Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Minhh KhanggCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Economic Growth 3rd Edition Weil Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesEconomic Growth 3rd Edition Weil Solutions Manualashleyfuentesdvm13051997noj100% (26)
- Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly MonopolyDocument55 pagesPerfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly MonopolyEricko Marvin KweknotoNo ratings yet
- Industry: EquilibriumDocument13 pagesIndustry: EquilibriumKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledBhebz Erin Mae0% (1)
- CH - 5 Forms of MarketDocument1 pageCH - 5 Forms of MarketkalynNo ratings yet
- 4 Market Structures ModifiedDocument4 pages4 Market Structures ModifiedDanaNo ratings yet
- Presented by Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDocument26 pagesPresented by Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDeepak NandaNo ratings yet
- Fase2-Natalia Cano - Estudio Sobre Las GeneralidadesDocument1 pageFase2-Natalia Cano - Estudio Sobre Las GeneralidadesIsabella SotoNo ratings yet
- MarketDocument22 pagesMarketAaditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit - VDocument27 pagesUnit - VDharshanth .SNo ratings yet
- Forms of MarketDocument17 pagesForms of Marketdil preetNo ratings yet
- Project EconomicsDocument12 pagesProject EconomicsBoomNo ratings yet
- Market TypesDocument1 pageMarket TypesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- MARKETDocument21 pagesMARKETJane BañaresNo ratings yet
- Types of OligopolyDocument3 pagesTypes of OligopolyIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Monopoly1Document37 pagesLecture 11 Monopoly1Daksh AnujNo ratings yet
- Quinalayo, Michael Kriz L. AB Political Science IIIB Market Structure Characteristics ExamplesDocument2 pagesQuinalayo, Michael Kriz L. AB Political Science IIIB Market Structure Characteristics ExamplesmichaelNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Unit 5Document19 pagesManagerial Economics - Unit 5sruthy santhoshNo ratings yet
- Question Tutorial 2Document7 pagesQuestion Tutorial 2Nabila HassanNo ratings yet
- Competition: Monopolistic Fairly LargeDocument4 pagesCompetition: Monopolistic Fairly LargeNagaraj BeeduNo ratings yet
- #3 Lesson 2.4-2.6Document3 pages#3 Lesson 2.4-2.6Chelsea A. SADSADNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7 9Document17 pagesChapters 7 9directo549No ratings yet
- Imperfect Competition and Output Decision: Presented By: Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDocument23 pagesImperfect Competition and Output Decision: Presented By: Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDeepak NandaNo ratings yet
- Eco102-Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets PDFDocument3 pagesEco102-Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets PDFCornelia MarquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.1 and 7.2 Group 1 ManEconDocument3 pagesChapter 7.1 and 7.2 Group 1 ManEconfrancheskaarcederaNo ratings yet
- Yogesh - A 19Bcc0028Document4 pagesYogesh - A 19Bcc0028Ash KetchumNo ratings yet
- Monopoly and MonopsonyDocument7 pagesMonopoly and MonopsonyCoreen AndradeNo ratings yet
- S19&20 - Perfect MarketDocument5 pagesS19&20 - Perfect MarketRohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 EconomicsDocument22 pagesUnit-4 Economicsrakshit konchadaNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument2 pagesMarket StructuresNyx MetopeNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 A. Answer The FollowingDocument3 pagesActivity #1 A. Answer The FollowingSean CatapangNo ratings yet
- Report Topic:: Market StructureDocument4 pagesReport Topic:: Market StructureAyisOgaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document13 pagesLecture 11yusufaldemir3455No ratings yet
- Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 12 Studyguide360Document24 pagesClass 11 Economics Notes Chapter 12 Studyguide360Ayush Singh BaghelNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ Week 5Document4 pagesApplied Econ Week 5Coleen Heart Migue PortonNo ratings yet
- 5-7 - Market Structures and EfficiencyDocument83 pages5-7 - Market Structures and EfficiencySamiyah Irfan 2023243No ratings yet
- Market Structure IDocument37 pagesMarket Structure ISargam MohlaNo ratings yet
- Main Market Forms HandoutsDocument6 pagesMain Market Forms HandoutsKishor CharsiNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument10 pagesUnit IvKhalid AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- PDF CropDocument80 pagesPDF Cropintexcloud978No ratings yet
- Market Structur E Characteristics Advantages/Disadvtanges Description ExampleDocument1 pageMarket Structur E Characteristics Advantages/Disadvtanges Description ExampleG12 Erika ManaigNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis - Meaning, Types, Determinants of Demand, Demand FunctionDocument11 pagesMarket Analysis - Meaning, Types, Determinants of Demand, Demand FunctionRaj ShravanthiNo ratings yet
- Demand & Supply PrintableDocument1 pageDemand & Supply Printableshubhamaffiliate20No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Theory of Monopoly: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 9 Theory of Monopoly: Structuresailajacse2005No ratings yet
- Reviewer MECODocument13 pagesReviewer MECOMary Tyfanie QuilantangNo ratings yet
- The Firm and Market StructuresDocument36 pagesThe Firm and Market StructuresPrince Agrawal100% (1)
- Class 7 PDFDocument34 pagesClass 7 PDFAzim HossainNo ratings yet
- Assignment On MicroeconomicsDocument4 pagesAssignment On MicroeconomicsAl-Nahian Bin HossainNo ratings yet
- Managing Perfect CompetitionsDocument8 pagesManaging Perfect CompetitionsBALBIDO, Jhyra S.No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1Likitha GangaramNo ratings yet
- Appeco Lecture 7Document13 pagesAppeco Lecture 7Isabella EgeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ix 1Document8 pagesPertemuan Ix 1Rumiati 72No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Understanding Markets and Industry ChangesDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Understanding Markets and Industry ChangesMelody BautistaNo ratings yet
- Be Group 2 (Before Mid)Document52 pagesBe Group 2 (Before Mid)Meutia AzisaNo ratings yet
- Market Structures PosterDocument8 pagesMarket Structures PosterSzczepan WasilukNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2 - Perfect CompetitionDocument13 pagesLecture 3.2 - Perfect CompetitionLakmal SilvaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Marketstructure - Perfect - MonopolyfffinalDocument25 pages12 - Marketstructure - Perfect - MonopolyfffinalAdheip BakshiNo ratings yet
- Market Structure: Fakultas Rekayasa IndustriDocument17 pagesMarket Structure: Fakultas Rekayasa Industrialiffian alifNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument7 pagesMarket StructureMuhammad AbrarrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document57 pagesChapter 9ying huiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleFrom EverandSummary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleNo ratings yet
