Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids Pre-Learning Homework
Quarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids Pre-Learning Homework
Uploaded by
Ganilyn PoncianoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids Pre-Learning Homework
Quarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids Pre-Learning Homework
Uploaded by
Ganilyn PoncianoCopyright:
Available Formats
Quarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids
Pre-learning Homework
Ganilyn D. Ponciano. STEM 12 – A GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2
1. What are the assumptions of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases?
Any gas is a collection of innumerable number of minuscule particles which are known as
molecules according to Avogadro’s law.
There are no forces of attraction or repulsion among the particles or between the molecules
and the surroundings.
The gas particles are always at straight, rapid, fast & random motion resulting in inevitable
collisions with other particles and the surroundings that changes direction of motion.
Since the particle are spherical, solid and elastic the collisions involving them are elastic in
nature as well i.e their kinetic energy is conserved even after collisions.
The total kinetic energy of the particles is proportional to the absolute temperature.
In some books two other assumptions are given as well:
The size or area of each particle is negligible compared to that of the container.
Pressure of gas is result of the continuous clash of the particles with the wall of the
container.
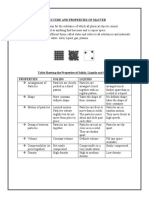
2. Fill in the blanks with the characteristics of solid, liquid, and gas in terms of certain properties:
State of Shape Volume Density Compressibility Motion of
Matter Particles
Gas Has no definite Has no definite is equal to its about ten times the continual straight-
shape or volume shape or volume mass divided diameter of the line motion
by its volume molecules
themselves
Liquid liquid has no Has definite a measure of Liquids are non- quite close
definite shape and volume how heavy it is compressible and together and
takes a shape for the have constant move with
dictated by its amount volume but can random motion
container measured change shape. throughout the
container
Solid Have a definite solid has high densities non-compressible particles do
shape. Some definite volume and have constant vibrate about
examples are: volume and constant their position in
Cone, Cuboid, shape the structure
Sphere, Cube and
Cylinder.
You might also like
- Lab Report 5. Investigating The Hydraulic JumpDocument12 pagesLab Report 5. Investigating The Hydraulic Jumpfazeen100% (1)
- 01.02 Cartisen Diver Lab ReportDocument2 pages01.02 Cartisen Diver Lab ReportKatara KittenNo ratings yet
- Mil Module 5Document9 pagesMil Module 5Ganilyn Ponciano75% (8)
- Mil Module 5Document9 pagesMil Module 5Ganilyn Ponciano75% (8)
- Matter & Its CompositionDocument16 pagesMatter & Its CompositionVenkat100% (1)
- Control System QuizDocument28 pagesControl System QuizSagar Ruchandani100% (5)
- General Chemistry 2Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Fayza Jalil BaladingNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lectures and TutorialsDocument164 pagesFluid Mechanics Lectures and TutorialsAnees Kadhum AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- Ram Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Document5 pagesRam Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Ram Gelo HawayNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DembureNo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids AutosavedDocument16 pages1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids Autosavedhinacay.jonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lectures and TutorialsDocument164 pagesFluid Mechanics Lectures and Tutorialsعوض أمحمدNo ratings yet
- What We Are Meaning by Fluids?: Fluid Mechanics Lectures and Tutorials 1Document4 pagesWhat We Are Meaning by Fluids?: Fluid Mechanics Lectures and Tutorials 1Anees Kadhum AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- Adrian Albacite - Worksheet 1.1 INTERACTIVE ACTIVITIESDocument3 pagesAdrian Albacite - Worksheet 1.1 INTERACTIVE ACTIVITIESAd Ri AnNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gas (Solid, Liquid) - Project YakapDocument16 pagesProperties of Gas (Solid, Liquid) - Project YakapGeraldine Angel MirandaNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter-17 2Document20 pages06 Chapter-17 2royalcamp2005No ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- Gases vs. Liquids and SolidsDocument67 pagesGases vs. Liquids and SolidsRenolsa EspinosaNo ratings yet
- The Gaseous StateDocument28 pagesThe Gaseous Stateevermorenicole42No ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument5 pagesStates of MatterSai SawantNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument23 pagesChap-2 - Kinetic Particle TheoryMin HanbyeolNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument15 pagesIntermolecular ForcesKrizthel RockwellNo ratings yet
- 5 The Gaseous StateDocument14 pages5 The Gaseous StateArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Particulate Nature of MatterDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - Particulate Nature of MatterPhillipe WalkerNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statistics and Dynamic Study Materials PDFDocument11 pagesFluid Statistics and Dynamic Study Materials PDFMurugeswariNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Summarymiss HalaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Document1 pageKinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Clint ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Module 1Document54 pagesFluids - Module 1plm.riveralarissaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- Review NotesDocument5 pagesReview NotesSuzuri LNo ratings yet
