Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3 Introduction To Basic Macroeconomic Markets: Household Sells and Firms Buy
Unit 3 Introduction To Basic Macroeconomic Markets: Household Sells and Firms Buy
Uploaded by
Cördïî X CördïîCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: University of Technology, JamaicaDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: University of Technology, JamaicaCördïî X Cördïî100% (1)
- IQ Series Installation Manual Part2Document77 pagesIQ Series Installation Manual Part2David MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios 3 Nodos y MallasDocument20 pagesEjercicios 3 Nodos y MallasOrlando FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3altemurcan kursunluNo ratings yet
- DMGT302 Fundamentals of Project Management PDFDocument229 pagesDMGT302 Fundamentals of Project Management PDFNIKHILTJ100% (1)
- Acm - 05 - 02 - 24Document3 pagesAcm - 05 - 02 - 24t82078044No ratings yet
- Ie4 Flta5: F I5:ueDocument2 pagesIe4 Flta5: F I5:ueOwais BhatNo ratings yet
- I Egi: T 306 T 308 T T 309Document6 pagesI Egi: T 306 T 308 T T 309Ervan Malradani HariyantoNo ratings yet
- Nota Pak Anton 2.08 - 9.08Document8 pagesNota Pak Anton 2.08 - 9.08Dkbp SamarindaNo ratings yet
- Gedalge Respuestas 1Document3 pagesGedalge Respuestas 1Samanosuke7ANo ratings yet
- 246 249Document2 pages246 249gtyd0% (1)
- Iner: SideDocument20 pagesIner: SiderbvzpgvqhbNo ratings yet
- GDP Mind MapDocument1 pageGDP Mind MapNora BuchmanNo ratings yet
- DGT Tracks - Technical-WebDocument1 pageDGT Tracks - Technical-WebhiteshNo ratings yet
- DM - Topic 2 - WebsiteDocument25 pagesDM - Topic 2 - WebsiteTài Nguyễn Đức AnhNo ratings yet
- Dictee 14 Sec 3 CorrigeDocument1 pageDictee 14 Sec 3 CorrigeiplanteNo ratings yet
- Pendarvis Suit With ExhibitsDocument26 pagesPendarvis Suit With ExhibitsMyrtleBeachSC newsNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0134 MCQ College Algebra 253Document1 pageIMG - 0134 MCQ College Algebra 253Hnqr584hNo ratings yet
- Calendar ArdennesDocument2 pagesCalendar ArdennesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- DGT Tracks - Managerial-WebDocument1 pageDGT Tracks - Managerial-WebIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- GTF XXX Cor 21016Document48 pagesGTF XXX Cor 21016AlexNo ratings yet
- Golf 7 - Active Info Display Theme Coding - Google SheetsDocument25 pagesGolf 7 - Active Info Display Theme Coding - Google SheetsSonuNo ratings yet
- Simplex Vacuum Selection MatrixDocument1 pageSimplex Vacuum Selection MatrixStefy CarrascoNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0080 MCQ College Algebra 151Document1 pageIMG - 0080 MCQ College Algebra 151bnqr584bNo ratings yet
- Contoh 1.1 Source Code Java Selection Sort: Public Class Int PublicDocument2 pagesContoh 1.1 Source Code Java Selection Sort: Public Class Int Publicnaufal29No ratings yet
- Img 20240417 0002Document2 pagesImg 20240417 0002IPODS Human ResourceNo ratings yet
- ACCT213 F13 Project 3 BergsmaDocument5 pagesACCT213 F13 Project 3 BergsmaDogmanNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of First Order CircuitsDocument13 pagesTransient Response of First Order Circuitsshilpa reddyNo ratings yet
- Pelayanan Ibu Nifas 2017 Erna CompressedDocument2 pagesPelayanan Ibu Nifas 2017 Erna CompressedFitriana MujiningrumNo ratings yet
- VKILLER Player ReferenceDocument10 pagesVKILLER Player Referencesoft tuber555No ratings yet
- VKILLERDocument26 pagesVKILLERsoft tuber555No ratings yet
- Theory of National Income DeterminationDocument50 pagesTheory of National Income DeterminationKunal KunduNo ratings yet
