Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alliah A. Molano BSA Mathematics Symbols and It'S Function
Alliah A. Molano BSA Mathematics Symbols and It'S Function
Uploaded by
alliah molanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alliah A. Molano BSA Mathematics Symbols and It'S Function
Alliah A. Molano BSA Mathematics Symbols and It'S Function
Uploaded by
alliah molanoCopyright:
Available Formats
Alliah A.
Molano
BSA
MATHEMATICS SYMBOLS AND IT’S FUNCTION
Mathematics or math is considered to be the language of science, vital to understanding and explaining science
behind natural occurrences and phenomena. It also happens to be one of the most dreaded subjects of most students the
world over. Utter the word mathematics and even grown ups are known to shudder at the mere mention of it! We shall not
delve into the reasons for this, but the variety of symbols used in equations also happen to add to the dread. Each branch
of mathematics has its own special symbols that represent a particular concept. Thus, it is necessary for you to at least
have a ready reference list of these conventions so that you don't mistake one for the other.
We have put forth a consolidated list of all the symbols used in various branches of mathematics. So, the next
time you try to solve any math problem, you will at least know what the notations stand for!
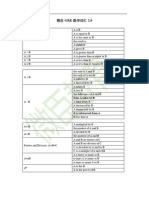
Name Symbols Meaning/Function
Plus + It signifies addition of values.
Minus - It symbolizes subtraction of values.
Multiplication x or * It signifies multiplication of values.
Division ÷ or / It denotes division of values.
Equals = It signifies two sides are equal.
Not Equal ≠ It denotes two sides are unequal.
Greater than > It shows one value is greater than the
other.
Less than < It implies one value is less than the
other.
Less than or equal to ≤ It indicates one value is less than or
equal to the other.
Greater than or equal to ≥ It symbolizes one value is greater
than or equal to the other
Plus-minus/ Minus-Plus It denotes, the value can be both plus
± and minus.
Brackets [] It indicates calculation of the
equation inside it should be carried
out first.
Parentheses () It implies calculation of the equation
inside it should be carried out first.
Exponent
a^b, ab It signifies the number of times the
number is used in multiplication.
Square root It symbolizes the value that can be
√a multiplied by itself to give the
original number.
Cube root It gives the value that can be
3
√a multiplied by itself three times to
give the original number.
Fourth root It is the value that can be multiplied
4
√a by itself four times to give the
original number.
Nth root (radical) It shows the value that can be
n
√a multiplied by itself n times to give
the original number.
Percent % It signifies ratio expressed as a
fraction of 100.
Per-mille It symbolizes number of parts per
‰ thousand.
Per-million ppm It indicates number of parts per
million.
Per- billion ppb It signifies number of parts per
billion.
Per-trillion ppt It symbolizes number of parts per
trillion.
Geometric Symbols
Angle It indicates the figure formed by two
∠ rays.
Measured Angle It signifies the angle whose value is
known.
Right Angle It indicates the angle that bisects the
∟ angle formed by two straight lines.
Spherical Angle It symbolizes the angle between two
intersecting arcs of a sphere.
Degree It indicates the measurement of plane
deg, ° angle representing one full rotation.
Line It shows the straight line with
negligible width and thickness.
Line segment AB It signifies the part of line with definite
start and endpoints.
Ray It indicates the line with start point but
no endpoint.
Arc It signifies the part of circumference of
circle or a curve.
Perpendicular It symbolizes lines that are at right
⊥ angles to each other.
Congruent It symbolizes the objects with similar
≅ geometric shape and size.
Parallel It indicates the lines that are
|| equidistant from each other.
Similarity It signifies objects with similar shape
~ but not similar size.
Triangle It indicates polygon with three vertices
Δ and three line segments as edges.
Distance It symbolizes the distance between the
|x-y| points x and y.
Grads Grad It symbolizes the unit of plane angle
measurement and is equal to 1/400 of 1
turn (360 deg).
Pi It gives the ratio between
Π circumference and diameter of a circle.
Radians Rad It signifies the unit of angle
measurement.
Algebra Symbols
Equivalence It indicates variables having same or
≡ identical value.
X variable It signifies an unknown value.
X
It symbolizes equality by definition It symbolizes equality by definition.
