Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gi L17 - Habcdv
Gi L17 - Habcdv
Uploaded by
Ian Evan Lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThis document summarizes and compares key aspects of 5 types of viral hepatitis: HAV, HBV, HCV, HDV, and HEV. It outlines their signatures, RNA/DNA type, virulence, carrier state potential, spread method, transmission period, incubation period, epidemiology, available vaccines, clinical features, diagnostic antibodies, and diagnosis methods. The viruses cause acute or chronic hepatitis and some can lead to liver cancer. They differ in factors like persistence in the body after infection and presence of vaccines.
Original Description:
Original Title
GI L17 - HABCDV
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes and compares key aspects of 5 types of viral hepatitis: HAV, HBV, HCV, HDV, and HEV. It outlines their signatures, RNA/DNA type, virulence, carrier state potential, spread method, transmission period, incubation period, epidemiology, available vaccines, clinical features, diagnostic antibodies, and diagnosis methods. The viruses cause acute or chronic hepatitis and some can lead to liver cancer. They differ in factors like persistence in the body after infection and presence of vaccines.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesGi L17 - Habcdv
Gi L17 - Habcdv
Uploaded by
Ian Evan LeeThis document summarizes and compares key aspects of 5 types of viral hepatitis: HAV, HBV, HCV, HDV, and HEV. It outlines their signatures, RNA/DNA type, virulence, carrier state potential, spread method, transmission period, incubation period, epidemiology, available vaccines, clinical features, diagnostic antibodies, and diagnosis methods. The viruses cause acute or chronic hepatitis and some can lead to liver cancer. They differ in factors like persistence in the body after infection and presence of vaccines.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
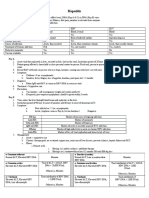
GI L17 – Acute Viral Hepatitis
HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV
Signature Acute; dirty food Gives HCC; HK and S China Gives HCC; no vaccine Friend of HBV Acute; dirty
food
RNA/DN ssRNA Part ssDNA Linear ssRNA Circular defective ssRNA ssRNA
A
Virulence Direct cytopathic HBV infects liver cells T cell attacks - Can transform mild chronic -
effect/T-cell HBV & own liver cells hepatitis hep B into severe chronic
mediated injury hep B & cirrhosis
(?)
Carrier No Yes Yes Yes Low risk/None
state? Acute, self- (95% full recovery) Wide spectrum of outcomes, Requires HBs-Agaemic to Full recovery
limiting disease May develop chronic hepatitis +/- similar to Hep B be effective expected
(99% full cirrhosis, +/- HCC (100x RR) 50% progress to chronic hepatitis & Co-infection: Simultaneous May cause
recovery), rarely *Infection in infants (~95% chronicity; cirrhosis +/- HCC introduction of HBV & HDV severe disease
fatal associated with poor cell-mediated Causes: Superinfection: HDV into esp. pregnant
immune response to HBV?) 1. Acute/chronic hepatitis HBsAg+ve host women
Broad definition: Presence of HBV 2. Carrier state
regardless of symptoms 3. End-stage liver
Narrow definition: replication of HBV 4. HCC
w/o symptoms
Spread Faecal-oral route Parenteral route Faecal-oral
Ingestion of 1. Transfusion of blood and blood products route
contaminated 2. Contamination of needles
water and foods 3. Medical and dental procedures
e.g. not well 4. Intimate contact esp. sexual
cooked shellfish 5. HBV: Vertical transmission during perinatal period (X pregnancy, V at the time of birth!)
