Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4-Great Minds Vocabulary: Do vs. Make: Past Simple Tense
Unit 4-Great Minds Vocabulary: Do vs. Make: Past Simple Tense
Uploaded by
Marianne Emil-1051Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Definition and Structure of Academic TextsDocument25 pagesDefinition and Structure of Academic TextsHakdog88% (8)
- Visual Elements in Philippine Traditional Motifs and CraftsDocument26 pagesVisual Elements in Philippine Traditional Motifs and CraftsKath Dayag83% (35)
- Narrative Rubric ModifiedDocument1 pageNarrative Rubric Modifiedapi-377468075No ratings yet
- Past Tense - Used ToDocument30 pagesPast Tense - Used ToRosalba BryanNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Missing Word(s)Document41 pagesFill in The Missing Word(s)Arnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- PRESENT PERFECT CompleteDocument7 pagesPRESENT PERFECT CompleteMónicaNo ratings yet
- Presentperfect 2ºESODocument21 pagesPresentperfect 2ºESOcamilo sanchezNo ratings yet
- Hi, Let's Learn About Present Perfect?Document21 pagesHi, Let's Learn About Present Perfect?João Henrique AlessioNo ratings yet
- Universitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIDocument19 pagesUniversitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIRiandy LiuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument19 pagesUNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectOliver TorresNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument11 pagesPresent Perfect TenseZahid Hussain BrohiNo ratings yet
- English7 Q1 Wk5 Past-PerfectTenseDocument11 pagesEnglish7 Q1 Wk5 Past-PerfectTenseRose Ann SelomNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary VerbsDocument21 pagesAuxiliary VerbsyasameenaniNo ratings yet
- The Present PerfectDocument26 pagesThe Present PerfectRAYZA ARIEL CURI ALCANTARANo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument19 pagesPresent Perfect Simpleapi-252190418100% (3)
- Present Perfect Tense - ExplanationDocument14 pagesPresent Perfect Tense - ExplanationMåyi Muñoz ArayąNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument16 pagesEnglish GrammarLyssia dfghjklNo ratings yet
- Lesson N°2 Present Perfect Simple and Continuous-Grammar RulesDocument7 pagesLesson N°2 Present Perfect Simple and Continuous-Grammar RulesKamil Henriquez100% (1)
- Perfect TenseDocument22 pagesPerfect Tensejulfika100% (2)
- Grammar 6 - Family and FriendsDocument12 pagesGrammar 6 - Family and FriendsDavidNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Simple Progressive Perfect Perfect ProgressiveDocument29 pagesTenses: Simple Progressive Perfect Perfect ProgressiveAlicia PerezNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Man and NatureDocument59 pagesUnit 4 Man and NatureAndres Sebastian Davila FalconesNo ratings yet
- P5 Eng Final 2022 - Essential PracticeDocument5 pagesP5 Eng Final 2022 - Essential Practiceณัฐธิดา ศรีภูธร100% (1)
- 4 Past Tenses in English With ExamplesDocument12 pages4 Past Tenses in English With ExamplesJojo LeaonNo ratings yet
- Simple Tenses: Present - Past - Future: Grammar UnderstandingDocument13 pagesSimple Tenses: Present - Past - Future: Grammar UnderstandingPratidinaDeboraNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument19 pagesEnglish TensesPS DigitalEraNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR LEVEL II (Todo)Document11 pagesGRAMMAR LEVEL II (Todo)atheous100% (1)
- Level 6: A) Noun EndingsDocument6 pagesLevel 6: A) Noun EndingsJavier RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- Lezione 1Document36 pagesLezione 1biancaavram88No ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleBondfriendsNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses: - Liew Miao Huei - Jenny Kong Yug Ying - Chan Ngik Cheng - Li Li Ping - Liaw Yien SzeDocument56 pagesPast Tenses: - Liew Miao Huei - Jenny Kong Yug Ying - Chan Ngik Cheng - Li Li Ping - Liaw Yien SzeJenny KongyyNo ratings yet
- (Use The If Time Is Indicated) in Sales. Tom Has ChangedDocument7 pages(Use The If Time Is Indicated) in Sales. Tom Has Changed테레 HernandezNo ratings yet
- Diapo 2 Ciclo 10 PDFDocument39 pagesDiapo 2 Ciclo 10 PDFDaniyar Quintanilla QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousFelipe R CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Nr.1: Simple Tenses Present Simple: 1. Clue WordsDocument4 pagesLesson Nr.1: Simple Tenses Present Simple: 1. Clue WordsAdamson MikhailNo ratings yet
