Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing Responsibilites
Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing Responsibilites
Uploaded by
Gino B. BulanaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CASE STUDY 10 NCPDocument46 pagesCASE STUDY 10 NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (8)
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument22 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument4 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Coli, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bacteroides Fragilis, B. Thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostr Eptococcus SpeciesDocument8 pagesColi, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bacteroides Fragilis, B. Thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostr Eptococcus SpeciesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LadyDocument8 pagesDrug Study LadyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- DS - Mod9Document2 pagesDS - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- Drugsstudy Different ObDocument8 pagesDrugsstudy Different ObElvis DuotNo ratings yet
- Omep, Ceftriaxone, FurosemideDocument3 pagesOmep, Ceftriaxone, FurosemideThyataira chuaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument8 pagesDrug AnalysisDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument10 pagesDrug Study FinalJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- MEROPENEMDocument1 pageMEROPENEMCarlo ToledooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RyDocument30 pagesDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- 4 Cefazolin Drug StudyDocument4 pages4 Cefazolin Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Ce Fur OximeDocument2 pagesCe Fur OximeDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- DS ObDocument7 pagesDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Banaag Antibacterial MedsDocument5 pagesBanaag Antibacterial MedsPrince JoaquinNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (Adult and Pediatric Patients)Document4 pagesComplicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (Adult and Pediatric Patients)Jonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Borres Drugstudy-M2w7Document3 pagesBorres Drugstudy-M2w7gnmalisaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyMark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ResumaDocument3 pagesDrug Study ResumaNicole Arriana ResumaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NOt COmpleteDocument6 pagesDrug Study NOt COmpletejiellianemaeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyJòhn Jâbéz CâsïlânNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument1 pageCefuroxime Drug StudyDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKathleen RagudoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- DRUG TABULATION EditedDocument7 pagesDRUG TABULATION EditedAlexa Nicole GayosoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batmc GeriaDocument3 pagesDrug Study Batmc GeriaLeslee Amor EspirituNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem Drug StudyDocument3 pagesErtapenem Drug StudyBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudygabbyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MugnaDocument7 pagesDrug Study Mugnakint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocument5 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- CS1 AntibioticsDocument4 pagesCS1 AntibioticsTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyyyAlleinad BarracasNo ratings yet
- Olores Drugstudy Cephalothin SodiumDocument7 pagesOlores Drugstudy Cephalothin SodiumTintin KingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument14 pagesDrug Study ICUAndrea Isabel U. O'Dell100% (1)
- Drug Study Maam JunsanDocument2 pagesDrug Study Maam JunsanBenedict SabellanoNo ratings yet
- ANCEFDocument2 pagesANCEFDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studymarie100% (27)
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesOmeprazole1adie1907No ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument2 pagesClindamycinassilamorNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument1 pageCeftriaxonecen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument3 pagesCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Date/Shift Time Focus D Data A Action R ResponseDocument2 pagesDate/Shift Time Focus D Data A Action R ResponseGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- FINAL-PSYCHE Without TranscribeDocument42 pagesFINAL-PSYCHE Without TranscribeGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Generic Name: Amoxicillin Mechanism of Action: IndicationDocument4 pagesDrug Action Generic Name: Amoxicillin Mechanism of Action: IndicationGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- A. History of IllnessDocument2 pagesA. History of IllnessGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetDocument8 pagesBreathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Dosage and Route Classification Action Side Effects Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument16 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Dosage and Route Classification Action Side Effects Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Generic Name: Albuterol Mechanism of Action: IndicationDocument3 pagesDrug Action Generic Name: Albuterol Mechanism of Action: IndicationGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Discharge SheetDocument1 pageDischarge SheetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument4 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drugs PDFDocument12 pagesAntiemetic Drugs PDFDanisha Laila100% (2)