≜, :=
Proportional It signifies changes in variables that are
∝ always related to each other, using a
constant.
Approximation It symbolizes variables that are
≈ approximately equal to each other.
Weak approximation It signifies variables that are weakly
~ similar to each other.
Factorial It signifies the product of all integers
n! less than or equal to n.
Lemniscate/ Infinity symbol It indicates a variable without any limit.
∞
Much greater than It indicates one variable is much greater
≫ than the other.
Much less than It symbolizes one variable is much less
≪ than the other.
Ceiling Brackets It indicates rounding the variable value
⌈x⌉ to higher integer.
Floor Brackets It refers rounding the variable value to
⌊x⌋ lower integer.
Function of It defines one variable in relation to the
f (x) other.
Absolute value It gives a non-negative value of x,
| x | ignoring its sign.
Capital pi It gives product of all values in the
∏ specified range.
Closed interval It gives the interval with specified end
[a,b] points.
Function composition It combines functions such that output
(f ∘ g) from function becomes input for the
other function.
Open interval It symbolizes interval has no limits, i.e.,
(a,b) without any end points.
Delta It refers to change or difference in
∆ values.
Discriminant It gives the nature of roots for a
∆ quadratic equation.
Sigma (Summation) It refers to summation of all values in
∑ the specified range.
Double Summation It signifies summation of values in two
∑∑ ranges.
Euler-mascheroni constant The constant is equal to 0.527721566...
γ
E-constant/ euler’s number Its value is equal to 2.718281828...
e
Golden ration constant It indicates ratio of two variables
φ should be equal to the ratio of their sum
to the larger of the two variables.
Linear Algebra Symbols
Cross product (Vector) X It refers to multiplying magnitudes of
vectors and sin of angle between them.
Dot Product (Scalar) It signifies multiplying magnitudes of
vectors and cosine of angle between
them.
Brackets [] It indicates rectangular array of
numbers arranged in rows and
columns.
Determinant It gives the value associated with a
| A | square matrix.
Norm It assigns positive length (size) to each
|| x || non-zero vector in space.
Inverse Matrix A-1 It symbolizes the matrix whose
multiplication with the original matrix
is an identical matrix.
Transpose At It refers to the matrix formed by
replacing rows of the given matrix
with columns and vice versa.
Hermitian matrix A+ A* It signifies matrix with complex
entries where the i-th row and j-th
column is equal to complex conjugate
of j-th row and i-th column.
Dimension Dim (U) It gives the number of rows and
columns of the matrix, written as rows
x columns.
Matrix Rank Rank (A) It indicates the number of non-zero
rows (or columns) in the reduced
matrix.
Probability & Statistics Symbols
Probability Function It signifies the likeliness of the
P(A) occurrence of the event A.
Probability density function Integral of function of a continuous
random variable gives the probability
f(x) that the value of the variable lies in the
given interval.
Union It denotes the probability of occurrence
P(A ∪ B) of events A and B
Intersection It denotes the probability of occurrence
P(A ∩ B) of events A or B.
Conditional probability function It denotes the probability of occurrence
P(A | B) of event A when event B has occurred.
Cumulative distribution function It denotes the probability that random
F(x) variable X takes a values less than or
equal to x.
Expectation value It denotes the expected value of
E(X) random variable X.
Population mean It denotes the arithmetic mean of the
μ population while considering each
member of the population.
Variance It expresses the spread of numbers of a
var(X) given set.
Conditional expectation It denotes the expected value of
E(X | Y) random variable X when the variable Y
is given.
Standard Deviation It denotes the variation from the
std(X), σX existing average value.
Standard Score It indicates the number of standard
zx deviations a variable is from the mean.
Covariance It measures how much two random
cov(X,Y) variables, X and Y, change together.
Median It denotes the middle value of random
variable X.
Correlation It denotes the statistical relationship
corr(X,Y), ρX,Y between two random variables, X and
Y.
Mode It signifies the most frequently
Mo occurring value in the given set.
Mid-range It signifies the arithmetic mean
MR between the maximum and minimum
value of the set.
Sample Median It denotes the average of all the values
Md of a given set.
First Quartile It denotes the 25th percentile of the
Q1 given set data.
Second Quartile It denotes the median of the given set.