- C1-C5 & C17 PDFDocument19 pagesC1-C5 & C17 PDFMervin LaudeNo ratings yet
- GTF-COR-21016 Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) Intervention Matrix Rev 0, Jun 2021Document48 pagesGTF-COR-21016 Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) Intervention Matrix Rev 0, Jun 2021Milandro Lou AcuzarNo ratings yet
- Rrl?o F ADocument1 pageRrl?o F AAlex BoisteanNo ratings yet
- 数学作业(2,3,4项)Document11 pages数学作业(2,3,4项)buybyuNo ratings yet
- Co Un T) : Shree Amar Kalyan Secondary School, Maijogmai 1 Nayabazar, IlamDocument4 pagesCo Un T) : Shree Amar Kalyan Secondary School, Maijogmai 1 Nayabazar, IlamDB BhandariNo ratings yet
- Gaming CertificateDocument1 pageGaming CertificateJustin Bobby BognotNo ratings yet
- Bešenje - Okružno 2011Document4 pagesBešenje - Okružno 2011Amila ČehićNo ratings yet
- Jawaban IonDocument1 pageJawaban Ionnata0lukytaNo ratings yet
- 6c0 22 02 2023Document12 pages6c0 22 02 2023Nam PhongNo ratings yet
- Horticulture Production Data 2019-20Document7 pagesHorticulture Production Data 2019-20Brijesh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income PPT (Auto Saved)Document16 pagesCircular Flow of Income PPT (Auto Saved)alexander.charmaineNo ratings yet
- Case Study EdFinancial Services Achieves NIST Compliance For Service AccountsDocument2 pagesCase Study EdFinancial Services Achieves NIST Compliance For Service AccountsRadu CostinNo ratings yet
- Img 0010Document1 pageImg 0010bhakti persadaNo ratings yet
- TS-Moving Average - ACF and StationarityDocument1 pageTS-Moving Average - ACF and StationarityzeliawillscumbergNo ratings yet
- Template Quarterly KRADocument5 pagesTemplate Quarterly KRASuba SriramNo ratings yet
- Baumer Product Overview Process Sensors CT en 1509 11148152Document55 pagesBaumer Product Overview Process Sensors CT en 1509 11148152bnn123No ratings yet
- Z Shortcuts Cheatsheet PP AdvancedDocument1 pageZ Shortcuts Cheatsheet PP AdvancedkateNo ratings yet
- Rotary Hybrid Stepping Motor 1.8°: ConventionalDocument2 pagesRotary Hybrid Stepping Motor 1.8°: ConventionalJollygreen21No ratings yet
- Đề 2 MI1124 20222Document9 pagesĐề 2 MI1124 20222tan12t1lhpNo ratings yet
- Hawak KamayDocument4 pagesHawak KamayAnn AligaNo ratings yet
- FichaTecnicaDuosPara JaimeResendizCLAROVSCLARODocument1 pageFichaTecnicaDuosPara JaimeResendizCLAROVSCLARORicardo SalasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document2 pagesLecture 12Ishmam SababNo ratings yet
- SCE Matrix InstructionsDocument4 pagesSCE Matrix InstructionsBrian FinnertyNo ratings yet
- Assembly Projects - Maintenance: Mecha Tronic SDocument8 pagesAssembly Projects - Maintenance: Mecha Tronic SAfter DarkNo ratings yet
- 5 FebDocument11 pages5 FebnhuzoraNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document6 pagesBook 1SanjoysaharoudraNo ratings yet
- Muhammad I RF An: Flat No 102, Saima Grand, Block H' North Nazimabad KarachiDocument1 pageMuhammad I RF An: Flat No 102, Saima Grand, Block H' North Nazimabad KarachiAbid HassaanNo ratings yet
- Manual PetrelDocument394 pagesManual Petrelmhouskal67% (3)
- IR Oise OllutionDocument52 pagesIR Oise OllutionCördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Document7 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and SportDocument13 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and SportCördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #9Document6 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #9Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #8Document13 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #8Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Practice Exam: (A) (B) (C) (D)Document9 pagesUnit 1 Practice Exam: (A) (B) (C) (D)Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 4.macro.2017Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 4.macro.2017Cördïî X Cördïî0% (1)