- "S" Present He-She-ItDocument5 pages"S" Present He-She-ItAlejandro BejaranoNo ratings yet
- GRAMMARxDocument7 pagesGRAMMARxClara PvNo ratings yet
- Tenses: PresentDocument11 pagesTenses: PresentGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument4 pagesPresent PerfectDessire FernandezNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandoutDocument10 pagesGrammar Handoutstonegrave68No ratings yet
- Bahan Ujian Akhir Semester 2 Kelas 10 Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesBahan Ujian Akhir Semester 2 Kelas 10 Bahasa InggrisIngrid ChristyNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect - ContinuousDocument23 pagesPresent Perfect - ContinuousAlexander HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Materia Ingles 4 y 5 UnidDocument6 pagesMateria Ingles 4 y 5 UnidFernando Daniel Jinez MontesdeocaNo ratings yet
- Aydade VenecoDocument21 pagesAydade VenecoFrank BluessNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference: Modal AuxiliariesDocument10 pagesGrammar Reference: Modal AuxiliariesAndrei IvanovichNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and ContinuousDocument46 pagesPresent Perfect and Continuouspmalencar100% (2)
- Book 12: Lesson 1: The ConditionalDocument12 pagesBook 12: Lesson 1: The ConditionalMario Maldonado VásquezNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Tense: Daniel Moreno Verbel March 2016Document10 pagesPast Simple Tense: Daniel Moreno Verbel March 2016Daniel Alfonso Moreno VerbelNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Document8 pagesPast Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Do Huynh Khiem CT20V1Q531No ratings yet
- Elliptical Sentences SMPDocument4 pagesElliptical Sentences SMPliaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Document9 pagesPast Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Ibad UllahNo ratings yet
- Units Report: Unit 1Document12 pagesUnits Report: Unit 1Lhy HernándezNo ratings yet
- Buat Ujian BinggrisDocument35 pagesBuat Ujian BinggrisFranklyn Goklas ManullangNo ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document8 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Syazwan ZentNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleAnca IonNo ratings yet
- Lesson N°1 Past Simple and ContinuousDocument6 pagesLesson N°1 Past Simple and ContinuousKamil HenriquezNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tense PPT - EbookDocument14 pagesPerfect Tense PPT - EbookEndah Ayu WinarniNo ratings yet
- Simple Past or Present PerfectDocument17 pagesSimple Past or Present PerfectMarainaNo ratings yet
- Elliptical SentencesDocument7 pagesElliptical SentencesSAMANTHA VIRGINIA TANSILNo ratings yet
- Guide Examjune 2015Document3 pagesGuide Examjune 2015Emigdio MartinezNo ratings yet
- WritingDocument7 pagesWritingMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Narrative Worksheet 2Document2 pagesNarrative Worksheet 2Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Video-Activity-Debating-Argumentation-Video-Movie-Activities - 108157 2Document1 pageVideo-Activity-Debating-Argumentation-Video-Movie-Activities - 108157 2Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Relative PronounsDocument1 pageRelative PronounsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Is Music A Type of Art - Google SearchDocument1 pageIs Music A Type of Art - Google SearchMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Prideand Prejudice PDFDocument6 pagesPrideand Prejudice PDFMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Into Space Answers PDFDocument1 pageInto Space Answers PDFMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Grammar RevisionDocument5 pagesGrammar RevisionMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- The Boy at The Back of The Class-Chapter - 2 - Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesThe Boy at The Back of The Class-Chapter - 2 - Questions and AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument13 pagesAdjectivesMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- West Side StoryDocument3 pagesWest Side StoryMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Unit 5-Ideas - Grammar ExplanationDocument2 pagesUnit 5-Ideas - Grammar ExplanationMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17 With AnswersDocument2 pagesJane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17 With AnswersMarianne Emil-1051100% (1)