- Notes 3rd QuarterDocument36 pagesNotes 3rd QuarterKent DanielNo ratings yet
- 10 Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument1 page10 Kinetic Molecular TheoryOwais Siddiqui IX-M-ANo ratings yet
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0No ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument36 pagesThree States of MatterFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemistry Chapter 1 Part B Notes 1624285704Document8 pages9 Chemistry Chapter 1 Part B Notes 1624285704RajiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document2 pagesLecture 1Gabriel JocsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Matter in NatureDocument1 pageChapter 5 Matter in NatureYuhannNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - CHANGES IN MATTERDocument17 pagesModule 5 - CHANGES IN MATTERJBM 0531No ratings yet
- Dungca, Catherine D. Gen Chem Worksheet 1Document2 pagesDungca, Catherine D. Gen Chem Worksheet 1Dungca, Catherine D.No ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- PHARM 121: Harmaceutical Norganic Hemistry: TitleDocument5 pagesPHARM 121: Harmaceutical Norganic Hemistry: TitleTrixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionDocument27 pagesThermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionSaad BBNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument1 pageMATTERL NarineNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument19 pagesStates of MatterLyn Liza SilvaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument8 pagesStates of Mattertanish.pujari17No ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Chemistry IiDocument3 pagesReviewer in General Chemistry IiGabrielle Anne OBOSNo ratings yet
- Mass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)Document2 pagesMass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)hajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- CT - 3Document45 pagesCT - 3Snehal BhasinNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction M1Document51 pagesProperties of Matter and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction M1Rj Delmundo NisperosNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Matter: Presented By: Prof. Jennifer B. EscobarDocument19 pagesMatter: Presented By: Prof. Jennifer B. EscobarJoshua KulotNo ratings yet
- 8i - Word - Sheets FluidsDocument2 pages8i - Word - Sheets FluidsJoshua ChungNo ratings yet
- 6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346Document5 pages6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346avantikajethani20No ratings yet
- 2024 - Chapter 2 - KPTDocument11 pages2024 - Chapter 2 - KPTkaylamok3No ratings yet
- Kinetic Model NotesDocument4 pagesKinetic Model NotesAbdul rafay ImranNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 SCIENCE 10 (4th Quarter)Document6 pagesMODULE 1 SCIENCE 10 (4th Quarter)Nanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument3 pagesStates of MatterShivaani TekaleNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Simultaneity: Relativity without Inertial FramesFrom EverandThe Logic of Simultaneity: Relativity without Inertial FramesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Ponciano, Ganilyn D. - STEM 12-A (MIL 1)Document6 pagesPonciano, Ganilyn D. - STEM 12-A (MIL 1)Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Eapp 2nd Quarter Output 1Document3 pagesEapp 2nd Quarter Output 1Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A General Chemistry 2Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A General Chemistry 2Ganilyn Ponciano0% (3)
- Ponciano, Ganilyn D. - STEM 12-A (MIL 3)Document5 pagesPonciano, Ganilyn D. - STEM 12-A (MIL 3)Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Ponciano, Ganilyn D. - STEM 12-A (MIL 2)Document5 pagesPonciano, Ganilyn D. - STEM 12-A (MIL 2)Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- DRR 1st Pre-ActivityDocument15 pagesDRR 1st Pre-ActivityGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Mil Quarter 1 Module 3 Lesson 4: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilDocument9 pagesMil Quarter 1 Module 3 Lesson 4: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- MIL QUARTER 1 MODULE 5 Kwentong Jollibee AdDocument1 pageMIL QUARTER 1 MODULE 5 Kwentong Jollibee AdGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- GEN PHYSICS 1 INFOGRAPHICS 1 (Ponciano, Ganilyn)Document5 pagesGEN PHYSICS 1 INFOGRAPHICS 1 (Ponciano, Ganilyn)Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Mil Quarter 1 Module 4: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilDocument5 pagesMil Quarter 1 Module 4: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilGanilyn Ponciano100% (1)
- Mil Quarter 1 Module 6: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilDocument3 pagesMil Quarter 1 Module 6: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 11 - A Reaserch in Daily LifeDocument2 pagesGanilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 11 - A Reaserch in Daily LifeGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Mil Quarter 1 Module 3: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilDocument6 pagesMil Quarter 1 Module 3: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics Module 1Document6 pagesGen Physics Module 1Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3: Thinking Aloud My Decisions Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Homeroom GuidanceDocument4 pagesMODULE 3: Thinking Aloud My Decisions Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Homeroom GuidanceGanilyn Ponciano100% (1)
