Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The Membrane
Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The Membrane
Uploaded by
Ирина КривошеяOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The Membrane
Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The Membrane
Uploaded by
Ирина КривошеяCopyright:
Available Formats
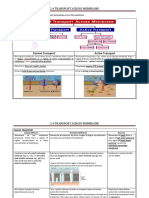
Membrane transport
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J5pWH1r3pgU
I. Pre-viewing tasks
Below you will find a list of words and collocations mentioned in the video.
In your opinion what are the processes named with the terms? What the video is
going to be about? Write or record your answers.
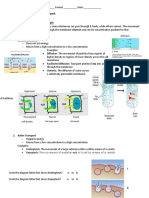
Cell, cell membrane, to transport, substances, structure of the membrane.
2. Watch the film and make sure that you were right.
II. While-watching- the-film tasks
1. Match the terms and phrases with their definitions.
Diffusion the movement of molecules
across a cell membrane from a
region of lower concentration to a
region of higher concentration—
against the concentration gradient.
The process requires cellular energy
to achieve this movement.
phospholipid bilayer a process by which molecules of
a solvent tend to pass through a
semipermeable membrane from a less
concentrated solution into a more
concentrated one.
interstitial fluid (of a material or membrane)
allowing liquids or gases to pass
through it
Channel mediated diffusion is the movement of a substance
from where it has a high
concentration to where it has a low
concentration, or the tendency of a
substance to spread out evenly over a
given space
active transport the substance that dissolves in a
solvent to produce a homogeneous
mixture.
Permeable to something the body fluid between blood
vessels and cells, containing nutrients
from capillaries by diffusion and
holding waste products discharged
out by cells due to metabolism.
solute diffusion that occurs via channel
proteins that allow ions and small
water-soluble molecules to pass in
and out of the cell.
osmosis another term for the cell
membrane.
2. Choose the correct ending a, b or c.
1. Simple diffusion occurs …
a) with solutes that are small and non-polar.
b) with solutes that are not small and polar.
c) with water.
2. If there is a higher concentration of oxygen O2 molecule outside of a
cell, …
a) they can move down the concentration gradient across the membrane
with assistance and from the cell until the concentration gradient is almost non-
existent.
b) they can move with no regard to the concentration gradient.
c) they can move down the concentration gradient across the membrane
without assistance and into the cell as long as the concentration gradient exists.
3. Facilitated diffusion.…
a) requires no assistance from the membrane to happen.
b) applies to solutes that are small and either charged or polar.
c) happens only in some particular type of cells.
4. The example of carrier mediated diffusion is …
a) when the vesicle membrane now becomes part of the plasma membrane..
b) when a sodium positive ion can pass through a sodium positive leak
channel continuously and a gated sodium positive channel will only open due to
a stimulus to allow the ion to pass through into the cell.
c) the process in which glucose binds to a carrier protein, which changes
shape and moves the glucose molecule to the other side of the membrane.
5. In … a large particle is engulfed by the newly formed vesicle and this
vesicle fuses with a lysosome, which is a membranous vesicle that contains
digestive enzymes that break down the particle into its component molecules.
a) phagocytosis
b) pinocytosis
c) receptor mediated endocytosis
6. … is the transport of large substances across the plasma membrane by a
vesicle, which is a membrane bound sac filled with materials.
a) Active transport
b) Vesicular transport
c) Osmosis.
7. In primary active transport …
a) a substance is moved against its concentration gradient by using energy
provided by the movement of a second substance down its concentration
gradient.
b) cellular protein pumps, called ion pumps, move ions across the
membrane against their concentration gradient.
c) materials are secreted from the cell to the interstitial fluid outside of the
cell.
8. … is also referred to as cell drinking.
a) phagocytosis
b) pinocytosis
c) receptor mediated endocytosis
9. Receptor mediated … involves using receptors on the outside of the
plasma membrane. These receptors bind with molecules in the interstitial fluid
and membrane folds enclosing the receptors and the bound molecules, to form a
vesicle for transport within the cell…
a) pinocytosis
b) osmosis.
c) endocytosis.
10. In … materials are secreted from the cell to the interstitial fluid outside
of the cell.
a) exocytosis.
b) endocytosis.
c) facilitated diffusion.
III. Post-viewing tasks
1. Below you will find a partially completed mind map that can be used
while making a report on the membrane transport.
2. Extend this mind map. Write down key words and expressions for each
heading.
3. Make up sentences using these words and expressions and combine then in
one report. If necessary, add some more information.