- Unit 8-Communities-Relative-PronounsDocument10 pagesUnit 8-Communities-Relative-PronounsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Grammar Sheet ConditionalsDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Grammar Sheet ConditionalsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre CH 13-14Document3 pagesJane Eyre CH 13-14Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17Document2 pagesJane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre Chapter 22 AnswersDocument1 pageJane Eyre Chapter 22 AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Unit 3-Stories Grammar Exercises Modal AnswersDocument5 pagesUnit 3-Stories Grammar Exercises Modal AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Question Tag WorksheetDocument1 pageQuestion Tag WorksheetMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudicce Chapters 2-3-4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesPride and Prejudicce Chapters 2-3-4 QuestionsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudice 5-6 AnswersDocument3 pagesPride and Prejudice 5-6 AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudic - Chapters 1-6 SummarydocxDocument6 pagesPride and Prejudic - Chapters 1-6 SummarydocxMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Great ExpectationsDocument5 pagesGreat ExpectationsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- The Gift of The MagiDocument3 pagesThe Gift of The MagiMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Narrative TensesDocument4 pagesNarrative TensesMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Macbeth Chapters 4 To 7 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMacbeth Chapters 4 To 7 QuestionsMarianne Emil-1051100% (1)
- Revision PrepositionsDocument2 pagesRevision PrepositionsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- The Gift of The Magi AnswersDocument1 pageThe Gift of The Magi AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Macbeth SummaryDocument2 pagesMacbeth SummaryMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- CV en Dhini Noor FhatdilllaDocument2 pagesCV en Dhini Noor FhatdilllaDhini noor FhatdillaNo ratings yet
- DLL FBS Week 2Document4 pagesDLL FBS Week 2MAUREEN DINGALANNo ratings yet
- Understanding Movies Syllabus Spring 24Document5 pagesUnderstanding Movies Syllabus Spring 24yili27807No ratings yet
- Hums. 2 (Creative Writing) - FidpDocument8 pagesHums. 2 (Creative Writing) - FidpSherly MojanaNo ratings yet
- ARNIC Online Intensive English ClassesDocument2 pagesARNIC Online Intensive English ClassesAl AbNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Verb To Be - Possessive PronounsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Verb To Be - Possessive PronounsFlorencia MirandaNo ratings yet
- Outlying MeaningDocument5 pagesOutlying MeaninghubibNo ratings yet
- The Silent Way MethodDocument2 pagesThe Silent Way MethodMichelle Andrea Garcia VillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Revised FebruaryDocument57 pagesChapter II Revised FebruaryKhoiri AzamNo ratings yet
- MEDIADocument1 pageMEDIAJulio FernandezNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 2ND Quarter ExamsDocument3 pagesOral Comm 2ND Quarter ExamsDarlene De PazNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Baltic LanguagesDocument728 pagesFoundations of Baltic LanguagesXweuis Hekuos KweNo ratings yet
- Speech Act Analysis Used by Hiro As One of Main Characters in Big Hero 6 Movie ScriptDocument16 pagesSpeech Act Analysis Used by Hiro As One of Main Characters in Big Hero 6 Movie ScriptYanti NtiNo ratings yet
- StructuralismDocument4 pagesStructuralismAttiaNo ratings yet
- 10 Motivational Phrases You Need To Write On Your Diary: Soo KoreanDocument4 pages10 Motivational Phrases You Need To Write On Your Diary: Soo KoreanShanay GilbertNo ratings yet
- Mata Kuliah: Esp For Primary Teacher Dosen: Dra. ROHANA. M.PDDocument10 pagesMata Kuliah: Esp For Primary Teacher Dosen: Dra. ROHANA. M.PDHardianti RidwanNo ratings yet