- MsmeDocument17 pagesMsmeshamirun ShahniNo ratings yet
- Post TestDocument7 pagesPost TestKRISTEL CAZANDRA EMPASNo ratings yet
- ADM 2350 Final Exam Winter 2011 Version 1 SolutionsDocument18 pagesADM 2350 Final Exam Winter 2011 Version 1 SolutionsIshan VashishtNo ratings yet
- Final Project: Submitted To: Ma'am Aqsa AkbarDocument45 pagesFinal Project: Submitted To: Ma'am Aqsa AkbarialimughalNo ratings yet
- Outsourcing in The Philippines: YearsDocument16 pagesOutsourcing in The Philippines: YearsarciblueNo ratings yet
- Acct Statement - XX8615 - 21012023Document9 pagesAcct Statement - XX8615 - 21012023NAGIREDDY ROHITNo ratings yet
- Rose Packing Co Vs CADocument6 pagesRose Packing Co Vs CAMalolosFire BulacanNo ratings yet
- Best in Class Practices - Procure To PayDocument31 pagesBest in Class Practices - Procure To PayAmaldev VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Card Number Booklet Number Merchant Outlet Descriptive Outlet NameDocument10 pagesCard Number Booklet Number Merchant Outlet Descriptive Outlet Namepawan soniNo ratings yet
- Bill PDFDocument15 pagesBill PDFJose AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Accounting Sample Paper 2011: QuestionsDocument21 pagesAccounting Sample Paper 2011: QuestionssunlightNo ratings yet
- Easter Seals 37th Annual Golf Tournament Program BookDocument36 pagesEaster Seals 37th Annual Golf Tournament Program BookEasterSealsCapitalRegionNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument2 pagesConclusionNeerajNo ratings yet
- IST 4030A Normalisation ExerciseDocument4 pagesIST 4030A Normalisation ExerciseHuzeifa Musajee100% (1)
- 2012-Noman TextileDocument3 pages2012-Noman TextileShahadat Hossain ShahinNo ratings yet
- PPSCI vs. Equitable PCI BankDocument4 pagesPPSCI vs. Equitable PCI BankAnonymous oDPxEkdNo ratings yet
- CV1 Shubhaditya Choudhary 61920460Document1 pageCV1 Shubhaditya Choudhary 61920460Harmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- XT Ekkamai Teaser GEDocument63 pagesXT Ekkamai Teaser GEChiến NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Commercial BQSDocument47 pagesCommercial BQSStefhanie Khristine PormanesNo ratings yet
- ABM Investama TBK.: Company Report: January 2019 As of 31 January 2019Document3 pagesABM Investama TBK.: Company Report: January 2019 As of 31 January 2019dhiladaikawaNo ratings yet
- Mortgage Payment Calculator - TD Canada TrustDocument3 pagesMortgage Payment Calculator - TD Canada TrustTomura ShigarakiNo ratings yet
- Financial MangementDocument3 pagesFinancial MangementAman JainNo ratings yet
- Procure To Pay CycleDocument20 pagesProcure To Pay CycleKatie RuizNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash - Exercise 1 (Solution)Document10 pagesAudit of Cash - Exercise 1 (Solution)Aby ReedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4hassan19951996hNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations For Quantitative Finance 9813202475 9789813202474 - CompressDocument222 pagesTheoretical Foundations For Quantitative Finance 9813202475 9789813202474 - CompressLynaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 Gov Grant, Borrowing, Forex (Q) - MergedDocument24 pagesTutorial 7 Gov Grant, Borrowing, Forex (Q) - MergedKelvin Chu JYNo ratings yet
