Rudra SathwaraNo ratings yet
- TPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) : Immunoassay Method 10050Document10 pagesTPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) : Immunoassay Method 10050Cindy Valenzuela RuedaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM Physical Science 1 Module4Document21 pagesGrade 12 LM Physical Science 1 Module4ladyheart ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Early Alt-RAMEC and Facial Mask Protocol in Class III MalocclusionDocument9 pagesEarly Alt-RAMEC and Facial Mask Protocol in Class III MalocclusionNievecillaNeiraNo ratings yet
- OSH SeminarDocument2 pagesOSH SeminarSahar Ulu JeruasNo ratings yet
- Dec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech ReviewDocument58 pagesDec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech Reviewadyjoy antonioNo ratings yet
- Iec Inverse Protection CurvesDocument1 pageIec Inverse Protection CurvesEng-Ahmad Abo-AledousNo ratings yet
- STOC03 (Emissions)Document20 pagesSTOC03 (Emissions)tungluongNo ratings yet
- Group3 Dilemmac pr6031Document8 pagesGroup3 Dilemmac pr6031api-576539858No ratings yet
- 2442 4348 2 PBDocument8 pages2442 4348 2 PBdev iNo ratings yet
- 04 - Protection GeneralDocument52 pages04 - Protection GeneralRK KNo ratings yet
- Sago Pudding - Recipes - Poh's KitchenDocument2 pagesSago Pudding - Recipes - Poh's KitchenXuxu TooNo ratings yet
- Bicycle ProjectDocument4 pagesBicycle Projectgaming channelNo ratings yet
- Thermolator Heatrac User GuideDocument98 pagesThermolator Heatrac User GuideValeria SarahiNo ratings yet
- Fantastic Four Drug For Heart FailureDocument47 pagesFantastic Four Drug For Heart FailurePutro Panji Asmoro BangunNo ratings yet
- Soil Acidity and LimingDocument12 pagesSoil Acidity and LimingEloi Carlos GoveNo ratings yet
- Corn Growth StagesDocument33 pagesCorn Growth StagesIvan JovanovićNo ratings yet
- The Development of A Heat Wave Vulnerability Index For London-2013Document10 pagesThe Development of A Heat Wave Vulnerability Index For London-2013gilberto777No ratings yet