You might also like
- Fact or Fake? Cards: The Neurons Are in Charge of The Involuntary Actions That Occur in Our Body (I.e., Heartbeat)Document1 pageFact or Fake? Cards: The Neurons Are in Charge of The Involuntary Actions That Occur in Our Body (I.e., Heartbeat)Ирина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document18 pagesLesson 5Mariz GenandaNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneDocument5 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneVenice LoNo ratings yet
- Transport MembraneDocument2 pagesTransport Membranesna240839No ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Group 4 G12 STEM Sept.30 General Biology Transport Mechanism in CellDocument38 pagesGroup 4 G12 STEM Sept.30 General Biology Transport Mechanism in CellAnime AddictNo ratings yet
- REVIEW TEST Sa Bio Q2Document2 pagesREVIEW TEST Sa Bio Q2zabala.vanessa.sixdaffodilNo ratings yet
- Directions: Put The Correct Term From The Word Bank Next To The Corresponding DefinitionDocument1 pageDirections: Put The Correct Term From The Word Bank Next To The Corresponding DefinitionSamantha MillarNo ratings yet
- Review Tests Subs - Mapeh, Biotech, Math Quarter 2Document4 pagesReview Tests Subs - Mapeh, Biotech, Math Quarter 2zabala.vanessa.sixdaffodilNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- (L9) Transport Across MembranesDocument22 pages(L9) Transport Across MembranesJhon TorresNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active TransportDocument3 pagesPassive and Active TransportEdelweiss AnwarNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDocument7 pages2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cell HandoutsDocument8 pagesPRINTED Cell HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document48 pagesCell 1Mihai ChirniciniiNo ratings yet
- Is Reviewer 2B Cell PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIs Reviewer 2B Cell Physiologyajuj jerNo ratings yet
- Year 11 BiologyDocument27 pagesYear 11 Biologyvy9423400No ratings yet
- Daniel Quiroz WORKSHOP CELL TRANSPORTDocument5 pagesDaniel Quiroz WORKSHOP CELL TRANSPORTDaniel QuirozNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANDocument15 pagesCell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANchfalgueraNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Revision BookletDocument17 pagesYear 9 Revision BookletmrsfarahnaazNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport ConceptDocument7 pagesCellular Transport ConceptRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Bio HomeworkDocument4 pagesBio HomeworkKamel BsaisoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- 2 5 Transport MechanismDocument25 pages2 5 Transport Mechanismıamnıkolaı 4100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- GenBio - 1st QuarterDocument13 pagesGenBio - 1st QuarterCc TvNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism: Lesson 2Document11 pagesTransport Mechanism: Lesson 2JGHUNGERNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document15 pagesGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisNo ratings yet
- U2 - Study GuideDocument6 pagesU2 - Study GuideJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument18 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneSivam DhanabalNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NoteDocument10 pagesBiology Short NotePatrix ParkerNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 8 Cell Transport Mechanisms Activity 1: Concept MappingDocument8 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 8 Cell Transport Mechanisms Activity 1: Concept MappingMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory 2Document18 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory 2ao868598No ratings yet
- Handout 4 Cell TransportDocument4 pagesHandout 4 Cell TransportCrissan Jejomar AbanesNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesCellular Structure and Functionsalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Membrane: Completed? Date Links Syllabus Point UnitDocument7 pagesTransportation in Membrane: Completed? Date Links Syllabus Point UnitJada DavisNo ratings yet
- From The Soil by The Root CellsDocument13 pagesFrom The Soil by The Root CellsChristina RañaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportshammmssNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- BodyDocument1 pageBodySaba.u AlmullaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsEugene VinaraoNo ratings yet
- Prelim Session 3 Cellular Transport MembraneDocument33 pagesPrelim Session 3 Cellular Transport MembraneAnxi XiNo ratings yet
- Cells ReviewerDocument3 pagesCells ReviewerIvy LumapacNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism SendDocument14 pagesTransport Mechanism Sendchloe rederrickNo ratings yet
- Concept 9Document12 pagesConcept 9Faustinalyn ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Biology - All About Transportation of Cells, Cellular Respiration + PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesBiology - All About Transportation of Cells, Cellular Respiration + PhotosynthesisAdelaide Fleona Marie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity3 The CellDocument5 pagesLec Activity3 The CellAlyssa GerioNo ratings yet
- Duma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Document3 pagesDuma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Cherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport NotesDocument39 pagesCellular Transport NotesShen ZuNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Dan TransportDocument67 pagesMembran Sel Dan TransportAlbet SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Transport Across CellDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Transport Across Celllidsay.fgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.4 Movement of SubstancesDocument31 pagesChapter 2.4 Movement of SubstancesRACHEL SINDHUNo ratings yet