- Tax InvoiceDocument4 pagesTax InvoiceMohamed Farook FarookNo ratings yet
Unit 3 Introduction To Basic Macroeconomic Markets: Household Sells and Firms Buy
Unit 3 Introduction To Basic Macroeconomic Markets: Household Sells and Firms Buy
Uploaded by
Cördïî X CördïîOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 3 Introduction To Basic Macroeconomic Markets: Household Sells and Firms Buy
Unit 3 Introduction To Basic Macroeconomic Markets: Household Sells and Firms Buy
Uploaded by
Cördïî X CördïîCopyright:
Available Formats
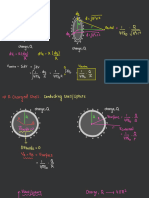
UNIT 3
INTRODUCTION TO BASIC MACROECONOMIC MARKETS
FOUR KEY MARKETS :
RESOURCE/FACTOR MARKET: A highly aggregated market encompassing all resources
(labour, physical capital, land and entrepreneurship) that contribute to the production of current
output. The labour market forms the largest component of this market. Household Sells and
Firms Buy
GOODS & SERVICES/PRODUCT MARKET: The highly aggregated market encompassing
the flow of all final user goods and services. The market counts all items that enter into GDP.
Thus, real output in this market is equal to real GDP. Firms Sell and Households Buy.
LOANABLE FUNDS MARKET: A general term used to describe the market arrangements
that coordinate the borrowing and the lending decisions of business firms and households.
Commercial Banks, savings and loans associations, the stock and bond market and insurance
companies are important financial institutions in this market.
FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET: The market in which the currencies of different countries
are bought and sold.
CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME :
It is a simplified exposition of the way in which income flows around the economy in exchange
for goods and services between the various sectors that contribute to overall economic activity.
That is, it captures the flow of resources from household to firms and of products from firms to
households.
INJECTIONS:
Additions to the circular flow of income representing any expenditures on domestic goods and
services which originate from outside the household sector, comprising Investment expenditure,
government expenditure and export revenues.
LEAKAGES:
This refers to the part of the National Income that is not spent on households on the consumption
of domestically produced goods and services, comprising savings, taxes and expenditure on
imports, also referred to withdrawals.
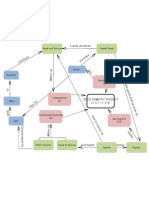
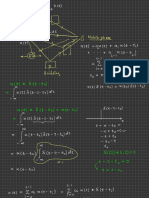
FIGURE
FIGURESHOWING
SHOWINGTHE
THECIRCULAR
CIRCULARFLOW
FLOWOF
OF
INCOME AND EXPENDITURE
INCOME AND EXPENDITURE
Rest of the
Financial System C+I World
)
C)
t (I
n(
en
io
pt 3
)
2
(G
tm
um C
Sa
IM)
+
es
es
s
on s ( X)
vi
I+ ort rts (
as
Inv
C
ng
p
G
ch
Im xpo
E
(S)
ur
tP
Investors 4
en
C+I+
rnm
ve
G + (X – IM)
Consumers
Go
Government
Di
sp
Tran
Firms
os
Taxe rs
5
ab
(produce the
sfe
le
In domestic product)
s
co 6
m )
e e (Y
(D ss
I) Gro Incom
l
Nationa
Important lesson
Factors of production are the inputs into the production process. Land, labor, and capital
are the three key factors of production.
circular flow implies that national income must equal national product
Spending creates revenue, but production creates income. The difference between
domestic production and domestic spending has three pieces: imports (included in
spending, but not part of domestic production), exports (not included in spending, but
part of domestic production), and the net change in business inventories (goods produced
during a year but not sold during that year).
