Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1
A Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1
Uploaded by
Anaina AnnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1
A Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1
Uploaded by
Anaina AnnaCopyright:
Available Formats
A+ BIOLOGY-IX
STD-9-BIOLOGY-FIRST BELL-CLASS-20
Chapter – 3
Simple Nutrients into cells
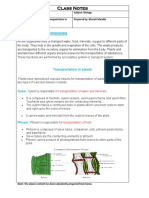
Transportation in plants
Transportation in plants through vascular system which extends from the roots to the leaves. It
consists of xylem and phloem. Xylem consists of tubes called vessels and tracheids. Phloem contains
sieve tubes and companion cells.
Vascular tissues in plants extend from roots to leaves in an interconnected manner.
Vascular tissue Function
Xylem The path through which water and salts absorbed by roots reach the leaves.
Phloem The path through which food prepared in the leaves reach the other parts of the
plant body.
Parts of xylem
Tracheids
vessels.
The structure of xylem
Xylem consists of dead cells called Tracheids and vessels.
The diameter of vessels is greater than that of tracheids.
Vessels are arranged one above the other. As the cell walls between the vessels disintegrate they look
like long pipes.
Conduction – through xylem
Conduction of water takes place through tracheids and vessels.
A+ BLOG-www.apluseducare.blogspot.com or Whatsapp 9746544422 Page 1
A+ BIOLOGY-IX
Ø: What are the processes by which water absorbed by roots reach the leaves and other parts of the
plant body?
Transpiration
Root pressure
Cohesion force (between water molecules themselves)
Adhesion force (property of water molecules to stick to the wall of xylem vessels.
Experiment to show transpiration in plants Aim: To prove that plants transpire through leaves.
Materials needed
Two potted plants of the same size and kind, Polythene covers, Rubber bands.
Procedure
Remove the leaves from one plant. Keep both the plants within polythene covers, The portion of
the cover around the pot is bound airtight using rubber bands. Keep the pots in the open. Observe
after two hours.
Observation
There are water drops on the inner side of the polythene bag covering the plant with leaves. There
are no water drops in the case of the plant without leaves.
Inference
Plants expel excess water through the leaves. Transpiration takes place through leaves.
Transpiration is the expulsion of water in plants by evaporation from-leaves.
Ø: What is meant by the term transpiration?
Water is expelled from leaves through the stomata by evaporation. This process is called
transpiration.
By transpiration, water is lost from the inter cellular spaces in leaves.
This reduces the pressure in leaf cells.
In order to equalise the pressure, water from adjacent cells enter the cells with low pressure by
osmosis.
Thus a suction force is formed upwards. This force makes water rise up.
Root pressure
Root cells receive water from the outside. This develops a pressure in these cells. . This is called
root pressure. This acts as a pushing force upwards. This causes water to rise up.
Cohesion force
Water molecules have the ability to stick to each other. This is called cohesion. Due to cohesion,
water molecules rise up, being attaches to one another.
Adhesion force
This is the ability of water molecules to stick to the walls of the xylem vessels. Due to this force,
water molecules do not get detaches from the xylem vessel.
A+ BLOG-www.apluseducare.blogspot.com or Whatsapp 9746544422 Page 2
A+ BIOLOGY-IX
Transport through Phloem
Parts of the phloem
Sieve tube
Companion cell
The structure of phloem
Among the phloem tubes, sieve tubes are seen as pipes arranged one above the other.
They have pores on their cross walls. Through these pores the cytoplasm of sieve tubes are
interconnected.
Through the sieve tubes transportation of food takes place in the form of sucrose. Companion cells
seen along with sieve tubes. They also help in the transportation of food.
Ø: How does transportation of food take place through the sieve tubes?
The cytoplasm in sieve tubes is connected through the pores in the cross walls. So food molecules can
pass from one sieve tube to the adjacent one. Companion cells also help transport.
Comparison of xylem and phloem
Xylem Phloem
Transports water and minerals. Transports prepared food.
Transports materials only in the upward Transports materials in any direction.
direction. From the leaf to any plant parts.
From the root to the leaves.
Xylem cells consist of tracheids and vessels Phloem consists of sieve tubes and companion
which are dead. cells which are living cells.
The cell walls between the vessels disintegrate They have pores on their cross walls.