- THUEDocument5 pagesTHUEMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- FTU Creative DevelopmentDocument2 pagesFTU Creative DevelopmentMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document1 pageChapter 6Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Social ResponsibilityDocument1 pageCorporate Governance and Social ResponsibilityMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Indentifying and Preventing Fraud: Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud What If Fraud?Document1 pageIndentifying and Preventing Fraud: Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud What If Fraud?Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- What If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent FraudDocument1 pageWhat If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent FraudMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- The Role of Accounting: Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingDocument1 pageThe Role of Accounting: Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Technology: Has Separated Legal Personality From Its Owners (Shareholders)Document1 pageTechnology: Has Separated Legal Personality From Its Owners (Shareholders)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Inflation: The Macroeconomic EnvironmentDocument1 pageInflation: The Macroeconomic EnvironmentMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Contractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersDocument1 pageContractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Business Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Document1 pageBusiness Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Siemens D3 Platform 3.0-MW.Document8 pagesSiemens D3 Platform 3.0-MW.Uhrin Imre100% (1)
- Contemporary World Notes - SEM 1Document15 pagesContemporary World Notes - SEM 1pancajas02No ratings yet
- Hotel Silver Leaf (A Unit of Narmada Hospitality) : GSTIN: 24AAOFN5286B1Z7 SAC: 996311Document3 pagesHotel Silver Leaf (A Unit of Narmada Hospitality) : GSTIN: 24AAOFN5286B1Z7 SAC: 996311Ashish JainNo ratings yet
- Rural Electrification Through Hybrid Solutions: Presented by Albert Ferrer, Chief Operation Officer Loraxian IncDocument13 pagesRural Electrification Through Hybrid Solutions: Presented by Albert Ferrer, Chief Operation Officer Loraxian IncAbiNo ratings yet
- (Frederic - S. - Mishkin) - Economics - of - Moneyy, - Banking - and - Financial MarketsDocument22 pages(Frederic - S. - Mishkin) - Economics - of - Moneyy, - Banking - and - Financial MarketsNouran MohamedNo ratings yet
- 3-Bedroom Bungalow EstimateDocument10 pages3-Bedroom Bungalow EstimateJohn Joseph Concepcion Ligero100% (1)
- Option Scalping Strategy Course - by Sivakumar Jaychandra - Upsurge - ClubDocument5 pagesOption Scalping Strategy Course - by Sivakumar Jaychandra - Upsurge - Clubinvestly.vruddhiNo ratings yet
- Money Lenders Renewal Application Form 2023Document2 pagesMoney Lenders Renewal Application Form 2023Donald MaasaNo ratings yet
- UPDATED The Mayor's Fund For Las Vegas LIFE Contributions Report For Records Request - FOIA 12.19.2019Document9 pagesUPDATED The Mayor's Fund For Las Vegas LIFE Contributions Report For Records Request - FOIA 12.19.2019Cody MillerNo ratings yet
- Capacity Planning StrategyDocument29 pagesCapacity Planning StrategySaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Test 2 AnswersDocument5 pagesAptitude Test 2 AnswersTrung PhạmNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and LabourDocument5 pagesGlobalisation and LabourFARHEEN ZIANo ratings yet
- September Month Current AffairsDocument7 pagesSeptember Month Current AffairsGoogle AccountNo ratings yet
- International Student Application For Financial Assistance 2022 11.05.2021Document7 pagesInternational Student Application For Financial Assistance 2022 11.05.2021Samuel AduNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Creating & Capturing Customer ValueDocument34 pagesMarketing: Creating & Capturing Customer Valuedua tanveerNo ratings yet
- General Instruction:: Elmer A. Consing, Mba Midterm ExaminationDocument2 pagesGeneral Instruction:: Elmer A. Consing, Mba Midterm ExaminationRovern Keith Oro CuencaNo ratings yet
- Form of Application For Registration of A Public TrustDocument4 pagesForm of Application For Registration of A Public Trustiqbalshaikh1960100% (1)