Q2 It denotes the 75th percentile of the
given set data
Sample mean It signifies the average of the given
X set ; the sum of the set divided by
number of entries in the set.
Sample standard deviation It indicates the standard deviation of
s the data set in the chosen sample size
Sample Variance S2 It indicates the variance of the data set
in the chosen sample size.
Bernoulli distribution Bern(p) It denotes the theoretical distribution of
number of successes in a finite data set
with constant probability of successes.
Distribution of x It indicates the distribution of random
X ~ variable X.
Uniform distribution U(a,b) It indicates the probability that each
value in the given data set has equal
interval length in the given range from
a to b.
Normal Distribution N(μ,σ2) It indicates the probability of an
observation falling between two real
numbers.
Exponential Distribution exp(λ) It signifies probability distribution
which describes time between
continuously occurring events at a
constant average rate.
Gamma Distribution gamma(c, It denotes the continuous two-
parameter distribution from which chi-
square and exponential distributions
are derived.
Chi-squared distribution χ 2(k) It signifies the distribution of sum of
squares of k independent standard
normal random variable.
F Distribution F (k1, k2) It denotes probability distribution
function, which is a ratio of two
independent random variables.
Binomial Distribution Bin(n,p) It denotes the discrete probability
distribution of the number of successes
in n number of experiments, where
each success is yielded by probability
p.
Geometric Distribution Geom(p) It signifies the negative binomial
distribution which is used to find out
the number of failures before single
success.
Hyper Geometric Distribution HG(N,K,n) It is used to calculate random selection
of a variable without repetition.
Combinatorics
Combination It indicates the possible arrangement of
things without any particular order.
nCk
Permutation It signifies the possible arrangement of
nPk things in a particular order
Set Theory
Intersection It indicates objects that belong to both
A∩B sets, A and B.
Set It signifies the collection of distant
{} elements.
Union It refers to objects that belong to either
A∪B set A or set B.
Subset It signifies few elements in the subset
A⊆B A are similar to the elements in set.
Not Subset It signifies that A is not a subset of the
A⊂B set B.
Proper subset It indicates that subset A has fewer
A⊄B elements than the set B.
Superset It symbolizes that set A has more or
A⊇B equal elements than set B.
Proper Superset A⊃B It indicates that set A has more
elements than set B.
Compliment Ac It represents objects that do not belong
to set A.
Equality A=B It signifies that sets A and B have same
elements.
Symmetric difference A ∆ B, A ⊖ B It indicates objects that belong to both
sets A and B but not to their
intersection.
Relative complement A\B It refers to objects that belong to set A
but not to set B.
Element of It symbolizes that a is an element of set
a∈A A.
Not element of It indicates that x is not an element of
x∉A set A.
Cartesian product It gives the product of two sets.
A×B
Ordered pair It represents collection of elements of a
(a,b) set in a particular order.
Aleph-null It indicates infinite cardinality (number
of elements of a set) of natural numbers
set.
Aleph-one It signifies cardinality (number of
elements of a set) of countable ordinal
(well ordered) numbers set.
Universal set It represents set having all possible
values.
Empty set It refers to set having no elements.
Ø
Integer numbers set It indicates set of integer numbers.
Natural/whole numbers set 0
It refers to set of whole/natural
numbers with zero.
Complex numbers set It represents set of complex numbers.
Real numbers set It refers to set of real
Cardinality It signifies the number of elements in
|A| set A.
Logic
And It signifies logical conjunction where
two true operands can only produce a
^, & true value. . Or It signifies
logical disjunction where two false
operands produce a false value.
Exclusive or (XOR) It denotes exclusive disjunction where
either of the operands should be true to
return a true value.
Not-negation It indicates negation of the given
value.
Equivalent It denotes material equivalence where
⇔ true value is returned only when both
operands are true or false.
Implies It indicates material implication where
⇒ true value is returned only if either of
the operand is true or false.
There does not exist It indicates existential quantification
∄ where function of the operand is true
only for one value of operand.
There exists It indicates existential quantification
∃ where function of the operand is true
only for one value of operand.
Because/since It is placed before a logical sequence
∵ indicating assumption or reason.
Therefore It is placed before a logical sequence
∴ indicating conclusion of the required
operation.
For all It signifies universal quantification
∀ where function of the operand is true
for all values of the operand.
