Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Auditing and Assurance Principles
Auditing and Assurance Principles
Uploaded by
Karla Alconis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views4 pagesThe document provides an overview of auditing and assurance principles. It discusses that financial statements are produced by accountants and audited by independent auditors to determine if they are fairly presented. The auditor obtains sufficient evidence following auditing standards to form an audit opinion on whether the financial statements comply with accounting standards. The audit opinion is the final output and provides intended users assurance on the reliability of the financial information.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of auditing and assurance principles. It discusses that financial statements are produced by accountants and audited by independent auditors to determine if they are fairly presented. The auditor obtains sufficient evidence following auditing standards to form an audit opinion on whether the financial statements comply with accounting standards. The audit opinion is the final output and provides intended users assurance on the reliability of the financial information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views4 pagesAuditing and Assurance Principles
Auditing and Assurance Principles
Uploaded by
Karla AlconisThe document provides an overview of auditing and assurance principles. It discusses that financial statements are produced by accountants and audited by independent auditors to determine if they are fairly presented. The auditor obtains sufficient evidence following auditing standards to form an audit opinion on whether the financial statements comply with accounting standards. The audit opinion is the final output and provides intended users assurance on the reliability of the financial information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
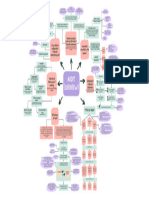
AN OVERVIEW ON THE AUDITING AND ASSURANCE
PRINCIPLES
Financial Statements are the final output of Accountants
The report of the external auditor is anchored on the final output of the accountant which is
the financial statements.
How will you know that financial statements are fairly presented – no bias; objective?
We should not only rely what the accountants say as users of financial reports. Primary
users are very concern on the financial statements because they have to make an
economic decision.
FS are fairly presented if it complies with all the requirements and provisions of the
accounting standards (PFRS) unless otherwise, immaterial (will not affect the economic
decision making).
Independent / External Auditor
Is not affiliated with the company. He / she is an independent body that will verify if
financial statements comply to the accounting standards.
His/her primary purpose is to give an opinion whether the financial statements are fairly
presented or not.
It is not their primary purpose to discover fraud because it comes along the way. There is a
separate engagement regarding fraud audit. The scope ng independent audit is the
fairness of FS and its compliance on the standards.
Audit Opinion / Audit Report
It is the auditor’s final output.
After all the procedures done by the independent auditor, he/she will make an audit opinion
and it is important for it to be seen by users of financial statements being attached to it
certifying that it is fairly presented in all material respect.
Audit
It is a systematic process. You are just like investigating to have a conclusion. Before an
auditor can give an audit opinion, he/she will go through a systematic process first because
there is what we call the Philippine Standards on Auditing (PSA)
The auditor must have a Sufficient Appropriate Evidence
Sufficient – you need to have the correct number or quantity of documents.
Appropriate – you need to have the right documents ; this pertains to the quality of
the evidence.
Evidences – contract, invoices and other kinds of supporting documents
BY DEFAULT, FINANCIAL STATEMENTS ARE FAIRLY PRESENTED BECAUSE EVERYONE
IS CONSIDERED TO BE INNOCENT UNLESS OTHERWISE PROVEN.
We just need to check in order to verify if it complies to the PFRS. You need to know the
applicable accounting standards and its provisions. You need to know the Philippine Standards
on Auditing so that you will know the recommendations. Clients are more concerned regarding
the tax so even though you are not expert, you need to learn it and be expert, making it the
reason why we are learning law. We need to know those kinds of laws because it will affect the
FS presentation.
INTRODUCTION TO AUDITING AND ASSURANCE PRINCIPLES
AND CONCEPTS
Introduction to Assurance Engagement
Assurance
guarantee ; it refers to practitioner’s (Independent CPAs, Auditor, Practicing Accountant)
satisfaction as to the reliability of an assertion (management representation just like the
accountant telling that financial statements are fairly presented) being made by one party
for the use of another party.
Three parties engaged:
Practitioner – should be satisfied on the reliability being claimed by the management. The
role of the practitioner is to make a conclusion or opinion regarding the reports if it is
clearly presented so that the intended users will be confident to use them in making
economic decisions (has something to do with the financial) because someone checked it
(check and balance). They engage to give conclusion regarding the reliability and fair
presentation of FS to increase the confidence level of intended users.