- Treatment of Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument8 pagesTreatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarumsuci triana putriNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY OnlyDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY OnlyShannon CabfitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drug Class Review PDFDocument24 pagesAntiemetic Drug Class Review PDFAhmad Zuhyardi LubisNo ratings yet
- Jiggar DrugsDocument3 pagesJiggar DrugsRockeven DesirNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting: A Palliative Care ImperativeDocument12 pagesNausea and Vomiting: A Palliative Care ImperativeMelissa Salazar EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Gastroparesis. ACGDocument45 pagesGastroparesis. ACGNaser EsmailiNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide - WikipediaDocument25 pagesMetoclopramide - WikipediaMuhammadafif SholehuddinNo ratings yet
- Acute Treatment of Migraine in AdultsDocument7 pagesAcute Treatment of Migraine in AdultsMo0oryNo ratings yet
- The Jere Beasley Report, Jun. 2007Document52 pagesThe Jere Beasley Report, Jun. 2007Beasley AllenNo ratings yet
- Adult Headache GuidelineDocument7 pagesAdult Headache GuidelineKhairunisaNo ratings yet
- Preanesthetic Medication JasminaDocument44 pagesPreanesthetic Medication Jasminaanjali sNo ratings yet
- NCP For ChildrenDocument17 pagesNCP For ChildrenRachel Niu IINo ratings yet
- Chronic Hiccups: Zachary Wilmer Reichenbach, MD, PHD Gregory M. Piech, MD, MPH Zubair Malik, MDDocument17 pagesChronic Hiccups: Zachary Wilmer Reichenbach, MD, PHD Gregory M. Piech, MD, MPH Zubair Malik, MDAndres ViverosNo ratings yet
- Preanesthetic Medication JasminaDocument44 pagesPreanesthetic Medication Jasminaanjali s100% (1)
- GIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument5 pagesGIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityEli Ezer SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- MaxolonDocument4 pagesMaxolonDaniel YamNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Leaflet Paediatric Paracetamol Elixir BP Paracetamol 120 mg/5 MLDocument4 pagesPatient Information Leaflet Paediatric Paracetamol Elixir BP Paracetamol 120 mg/5 MLmarhamatul laiyinahNo ratings yet
- HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM GT 69 NotesDocument6 pagesHYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM GT 69 NotesFara WakeshimaNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Audit PresentationDocument68 pagesNausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Audit PresentationGonzalo MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY FINAL (Onco) PDFDocument14 pagesDRUG STUDY FINAL (Onco) PDFFrancis Anthony LoslosoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic GastroparesisDocument8 pagesManagement of Diabetic GastroparesisboomNo ratings yet
- ANTIEMETICSDocument26 pagesANTIEMETICSkhurshidghorihumaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationDocument11 pagesGeneric Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- BP602T Unit 1-3Document207 pagesBP602T Unit 1-3Gyampoh SolomonNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Nausea and VomitingDocument8 pagesPost-Operative Nausea and Vomitingika lindaNo ratings yet
- Regañon - Rle Case # 1Document22 pagesRegañon - Rle Case # 1Darla Janyll RegañonNo ratings yet
Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing Responsibilites
Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing Responsibilites
Uploaded by
Gino B. BulanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing Responsibilites
Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing Responsibilites
Uploaded by
Gino B. BulanaCopyright:
Available Formats
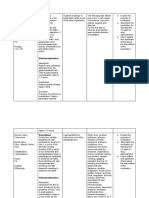
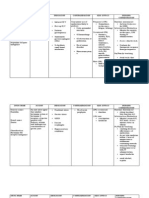
Drug Action Indications and Nursing Responsibilites
Contraindications
Generic Name: Mechanism of action: Indication: Observe 12 rights of
medication
Cefuroxime Cefuroxime inhibits bacterial cell wall Cefuroxime is a cephalosporin
Observe for signs and
synthesis by binding to one 1 or more indicated for the treatment of a
symptoms of
of the penicillin-binding proteins variety of infections including acute
anaphylaxis during 1st
Classification: (PBPs) which in turn inhibit the final bacterial otitis media, several upper
dose.
transpeptidation step of respiratory tract infections, skin
Cephalosporins Monitor prothrombin
peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial infections, urinary tract infections,
time in patients at risk
cell walls, thus inhibiting cell wall gonorrhea, early Lyme disease, and
of prolongation during
biosynthesis and arresting cell wall impetigo.
Dose: cephalosporin therapy
assembly resulting in bacterial cell
Contraindication:
1.5g ANST as loading dose at death.
9am Hypersensitivity to cefuroxime or to
Side effects:
other cephalosporins.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, strange
Timing: taste in the mouth, or stomach pain
Q8 Adverse Reactions:
Rash, fever, pruritus, erythema,
urticarial, GI bleeding and infection,
Route: abdominal pain, flatulence, ptyalism,
indigestion, mouth ulcers, swollen
Intravenous
tongue
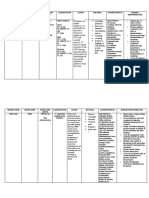
Drug Action Indications and Nursing Responsibilites
Contraindications
Generic Name: Mechanism of action: Indication: Observe 12 rights of
medication
Metoclopramide Metoclopramide is a substituted Metoclopramide is used to relieve
Monitor BP carefully
benzamide with prokinetic and heartburn and speed the healing of
during IV
antiemetic properties. It stimulates ulcers and sores in the esophagus
administration.