[Food to
subject/subject
to subject]
Transmis Shed in stool 2-3 - - - Caused
sion weeks before massive
and 1 week after outbreaks
onset of jaundice water-borne
hepatitis
Incubatio Short Long Long Long Short
n period 15-40 days (1 1-4 months 7-8 weeks 1-4 months 4-5 weeks
month)
HK % - 1/10 = carrier <1% - -
4/10 = recovered (exclude vaccinated)
Epidemol Occurs Extremely common in HK and S China N Africa - -
ogy throughout the 400 million HBV subjects; 75% Chinese Case: Egypt 1960-70s,
world Incidence varies greatly in different schistosomiasis vaccination; use
Endemic in parts of the world same needle HCV
countries with 1. Urban > rural
substandard 2. Male > female
hygiene and 3. Certain groups regardless of
sanitation location
4. Poor SES
[HBsAg in 5-20% of apparently healthy
persons in SE Asia and tropical Africa;
0.1-0.6% in W Europe and USA]
Vaccine Yes Yes No No; use HBV vaccine Yes, safe?
Clinical - Acute Hep B tend to be more severe Mild clinically Acute HBV/HDV infection -
features than Hep A/C may be indistinguishable
Subclinical infection frequent esp. in from hep B, but associated
infants and children with relatively high rate of
fulminant hepatitis
Antibody Anti-HAV - Anti-HCV not protective - -
appears during Appears several weeks later than
attack and HCV RNA
persists
Diagnosis Serum IgM HBsAg/Ab to HBcAg 1. +ve anti-HCV Ab; PCR for HCV IgM & IgG PCR for HEV
RNA HDV RNA serum RNA
2. Raised AST, ALT HDAg in liver Serum IgM &
3. Biopsy IgG
a. Portal tract inflammatory
infiltrates rich in
lymphocytes
b. Interface hepatitis
c. Macrovesicular steatosis
(fatty change)
Macro = nucleus distorted
Micro = nucleus X distorted
You might also like
- Case Study Infectious CureDocument4 pagesCase Study Infectious CureAndrea Bassett100% (1)
- Awakening the Spiritual Heart: How to Fall in Love with LifeFrom EverandAwakening the Spiritual Heart: How to Fall in Love with LifeNo ratings yet
- The Laws of The UniverseDocument2 pagesThe Laws of The UniverseJason MichaelNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viruses: Dr. Muna. M. A. Yousif M.D Clinical MicrobiologyDocument45 pagesHepatitis Viruses: Dr. Muna. M. A. Yousif M.D Clinical MicrobiologyMAxeneNo ratings yet
- HIV&HepatitisDocument46 pagesHIV&HepatitisRaja RuzannaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis (Part I)Document12 pagesViral Hepatitis (Part I)Maarveen RajNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyDocument44 pagesHepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyJosé Luis García GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-EDocument34 pagesHepatitis A-EVer Garcera TalosigNo ratings yet
- Hep B VirusDocument20 pagesHep B VirusBhupesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Part 2 of Medical VirologyDocument113 pagesPart 2 of Medical Virologygatete samNo ratings yet
- TASH CI HepatitisDocument47 pagesTASH CI HepatitisBeamlak Getachew WoldeselassieNo ratings yet
- 2018 Hepatitis Viral InfectionDocument51 pages2018 Hepatitis Viral Infectionkomang nickoNo ratings yet
- 05 Prevention of TransmissionDocument35 pages05 Prevention of TransmissionANUAR ASISNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHDocument55 pagesPresented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Hepatitis A, B and C VirusDocument46 pagesHepatitis A, B and C VirusChyzhi SylviaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis FinalDocument73 pagesHepatitis FinalAkhil MuraliNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument55 pagesHepatitisAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument55 pagesHepatitisdebdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- Presented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHDocument55 pagesPresented By:-Himanshu Dev DMLT VI TH Sem. VMMC & SJHwira guna pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology: Hepatotrophic Viruses - May 3, 2017Document7 pagesMedical Microbiology: Hepatotrophic Viruses - May 3, 2017Claire DuNo ratings yet
- 1010 M Balm - Viral HepatitisDocument17 pages1010 M Balm - Viral HepatitisSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument55 pagesHepatitisSUTHAN100% (1)