- 2023C8C441EBDADFDocument1 page2023C8C441EBDADFitmaster onlineNo ratings yet
- Fco 084 Wcaf 23122Document2 pagesFco 084 Wcaf 23122Bacot MakassarNo ratings yet
- Arx Malbikunarvaltarar Fra AmmannDocument24 pagesArx Malbikunarvaltarar Fra AmmannhathamphanNo ratings yet
- NS INTERNATIONAL - UpdatedDocument12 pagesNS INTERNATIONAL - UpdatedSumreenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 An Astrologer's Day: Questions and Answers Based On Inference/Interpretation/Personal ResponseDocument4 pagesLesson 1 An Astrologer's Day: Questions and Answers Based On Inference/Interpretation/Personal ResponseShubham Surve0% (1)
- List of IfrsDocument2 pagesList of IfrsKrishal Budhathoki100% (1)
- Session - Oligopoly1Document62 pagesSession - Oligopoly1akshat mathurNo ratings yet
- ERS 3.0 - Product SheetDocument2 pagesERS 3.0 - Product SheetTonilleNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation November 2022 FINALDocument8 pagesInvestor Presentation November 2022 FINALAdvanilson SousaNo ratings yet
- Respondant MemorialDocument49 pagesRespondant MemorialAnshuSinghNo ratings yet
- Advantages of FDIDocument2 pagesAdvantages of FDIr09033No ratings yet
- M5-Global and Regional Economic Cooperation and IntegrationDocument9 pagesM5-Global and Regional Economic Cooperation and IntegrationSharon Cadampog MananguiteNo ratings yet
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Minhh KhanggOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Minhh KhanggCopyright:
Available Formats
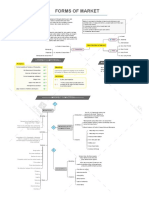
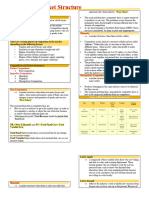
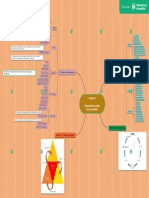
A market has a few dominant producers
Ex: Auto industry, cable television, and commercial air travel Oligopoly
Oligopolistic markets are often characterized by complex product differentiation, Supply and demand
significant barriers to entry and a high level of influence on prices
Demand is inelastic
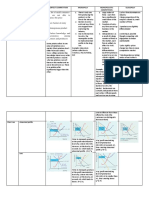
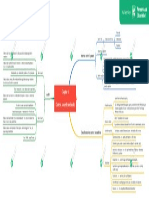
set below the equilibrium price P produces a shortage AB since at price M, quantity
A market has only one producer B is demanded but only quantity A is supplied. However quantity A could be fully
Ex: Microsoft and Windows, DeBeers and diamonds, your local natural gas company Monopoly utilized by purchasers who willing to pay price Z, so a black market maybe created
Usually subject to control by government or a government agency.
to divert production to consumers at this price
A monopoly can set its own price in the marketplace, which can result in what
economists refer to as 'super-normal profits’.
The demand is perfectly elastic
Chapter 4
The market is easy to enter and exit and it is a perfect knowledge market Types of market
There are few, if any, truly perfectly competitive markets in the real world
Ex: Selling a popular good on the internet through a service like e-bay Perfect competition Microeconomic factors A maximum price
The price and level of output under perfect competition tends towards the equilibrium
point.
A perfectly competitive market has many firms producing the same (i.e.
homogeneous) goods or services.
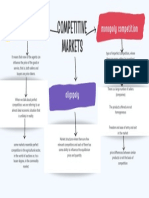
The term 'imperfect competition' applies to any market that is not perfect
Imperfect competition
Ex: Supermarket Ex: The government may set a maximum price of bread of £1 – or a maximum price
of a weekly rent of £150
Few barriers to entry or exit
Monopolistic competition Type of price mechanism set above the equilibrium price P produces a surplus AB since at price M, quantity B
Ex: Restaurants, cereal, clothing, shoes, and service industries in large cities Monopolistic competition arises when the market comprises many producers who
is supplied but only quantity A is demanded. Government thus can also set a limit to
tend to use product differentiation to distinguish themselves from others.