Classification: the motility of the upper (tube that connects the mouth to
History: Allergy to
gastrointestinal tract and accelerates the stomach) in people who have
Antiemetics metoclopramide, GI
gastric peristalsis without stimulating gastroesophageal reflux disease
hemorrhage,
gastric, biliary or pancreatic (GERD; condition in which backward
mechanical
secretions, leading to increased flow of acid from the stomach
Dose: obstruction or
gastric emptying and intestinal transit causes heartburn and injury of the
perforation,
1 ampule time. It blocks dopamine receptors esophagus) that did not get better
pheochromocytoma,
and serotonin receptors (at higher with other treatments.
epilepsy, lactation,
doses) in chemoreceptor trigger zone
Contraindication: previously detected
of the CNS.
Timing: breast cancer
Patient with gastrointestinal
Side effects: Monitor for
9:30 am perforation, haemorrhage or
extrapyramidal
feeling restless; mechanical obstruction, suspected
reactions, and consult
feeling drowsy or tired; or known pheochromocytoma or
physician if they occur.
Route: other catecholamine-releasing
lack of energy;
paragangliomas, history of
Intravenous nausea, vomiting; neuroleptic or drug-induced tardive
headache, confusion; or. dyskinesia, seizure disorder (e.g.
sleep problems epilepsy), Parkinson’s disease,
(insomnia). known history of
methaemoglobinaemia with
metoclopramide or nicotinamide
Adverse Reactions: adenine dinucleotide-cytochrome
b5 reductase (NADH-Cyb5R)
Blood and lymphatic system
disorders: Rarely, agranulocytosis, deficiency.
leucopenia, neutropenia,
sulfhaemoglobinaemia.
Eye disorders: Visual disturbance.
Cardiac disorders: Supraventricular
tachycardia, acute CHF, AV block.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Diarrhoea,
nausea, vomiting, bowel disturbance.
General disorders and admin site
conditions: Asthenia, fatigue.
You might also like
- CASE STUDY 10 NCPDocument46 pagesCASE STUDY 10 NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (8)
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument22 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument4 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Coli, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bacteroides Fragilis, B. Thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostr Eptococcus SpeciesDocument8 pagesColi, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bacteroides Fragilis, B. Thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostr Eptococcus SpeciesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LadyDocument8 pagesDrug Study LadyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- DS - Mod9Document2 pagesDS - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- Drugsstudy Different ObDocument8 pagesDrugsstudy Different ObElvis DuotNo ratings yet
- Omep, Ceftriaxone, FurosemideDocument3 pagesOmep, Ceftriaxone, FurosemideThyataira chuaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument8 pagesDrug AnalysisDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument10 pagesDrug Study FinalJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- MEROPENEMDocument1 pageMEROPENEMCarlo ToledooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RyDocument30 pagesDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- 4 Cefazolin Drug StudyDocument4 pages4 Cefazolin Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Ce Fur OximeDocument2 pagesCe Fur OximeDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- DS ObDocument7 pagesDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Banaag Antibacterial MedsDocument5 pagesBanaag Antibacterial MedsPrince JoaquinNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (Adult and Pediatric Patients)Document4 pagesComplicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (Adult and Pediatric Patients)Jonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Borres Drugstudy-M2w7Document3 pagesBorres Drugstudy-M2w7gnmalisaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyMark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ResumaDocument3 pagesDrug Study ResumaNicole Arriana ResumaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NOt COmpleteDocument6 pagesDrug Study NOt COmpletejiellianemaeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyJòhn Jâbéz CâsïlânNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument1 pageCefuroxime Drug StudyDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKathleen RagudoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- DRUG TABULATION EditedDocument7 pagesDRUG TABULATION EditedAlexa Nicole GayosoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batmc GeriaDocument3 pagesDrug Study Batmc GeriaLeslee Amor EspirituNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem Drug StudyDocument3 pagesErtapenem Drug StudyBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudygabbyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MugnaDocument7 pagesDrug Study Mugnakint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocument5 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- CS1 AntibioticsDocument4 pagesCS1 AntibioticsTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyyyAlleinad BarracasNo ratings yet
- Olores Drugstudy Cephalothin SodiumDocument7 pagesOlores Drugstudy Cephalothin SodiumTintin KingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument14 pagesDrug Study ICUAndrea Isabel U. O'Dell100% (1)
