Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knowing Your Self Is The Beginning of All Wisdom
Knowing Your Self Is The Beginning of All Wisdom
Uploaded by
Joela CastilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowing Your Self Is The Beginning of All Wisdom
Knowing Your Self Is The Beginning of All Wisdom
Uploaded by
Joela CastilCopyright:
Available Formats
Models of Communication
Communication Model:
◉ Communication models are systematic representations of the process
which helps in understanding how communication works can be done.
◉ Models show the process metaphorically and in symbols.
◉ They form general perspectives on communication by breaking
communication from complex to simple and keeps the components in
order.
Different Communication Model:
◉ Aristotle’s Model of Communication
◉ Shannon-Weaver’s Model of Communication
◉ Osgood-Schramm Model of Communication
◉ Eugene White's Model of Communication
Who is Aristotle?
“Knowing your self is the beginning of all wisdom”
Aristotle (384 B.C. to 322 B.C.)
◉ Was an Ancient Greek philosopher and scientist who is still considered
one of the greatest thinkers in politics, psychology and ethics.
◉ When Aristotle turned 17, he enrolled in Plato’s Academy. In 338, he
began tutoring Alexander the Great.
In 335, Aristotle founded his own school, the Lyceum, in Athens, where
he spent most of the rest of his life studying, teaching and writing.
Some of his most notable works include Nichomachean Ethics, Politics,
Metaphysics, Poetics and Prior Analytics.
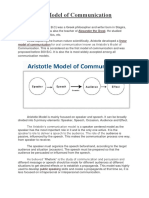
Aristotle’s Model of Communication:
Aristotle was the first one to take an initiative and design and developed
a linear model of oral communication.
This is considered as the first model of communication and was
proposed before 300 B.C.
It is also the most widely accepted among all communication models.
Speaker plays the most important role in communication and it is the
only one who holds the responsibility to influence his/her audience
through public speaking.
Critical Elements of A good Communicator:
Ethos
Is the characteristic which makes you credible in front of the audience.
For Example:
◉ The mass will not listen to the promises of a corrupt politician, but if a
politician is known for his good deeds, there’s a high change his speech
will be heard.
Pathos
If what you say matters to them and they can connect with it, then they
will be more interested and they will think you are more credible.
For Example:
o If people of a village needs water and the politician tells them that he
will help in building roads, the people will not get influenced but might
be more influenced if he says he’ll build a dam for drinking water and
irrigation.
Logos
Logos is logic. People believe in you only if they understand what you
are trying to say. People find logic in everything.
For Example:
o A presenter using factual data in an awareness program will attract the
audience’s attention and will make them believe in the need of
awareness in the particular matter.
Elements of Communication:
1. Speaker
2. Speech
3. Audience
4. Occasion
5. Audience Effect
I. Speaker- the speaker is the initiator of communication.
II. Speech- is the message of the speaker.
III. Audience- is one or more people who come together to listen to the
speaker
IV. Occasion- is the setting or the event the communication take place
V. Effect- the result or the reaction of the audience after your speech. The
audience is passive, influenced by the speech.
Examples:
A politician (speaker) gives a speech to get votes from the civilians
(audience) at the time of election (occasion). The civilians only vote if they are
influenced by the things the politician says in his speech so the content must
be very impressive to influence the mass and the speaker must design the
message very carefully.
Seminars
Business summit/ Business related occasion
Lectures
Criticisms of Aristotle’s Model of Communication:
◉ There is no concept of feedback, it is one way from speaker to audience.
◉ There is no concept of communication failure like noise and barriers.
◉ This model can only be used in public speaking.
◉ The Aristotle’s Model of Communication is a speaker centered model as
the speaker has the most important role in it and is the only one active.
It is the speaker’s role to deliver a speech to the audience. This makes
the communication process one way, from speaker to receiver.