- Assignment OUMH 2103 English For Science and Technical Purposes May 2020 SemesterDocument7 pagesAssignment OUMH 2103 English For Science and Technical Purposes May 2020 Semestersya assignmentNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning A Lesson Plan On Listening Skills: Level: Topic: AimsDocument18 pagesLesson Planning A Lesson Plan On Listening Skills: Level: Topic: AimsNur AnnisahNo ratings yet
- Rubrica para La Evaluación Del Examen OralDocument1 pageRubrica para La Evaluación Del Examen Oralnoemi reyes jaimesNo ratings yet
- 11Document5 pages11Kasthuri LetchumanNo ratings yet
- AdjactiveDocument6 pagesAdjactiveKutman UlanbekovNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Music Education in Primary SchoolsDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Music Education in Primary SchoolsmulemeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 16 Application-Letter-for-COLLEGE-ADMISSIONDocument14 pagesLESSON 16 Application-Letter-for-COLLEGE-ADMISSIONDennis EmNo ratings yet
- Bilingual Acquisition - Genessee 2006Document3 pagesBilingual Acquisition - Genessee 2006api-255613967No ratings yet
- Guide Book Lovecomp 2021Document25 pagesGuide Book Lovecomp 2021NINANo ratings yet
- Ficha de Ingles 6 º Ano Can Can T Possessive Pronouns Adjectives Fruit Abd Parts of The House VocabularyDocument4 pagesFicha de Ingles 6 º Ano Can Can T Possessive Pronouns Adjectives Fruit Abd Parts of The House VocabularyVera PintoNo ratings yet
- ZanettinDocument17 pagesZanettinZivagoNo ratings yet
Unit 4-Great Minds Vocabulary: Do vs. Make: Past Simple Tense
Unit 4-Great Minds Vocabulary: Do vs. Make: Past Simple Tense
Uploaded by
Marianne Emil-1051Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4-Great Minds Vocabulary: Do vs. Make: Past Simple Tense
Unit 4-Great Minds Vocabulary: Do vs. Make: Past Simple Tense
Uploaded by
Marianne Emil-1051Copyright:
Available Formats
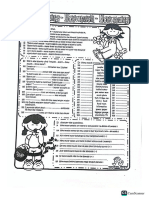
Unit 4- Great Minds
Vocabulary: Do vs. Make
Use DO for actions, obligations, and repetitive tasks. DO generally refers to the action itself.
For example, if you “do” your HW,” you are referring to the action of doing the HW itself.
Use MAKE for creating or producing something, and for actions you choose to do. MAKE
usually refers to the result.
For example, if you “make breakfast,” the result is an omelet!
Grammar:
Past Simple Tense:
The Simple Past Tense is used to express an action which took place in the past and is
completed by the time of speaking. Action can not be a repeated action. Action had a SPECIFIC
TIME WHEN IT TOOK PLACE.
IN 1975/1980(any past dates)- In my boyhood days- Last
Keywords: week/year…etc - ago-Once-Yesterday
General Form :
Subject (I / He / She / It / We / You / They) + Verb in Past tense form
Examples :
Our school started last week.
We bought a new car yesterday.
Did you meet her two days ago? (Use Did +verb in affirmative form when
asking questions in past)
People didn’t travel in trains a hundred years ago. (Use did not +verb in
affirmative form when the phrase is in negative form)
Present Perfect Tense:
It is used, if an action happened in the past and there is a connection to the present.
Action could be repeated.There's no exact time expressed when the action happened.
General Form
+ has / have + Past Participle
Subject (He / She / It ) +has + Past Participle
Subject (I / We / You / They )+ have + Past Participle
already, just , yet(use Not in negative sentences) ever ,never ,
Keywords:
for ,since ,so far, up to now ,not yet , lately , before, recently
Examples :
He has just gone out.
We have just started our breakfast. Do please join us.
I have not eaten anything for five hours.
Have you ever walked into a long tunnel?
Present Perfect with Since and For:
Examples :
My brother hasn’t come home since 1997.
There has been no rain here for six months.
I have not met my grandmother since June.
The owner of the shop has been ill for ten days.
MODALS: CAN, MAY, MUST, HAVE TO
CAN MUST
1) Obligation
1) Ability
I must do my homework.
I can drive
2) For an opinion that you think has a good
2) Possibility
possibility of being true.
She can sing
Look at his uniform. He must be a policeman.
HAVE TO
1) In the affirmative: HAVE TO has a meaning similar to MUST.
I have to go to the school.
2) In the negative: HAVE TO has a different meaning: "you don't need to dot that"
It's Sunday! I don't have to go to school.