Prepared by:
Riyas
PPMHSS Kottukkara
Kondotty-Malappuram
9747944422
More Resources, Visit https://apluseducare.blogspot.com/
Telegram Group: https://t.me/joinchat/ELv60hbE_g9Hvimlp0s1BA
A+ BLOG-www.apluseducare.blogspot.com or Whatsapp 9746544422 Page 3
You might also like
- Marx's Theory of Scientific Knowledge - Patrick MurrayDocument297 pagesMarx's Theory of Scientific Knowledge - Patrick Murraysergevictor100% (8)
- Homework Coaching Questions 1Document4 pagesHomework Coaching Questions 1Makkai BarbaraNo ratings yet
- KLB Biology F3 NoteDocument49 pagesKLB Biology F3 NoteSocdal Abdi100% (2)
- Bodyweight Sports TrainingDocument56 pagesBodyweight Sports TrainingJoshp3c100% (18)
- 3.1.2 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages3.1.2 Transport in PlantssjNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form 2Document49 pagesBiology Notes Form 2mburustan956No ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument49 pagesBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsPeter Osundwa Kiteki100% (4)
- Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in Flowering PlantsSNG UZZINo ratings yet
- Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 (2) - RemovedDocument249 pagesBiology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 (2) - RemovedMathableNo ratings yet
- Transport System in PlantDocument16 pagesTransport System in PlantAbu-Omar50% (4)
- Complex Permanent TissueDocument1 pageComplex Permanent TissueFirliana PramesdyaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 NotesDocument80 pagesBiology Form 2 NotesLutern RayNo ratings yet
- Biology PosterDocument5 pagesBiology PosterMenara RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Paper 2Document2 pagesPlant Transport Paper 2Heneral Drew de LunaNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecDocument24 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecnatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- ch7 NotesDocument6 pagesch7 Notesisabella cucumberNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument11 pagesTransport in Plantsmubasherkatbar562No ratings yet
- Transport System in Plants: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatDocument20 pagesTransport System in Plants: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatAkiela JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Transport in PlantsDocument5 pages3.3. Transport in PlantsFatima NissaNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT in PLANTSDocument27 pagesTRANSPORT in PLANTSRish HeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Transport in PlantsDocument8 pagesLecture 12 - Transport in PlantsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Transport and Transpiration in Plants NOTESDocument10 pagesTransport and Transpiration in Plants NOTESYasmin YehiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 - Transportation in PlantsDocument13 pagesChapter 3.1 - Transportation in Plantsbabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Transport in Multicellular Plants: SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 10: Transport in Multicellular Plants: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6: Plant Structure & FunctionDocument36 pagesTopic 6: Plant Structure & FunctionChiangshiuan SooNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsAbhyudaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- MF009 5C Transportation James L2Document19 pagesMF009 5C Transportation James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Biology - DynessDocument45 pagesBiology - DynessmalikachinyantaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes TransportDocument12 pagesLife Processes TransportYashaswini.V.No ratings yet
- Xylem: A Vascular Tissue in Land PlantsDocument4 pagesXylem: A Vascular Tissue in Land PlantsJoshua-Jonai JulyeNo ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesTransport of Materials in Flowering PlantsMd SafwatNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesCh-8 Transport in Plantsdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument14 pagesTransport in PlantsMuhammad Faizan KaleemNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems in Plants: Stem Structure Root StructureDocument12 pagesTransport Systems in Plants: Stem Structure Root StructureJonathon HayesNo ratings yet
- How Minerals Are Transported in PlantsDocument2 pagesHow Minerals Are Transported in PlantsMariam KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument8 pagesTransport in PlantsKomalsh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport To WriteDocument17 pagesPlant Transport To WritelaibahundekarNo ratings yet
- 7.transport in Plants NotesDocument18 pages7.transport in Plants NotesAhmed Noor100% (1)
- Transportation in PlantsDocument31 pagesTransportation in PlantssamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- Science Assignment: Made By: Syed Ammar Ahmed Viii - CDocument4 pagesScience Assignment: Made By: Syed Ammar Ahmed Viii - CSYED AMMAR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Y10 Plant Transport Lesson 1Document27 pagesY10 Plant Transport Lesson 1Sherry LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Transport in Plants 8.1 & 8.2Document52 pagesChapter 8 Transport in Plants 8.1 & 8.2Ali OpNo ratings yet
- Botany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument47 pagesBotany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisManar AnwerNo ratings yet
- What Is Translocation in PlantsDocument9 pagesWhat Is Translocation in PlantsZakia BariNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesTransport in PlantsmichaeltrobiaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 BioDocument13 pagesGrade 9 BioMohammad Hamza AwanNo ratings yet
- Plant Vs Animal TransportCirculatory System PDFDocument46 pagesPlant Vs Animal TransportCirculatory System PDFJezreel IsipinNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: By:-Mr - Deepak Upreti Biology Teacher Gmis, JakartaDocument26 pagesTransport in Plants: By:-Mr - Deepak Upreti Biology Teacher Gmis, Jakartakiera angNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Transportation in OrganismsDocument4 pagesClass Notes: Transportation in OrganismsRouful RasoolNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes SummaryDocument12 pagesBiology Notes Summaryrobin.kipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 6-1Document200 pagesBiology Form 6-1Justine MakolokaNo ratings yet