You might also like
- How To Get A Woman To Pay You Volume 2 (Guy Blaze) (Z-Library)Document54 pagesHow To Get A Woman To Pay You Volume 2 (Guy Blaze) (Z-Library)neverlosetime8952No ratings yet
- Elements of A Short Story Lesson PlanDocument21 pagesElements of A Short Story Lesson PlanJoela Castil50% (2)
- Effective Communication Leson PlanDocument17 pagesEffective Communication Leson PlanJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- 2 Aristotle's Model of CommunicationDocument3 pages2 Aristotle's Model of CommunicationLow CheeXiang100% (3)
- International Sale Contract Model TemplateDocument7 pagesInternational Sale Contract Model TemplateCarina-Ioana Paraschiv50% (2)
- Fable - The Lion and The Mouse Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesFable - The Lion and The Mouse Lesson PlanJoela Castil100% (1)
- Speech and Theater ArtsDocument33 pagesSpeech and Theater ArtsJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Rangkuman Dan LatihanDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Rangkuman Dan LatihanTata SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Alang Ship BreakersDocument29 pagesAlang Ship Breakerspureman35100% (1)
- How Can The Law Be Used As An Instrument For Creating Social Change - IpleadersDocument13 pagesHow Can The Law Be Used As An Instrument For Creating Social Change - IpleadersLeelakrishna VemuruNo ratings yet
- Aristotle'S Communication ModelDocument11 pagesAristotle'S Communication ModelJulanni Sawabe100% (1)
- 2 Aristotle S Model of CommunicationDocument3 pages2 Aristotle S Model of CommunicationSaqi abroNo ratings yet
- Models of BCDocument16 pagesModels of BCNihal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Model of CommunicationDocument3 pagesAristotle's Model of CommunicationChristian Dave AndresNo ratings yet
- Genova John FelixDocument1 pageGenova John FelixJohn Felix GenovaNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument2 pagesAristotleAr Raymar Balisi ArabesNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Model of CommunicationDocument3 pagesAristotle's Model of CommunicationMiss ANo ratings yet
- Aristotle'S Classical Model: Dr. Tinam Borah Assistant Professor DME Media SchoolDocument11 pagesAristotle'S Classical Model: Dr. Tinam Borah Assistant Professor DME Media SchoolG SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Model of CommunicationDocument1 pageAristotle Model of CommunicationCrystelleNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Model of Communication: To Be Submitted To Mr. Ricky M. LatosaDocument8 pagesAristotle's Model of Communication: To Be Submitted To Mr. Ricky M. LatosaSalva TrinidadNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument3 pagesAristotleKaren QuezonNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Communication ModelDocument3 pagesAristotle Communication ModelSophia Nicole ZaraNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Model of CommunicationDocument10 pagesAristotle's Model of CommunicationDyrdrei GarciaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Model of CommunicationDocument5 pagesAristotle's Model of CommunicationKassNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Communication ModelsDocument5 pagesUnit II - Communication ModelsDigi StrengthNo ratings yet
- MOOC - Introduction To Communication Science - SCDocument15 pagesMOOC - Introduction To Communication Science - SCAmaiaNo ratings yet
- GROUP1 Aristotles Model of CommunicationDocument15 pagesGROUP1 Aristotles Model of CommunicationNATHANIEL LIAM D. SUBRADONo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Communication Model " AristotleDocument2 pagesAristotle's Communication Model " Aristotlewenny capplemanNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReportDocument15 pagesOral Communication Reportleiste zeitNo ratings yet
- What Is Aristotle's Model of Communication?: August 23, 2021 Lesson 2Document5 pagesWhat Is Aristotle's Model of Communication?: August 23, 2021 Lesson 2Roanne FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Model of CommunicationDocument2 pagesAristotle Model of CommunicationDaryll RebellonNo ratings yet
- Shannon-Weaver ModelDocument12 pagesShannon-Weaver Modelkusumakar royNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's: Model of CommunicationDocument9 pagesAristotle's: Model of CommunicationAhtasham Ali RajputNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument20 pagesPurposive CommunicationJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument27 pagesPurposive CommunicationJean Marie LuposNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument17 pagesModels of CommunicationMousumi KuilaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Communication ModelsDocument11 pagesLesson 8 - Communication ModelsALLIA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Purposive Communication Module 1 PRDocument13 pagesToaz - Info Purposive Communication Module 1 PRAndrea ElcanoNo ratings yet