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Homeroom GuidanceDocument3 pagesGanilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Homeroom GuidanceGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Group-Activity-2 Valentino Ponciano Basilio Stem-12-ADocument2 pagesGroup-Activity-2 Valentino Ponciano Basilio Stem-12-AGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Assignment 3Document2 pagesEapp Assignment 3Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Mil Quarter 1 Module 1Document8 pagesMil Quarter 1 Module 1Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Assignment 4Document2 pagesEapp Assignment 4Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Quarter Module 1: Activity 1Document7 pagesHomework 1 Quarter Module 1: Activity 1Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Mil Quarter 1 Module 2: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilDocument7 pagesMil Quarter 1 Module 2: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A MilGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Homeroom GuidanceDocument5 pagesGanilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Homeroom GuidanceGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Checking of Understanding 1 Quarter Module 1Document1 pageChecking of Understanding 1 Quarter Module 1Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q1W1 Module 1 - "Activity: Academic or Not?"Document1 pageEapp Q1W1 Module 1 - "Activity: Academic or Not?"Ganilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Activity 1 SummaryDocument2 pagesEapp Activity 1 SummaryGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- DRR ReportingDocument2 pagesDRR ReportingGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- COT2 Presentation - HeatEngineDocument15 pagesCOT2 Presentation - HeatEngineMark Laurence MasellonesNo ratings yet
- PIEAS 1 Past Paper PakLearningSpotDocument13 pagesPIEAS 1 Past Paper PakLearningSpotMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 8 Q1 Week5Document9 pagesDLL Science 8 Q1 Week5jennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- BUSSTEPP Lectures PDFDocument163 pagesBUSSTEPP Lectures PDFzcapg17No ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering Tutorial Questions (With Solution)Document19 pagesReliability Engineering Tutorial Questions (With Solution)WANG_JUN0508100% (6)
- Energy: Jesús Polo, Jesús Ballestrín, Elena CarraDocument8 pagesEnergy: Jesús Polo, Jesús Ballestrín, Elena CarraDuvan Leandro Parra VelandiaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Radar Cross Section For Effective Warship DesignDocument1 pageEstimation of Radar Cross Section For Effective Warship DesignVishNo ratings yet
- Spherical Plain Bearings, Plain Bushes, Rod Ends: Catalogue 238Document181 pagesSpherical Plain Bearings, Plain Bushes, Rod Ends: Catalogue 238durvalmedinasNo ratings yet
- Ans and Sol JEE Main 2024 PH 1-27-01 2024 Shift 1 MorningDocument17 pagesAns and Sol JEE Main 2024 PH 1-27-01 2024 Shift 1 MorningShobha SangeetNo ratings yet
- Permanent Adjustment of Theodolite: Figure 21.2aDocument4 pagesPermanent Adjustment of Theodolite: Figure 21.2aahmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sputtering, Targets and Utilization PDFDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Sputtering, Targets and Utilization PDFanon_876950641No ratings yet
- Scaffolds Under Eccentric LoadsDocument14 pagesScaffolds Under Eccentric LoadsMalik AtikNo ratings yet
- Minifrac Analysis and DesignDocument28 pagesMinifrac Analysis and DesignTarek Tarkan100% (1)
- Tut 1 emDocument2 pagesTut 1 emBishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- Diffraction F. M. Grimaldi: Click On The Image For DetailsDocument5 pagesDiffraction F. M. Grimaldi: Click On The Image For DetailsGxilleNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor: General Information On Stepper MotorsDocument10 pagesStepper Motor: General Information On Stepper MotorsMasrul Nizam MahmodNo ratings yet
- Gauge Capability Studies PDFDocument4 pagesGauge Capability Studies PDFAnonymous NDwgQe7MNo ratings yet
- 80113-334 ERBE US VIO 300 D V 2 2 X D044265Document170 pages80113-334 ERBE US VIO 300 D V 2 2 X D044265RodrigoGutierrezDjmoscuNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument8 pagesPre CalculusBryan SaligaoNo ratings yet
- Twelve Books That Changed The WorldDocument6 pagesTwelve Books That Changed The Worldapi-19838084No ratings yet
- CVG 4184 - 6305 - Ch4 - Rock Mass Classification PDFDocument52 pagesCVG 4184 - 6305 - Ch4 - Rock Mass Classification PDFStar998No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies (Repaired)Document52 pagesChapter 17 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies (Repaired)Ng Shin JouNo ratings yet
- Codigos MercedesDocument8 pagesCodigos MercedesPrudencioTeodosioNo ratings yet
- Touchless BinDocument19 pagesTouchless BinJuliana AndresNo ratings yet
- Monte Carlo Methods For Radiation Transport: Fundamentals and Advanced Topics 1st Edition Oleg N. Vassiliev (Auth.)Document43 pagesMonte Carlo Methods For Radiation Transport: Fundamentals and Advanced Topics 1st Edition Oleg N. Vassiliev (Auth.)david.mager792100% (19)
- Sequence Guide - Soda Can Calorimeter Student SampleDocument3 pagesSequence Guide - Soda Can Calorimeter Student Sampleapi-334553540No ratings yet
- Digital Weighing MachineDocument33 pagesDigital Weighing MachineUmakant RajpootNo ratings yet