- L3The Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument45 pagesL3The Cell Structure and Functions PDFVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Cellular Level Cell MembraneDocument4 pagesCellular Level Cell MembranePharmaNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membranes Sheet AnswersDocument3 pagesPlasma Membranes Sheet Answerskim szymanskiNo ratings yet
- OsteogenesisDocument3 pagesOsteogenesisИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Body/human-Body/brain/: The Human Brain Lead In. Pre-Viewing TasksDocument3 pagesBody/human-Body/brain/: The Human Brain Lead In. Pre-Viewing TasksИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Brain DisordersDocument1 pageBrain DisordersИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Here Are Some Key-Terms To Support Your Guess:: How The Heart Works I. Lead In. Pre-Viewing TasksDocument2 pagesHere Are Some Key-Terms To Support Your Guess:: How The Heart Works I. Lead In. Pre-Viewing TasksИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- The Fittest Theory That Explains Our Evolution Is The Selection ProcessDocument3 pagesThe Fittest Theory That Explains Our Evolution Is The Selection ProcessИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Forensic EntomologyDocument9 pagesForensic EntomologyИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- cell and its structure (разработка)Document8 pagescell and its structure (разработка)Ирина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- The Brain. The Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesThe Brain. The Nervous SystemИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imaging I. Pre-Viewing TasksDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Imaging I. Pre-Viewing TasksИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Turekian, Wedepohl - 1961 - Distribution of The Elements in Some Major Units of The Earth's CrustDocument18 pagesTurekian, Wedepohl - 1961 - Distribution of The Elements in Some Major Units of The Earth's CrustMariana VezzoneNo ratings yet
- Past Year CHM 678 (Chapt 2)Document16 pagesPast Year CHM 678 (Chapt 2)Nurul Aiman HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Arenes / Benzene Chemistry: Question PaperDocument9 pagesArenes / Benzene Chemistry: Question Papervintu pvNo ratings yet
- Sterner Lighting Bollards and Pathway Brochure 1982Document14 pagesSterner Lighting Bollards and Pathway Brochure 1982Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- CHE 1000 Tutorial Sheet 12 - Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesCHE 1000 Tutorial Sheet 12 - Organic ChemistryStanley SitaliNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document24 pagesModule 4MARIE ANN DIAMANo ratings yet
- All Three Systems Nano EnergyDocument15 pagesAll Three Systems Nano EnergyNanaji KNo ratings yet
- Viton FtirDocument53 pagesViton FtirTanzil ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Chem Exercise 20 PDFDocument2 pagesChem Exercise 20 PDFUniversityJCNo ratings yet
- Strength Properties of Slag and Fly Ash Blends Activated With Sodium Metasilicate, Sodium Hydroxide and Silica FumeDocument6 pagesStrength Properties of Slag and Fly Ash Blends Activated With Sodium Metasilicate, Sodium Hydroxide and Silica FumeJason BorejszoNo ratings yet
- Reactions of CarbocationsDocument33 pagesReactions of CarbocationsreddygrNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure: The Peptide BondDocument13 pagesProtein Structure: The Peptide BondanaNo ratings yet
- 9 Introduction To Metabolism and Bioenergetics Reading ModuleDocument17 pages9 Introduction To Metabolism and Bioenergetics Reading ModuleSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- PEH Periodic Table (Principles) - Get The Table Organized in Time! Lab Manual (English)Document6 pagesPEH Periodic Table (Principles) - Get The Table Organized in Time! Lab Manual (English)Monette CabugayanNo ratings yet
- ATPS Aqueous Two Phase System As The Answer To Protein Separation For Protein Processing Food IndustryDocument15 pagesATPS Aqueous Two Phase System As The Answer To Protein Separation For Protein Processing Food IndustryBruno PereiraNo ratings yet
- Free RadicalsDocument35 pagesFree RadicalsSF ShagorNo ratings yet
- Orientation ReportDocument43 pagesOrientation ReportRyan eqbalNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials: Asst - Prof. Dr. Ayşe KALEMTAŞDocument32 pagesComposite Materials: Asst - Prof. Dr. Ayşe KALEMTAŞŞebnem Gül İlarslanNo ratings yet
- RutheniumDocument16 pagesRutheniumjosevitorromualdoNo ratings yet
- Module (Amino Acids and Proteins)Document18 pagesModule (Amino Acids and Proteins)Edgie JunelaNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project in Physics LatestDocument18 pagesInvestigatory Project in Physics Latestapi-279641493No ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigatiionDocument4 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigatiionRico T. MusongNo ratings yet
- 4MBBS101 Lecture 5 Properties of Enzymes - Enzyme KineticsDocument51 pages4MBBS101 Lecture 5 Properties of Enzymes - Enzyme KineticsArm UdomratNo ratings yet
- NanozymesDocument10 pagesNanozymesdd donNo ratings yet
- Anion AnalysisDocument3 pagesAnion AnalysisPatrick Juacalla100% (2)
- AP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDavina MarstonNo ratings yet
- Hakim Khan CaseDocument7 pagesHakim Khan CaseSamerNo ratings yet
- 2 Preparation of Chemical ReagentsDocument9 pages2 Preparation of Chemical ReagentsMagnus JordanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Molecular Luminescence SpectrometryDocument30 pagesChapter 15 Molecular Luminescence SpectrometrySaurion21No ratings yet
- 2022 - 3NA - Separation Technique - NotesDocument19 pages2022 - 3NA - Separation Technique - NotesNitin Yadav Praduman (Qss)No ratings yet