- HepatitisDocument29 pagesHepatitisRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Document44 pagesViral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Eleni HagosNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis - An Overview: Dr. JayalakshmiDocument77 pagesHepatitis - An Overview: Dr. JayalakshmiNithin SundarNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-EDocument56 pagesHepatitis A-EAmala SebastianNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaDocument36 pagesHepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaKarina Mega WNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viral - Dr. José Gonzáles BenavidesDocument64 pagesHepatitis Viral - Dr. José Gonzáles BenavidesEfrain Brian SilvaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BUMIL, Materi DR - Emil, SP - Pd.Document36 pagesHepatitis BUMIL, Materi DR - Emil, SP - Pd.yuliyanto.efendiNo ratings yet
- Serology of Viral Infections PDFDocument72 pagesSerology of Viral Infections PDFAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- 1 HepatitisDocument62 pages1 HepatitisKamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-E Viruses: Ini PPT DR - Catur Dari InternetDocument48 pagesHepatitis A-E Viruses: Ini PPT DR - Catur Dari InternetNurhidayahNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viruses Combination (Blood Borne Pathogens)Document51 pagesHepatitis Viruses Combination (Blood Borne Pathogens)Hosam GomaaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-E Viruses: An OverviewDocument48 pagesHepatitis A-E Viruses: An OverviewPrajakta TawdeNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaDocument27 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaAsmorowatiNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Steve HartDocument36 pagesHepatitis B: Steve HartangelinaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis: Nining Sri Wuryaningsih Bagian Patologi Klinik FK UNSDocument36 pagesViral Hepatitis: Nining Sri Wuryaningsih Bagian Patologi Klinik FK UNSdayanr02No ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - Viral HepatitisDocument2 pagesGastroenterology - Viral HepatitisEugen MNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis RevDocument83 pagesVirus Hepatitis RevSukma WinahyuNo ratings yet
- CCE090 Liver and Biliary TractDocument21 pagesCCE090 Liver and Biliary TractBharathi ManiyanNo ratings yet
- 3.0HEPATIT Lecture 5Document48 pages3.0HEPATIT Lecture 5Jiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viruses: VIRUS:Hepatitis A, B, CDocument25 pagesHepatitis Viruses: VIRUS:Hepatitis A, B, Carisita firmanNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-E Viruses: Farida Purnamasari.,SKM 2012Document51 pagesHepatitis A-E Viruses: Farida Purnamasari.,SKM 2012siapaa01No ratings yet
- He HepatitisDocument4 pagesHe HepatitisMayar JaradNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A VirusDocument27 pagesHepatitis A VirusAna KarlaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Dan C Dalam KehamilanDocument15 pagesHepatitis B Dan C Dalam Kehamilanzrombie7No ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument23 pagesHepatitis BMarty Asis100% (1)
- Week 6. Liver, Renal PathologyDocument33 pagesWeek 6. Liver, Renal PathologyAmber LeJeuneNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis: by Dimie Ogoina Internal Medicine Ndu/NduthDocument16 pagesViral Hepatitis: by Dimie Ogoina Internal Medicine Ndu/NduthPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-E Viruses: An OverviewDocument55 pagesHepatitis A-E Viruses: An OverviewRitu TripathiNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument3 pagesHepatitisapi-648401824No ratings yet
- Hepatitis D Virus (HDV) : PathogenesisDocument30 pagesHepatitis D Virus (HDV) : PathogenesisJc GaldosNo ratings yet
- HEPATITIS B EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesHEPATITIS B Epidemiologytarun_apr25No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Dalam KehamilanDocument15 pagesHepatitis B Dalam KehamilanjenniNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis: DR - Abiy F. Nov 2019 Arsi UniversityDocument67 pagesViral Hepatitis: DR - Abiy F. Nov 2019 Arsi UniversityWakjira NigusuNo ratings yet