Calculus Symbols
Epsilon It represents a very small number
ε nearing zero.
Limit It denotes the value that function
approaches when input approaches
specified value.
Derivative It indicates change in the function
y ' when the input values change.
Second derivative It returns a value which is the
y '' derivative of the derivative of the
given function.
Time derivative It indicates change in the function
with respect to change in time.
Nth Derivative It returns a value which is calculated
by deriving the given function for n
times.
Integral It refers to antiderivative, and is the
∫ signed area of a region which is
bounded by graph (definite integral).
Partial Derivative It denotes the value that is obtained by
calculating derivative with respect to
one variable, while other variables are
constant.
Triple integral It denotes the integration of a function
∫∫∫ of three variables.
Double integral It denotes the integration of a function
∫∫ of two variables.
Imaginary unit It indicates the square root of -1.
I
Closed contour / line integral It denotes the integral of a function
∮ evaluated along a curve, i.e., with
respect to arc length.
Complex conjugate It indicates the pair of complex
numbers with same real part and
z*, z imaginary part with equal magnitude
but opposite signs.
Nabla / del It denotes the gradient and vector
∇ derivatives.
Unit vector It signifies a vector with magnitude 1.
Vector It indicates quantity with magnitude
and direction.
Convolution It defines the integral of product of
x * y two functions when one function is
reversed and shifted.
Delta function It is defined as the limit of a class of
δ delta sequences.
Fourier transform It signifies the transformation of
signals into time and frequency
domains.
Laplace transform It indicates the linear operator of
function f which transforms.
You might also like
- HW 7Document7 pagesHW 7C FNo ratings yet
- Alliah A. Molano BSA Mathematics Symbols and It'S FunctionDocument10 pagesAlliah A. Molano BSA Mathematics Symbols and It'S Functionalliah molanoNo ratings yet
- Math Vocab To KnowDocument3 pagesMath Vocab To Knowapi-262631905No ratings yet
- Real Number Sys-WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesReal Number Sys-WPS OfficeCali Shandy H.100% (1)
- 6th Grade Math VocabularyDocument4 pages6th Grade Math Vocabularyapi-518569859No ratings yet
- Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division EqualityDocument1 pageAddition Subtraction Multiplication Division EqualityIsmail Medhat SalahNo ratings yet
- Abstraction and SymbolsDocument14 pagesAbstraction and Symbolsflynn riderNo ratings yet
- Algebra Hand 0utsDocument8 pagesAlgebra Hand 0utsmary christy mantalabaNo ratings yet
- Character SetsDocument2 pagesCharacter Setshappy kumarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in EnglishDocument17 pagesMathematics in EnglishMihaela IlașNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Symbols List PDFDocument14 pagesMathematical Symbols List PDFAhmed Zezo100% (2)
- Mathematical Symbols ListDocument14 pagesMathematical Symbols ListAhmed ZezoNo ratings yet
- PD.1.Introduction To AlgebraDocument45 pagesPD.1.Introduction To AlgebraRaihan Putri100% (1)
- Math Symbols Are Shorthand Marks That Represent Mathematical ConceptsDocument2 pagesMath Symbols Are Shorthand Marks That Represent Mathematical ConceptsDave100% (3)
- in MathDocument32 pagesin MathRICHELLE EVORANo ratings yet
- Decimals Comp PacketDocument33 pagesDecimals Comp Packetapi-235199292No ratings yet
- t2 M 4551 Year 6 Maths Vocabulary Word Mats - Ver - 2Document17 pagest2 M 4551 Year 6 Maths Vocabulary Word Mats - Ver - 2kubashaniNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Symbols List (+,-,X, - , , - , - ,... )Document17 pagesMathematical Symbols List (+,-,X, - , , - , - ,... )Sachin KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Language and SymbolsDocument8 pagesMathematics of Language and SymbolsLucy CalilanNo ratings yet
- Algebra Hand 0utsDocument9 pagesAlgebra Hand 0utsKRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- Intro To Python ProgrammingDocument4 pagesIntro To Python Programmingyahia farouqNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document8 pagesCH 1Mohamed AbdalhakamNo ratings yet