- Drug Study Maam JunsanDocument2 pagesDrug Study Maam JunsanBenedict SabellanoNo ratings yet
- ANCEFDocument2 pagesANCEFDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studymarie100% (27)
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesOmeprazole1adie1907No ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument2 pagesClindamycinassilamorNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument1 pageCeftriaxonecen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument3 pagesCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Date/Shift Time Focus D Data A Action R ResponseDocument2 pagesDate/Shift Time Focus D Data A Action R ResponseGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- FINAL-PSYCHE Without TranscribeDocument42 pagesFINAL-PSYCHE Without TranscribeGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Generic Name: Amoxicillin Mechanism of Action: IndicationDocument4 pagesDrug Action Generic Name: Amoxicillin Mechanism of Action: IndicationGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- A. History of IllnessDocument2 pagesA. History of IllnessGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetDocument8 pagesBreathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Dosage and Route Classification Action Side Effects Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument16 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Dosage and Route Classification Action Side Effects Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Generic Name: Albuterol Mechanism of Action: IndicationDocument3 pagesDrug Action Generic Name: Albuterol Mechanism of Action: IndicationGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Discharge SheetDocument1 pageDischarge SheetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument4 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drugs PDFDocument12 pagesAntiemetic Drugs PDFDanisha Laila100% (2)
- Treatment of Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument8 pagesTreatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarumsuci triana putriNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY OnlyDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY OnlyShannon CabfitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drug Class Review PDFDocument24 pagesAntiemetic Drug Class Review PDFAhmad Zuhyardi LubisNo ratings yet
- Jiggar DrugsDocument3 pagesJiggar DrugsRockeven DesirNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting: A Palliative Care ImperativeDocument12 pagesNausea and Vomiting: A Palliative Care ImperativeMelissa Salazar EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Gastroparesis. ACGDocument45 pagesGastroparesis. ACGNaser EsmailiNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide - WikipediaDocument25 pagesMetoclopramide - WikipediaMuhammadafif SholehuddinNo ratings yet
- Acute Treatment of Migraine in AdultsDocument7 pagesAcute Treatment of Migraine in AdultsMo0oryNo ratings yet
- The Jere Beasley Report, Jun. 2007Document52 pagesThe Jere Beasley Report, Jun. 2007Beasley AllenNo ratings yet
- Adult Headache GuidelineDocument7 pagesAdult Headache GuidelineKhairunisaNo ratings yet
- Preanesthetic Medication JasminaDocument44 pagesPreanesthetic Medication Jasminaanjali sNo ratings yet
- NCP For ChildrenDocument17 pagesNCP For ChildrenRachel Niu IINo ratings yet
- Chronic Hiccups: Zachary Wilmer Reichenbach, MD, PHD Gregory M. Piech, MD, MPH Zubair Malik, MDDocument17 pagesChronic Hiccups: Zachary Wilmer Reichenbach, MD, PHD Gregory M. Piech, MD, MPH Zubair Malik, MDAndres ViverosNo ratings yet
- Preanesthetic Medication JasminaDocument44 pagesPreanesthetic Medication Jasminaanjali s100% (1)
- GIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument5 pagesGIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityEli Ezer SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- MaxolonDocument4 pagesMaxolonDaniel YamNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Leaflet Paediatric Paracetamol Elixir BP Paracetamol 120 mg/5 MLDocument4 pagesPatient Information Leaflet Paediatric Paracetamol Elixir BP Paracetamol 120 mg/5 MLmarhamatul laiyinahNo ratings yet
- HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM GT 69 NotesDocument6 pagesHYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM GT 69 NotesFara WakeshimaNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Audit PresentationDocument68 pagesNausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Audit PresentationGonzalo MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY FINAL (Onco) PDFDocument14 pagesDRUG STUDY FINAL (Onco) PDFFrancis Anthony LoslosoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic GastroparesisDocument8 pagesManagement of Diabetic GastroparesisboomNo ratings yet
- ANTIEMETICSDocument26 pagesANTIEMETICSkhurshidghorihumaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationDocument11 pagesGeneric Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- BP602T Unit 1-3Document207 pagesBP602T Unit 1-3Gyampoh SolomonNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Nausea and VomitingDocument8 pagesPost-Operative Nausea and Vomitingika lindaNo ratings yet
- Regañon - Rle Case # 1Document22 pagesRegañon - Rle Case # 1Darla Janyll RegañonNo ratings yet