production quota or they can buy the excess and export it or the suppliers just have
to sell at less than the quantity B
A minimum price
Ex: Price floors in agricultural product markets (big thing in the European Union)
You might also like
- Economic Growth 3rd Edition Weil Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesEconomic Growth 3rd Edition Weil Solutions Manualashleyfuentesdvm13051997noj100% (26)
- Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly MonopolyDocument55 pagesPerfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly MonopolyEricko Marvin KweknotoNo ratings yet
- Industry: EquilibriumDocument13 pagesIndustry: EquilibriumKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledBhebz Erin Mae0% (1)
- CH - 5 Forms of MarketDocument1 pageCH - 5 Forms of MarketkalynNo ratings yet
- 4 Market Structures ModifiedDocument4 pages4 Market Structures ModifiedDanaNo ratings yet
- Presented by Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDocument26 pagesPresented by Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDeepak NandaNo ratings yet
- Fase2-Natalia Cano - Estudio Sobre Las GeneralidadesDocument1 pageFase2-Natalia Cano - Estudio Sobre Las GeneralidadesIsabella SotoNo ratings yet
- MarketDocument22 pagesMarketAaditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit - VDocument27 pagesUnit - VDharshanth .SNo ratings yet
- Forms of MarketDocument17 pagesForms of Marketdil preetNo ratings yet
- Project EconomicsDocument12 pagesProject EconomicsBoomNo ratings yet
- Market TypesDocument1 pageMarket TypesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- MARKETDocument21 pagesMARKETJane BañaresNo ratings yet
- Types of OligopolyDocument3 pagesTypes of OligopolyIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Monopoly1Document37 pagesLecture 11 Monopoly1Daksh AnujNo ratings yet
- Quinalayo, Michael Kriz L. AB Political Science IIIB Market Structure Characteristics ExamplesDocument2 pagesQuinalayo, Michael Kriz L. AB Political Science IIIB Market Structure Characteristics ExamplesmichaelNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Unit 5Document19 pagesManagerial Economics - Unit 5sruthy santhoshNo ratings yet
- Question Tutorial 2Document7 pagesQuestion Tutorial 2Nabila HassanNo ratings yet
- Competition: Monopolistic Fairly LargeDocument4 pagesCompetition: Monopolistic Fairly LargeNagaraj BeeduNo ratings yet
- #3 Lesson 2.4-2.6Document3 pages#3 Lesson 2.4-2.6Chelsea A. SADSADNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7 9Document17 pagesChapters 7 9directo549No ratings yet
- Imperfect Competition and Output Decision: Presented By: Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDocument23 pagesImperfect Competition and Output Decision: Presented By: Ananya Sengupta Deepak Nanda Kush RaiDeepak NandaNo ratings yet
- Eco102-Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets PDFDocument3 pagesEco102-Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets PDFCornelia MarquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.1 and 7.2 Group 1 ManEconDocument3 pagesChapter 7.1 and 7.2 Group 1 ManEconfrancheskaarcederaNo ratings yet
- Yogesh - A 19Bcc0028Document4 pagesYogesh - A 19Bcc0028Ash KetchumNo ratings yet
- Monopoly and MonopsonyDocument7 pagesMonopoly and MonopsonyCoreen AndradeNo ratings yet
- S19&20 - Perfect MarketDocument5 pagesS19&20 - Perfect MarketRohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 EconomicsDocument22 pagesUnit-4 Economicsrakshit konchadaNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument2 pagesMarket StructuresNyx MetopeNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 A. Answer The FollowingDocument3 pagesActivity #1 A. Answer The FollowingSean CatapangNo ratings yet
- Report Topic:: Market StructureDocument4 pagesReport Topic:: Market StructureAyisOgaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document13 pagesLecture 11yusufaldemir3455No ratings yet
- Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 12 Studyguide360Document24 pagesClass 11 Economics Notes Chapter 12 Studyguide360Ayush Singh BaghelNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ Week 5Document4 pagesApplied Econ Week 5Coleen Heart Migue PortonNo ratings yet
- 5-7 - Market Structures and EfficiencyDocument83 pages5-7 - Market Structures and EfficiencySamiyah Irfan 2023243No ratings yet