- ZJsy OEDocument9 pagesZJsy OEnazias891No ratings yet
- Module 1-Mathematics As A Language: Maribel D. Cariñ0Document4 pagesModule 1-Mathematics As A Language: Maribel D. Cariñ0KhalidNo ratings yet
- Lecture College AlgebraDocument9 pagesLecture College AlgebraGamer's GroundNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade CCSS Math Vocabulary Word ListDocument10 pages4th Grade CCSS Math Vocabulary Word ListtizuliveNo ratings yet
- Mathematics TermsDocument11 pagesMathematics TermsTangkas PangestuNo ratings yet
- Math Bridging TransesL1Document6 pagesMath Bridging TransesL1Ara Belle PonceNo ratings yet
- Math Symbols List (+,-,X, - , ,... )Document14 pagesMath Symbols List (+,-,X, - , ,... )Stacey PocongNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE AND SYMBOLS. (Part 1)Document4 pagesMATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE AND SYMBOLS. (Part 1)Ronaldo RamosNo ratings yet
- Math SymbolsDocument36 pagesMath SymbolsTina Timmons100% (3)
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument3 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsHyacinth MartinezNo ratings yet
- Pre-Algebra FormulasDocument16 pagesPre-Algebra FormulasSipho MpisaneNo ratings yet
- Licensure Examination For Teachers General Education - MathematicsDocument31 pagesLicensure Examination For Teachers General Education - MathematicsJhay B. MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Math Word BankDocument2 pagesMath Word BankelariaattiaNo ratings yet
- TermsDocument2 pagesTermsReynaldo AldamarNo ratings yet
- New Words Meaning New Words Meaning Rational Numbers Power of 10 Any of The Whole Valued Exponents of The Number 10Document3 pagesNew Words Meaning New Words Meaning Rational Numbers Power of 10 Any of The Whole Valued Exponents of The Number 10Tung thoe NguyenNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers - Integers & DecimalsDocument34 pagesRational Numbers - Integers & DecimalsbozicaNo ratings yet
- Useful Mathematics Symbols Useful Mathematics Symbols: 2 4 X y X yDocument1 pageUseful Mathematics Symbols Useful Mathematics Symbols: 2 4 X y X yGwynn Charlance PedralbaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 The Language of MathematicsDocument25 pagesUnit 2 The Language of MathematicsRandolf Byron S. VirayNo ratings yet
- 2015 Iut MathDocument2 pages2015 Iut MathNodirbek SobirjonovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solving Linear EquationsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Solving Linear EquationsNina HNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-MMWDocument40 pagesChapter 2-MMWCarlaMaeMaquirangNo ratings yet
- Edilcia Guerra 1Document1 pageEdilcia Guerra 1api-533506683No ratings yet
- CLASS VII - Operations On Rational NumbersDocument25 pagesCLASS VII - Operations On Rational NumbersAbhijit PatraNo ratings yet
- Math HandbookDocument24 pagesMath HandbookMariama BooneNo ratings yet
- Edsc 304 - Student Example Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageEdsc 304 - Student Example Graphic Organizerapi-376816152No ratings yet
- Chapter P Prerequisites: Operations With Real NumbersDocument15 pagesChapter P Prerequisites: Operations With Real NumbersAnisaPratiwiArumningsihNo ratings yet
- FractionsnotessheetDocument2 pagesFractionsnotessheetapi-293306021No ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Maths Linear Exam Topic List - HIGHER NumberDocument24 pagesEdexcel GCSE Maths Linear Exam Topic List - HIGHER NumberkaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Learning OutcomesDocument55 pagesGrade 9 - Learning OutcomesMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Revit Families Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesRevit Families Cheat SheetCláudia MarquesNo ratings yet
- Examples of Mathematical PhrasesDocument1 pageExamples of Mathematical PhrasesCelhes de leonNo ratings yet
- Common Math Symbols: + Addition, Plus, PositiveDocument7 pagesCommon Math Symbols: + Addition, Plus, PositivePRINCESS GAY AGDUYENGNo ratings yet