*****
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: University of Technology, JamaicaDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: University of Technology, JamaicaCördïî X Cördïî100% (1)
- IQ Series Installation Manual Part2Document77 pagesIQ Series Installation Manual Part2David MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios 3 Nodos y MallasDocument20 pagesEjercicios 3 Nodos y MallasOrlando FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3altemurcan kursunluNo ratings yet
- DMGT302 Fundamentals of Project Management PDFDocument229 pagesDMGT302 Fundamentals of Project Management PDFNIKHILTJ100% (1)
- Acm - 05 - 02 - 24Document3 pagesAcm - 05 - 02 - 24t82078044No ratings yet
- Ie4 Flta5: F I5:ueDocument2 pagesIe4 Flta5: F I5:ueOwais BhatNo ratings yet
- I Egi: T 306 T 308 T T 309Document6 pagesI Egi: T 306 T 308 T T 309Ervan Malradani HariyantoNo ratings yet
- Nota Pak Anton 2.08 - 9.08Document8 pagesNota Pak Anton 2.08 - 9.08Dkbp SamarindaNo ratings yet
- Gedalge Respuestas 1Document3 pagesGedalge Respuestas 1Samanosuke7ANo ratings yet
- 246 249Document2 pages246 249gtyd0% (1)
- Iner: SideDocument20 pagesIner: SiderbvzpgvqhbNo ratings yet
- GDP Mind MapDocument1 pageGDP Mind MapNora BuchmanNo ratings yet
- DGT Tracks - Technical-WebDocument1 pageDGT Tracks - Technical-WebhiteshNo ratings yet
- DM - Topic 2 - WebsiteDocument25 pagesDM - Topic 2 - WebsiteTài Nguyễn Đức AnhNo ratings yet
- Dictee 14 Sec 3 CorrigeDocument1 pageDictee 14 Sec 3 CorrigeiplanteNo ratings yet
- Pendarvis Suit With ExhibitsDocument26 pagesPendarvis Suit With ExhibitsMyrtleBeachSC newsNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0134 MCQ College Algebra 253Document1 pageIMG - 0134 MCQ College Algebra 253Hnqr584hNo ratings yet
- Calendar ArdennesDocument2 pagesCalendar ArdennesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- DGT Tracks - Managerial-WebDocument1 pageDGT Tracks - Managerial-WebIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- GTF XXX Cor 21016Document48 pagesGTF XXX Cor 21016AlexNo ratings yet
- Golf 7 - Active Info Display Theme Coding - Google SheetsDocument25 pagesGolf 7 - Active Info Display Theme Coding - Google SheetsSonuNo ratings yet
- Simplex Vacuum Selection MatrixDocument1 pageSimplex Vacuum Selection MatrixStefy CarrascoNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0080 MCQ College Algebra 151Document1 pageIMG - 0080 MCQ College Algebra 151bnqr584bNo ratings yet
- Contoh 1.1 Source Code Java Selection Sort: Public Class Int PublicDocument2 pagesContoh 1.1 Source Code Java Selection Sort: Public Class Int Publicnaufal29No ratings yet
- Img 20240417 0002Document2 pagesImg 20240417 0002IPODS Human ResourceNo ratings yet
- ACCT213 F13 Project 3 BergsmaDocument5 pagesACCT213 F13 Project 3 BergsmaDogmanNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of First Order CircuitsDocument13 pagesTransient Response of First Order Circuitsshilpa reddyNo ratings yet
- Pelayanan Ibu Nifas 2017 Erna CompressedDocument2 pagesPelayanan Ibu Nifas 2017 Erna CompressedFitriana MujiningrumNo ratings yet
- VKILLER Player ReferenceDocument10 pagesVKILLER Player Referencesoft tuber555No ratings yet
- VKILLERDocument26 pagesVKILLERsoft tuber555No ratings yet
- Theory of National Income DeterminationDocument50 pagesTheory of National Income DeterminationKunal KunduNo ratings yet
- C1-C5 & C17 PDFDocument19 pagesC1-C5 & C17 PDFMervin LaudeNo ratings yet