Management
Another Party – the party who will make an economic decision
Assurance Engagement or Services
It is an engagement where the practitioner expresses conclusion. It is designed to enhance
the degree of confidence of the intended users (other than responsible party). It is about
the outcome of the evaluation or measurement of a subject matter (Financial Report)
against a criteria (PAS / PFRS).
Auditor should be knowledgeable regarding the criteria.
AUDITING IS AN ASSURANCE ENGAGEMENT BECAUSE IT GIVES CONCLUSION. IT IS
JUST ONE ENGAGEMENT UNDER ASSURANCE
Objective of Assurance Engagements or Services
It is to evaluate or measure the subject matter (Financial Statements) that is responsibility
of another party (management running the company) against identified suitable criteria
(PFRS) and express a conclusion that provides the intended user with level of assurance
about the subject matter.
Auditors should be confident enough that the intended users made a correct economic
decision since someone checked it and evaluated the FS and it is reliable. Balance of the
financial statements shoukd be checked. That is the concept of assurance and auditing.
Elements of Assurance Engagement
Three party relationship (practitioner, responsible party and intended users)
This is unlike the non-assurance engagement – an engagement wherein one does not
need to give a conclusion or opinion. Two party relationship (practitioner and
responsible party) since it is more on internal
Appropriate subject matter – may ginagawa na report na chinecheck ni practitioner.
Suitable Criteria – Accounting standards , PFRS
Sufficient Appropriate Evidence and;
Written Assurance Report (Conclusion) in the form to:
Reasonable Assurance Engagement – example is auditing
Limited Assurance Engagement – hindi full blown procedures, kapag review
engagement lang
There is no 100 % assurance / guarantee
You might also like
- Assurance NotesDocument15 pagesAssurance NotesampriestNo ratings yet
- Concepts of AuditDocument4 pagesConcepts of AuditMarilou BonaguaNo ratings yet
- Auditing ReviewerDocument8 pagesAuditing ReviewerHana DoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Audit f8 - 2.3Document25 pagesChapter 1 Audit f8 - 2.3JosephineMicheal17No ratings yet
- Notes and ReviewerDocument1,116 pagesNotes and ReviewerJeric Ramos De LeonNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Audit NOTESDocument65 pagesGeneral Principles of Audit NOTESHanna Sobreviñas AmanteNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Audit NOTESDocument44 pagesGeneral Principles of Audit NOTESHanna Sobreviñas AmanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter#2 True and Fair View: Assurance EngagementsDocument4 pagesChapter#2 True and Fair View: Assurance EngagementsArham khanNo ratings yet
- Discussion From MiriamDocument68 pagesDiscussion From MiriamHeidi OpadaNo ratings yet
- Aaa Topic 1Document8 pagesAaa Topic 1Cindy ClollyNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document8 pagesCH 02Jolina I. BadoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesABIGAIL DAYOTNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesPeter BanjaoNo ratings yet
- Review and Audit AssuranceDocument6 pagesReview and Audit AssuranceReg DungcaNo ratings yet
- Audit Chapter 1Document3 pagesAudit Chapter 1Aitzaz UddinNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 AaaDocument5 pagesTopic 1 AaaIsaac OsoroNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Audit An OverviewDocument17 pagesCH1 - Audit An Overviewjaypee.bignoNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance EngagementDocument36 pagesAudit and Assurance EngagementHillary MageroNo ratings yet
- Class Synopsis-01Document5 pagesClass Synopsis-01zangzop5No ratings yet
- Practice of Public AccountancyDocument50 pagesPractice of Public AccountancyLaezelie PalajeNo ratings yet
- Test 1 7ddDocument94 pagesTest 1 7ddMbadilishaji DuniaNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument35 pagesQuestionsHeart SebNo ratings yet