- Market Structure IDocument37 pagesMarket Structure ISargam MohlaNo ratings yet
- Main Market Forms HandoutsDocument6 pagesMain Market Forms HandoutsKishor CharsiNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument10 pagesUnit IvKhalid AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- PDF CropDocument80 pagesPDF Cropintexcloud978No ratings yet
- Market Structur E Characteristics Advantages/Disadvtanges Description ExampleDocument1 pageMarket Structur E Characteristics Advantages/Disadvtanges Description ExampleG12 Erika ManaigNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis - Meaning, Types, Determinants of Demand, Demand FunctionDocument11 pagesMarket Analysis - Meaning, Types, Determinants of Demand, Demand FunctionRaj ShravanthiNo ratings yet
- Demand & Supply PrintableDocument1 pageDemand & Supply Printableshubhamaffiliate20No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Theory of Monopoly: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 9 Theory of Monopoly: Structuresailajacse2005No ratings yet
- Reviewer MECODocument13 pagesReviewer MECOMary Tyfanie QuilantangNo ratings yet
- The Firm and Market StructuresDocument36 pagesThe Firm and Market StructuresPrince Agrawal100% (1)
- Class 7 PDFDocument34 pagesClass 7 PDFAzim HossainNo ratings yet
- Assignment On MicroeconomicsDocument4 pagesAssignment On MicroeconomicsAl-Nahian Bin HossainNo ratings yet
- Managing Perfect CompetitionsDocument8 pagesManaging Perfect CompetitionsBALBIDO, Jhyra S.No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1Likitha GangaramNo ratings yet
- Appeco Lecture 7Document13 pagesAppeco Lecture 7Isabella EgeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ix 1Document8 pagesPertemuan Ix 1Rumiati 72No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Understanding Markets and Industry ChangesDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Understanding Markets and Industry ChangesMelody BautistaNo ratings yet
- Be Group 2 (Before Mid)Document52 pagesBe Group 2 (Before Mid)Meutia AzisaNo ratings yet
- Market Structures PosterDocument8 pagesMarket Structures PosterSzczepan WasilukNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2 - Perfect CompetitionDocument13 pagesLecture 3.2 - Perfect CompetitionLakmal SilvaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Marketstructure - Perfect - MonopolyfffinalDocument25 pages12 - Marketstructure - Perfect - MonopolyfffinalAdheip BakshiNo ratings yet
- Market Structure: Fakultas Rekayasa IndustriDocument17 pagesMarket Structure: Fakultas Rekayasa Industrialiffian alifNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument7 pagesMarket StructureMuhammad AbrarrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document57 pagesChapter 9ying huiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleFrom EverandSummary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleNo ratings yet
- THUEDocument5 pagesTHUEMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- FTU Creative DevelopmentDocument2 pagesFTU Creative DevelopmentMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document1 pageChapter 6Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Social ResponsibilityDocument1 pageCorporate Governance and Social ResponsibilityMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Indentifying and Preventing Fraud: Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud What If Fraud?Document1 pageIndentifying and Preventing Fraud: Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud What If Fraud?Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- What If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent FraudDocument1 pageWhat If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent FraudMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- The Role of Accounting: Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingDocument1 pageThe Role of Accounting: Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Technology: Has Separated Legal Personality From Its Owners (Shareholders)Document1 pageTechnology: Has Separated Legal Personality From Its Owners (Shareholders)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Inflation: The Macroeconomic EnvironmentDocument1 pageInflation: The Macroeconomic EnvironmentMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Contractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersDocument1 pageContractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Business Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Document1 pageBusiness Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Siemens D3 Platform 3.0-MW.Document8 pagesSiemens D3 Platform 3.0-MW.Uhrin Imre100% (1)