You might also like
- Definition and Structure of Academic TextsDocument25 pagesDefinition and Structure of Academic TextsHakdog88% (8)
- Visual Elements in Philippine Traditional Motifs and CraftsDocument26 pagesVisual Elements in Philippine Traditional Motifs and CraftsKath Dayag83% (35)
- Narrative Rubric ModifiedDocument1 pageNarrative Rubric Modifiedapi-377468075No ratings yet
- Past Tense - Used ToDocument30 pagesPast Tense - Used ToRosalba BryanNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Missing Word(s)Document41 pagesFill in The Missing Word(s)Arnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- PRESENT PERFECT CompleteDocument7 pagesPRESENT PERFECT CompleteMónicaNo ratings yet
- Presentperfect 2ºESODocument21 pagesPresentperfect 2ºESOcamilo sanchezNo ratings yet
- Hi, Let's Learn About Present Perfect?Document21 pagesHi, Let's Learn About Present Perfect?João Henrique AlessioNo ratings yet
- Universitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIDocument19 pagesUniversitas Prima Indonesia 2018: Bahasa Inggris Bisnis Ii Pertemuan IIRiandy LiuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument19 pagesUNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectOliver TorresNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument11 pagesPresent Perfect TenseZahid Hussain BrohiNo ratings yet
- English7 Q1 Wk5 Past-PerfectTenseDocument11 pagesEnglish7 Q1 Wk5 Past-PerfectTenseRose Ann SelomNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary VerbsDocument21 pagesAuxiliary VerbsyasameenaniNo ratings yet
- The Present PerfectDocument26 pagesThe Present PerfectRAYZA ARIEL CURI ALCANTARANo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument19 pagesPresent Perfect Simpleapi-252190418100% (3)
- Present Perfect Tense - ExplanationDocument14 pagesPresent Perfect Tense - ExplanationMåyi Muñoz ArayąNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument16 pagesEnglish GrammarLyssia dfghjklNo ratings yet
- Lesson N°2 Present Perfect Simple and Continuous-Grammar RulesDocument7 pagesLesson N°2 Present Perfect Simple and Continuous-Grammar RulesKamil Henriquez100% (1)
- Perfect TenseDocument22 pagesPerfect Tensejulfika100% (2)
- Grammar 6 - Family and FriendsDocument12 pagesGrammar 6 - Family and FriendsDavidNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Simple Progressive Perfect Perfect ProgressiveDocument29 pagesTenses: Simple Progressive Perfect Perfect ProgressiveAlicia PerezNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Man and NatureDocument59 pagesUnit 4 Man and NatureAndres Sebastian Davila FalconesNo ratings yet
- P5 Eng Final 2022 - Essential PracticeDocument5 pagesP5 Eng Final 2022 - Essential Practiceณัฐธิดา ศรีภูธร100% (1)
- 4 Past Tenses in English With ExamplesDocument12 pages4 Past Tenses in English With ExamplesJojo LeaonNo ratings yet
- Simple Tenses: Present - Past - Future: Grammar UnderstandingDocument13 pagesSimple Tenses: Present - Past - Future: Grammar UnderstandingPratidinaDeboraNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument19 pagesEnglish TensesPS DigitalEraNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR LEVEL II (Todo)Document11 pagesGRAMMAR LEVEL II (Todo)atheous100% (1)
- Level 6: A) Noun EndingsDocument6 pagesLevel 6: A) Noun EndingsJavier RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- Lezione 1Document36 pagesLezione 1biancaavram88No ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleBondfriendsNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses: - Liew Miao Huei - Jenny Kong Yug Ying - Chan Ngik Cheng - Li Li Ping - Liaw Yien SzeDocument56 pagesPast Tenses: - Liew Miao Huei - Jenny Kong Yug Ying - Chan Ngik Cheng - Li Li Ping - Liaw Yien SzeJenny KongyyNo ratings yet
- (Use The If Time Is Indicated) in Sales. Tom Has ChangedDocument7 pages(Use The If Time Is Indicated) in Sales. Tom Has Changed테레 HernandezNo ratings yet
- Diapo 2 Ciclo 10 PDFDocument39 pagesDiapo 2 Ciclo 10 PDFDaniyar Quintanilla QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousFelipe R CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Nr.1: Simple Tenses Present Simple: 1. Clue WordsDocument4 pagesLesson Nr.1: Simple Tenses Present Simple: 1. Clue WordsAdamson MikhailNo ratings yet
- "S" Present He-She-ItDocument5 pages"S" Present He-She-ItAlejandro BejaranoNo ratings yet
- GRAMMARxDocument7 pagesGRAMMARxClara PvNo ratings yet
- Tenses: PresentDocument11 pagesTenses: PresentGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument4 pagesPresent PerfectDessire FernandezNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandoutDocument10 pagesGrammar Handoutstonegrave68No ratings yet