- Summary Book Modules Louwers Et AlDocument7 pagesSummary Book Modules Louwers Et AlWendy KluijtNo ratings yet
- 20 AIS 044, Tonmoy DebnathDocument4 pages20 AIS 044, Tonmoy Debnathtanmoydebnath474No ratings yet
- CH 1 (Audit)Document14 pagesCH 1 (Audit)UmerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AuditingDocument12 pagesIntroduction To AuditingJahnavi BadlaniNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument13 pagesAuditingRamos JovelNo ratings yet
- Audit OverviewDocument17 pagesAudit OverviewAnson Dy100% (1)
- Advanced Auditing CH 1Document40 pagesAdvanced Auditing CH 1mirogNo ratings yet
- Audit ProjectDocument23 pagesAudit ProjectPriyanka KhotNo ratings yet
- AUDITINGDocument13 pagesAUDITINGGrace AlolorNo ratings yet
- Assignment of AuditingDocument8 pagesAssignment of AuditingMrinal BishtNo ratings yet
- Index: SR - No. Particulars SignatureDocument20 pagesIndex: SR - No. Particulars SignatureMohammedAhmedRazaNo ratings yet
- Mod 1Document15 pagesMod 1Marie claire Delos santosNo ratings yet
- ABS-LECTURE 1 (Nature & Issues of Audit)Document57 pagesABS-LECTURE 1 (Nature & Issues of Audit)Lordwin ArcherNo ratings yet
- Chapter One An Overview of AuditingDocument9 pagesChapter One An Overview of AuditingMulatu LombamoNo ratings yet
- Sabid - MC Neill - Bsma - 4 - I Am Lost! I Know I UnderstandDocument11 pagesSabid - MC Neill - Bsma - 4 - I Am Lost! I Know I UnderstandMC NEILL SABIDNo ratings yet
- Auditing Tutorial Sheet 1Document5 pagesAuditing Tutorial Sheet 1Isaac PortelliNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Principles: Prof. Zeus A. Aboy, CPA MBA EDL (Candidate)Document26 pagesAuditing and Assurance Principles: Prof. Zeus A. Aboy, CPA MBA EDL (Candidate)Io AyaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Lec 1Document6 pagesAuditing Lec 1muhammad sulemanNo ratings yet
- PSA 120, PSA 200, AND Attestation Audit ACCTG 4110: Agreed Upon-ProceduresDocument12 pagesPSA 120, PSA 200, AND Attestation Audit ACCTG 4110: Agreed Upon-ProceduresMC NEILL SABIDNo ratings yet
- Aguanta Princess Nicole Allyson 01 JournalDocument4 pagesAguanta Princess Nicole Allyson 01 JournalNicole Allyson AguantaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Reading MaterialDocument58 pagesAuditing Reading MaterialSnn News TubeNo ratings yet
- Aguanta Princess Nicole Allyson 02 JournalDocument3 pagesAguanta Princess Nicole Allyson 02 JournalNicole Allyson AguantaNo ratings yet
- Pre Test - Communication of Audit ResultsDocument2 pagesPre Test - Communication of Audit ResultsSHARMAINE CORPUZ MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet - Module 2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet - Module 2Elisabeth HenangerNo ratings yet
- The Following Are The Journal Questions For This ModuleDocument4 pagesThe Following Are The Journal Questions For This ModuleJane DizonNo ratings yet
- Continuation in Auditing OverviewDocument21 pagesContinuation in Auditing OverviewJayNo ratings yet
- 01 JournalDocument5 pages01 Journalits me keiNo ratings yet
- Auditing & Assurance Principles-Lesson 1Document12 pagesAuditing & Assurance Principles-Lesson 1Joe P PokaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Concept of Audit and Other Assurance Engagements Part 1Document7 pagesLesson: Concept of Audit and Other Assurance Engagements Part 1Marielle UyNo ratings yet
- Audit ReportsDocument6 pagesAudit ReportsM. JAHANZAIB UnknownNo ratings yet
- AUDITING PRINCIPLES I - NotesDocument69 pagesAUDITING PRINCIPLES I - Notesyebegashet100% (1)
- At - Overview ReadDocument3 pagesAt - Overview ReadDavidCruzNo ratings yet
- Audit 0 Investigation Presentation Module 1 To 3Document72 pagesAudit 0 Investigation Presentation Module 1 To 3Bashiir GelleNo ratings yet
- CRR BK 5thed.2015 10.27Document402 pagesCRR BK 5thed.2015 10.27Ching RasalanNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics/MB/CAP II/AOC: Assurance Provided by AuditDocument17 pagesCode of Ethics/MB/CAP II/AOC: Assurance Provided by AuditMandeep BashisthaNo ratings yet