- Plant TransportDocument23 pagesPlant TransportBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in PlantsX's musicNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport SystemsDocument20 pagesPlant Transport Systemscale suarezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Transport in Vascular Plants Student NoteDocument3 pagesLesson 6 Transport in Vascular Plants Student NoteallaboutamaliaNo ratings yet
- Transportation: FunctionDocument21 pagesTransportation: Functionvivek tripathiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 12 Biology Revision Notes Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument33 pagesGrade 10 12 Biology Revision Notes Transport in Plants and AnimalsMapalo ChirwaNo ratings yet
- Quarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sDocument17 pagesQuarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sTristan Paul PagalananNo ratings yet
- Transport System AutorecoveredDocument8 pagesTransport System Autorecovereduser alohaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument25 pagesTransport in Plantsruthmahase12No ratings yet
- Green and Pink Gradient Minimalist Motivational PosterDocument1 pageGreen and Pink Gradient Minimalist Motivational PosterAnaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- Main QimgDocument7 pagesMain QimgAnaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants IDocument45 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants IAnaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- PoemDocument1 pagePoemAnaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- PROCESSES of rDNA TECHNOLOGYDocument6 pagesPROCESSES of rDNA TECHNOLOGYAnaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- It Does/doesn't Do? That's A Reality I Need To Reinforce Over These Next Few WeeksDocument5 pagesIt Does/doesn't Do? That's A Reality I Need To Reinforce Over These Next Few WeeksAnaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- Notes From "The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F CK"Document7 pagesNotes From "The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F CK"Anaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- FIP 504 NAA Assignment 1Document2 pagesFIP 504 NAA Assignment 1Srushti RajNo ratings yet
- Semantics. Abnormality in Syntagmatic Relations. 3 December 2020Document21 pagesSemantics. Abnormality in Syntagmatic Relations. 3 December 2020Marina TanovićNo ratings yet
- Asia Bibi Blasphemy CaseDocument14 pagesAsia Bibi Blasphemy CaseRadovan SpiridonovNo ratings yet
- Water Supply & Sanitaion TM (V5) 2012Document79 pagesWater Supply & Sanitaion TM (V5) 2012Shafiqullah GowharyNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI HiSecEngine USG6500E Series Firewalls (Fixed-Configuration) DatasheetDocument9 pagesHUAWEI HiSecEngine USG6500E Series Firewalls (Fixed-Configuration) DatasheethugobiarNo ratings yet
- 126 1043 8 PB 1Document12 pages126 1043 8 PB 1MussyNo ratings yet
- Threading (Manufacturing) : Threading Is The Process of Creating ADocument16 pagesThreading (Manufacturing) : Threading Is The Process of Creating AAnonymous mRCnYKz7xBNo ratings yet
- Essence: By: Bisma Kalsoom and Adeen MumtaazDocument8 pagesEssence: By: Bisma Kalsoom and Adeen MumtaazBisma KalsoomNo ratings yet
- Revisión de Las Especies de Melipona - Grupo Fulginosa PDFDocument17 pagesRevisión de Las Especies de Melipona - Grupo Fulginosa PDFmecopa2718No ratings yet
- Multilocularis) - The Oncosphere Develops Into A Multi-ChamberedDocument2 pagesMultilocularis) - The Oncosphere Develops Into A Multi-Chamberedzoology qauNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MGT501Document1 pageAssignment 2 MGT501Aamir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Turbo-Couplings-Fluid Couplings-with-Constant-Fill - Operating-ManualDocument108 pagesTurbo-Couplings-Fluid Couplings-with-Constant-Fill - Operating-ManualCarollina AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Sociology Module B1 2017Document3 pagesSociology Module B1 2017Aerielle CanoNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - e A Tire Tracks Lesson 4Document3 pagesGrade 6 - e A Tire Tracks Lesson 4api-283081427No ratings yet
- Potato ProductionDocument6 pagesPotato ProductionviamussNo ratings yet
- Sport Management Review: Evald Bundgaard Iversen, Graham CuskellyDocument13 pagesSport Management Review: Evald Bundgaard Iversen, Graham CuskellyGabriela Ioana IonitaNo ratings yet
- Advisory Board By-LawsDocument3 pagesAdvisory Board By-LawsViola GilbertNo ratings yet
- 14 - Ty Gibson, James Rafferty - Papal-US Aliance in ProphecyDocument2 pages14 - Ty Gibson, James Rafferty - Papal-US Aliance in ProphecybillwullurNo ratings yet
- Bernard Barber's Social System Theory: The American Sociologist June 2002Document20 pagesBernard Barber's Social System Theory: The American Sociologist June 2002Rainman1618No ratings yet
- Entrepreneur ReportDocument35 pagesEntrepreneur ReportMaryfhel LeyteNo ratings yet
- Del Rosario-Igtiben V RepublicDocument1 pageDel Rosario-Igtiben V RepublicGel TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Conflicts and Negotiations in Project ManagementDocument7 pagesLecture 6 - Conflicts and Negotiations in Project ManagementFrenz FerdyNo ratings yet
- A La Nanita NanaDocument1 pageA La Nanita Nanabill desaillyNo ratings yet
- Mvno - Encik KunciDocument15 pagesMvno - Encik KunciJolliffe NicholasNo ratings yet
- People Vs Que Po LayDocument3 pagesPeople Vs Que Po LayJet jet NuevaNo ratings yet
- Webinar Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesWebinar Reflection Paperqwert qwertyNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Maze Solving Robot Using Arduino: A Project Seminar Report OnDocument4 pagesAutonomous Maze Solving Robot Using Arduino: A Project Seminar Report OnAkhilaNo ratings yet