- Bahan Ujian Akhir Semester 2 Kelas 10 Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesBahan Ujian Akhir Semester 2 Kelas 10 Bahasa InggrisIngrid ChristyNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect - ContinuousDocument23 pagesPresent Perfect - ContinuousAlexander HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Materia Ingles 4 y 5 UnidDocument6 pagesMateria Ingles 4 y 5 UnidFernando Daniel Jinez MontesdeocaNo ratings yet
- Aydade VenecoDocument21 pagesAydade VenecoFrank BluessNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference: Modal AuxiliariesDocument10 pagesGrammar Reference: Modal AuxiliariesAndrei IvanovichNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and ContinuousDocument46 pagesPresent Perfect and Continuouspmalencar100% (2)
- Book 12: Lesson 1: The ConditionalDocument12 pagesBook 12: Lesson 1: The ConditionalMario Maldonado VásquezNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Tense: Daniel Moreno Verbel March 2016Document10 pagesPast Simple Tense: Daniel Moreno Verbel March 2016Daniel Alfonso Moreno VerbelNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Document8 pagesPast Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Do Huynh Khiem CT20V1Q531No ratings yet
- Elliptical Sentences SMPDocument4 pagesElliptical Sentences SMPliaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Document9 pagesPast Simple: How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Ibad UllahNo ratings yet
- Units Report: Unit 1Document12 pagesUnits Report: Unit 1Lhy HernándezNo ratings yet
- Buat Ujian BinggrisDocument35 pagesBuat Ujian BinggrisFranklyn Goklas ManullangNo ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document8 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Syazwan ZentNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleAnca IonNo ratings yet
- Lesson N°1 Past Simple and ContinuousDocument6 pagesLesson N°1 Past Simple and ContinuousKamil HenriquezNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tense PPT - EbookDocument14 pagesPerfect Tense PPT - EbookEndah Ayu WinarniNo ratings yet
- Simple Past or Present PerfectDocument17 pagesSimple Past or Present PerfectMarainaNo ratings yet
- Elliptical SentencesDocument7 pagesElliptical SentencesSAMANTHA VIRGINIA TANSILNo ratings yet
- Guide Examjune 2015Document3 pagesGuide Examjune 2015Emigdio MartinezNo ratings yet
- WritingDocument7 pagesWritingMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Narrative Worksheet 2Document2 pagesNarrative Worksheet 2Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Video-Activity-Debating-Argumentation-Video-Movie-Activities - 108157 2Document1 pageVideo-Activity-Debating-Argumentation-Video-Movie-Activities - 108157 2Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Relative PronounsDocument1 pageRelative PronounsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Is Music A Type of Art - Google SearchDocument1 pageIs Music A Type of Art - Google SearchMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Prideand Prejudice PDFDocument6 pagesPrideand Prejudice PDFMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Into Space Answers PDFDocument1 pageInto Space Answers PDFMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Grammar RevisionDocument5 pagesGrammar RevisionMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- The Boy at The Back of The Class-Chapter - 2 - Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesThe Boy at The Back of The Class-Chapter - 2 - Questions and AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument13 pagesAdjectivesMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- West Side StoryDocument3 pagesWest Side StoryMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Unit 5-Ideas - Grammar ExplanationDocument2 pagesUnit 5-Ideas - Grammar ExplanationMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17 With AnswersDocument2 pagesJane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17 With AnswersMarianne Emil-1051100% (1)
- Unit 8-Communities-Relative-PronounsDocument10 pagesUnit 8-Communities-Relative-PronounsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Grammar Sheet ConditionalsDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Grammar Sheet ConditionalsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre CH 13-14Document3 pagesJane Eyre CH 13-14Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17Document2 pagesJane Eyre-Chapter 15-16-17Marianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre Chapter 22 AnswersDocument1 pageJane Eyre Chapter 22 AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Unit 3-Stories Grammar Exercises Modal AnswersDocument5 pagesUnit 3-Stories Grammar Exercises Modal AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Question Tag WorksheetDocument1 pageQuestion