- Audit Framework and RegulationDocument16 pagesAudit Framework and RegulationTousif Galib100% (2)
- Module 2 - Introduction To FS AuditDocument5 pagesModule 2 - Introduction To FS AuditLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- Finance for Nonfinancial Managers: A Guide to Finance and Accounting Principles for Nonfinancial ManagersFrom EverandFinance for Nonfinancial Managers: A Guide to Finance and Accounting Principles for Nonfinancial ManagersNo ratings yet
- Auditing MidtermsDocument2 pagesAuditing MidtermsCathleen Drew TuazonNo ratings yet
- f8 Pilot Paper IntDocument20 pagesf8 Pilot Paper IntXin LiNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 1Document1 pageMind Map 1darylle roblesNo ratings yet
- Arens Auditing16e SM 26Document15 pagesArens Auditing16e SM 26김현중No ratings yet
- 8kmiles Final OutlookDocument47 pages8kmiles Final OutlookDebashis MitraNo ratings yet
- ACCA - Audit and Assurance (AA) - Chapter 1Document54 pagesACCA - Audit and Assurance (AA) - Chapter 1Ishana Kaur100% (1)
- PSA 700, 705, 706, 710, 720 ExercisesDocument11 pagesPSA 700, 705, 706, 710, 720 ExercisesRalph Francis BirungNo ratings yet
- Aplication Level Audit Assurance Nov Dec 2013Document2 pagesAplication Level Audit Assurance Nov Dec 2013Noman_TufailNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics Case LawDocument253 pagesCode of Ethics Case LawDummy ContactNo ratings yet
- XBRL Document in Respect Consolidated Financial Statement-15022022Document232 pagesXBRL Document in Respect Consolidated Financial Statement-15022022Bhagwan BachaiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Icwai Group I Objective Type Questions and Answers: Narayan@icwahelpn - Co.inDocument11 pagesAuditing Icwai Group I Objective Type Questions and Answers: Narayan@icwahelpn - Co.inHaider ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Ch14 23 24Document56 pagesCh14 23 24lobsterkarlobbNo ratings yet
- CSA Vs Internal Audit FunctionDocument3 pagesCSA Vs Internal Audit FunctionraeanncNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 - Internal Audit Report STDTDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 9 - Internal Audit Report STDTNor Syahra Ajinim100% (1)
- Isa 580-810 PPT Group 3Document32 pagesIsa 580-810 PPT Group 3Niyitegeka EricNo ratings yet
- Standards On AuditingDocument37 pagesStandards On AuditingAryan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Sample Audit ReportsDocument44 pagesSample Audit ReportsNazia Sultana100% (1)
- Auditing Desktop Itud1j8Document59 pagesAuditing Desktop Itud1j8Cici homeNo ratings yet
- Aas 19 Subsequent EventsDocument2 pagesAas 19 Subsequent EventsRishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- APE Company & Services: Mrs. Sittie Ayesa Lacelle Gadia CEODocument18 pagesAPE Company & Services: Mrs. Sittie Ayesa Lacelle Gadia CEOPia De LaraNo ratings yet
- SA 510 QuestionsDocument6 pagesSA 510 Questionshimani guptaNo ratings yet
- ISO 19011 ReportDocument76 pagesISO 19011 Reportabdelmutalab100% (4)
- ACC451Document6 pagesACC451Bhatt RoshniNo ratings yet
- Drug Fund and Pharmaceuticals Supply AgencyDocument9 pagesDrug Fund and Pharmaceuticals Supply AgencyMasresha MiwedewNo ratings yet
- PICPA QAR Peer Review ChecklistDocument45 pagesPICPA QAR Peer Review ChecklistErlene CompraNo ratings yet
- Audit. Finals LABAN LANGDocument12 pagesAudit. Finals LABAN LANGhsjhsNo ratings yet
- GAIL Annual Report 2019Document43 pagesGAIL Annual Report 2019Umer AzizNo ratings yet
- FINALS 2021 - Auditing TheoryDocument17 pagesFINALS 2021 - Auditing TheoryJoyce Anne GarduqueNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview of Audit and AssuranceDocument49 pagesIntroduction and Overview of Audit and AssuranceLottie Santana100% (34)
- Auditors & Caro HandoutDocument30 pagesAuditors & Caro HandoutSrikantNo ratings yet