- GTF-COR-21016 Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) Intervention Matrix Rev 0, Jun 2021Document48 pagesGTF-COR-21016 Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) Intervention Matrix Rev 0, Jun 2021Milandro Lou AcuzarNo ratings yet
- Rrl?o F ADocument1 pageRrl?o F AAlex BoisteanNo ratings yet
- 数学作业(2,3,4项)Document11 pages数学作业(2,3,4项)buybyuNo ratings yet
- Co Un T) : Shree Amar Kalyan Secondary School, Maijogmai 1 Nayabazar, IlamDocument4 pagesCo Un T) : Shree Amar Kalyan Secondary School, Maijogmai 1 Nayabazar, IlamDB BhandariNo ratings yet
- Gaming CertificateDocument1 pageGaming CertificateJustin Bobby BognotNo ratings yet
- Bešenje - Okružno 2011Document4 pagesBešenje - Okružno 2011Amila ČehićNo ratings yet
- Jawaban IonDocument1 pageJawaban Ionnata0lukytaNo ratings yet
- 6c0 22 02 2023Document12 pages6c0 22 02 2023Nam PhongNo ratings yet
- Horticulture Production Data 2019-20Document7 pagesHorticulture Production Data 2019-20Brijesh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income PPT (Auto Saved)Document16 pagesCircular Flow of Income PPT (Auto Saved)alexander.charmaineNo ratings yet
- Case Study EdFinancial Services Achieves NIST Compliance For Service AccountsDocument2 pagesCase Study EdFinancial Services Achieves NIST Compliance For Service AccountsRadu CostinNo ratings yet
- Img 0010Document1 pageImg 0010bhakti persadaNo ratings yet
- TS-Moving Average - ACF and StationarityDocument1 pageTS-Moving Average - ACF and StationarityzeliawillscumbergNo ratings yet
- Template Quarterly KRADocument5 pagesTemplate Quarterly KRASuba SriramNo ratings yet
- Baumer Product Overview Process Sensors CT en 1509 11148152Document55 pagesBaumer Product Overview Process Sensors CT en 1509 11148152bnn123No ratings yet
- Z Shortcuts Cheatsheet PP AdvancedDocument1 pageZ Shortcuts Cheatsheet PP AdvancedkateNo ratings yet
- Rotary Hybrid Stepping Motor 1.8°: ConventionalDocument2 pagesRotary Hybrid Stepping Motor 1.8°: ConventionalJollygreen21No ratings yet
- Đề 2 MI1124 20222Document9 pagesĐề 2 MI1124 20222tan12t1lhpNo ratings yet
- Hawak KamayDocument4 pagesHawak KamayAnn AligaNo ratings yet
- FichaTecnicaDuosPara JaimeResendizCLAROVSCLARODocument1 pageFichaTecnicaDuosPara JaimeResendizCLAROVSCLARORicardo SalasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document2 pagesLecture 12Ishmam SababNo ratings yet
- SCE Matrix InstructionsDocument4 pagesSCE Matrix InstructionsBrian FinnertyNo ratings yet
- Assembly Projects - Maintenance: Mecha Tronic SDocument8 pagesAssembly Projects - Maintenance: Mecha Tronic SAfter DarkNo ratings yet
- 5 FebDocument11 pages5 FebnhuzoraNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document6 pagesBook 1SanjoysaharoudraNo ratings yet
- Muhammad I RF An: Flat No 102, Saima Grand, Block H' North Nazimabad KarachiDocument1 pageMuhammad I RF An: Flat No 102, Saima Grand, Block H' North Nazimabad KarachiAbid HassaanNo ratings yet
- Manual PetrelDocument394 pagesManual Petrelmhouskal67% (3)
- IR Oise OllutionDocument52 pagesIR Oise OllutionCördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Document7 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and SportDocument13 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and SportCördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #9Document6 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #9Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #8Document13 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Environmental Studies Lecture #8Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Practice Exam: (A) (B) (C) (D)Document9 pagesUnit 1 Practice Exam: (A) (B) (C) (D)Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 4.macro.2017Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 4.macro.2017Cördïî X Cördïî0% (1)