- Contemporary World Notes - SEM 1Document15 pagesContemporary World Notes - SEM 1pancajas02No ratings yet
- Hotel Silver Leaf (A Unit of Narmada Hospitality) : GSTIN: 24AAOFN5286B1Z7 SAC: 996311Document3 pagesHotel Silver Leaf (A Unit of Narmada Hospitality) : GSTIN: 24AAOFN5286B1Z7 SAC: 996311Ashish JainNo ratings yet
- Rural Electrification Through Hybrid Solutions: Presented by Albert Ferrer, Chief Operation Officer Loraxian IncDocument13 pagesRural Electrification Through Hybrid Solutions: Presented by Albert Ferrer, Chief Operation Officer Loraxian IncAbiNo ratings yet
- (Frederic - S. - Mishkin) - Economics - of - Moneyy, - Banking - and - Financial MarketsDocument22 pages(Frederic - S. - Mishkin) - Economics - of - Moneyy, - Banking - and - Financial MarketsNouran MohamedNo ratings yet
- 3-Bedroom Bungalow EstimateDocument10 pages3-Bedroom Bungalow EstimateJohn Joseph Concepcion Ligero100% (1)
- Option Scalping Strategy Course - by Sivakumar Jaychandra - Upsurge - ClubDocument5 pagesOption Scalping Strategy Course - by Sivakumar Jaychandra - Upsurge - Clubinvestly.vruddhiNo ratings yet
- Money Lenders Renewal Application Form 2023Document2 pagesMoney Lenders Renewal Application Form 2023Donald MaasaNo ratings yet
- UPDATED The Mayor's Fund For Las Vegas LIFE Contributions Report For Records Request - FOIA 12.19.2019Document9 pagesUPDATED The Mayor's Fund For Las Vegas LIFE Contributions Report For Records Request - FOIA 12.19.2019Cody MillerNo ratings yet
- Capacity Planning StrategyDocument29 pagesCapacity Planning StrategySaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Test 2 AnswersDocument5 pagesAptitude Test 2 AnswersTrung PhạmNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and LabourDocument5 pagesGlobalisation and LabourFARHEEN ZIANo ratings yet
- September Month Current AffairsDocument7 pagesSeptember Month Current AffairsGoogle AccountNo ratings yet
- International Student Application For Financial Assistance 2022 11.05.2021Document7 pagesInternational Student Application For Financial Assistance 2022 11.05.2021Samuel AduNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Creating & Capturing Customer ValueDocument34 pagesMarketing: Creating & Capturing Customer Valuedua tanveerNo ratings yet
- General Instruction:: Elmer A. Consing, Mba Midterm ExaminationDocument2 pagesGeneral Instruction:: Elmer A. Consing, Mba Midterm ExaminationRovern Keith Oro CuencaNo ratings yet
- Form of Application For Registration of A Public TrustDocument4 pagesForm of Application For Registration of A Public Trustiqbalshaikh1960100% (1)
- 2023C8C441EBDADFDocument1 page2023C8C441EBDADFitmaster onlineNo ratings yet
- Fco 084 Wcaf 23122Document2 pagesFco 084 Wcaf 23122Bacot MakassarNo ratings yet
- Arx Malbikunarvaltarar Fra AmmannDocument24 pagesArx Malbikunarvaltarar Fra AmmannhathamphanNo ratings yet
- NS INTERNATIONAL - UpdatedDocument12 pagesNS INTERNATIONAL - UpdatedSumreenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 An Astrologer's Day: Questions and Answers Based On Inference/Interpretation/Personal ResponseDocument4 pagesLesson 1 An Astrologer's Day: Questions and Answers Based On Inference/Interpretation/Personal ResponseShubham Surve0% (1)
- List of IfrsDocument2 pagesList of IfrsKrishal Budhathoki100% (1)
- Session - Oligopoly1Document62 pagesSession - Oligopoly1akshat mathurNo ratings yet
- ERS 3.0 - Product SheetDocument2 pagesERS 3.0 - Product SheetTonilleNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation November 2022 FINALDocument8 pagesInvestor Presentation November 2022 FINALAdvanilson SousaNo ratings yet
- Respondant MemorialDocument49 pagesRespondant MemorialAnshuSinghNo ratings yet
- Advantages of FDIDocument2 pagesAdvantages of FDIr09033No ratings yet
- M5-Global and Regional Economic Cooperation and IntegrationDocument9 pagesM5-Global and Regional Economic Cooperation and IntegrationSharon Cadampog MananguiteNo ratings yet