- Aristotlelian Model of CommunicationDocument3 pagesAristotlelian Model of CommunicationClarisseNo ratings yet
- Aristotle'sDocument24 pagesAristotle'sRaqeelyna GadjaliNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument18 pagesCommunication ModelmaymorcoNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument4 pagesAristotlejonas rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 1title For ReviweierDocument12 pages1title For ReviweierNoelle Adrian MartinNo ratings yet
- 2 Communication ModelsDocument36 pages2 Communication ModelsTheo SeriyeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To CommunicationDocument27 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Communicationgamingarmy0613No ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1Hannah Michaela GemidaNo ratings yet
- Important Communication ModelsDocument76 pagesImportant Communication ModelsSmart StudyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2Document13 pagesChapter 1 & 2clarisseNo ratings yet
- Judy Ann Mahusay Cresencio Bachelor of Science in Criminology 1 Purposive Communication Activity 1Document7 pagesJudy Ann Mahusay Cresencio Bachelor of Science in Criminology 1 Purposive Communication Activity 1Ma. Re-anne AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive CommunicationCynthialyn OwacanNo ratings yet
- The Five Basic Elements of The Model AreDocument2 pagesThe Five Basic Elements of The Model AreMichael RiveraNo ratings yet
- MIL Lesson 1Document24 pagesMIL Lesson 125princeperezNo ratings yet
- Applied Social Sciences - 062708Document25 pagesApplied Social Sciences - 062708Eldrick CortezNo ratings yet
- Media and Infromation LiteracyDocument34 pagesMedia and Infromation LiteracyJeuel RobiatoNo ratings yet
- Oral-Communication Q1 LP-4Document8 pagesOral-Communication Q1 LP-4Ayela Kim PiliNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication: Mrs. Nadeth CruzDocument27 pagesPurposive Communication: Mrs. Nadeth CruzDonnnaan OreaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument13 pagesPurposive CommunicationKate Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Communicating Effectively in Spoken English in Selected Social ContextsDocument12 pagesCommunicating Effectively in Spoken English in Selected Social ContextsRazul Rafie Bin SuhimanNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument20 pagesPhilosophyMahdi BobakarNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication: Communication Theory - M2 Assignment No: 01Document12 pagesModels of Communication: Communication Theory - M2 Assignment No: 01Zargham AliNo ratings yet
- Aristotle PDFDocument3 pagesAristotle PDFjeremiah paul declasenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CommunicationDocument5 pagesIntroduction To CommunicationXhiella Mhae Garces PaltepNo ratings yet
- Puc Group 7 ResearchDocument10 pagesPuc Group 7 ResearchKen RosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Gec 5Document17 pagesChapter 1 Gec 5Mabini BernadaNo ratings yet
- Communication Models: What Is A ModelDocument6 pagesCommunication Models: What Is A ModelSabrina MañulitNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication q1 LP 4Document7 pagesOral Communication q1 LP 4MICHAEL MORILLONo ratings yet
- Linear Models ExamplesDocument12 pagesLinear Models Examplesgeorgia mae lacsonNo ratings yet
- Field Trip TemplateDocument11 pagesField Trip TemplateJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- GASDocument5 pagesGASJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Literature SemifinalsDocument140 pagesAdolescent Literature SemifinalsJoela Castil100% (1)
- Feathers-in-colors-Recreation-PowerPoint-Templates-Widescreen (Autosaved)Document2 pagesFeathers-in-colors-Recreation-PowerPoint-Templates-Widescreen (Autosaved)Joela CastilNo ratings yet
- GE12Document6 pagesGE12Joela CastilNo ratings yet
- Shannon-Weaver Model of CommunicationDocument7 pagesShannon-Weaver Model of CommunicationJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication: Submitted To: MS. DINA B. GUINITARANDocument12 pagesPurposive Communication: Submitted To: MS. DINA B. GUINITARANJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Meaning of MesopotamiaDocument57 pagesMeaning of MesopotamiaJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- The Lesser Known Banwaon People Banwaon Tribe: (Also Known As: Adgawanon, Banuaonon, Banwanon, Higaonon-Banwaon, Manobo)Document6 pagesThe Lesser Known Banwaon People Banwaon Tribe: (Also Known As: Adgawanon, Banuaonon, Banwanon, Higaonon-Banwaon, Manobo)Joela Castil67% (6)