- Jaundice and Hepatitis in Children: Dr. MwendwaDocument46 pagesJaundice and Hepatitis in Children: Dr. MwendwaAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument19 pagesHepatitisDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Hepatotrophic Viruses PDFDocument9 pagesHepatotrophic Viruses PDFRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B & DDocument40 pagesHepatitis B & DMeena CtNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Document5 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Kim LompotNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MD Edited by Willy ChouDocument32 pagesInfectious Diseases: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MD Edited by Willy Chouwildan mullerNo ratings yet
- Mystery Respiratory Illness, Greenspring Near Fort Detrick (July 2019) - CDC No ResultDocument4 pagesMystery Respiratory Illness, Greenspring Near Fort Detrick (July 2019) - CDC No ResultKevin SteinerNo ratings yet
- Slma Vaccines Guidelines 2011Document111 pagesSlma Vaccines Guidelines 2011Jude Roshan WijesiriNo ratings yet
- Colibacillosis in Poultry PDFDocument2 pagesColibacillosis in Poultry PDFAngelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Mae CanlasNo ratings yet
- Influenza Virus in Children: What Is The Flu?Document3 pagesInfluenza Virus in Children: What Is The Flu?An NukmanNo ratings yet
- AntifungalsDocument29 pagesAntifungalszeenatkhatoon78No ratings yet
- Daftar Penyakit Kompetensi 4ADocument12 pagesDaftar Penyakit Kompetensi 4ARoy Sandy PermanaNo ratings yet
- Infographic Health and Well BeingDocument1 pageInfographic Health and Well BeingsomayaNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous MycosesDocument3 pagesCutaneous MycosesLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc AngodNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Allium Cepa PDFDocument1 pageAntimicrobial Activity of Allium Cepa PDFJoana San Pedro100% (1)
- Cultural Characterization of MicroorganismsDocument3 pagesCultural Characterization of MicroorganismsANo ratings yet
- Swine Infectious Gastrointestinal DiseasesDocument6 pagesSwine Infectious Gastrointestinal DiseasesnessimmounirNo ratings yet
- COURSE PLAN MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesCOURSE PLAN MicrobiologyPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Skinlife Force 2.0: Anti-Microbial Solution For TextileDocument11 pagesSkinlife Force 2.0: Anti-Microbial Solution For TextilejazzyzNo ratings yet
- Classification of BacteriaDocument10 pagesClassification of BacteriaSajid Ali100% (1)
- Mbbs-I Roll No.: Topic-Vaccine Development in India ForDocument3 pagesMbbs-I Roll No.: Topic-Vaccine Development in India ForJiyaa PatelNo ratings yet
- Surgical InfectionsDocument310 pagesSurgical InfectionsOmar Ed ChavezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials - New and Old Molecules in The Fight Against Multi-Resistant BacteriaDocument363 pagesAntimicrobials - New and Old Molecules in The Fight Against Multi-Resistant BacteriaŽaba Od ŽadaNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Pemfiksasi Nitrogen Azotobacter Sebagai Pupuk Hayati Dan Pengendali Penyakit Pada Tanaman Kacang PanjangDocument8 pagesBakteri Pemfiksasi Nitrogen Azotobacter Sebagai Pupuk Hayati Dan Pengendali Penyakit Pada Tanaman Kacang PanjangcwidiNo ratings yet
- LifeStraw - Personal Water Filter - Filtration Performance SheetDocument1 pageLifeStraw - Personal Water Filter - Filtration Performance SheettorgeNo ratings yet
- Clostridium PerfingensDocument7 pagesClostridium PerfingensEma KurgasNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Isolation of Listeria MonocytogenesDocument5 pagesProcedure For Isolation of Listeria MonocytogenesclairealbertiniNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Public Health at A GlanceDocument169 pagesVeterinary Public Health at A GlanceKian TakallouNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis Infection Prevention and Control SOPDocument9 pagesGastroenteritis Infection Prevention and Control SOPM Ukrio Zefri ZonNo ratings yet
- Sharon Biomix ClearDocument1 pageSharon Biomix ClearIsrael ExporterNo ratings yet
- 10 - Medical MycologyDocument74 pages10 - Medical Mycologyjames rukenyaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The MicroworldDocument10 pagesUnderstanding The MicroworldLOON, TRISHA ANN, D.No ratings yet
- STS Video ScriptDocument2 pagesSTS Video ScriptCynthia Y De VeraNo ratings yet