Tag WorksheetMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudicce Chapters 2-3-4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesPride and Prejudicce Chapters 2-3-4 QuestionsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudice 5-6 AnswersDocument3 pagesPride and Prejudice 5-6 AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudic - Chapters 1-6 SummarydocxDocument6 pagesPride and Prejudic - Chapters 1-6 SummarydocxMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Great ExpectationsDocument5 pagesGreat ExpectationsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- The Gift of The MagiDocument3 pagesThe Gift of The MagiMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Narrative TensesDocument4 pagesNarrative TensesMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Macbeth Chapters 4 To 7 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMacbeth Chapters 4 To 7 QuestionsMarianne Emil-1051100% (1)
- Revision PrepositionsDocument2 pagesRevision PrepositionsMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- The Gift of The Magi AnswersDocument1 pageThe Gift of The Magi AnswersMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- Macbeth SummaryDocument2 pagesMacbeth SummaryMarianne Emil-1051No ratings yet
- CV en Dhini Noor FhatdilllaDocument2 pagesCV en Dhini Noor FhatdilllaDhini noor FhatdillaNo ratings yet
- DLL FBS Week 2Document4 pagesDLL FBS Week 2MAUREEN DINGALANNo ratings yet
- Understanding Movies Syllabus Spring 24Document5 pagesUnderstanding Movies Syllabus Spring 24yili27807No ratings yet
- Hums. 2 (Creative Writing) - FidpDocument8 pagesHums. 2 (Creative Writing) - FidpSherly MojanaNo ratings yet
- ARNIC Online Intensive English ClassesDocument2 pagesARNIC Online Intensive English ClassesAl AbNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Verb To Be - Possessive PronounsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Verb To Be - Possessive PronounsFlorencia MirandaNo ratings yet
- Outlying MeaningDocument5 pagesOutlying MeaninghubibNo ratings yet
- The Silent Way MethodDocument2 pagesThe Silent Way MethodMichelle Andrea Garcia VillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Revised FebruaryDocument57 pagesChapter II Revised FebruaryKhoiri AzamNo ratings yet
- MEDIADocument1 pageMEDIAJulio FernandezNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 2ND Quarter ExamsDocument3 pagesOral Comm 2ND Quarter ExamsDarlene De PazNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Baltic LanguagesDocument728 pagesFoundations of Baltic LanguagesXweuis Hekuos KweNo ratings yet
- Speech Act Analysis Used by Hiro As One of Main Characters in Big Hero 6 Movie ScriptDocument16 pagesSpeech Act Analysis Used by Hiro As One of Main Characters in Big Hero 6 Movie ScriptYanti NtiNo ratings yet
- StructuralismDocument4 pagesStructuralismAttiaNo ratings yet
- 10 Motivational Phrases You Need To Write On Your Diary: Soo KoreanDocument4 pages10 Motivational Phrases You Need To Write On Your Diary: Soo KoreanShanay GilbertNo ratings yet
- Mata Kuliah: Esp For Primary Teacher Dosen: Dra. ROHANA. M.PDDocument10 pagesMata Kuliah: Esp For Primary Teacher Dosen: Dra. ROHANA. M.PDHardianti RidwanNo ratings yet
- Assignment OUMH 2103 English For Science and Technical Purposes May 2020 SemesterDocument7 pagesAssignment OUMH 2103 English For Science and Technical Purposes May 2020 Semestersya assignmentNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning A Lesson Plan On Listening Skills: Level: Topic: AimsDocument18 pagesLesson Planning A Lesson Plan On Listening Skills: Level: Topic: AimsNur AnnisahNo ratings yet
- Rubrica para La Evaluación Del Examen OralDocument1 pageRubrica para La Evaluación Del Examen Oralnoemi reyes jaimesNo ratings yet
- 11Document5 pages11Kasthuri LetchumanNo ratings yet
- AdjactiveDocument6 pagesAdjactiveKutman UlanbekovNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Music Education in Primary SchoolsDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Music Education in Primary SchoolsmulemeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 16 Application-Letter-for-COLLEGE-ADMISSIONDocument14 pagesLESSON 16 Application-Letter-for-COLLEGE-ADMISSIONDennis EmNo ratings yet
- Bilingual Acquisition - Genessee 2006Document3 pagesBilingual Acquisition - Genessee 2006api-255613967No ratings yet
- Guide Book Lovecomp 2021Document25 pagesGuide Book Lovecomp 2021NINANo ratings yet
- Ficha de Ingles 6 º Ano Can Can T Possessive Pronouns Adjectives Fruit Abd Parts of The House VocabularyDocument4 pagesFicha de Ingles 6 º Ano Can Can T Possessive Pronouns Adjectives Fruit Abd Parts of The House VocabularyVera PintoNo ratings yet
- ZanettinDocument17 pagesZanettinZivagoNo ratings yet