- Algebra Vocab ListDocument1 pageAlgebra Vocab ListSally WangNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed MathematicsDocument28 pagesGen Ed MathematicsVe Jay Angela Guimte0% (1)
- 微臣GRE数学词汇2 0Document10 pages微臣GRE数学词汇2 0xueqiyao40No ratings yet
- English For Students 1Document4 pagesEnglish For Students 1indaNo ratings yet
- Find + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Document3 pagesFind + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Pherngy CadanoNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Algebraic Expressions - Class 8Document10 pagesCH 12 Algebraic Expressions - Class 8Aditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Draft Resolution 1.2 - CyberterrorismDocument8 pagesDraft Resolution 1.2 - CyberterrorismNimra Afzal100% (4)
- Calculating The International Runway Friction Index: Standard Practice ForDocument5 pagesCalculating The International Runway Friction Index: Standard Practice ForDannyChaconNo ratings yet
- Building An Innovation CultureDocument21 pagesBuilding An Innovation CultureMainford MutandavariNo ratings yet
- CET324 - Advanced Cyber Security Assignment 2Document12 pagesCET324 - Advanced Cyber Security Assignment 2Prince P AppiahNo ratings yet
- Kuliah3 Kinetika-Katalis-Heterogen 2020Document33 pagesKuliah3 Kinetika-Katalis-Heterogen 2020Rasyid SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk6 - Collecting and Analyzing InformationDocument3 pagesModule - Wk6 - Collecting and Analyzing Informationaudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument321 pagesUntitledSumonto Mehedi (Adnan)No ratings yet
- Shell Omala S2 GX 100 TDSDocument2 pagesShell Omala S2 GX 100 TDSEdgar Leonel CortésNo ratings yet
- Weston TV... Ever Wondered What Happened To It? It Is Back in The Market and Doing Brisk Business in A Redefined Business ModelDocument6 pagesWeston TV... Ever Wondered What Happened To It? It Is Back in The Market and Doing Brisk Business in A Redefined Business ModelNiveshakBharat TalksNo ratings yet
- A4 Nur Fatihah Binti Mat AhirDocument6 pagesA4 Nur Fatihah Binti Mat AhirNur FatihahNo ratings yet
- 000-Jet pumps-EN-220907-webDocument8 pages000-Jet pumps-EN-220907-webalicardozoNo ratings yet
- Final Resume EditDocument2 pagesFinal Resume EditPratik PaudelNo ratings yet
- SOP For Reduce Testing For Raw MaterialDocument3 pagesSOP For Reduce Testing For Raw MaterialMubarak Patel67% (3)
- Junniper - MX480Document560 pagesJunniper - MX480BetoNo ratings yet
- Session1 - Introduction To Data ScienceDocument44 pagesSession1 - Introduction To Data ScienceRhisa Adika PutriNo ratings yet
- Resume - Manas Kumar Latest AugustDocument3 pagesResume - Manas Kumar Latest AugustManas PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Solar PV 6-InverterDocument25 pagesSolar PV 6-Inverternebex12No ratings yet
- 1.LA BIBLIA de LA COSTURA - Compressed (1) .PDF Versión 1Document232 pages1.LA BIBLIA de LA COSTURA - Compressed (1) .PDF Versión 1ganso4596No ratings yet
- User Manual SR X2000 HDDocument49 pagesUser Manual SR X2000 HDAnonymous tVTE9xUca100% (1)
- Block 3 PDFDocument39 pagesBlock 3 PDFop marwalNo ratings yet
- Anglais ExposeDocument2 pagesAnglais ExposeKonan Armel KobenanNo ratings yet
- PM-DM/DMR / Pm-2Dm/2Dmr: Digital MultimetersDocument2 pagesPM-DM/DMR / Pm-2Dm/2Dmr: Digital MultimeterstonielhageNo ratings yet
- Air Core ToroidDocument10 pagesAir Core ToroidChandra ShettyNo ratings yet
- Coupling CatalogDocument84 pagesCoupling CatalogTuan buivietNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument7 pagesResearch ProposalGrace MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Astm d86Document27 pagesAstm d86ahmedNo ratings yet
- Colorado Rental Application FormDocument5 pagesColorado Rental Application FormMichelle TaylorNo ratings yet
- 3500 50M DatasheetDocument12 pages3500 50M Datasheetathmane ararNo ratings yet
- SW15-Labeling Application Operation Manual - A2.17 - en (A5) PDFDocument24 pagesSW15-Labeling Application Operation Manual - A2.17 - en (A5) PDFVirlan RodionNo ratings yet