- MsmeDocument17 pagesMsmeshamirun ShahniNo ratings yet
- Post TestDocument7 pagesPost TestKRISTEL CAZANDRA EMPASNo ratings yet
- ADM 2350 Final Exam Winter 2011 Version 1 SolutionsDocument18 pagesADM 2350 Final Exam Winter 2011 Version 1 SolutionsIshan VashishtNo ratings yet
- Final Project: Submitted To: Ma'am Aqsa AkbarDocument45 pagesFinal Project: Submitted To: Ma'am Aqsa AkbarialimughalNo ratings yet
- Outsourcing in The Philippines: YearsDocument16 pagesOutsourcing in The Philippines: YearsarciblueNo ratings yet
- Acct Statement - XX8615 - 21012023Document9 pagesAcct Statement - XX8615 - 21012023NAGIREDDY ROHITNo ratings yet
- Rose Packing Co Vs CADocument6 pagesRose Packing Co Vs CAMalolosFire BulacanNo ratings yet
- Best in Class Practices - Procure To PayDocument31 pagesBest in Class Practices - Procure To PayAmaldev VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Card Number Booklet Number Merchant Outlet Descriptive Outlet NameDocument10 pagesCard Number Booklet Number Merchant Outlet Descriptive Outlet Namepawan soniNo ratings yet
- Bill PDFDocument15 pagesBill PDFJose AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Accounting Sample Paper 2011: QuestionsDocument21 pagesAccounting Sample Paper 2011: QuestionssunlightNo ratings yet
- Easter Seals 37th Annual Golf Tournament Program BookDocument36 pagesEaster Seals 37th Annual Golf Tournament Program BookEasterSealsCapitalRegionNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument2 pagesConclusionNeerajNo ratings yet
- IST 4030A Normalisation ExerciseDocument4 pagesIST 4030A Normalisation ExerciseHuzeifa Musajee100% (1)
- 2012-Noman TextileDocument3 pages2012-Noman TextileShahadat Hossain ShahinNo ratings yet
- PPSCI vs. Equitable PCI BankDocument4 pagesPPSCI vs. Equitable PCI BankAnonymous oDPxEkdNo ratings yet
- CV1 Shubhaditya Choudhary 61920460Document1 pageCV1 Shubhaditya Choudhary 61920460Harmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- XT Ekkamai Teaser GEDocument63 pagesXT Ekkamai Teaser GEChiến NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Commercial BQSDocument47 pagesCommercial BQSStefhanie Khristine PormanesNo ratings yet
- ABM Investama TBK.: Company Report: January 2019 As of 31 January 2019Document3 pagesABM Investama TBK.: Company Report: January 2019 As of 31 January 2019dhiladaikawaNo ratings yet
- Mortgage Payment Calculator - TD Canada TrustDocument3 pagesMortgage Payment Calculator - TD Canada TrustTomura ShigarakiNo ratings yet
- Financial MangementDocument3 pagesFinancial MangementAman JainNo ratings yet
- Procure To Pay CycleDocument20 pagesProcure To Pay CycleKatie RuizNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash - Exercise 1 (Solution)Document10 pagesAudit of Cash - Exercise 1 (Solution)Aby ReedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4hassan19951996hNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations For Quantitative Finance 9813202475 9789813202474 - CompressDocument222 pagesTheoretical Foundations For Quantitative Finance 9813202475 9789813202474 - CompressLynaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 Gov Grant, Borrowing, Forex (Q) - MergedDocument24 pagesTutorial 7 Gov Grant, Borrowing, Forex (Q) - MergedKelvin Chu JYNo ratings yet
- Tax InvoiceDocument4 pagesTax InvoiceMohamed Farook FarookNo ratings yet