- Determining The Variables That Affect The Reading Motivation of Educational Faculty StudentsDocument17 pagesDetermining The Variables That Affect The Reading Motivation of Educational Faculty StudentsJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Degrees of Comparison of AdjectivesDocument20 pagesDegrees of Comparison of AdjectivesJoela Castil100% (1)
- The World Is An AppleDocument7 pagesThe World Is An AppleJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Once Upon A Time by Nadine GordimerDocument9 pagesOnce Upon A Time by Nadine GordimerJoela Castil100% (1)
- Spoken Grammar vs. Written GrammarDocument10 pagesSpoken Grammar vs. Written GrammarJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of African LiteratureDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of African LiteratureJoela Castil67% (3)
- The Elements Characters:: Anticipation BY:Mabel Dove DanquahDocument3 pagesThe Elements Characters:: Anticipation BY:Mabel Dove DanquahJoela Castil100% (1)
- Focus Questions:: - What Is School Culture, and How Does It Affect Leading, Teaching, and Learning?Document47 pagesFocus Questions:: - What Is School Culture, and How Does It Affect Leading, Teaching, and Learning?Joela CastilNo ratings yet
- Literature SummaryDocument14 pagesLiterature SummaryJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Map of Africa: Quick Facts About AfricaDocument11 pagesMap of Africa: Quick Facts About AfricaJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Africa by David DiopDocument9 pagesAfrica by David DiopJoela Castil100% (1)
- Afro-Asian Literature: Description About AfricaDocument11 pagesAfro-Asian Literature: Description About AfricaJoela CastilNo ratings yet
- Resisting Colonialism Through A Ghanaian LensDocument6 pagesResisting Colonialism Through A Ghanaian LensAyeni KhemiNo ratings yet
- The Minorities in USA NewDocument22 pagesThe Minorities in USA NewAndreea MarilenaNo ratings yet
- Pa CourseworkDocument5 pagesPa Courseworkafjwoamzdxwmct100% (2)
- Ingles V e VIDocument314 pagesIngles V e VIAntonio MacaiaNo ratings yet
- Rockefeller 1933 Annual ReportDocument493 pagesRockefeller 1933 Annual ReportConstitutionReportNo ratings yet
- People v. RiveraDocument17 pagesPeople v. RiveraYori AvilaNo ratings yet
- Steering SOLAS RegulationsDocument2 pagesSteering SOLAS Regulationsmy print100% (1)
- Group 1 - OfW RemittancesDocument22 pagesGroup 1 - OfW RemittancesFLORENCE MAY SUMINDOLNo ratings yet
- West Houston PlanDocument34 pagesWest Houston PlanHouston ChronicleNo ratings yet
- Corpas Pastor, G. & Gaber, M. Noviembre, 2020 Remote Interpreting in Public Service Settings Technology, Perceptions and PracticeDocument22 pagesCorpas Pastor, G. & Gaber, M. Noviembre, 2020 Remote Interpreting in Public Service Settings Technology, Perceptions and PracticeLuis TraductorNo ratings yet
- Administradora de Estaciones de Servicio Sa de CV: BPJURIH 10852 76100Document1 pageAdministradora de Estaciones de Servicio Sa de CV: BPJURIH 10852 76100gordoasesinoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Music - Harmony Texture & FormsDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Music - Harmony Texture & FormsAaron John Pempengco Tolentino100% (2)
- Design Specifications of PV-diesel Hybrid SystemDocument7 pagesDesign Specifications of PV-diesel Hybrid Systemibrahim salemNo ratings yet
- REFLECTION Paper About Curriculum and Fishbowl ActivityDocument1 pageREFLECTION Paper About Curriculum and Fishbowl ActivityTrisha Mae BonaobraNo ratings yet
- (Me 15) Bosh - Lecture 02Document36 pages(Me 15) Bosh - Lecture 02Strong Boy OgkoNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakanarulianNo ratings yet
- Hyundai R290Lc 7 Hydraulic Excavator: Brazo Opción Boom/Stick Option (HEX) 1Document3 pagesHyundai R290Lc 7 Hydraulic Excavator: Brazo Opción Boom/Stick Option (HEX) 1Beatriz PinedoNo ratings yet
- The Global City-Wps OfficeDocument10 pagesThe Global City-Wps OfficeJunel Dumandan LabradorNo ratings yet
- Ap Lang Syllabus 2013 PDFDocument9 pagesAp Lang Syllabus 2013 PDFjbk23No ratings yet
- Managing The Menopausal Midsection: Is It Even Possible?: Home: CorrespondenceDocument44 pagesManaging The Menopausal Midsection: Is It Even Possible?: Home: CorrespondenceArjun ShawNo ratings yet
- TX2 - 1st MQDocument10 pagesTX2 - 1st MQJeasmine Andrea Diane PayumoNo ratings yet
- Learning Disabilities Summary1Document11 pagesLearning Disabilities Summary1fordmayNo ratings yet
- Ozone Mag #59 - Sep 2007Document100 pagesOzone Mag #59 - Sep 2007Ozone MagazineNo ratings yet
- UG First Year SyllabusDocument264 pagesUG First Year SyllabusAnwesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- Thank-You For Downloading The SW Tool IQ-OQ-PQ Template!Document14 pagesThank-You For Downloading The SW Tool IQ-OQ-PQ Template!MichelleNo ratings yet
- Danika Tynes ResumeDocument6 pagesDanika Tynes ResumeDanika Tynes100% (1)