Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Science: Other Theories On The Origin of Universe
Earth and Life Science: Other Theories On The Origin of Universe
Uploaded by
Argueza, John Ryan V.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
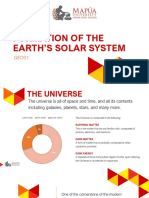
21 views3 pagesThe solar nebular disk model describes the formation of the solar system from an interstellar cloud of gas and dust following the Big Bang. It involves 5 key steps:
1) An interstellar cloud collapsed due to gravity and began rotating, forming a disk.
2) The center became hot enough through nuclear fusion to form a star (the Sun).
3) A protoplanetary disk of gas and dust formed around the young star.
4) Planets formed from the accretion of dust and rocks in the disk.
5) The solar wind blew away parts of the disk, leaving planets and other objects in stable orbits around the Sun.
Original Description:
Original Title
EARTH-AND-LIFE-SCIENCE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe solar nebular disk model describes the formation of the solar system from an interstellar cloud of gas and dust following the Big Bang. It involves 5 key steps:
1) An interstellar cloud collapsed due to gravity and began rotating, forming a disk.
2) The center became hot enough through nuclear fusion to form a star (the Sun).
3) A protoplanetary disk of gas and dust formed around the young star.
4) Planets formed from the accretion of dust and rocks in the disk.
5) The solar wind blew away parts of the disk, leaving planets and other objects in stable orbits around the Sun.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesEarth and Life Science: Other Theories On The Origin of Universe
Earth and Life Science: Other Theories On The Origin of Universe
Uploaded by
Argueza, John Ryan V.The solar nebular disk model describes the formation of the solar system from an interstellar cloud of gas and dust following the Big Bang. It involves 5 key steps:
1) An interstellar cloud collapsed due to gravity and began rotating, forming a disk.
2) The center became hot enough through nuclear fusion to form a star (the Sun).
3) A protoplanetary disk of gas and dust formed around the young star.
4) Planets formed from the accretion of dust and rocks in the disk.
5) The solar wind blew away parts of the disk, leaving planets and other objects in stable orbits around the Sun.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
SNDM – SOLAR NEBULAR DISK MODEL
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE
1. Interstellar cloud of gas & dust (nebula)
BIGBANG THEORY (Georges Lemaitre – Belgian *from bigbang
cosmologist and a Catholic priest) *from explosion of different stars
Expansion 2. Collapse
Singularity (size of an atom “nucleus of an *quickly rotating in the middle
atom”) *nuclear reaction --> star
a) Inflation (electroweak era) 3. Protosun
10-35 seconds inflated *pulling the gas & dusts to make the sun bigger
1035 meters expanded 4. Accretion disks
b) Protons, neutrons, quarks (particle era) *origin of planets
c) Nucleosynthesis (hydrogen & helium) *rocks & metals, ice
d) Radiation era 5. Solar wind
e) Matter domination [matter (+) & anti- *release sun charge particles
matter (-)]
f) Galaxies
Proofs/Evidences SUB-SYSTEMS
1. Red Shift (Edwin Hubble)
1. Geosphere
2. CMBR (Cosmic Microwave Background
[Sorry, can’t provide the exact diagram. You
Radiation) – remnant of radiation era.
can search for it or you can PM me (Phine
>made by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson
Leon) so that I can give you a picture of its
>George Gamow – developed the Bigbang
diagram from my original copy]
Theory
2. Atmosphere – ‘atmo’ means air
3. Hydrogen and Helium Ratio (75% Hydrogen
[Sorry, can’t provide the exact diagram. You
& 25% Helium)
can search for it or you can PM me (Phine
Other Theories on the Origin of Universe Leon) so that I can give you a picture of its
diagram from my original copy]
1. Steady State Theory (Fred Hoyle, Hermann 3. Hydrosphere (by oceanographers)
Bondi, Tommy Gold) – universe is uniform in 71% of Earth’s Surface
space and has unchanging time.
Discovery of quasars – older galaxies were
indeed located exceedingly farther than the
young nearby galaxies (favor in big bang 97% 3%
theory). saltwater freshwater
CMB 77% frozen
2. Oscillating Universe Theory – universe 22% ground water
currently exists between the big bang and the big 1% lakes,
crunch. rivers, streams
3. Eternal Inflation Theory – inflation never
stops 4. Biosphere
Biomes – communities
Nebular Hypothesis (Immanuel Kant and Pierre
*forest *aquatic *dessert
Simon Laplace) – solar system formed from a slowly-
rotating cloud of gas or a solar nebula that collapsed and Goldilocks Zone – indicates that the distance of Earth
flattened with a hot central region known as the sun and from the sun such that the amount of energy received is
the remaining materials because the planets and just enough to make the temperature of Earth neither too
everything else; would not able to form the rings nor hot nor too cold.
planets.
Jovian Planets – are also called gas giants.
Solar Nebula Theory – combined the idea of a
flattening solar nebula with that of a condensing Current Information about Solar System
interstellar dust as the nebula cooled, which serves as a 1. Flat
condensation nuclei where matter accumulated. 2. Revolution of the planets are counter clockwise
3. Rotation = clockwise
Other members or Solar System: Evidences of Continental Drift Theory
1. Asteroids main asteroid belt (between Mars 1. Topographic
& Jupiter) = “mini planets” 2. Fossils
2. Comets ice (because they are from in the 3. Rock & Mountain correlation
edge of planets) Kuper Belt 4. Climatic
3. Meteoroids -----> space
Meteors ---------> atmosphere Plate Tectonics Theory – supported the idea that
Meteorite -------> surface continents were moving and gave a more convincing
explanation as to how it moved.
A PLANET should be:
Plate boundaries – location where two tectonic plates
1. Orbiting the sun meet.
2. Round – for gravity
3. Clear its neighborhood 1. Convergent – plates that move towards each
other.
OCEANIC ZONES 2. Divergent – plates that move away from each
other.
Horizontal: 3. Transform – slide against each other.
a. Coastal – sometimes covered by the water. Seafloor spreading – ocean floor is split along the
b. Pelagic – covered by the water ridge and that is where the magma rises to form the new
Vertical: ocean floor.
1. Epipelagic – ‘sunlight zone’ Volcanism – phenomena connected with volcanoes and
2. Mesopelagic – dim light or ‘twig light zone’ volcanic activity; release of Earth materials from the
3. Bathypelagic – no sunlight or ‘The Midnight surface of the earth from volcanoes.
Zone’ Pacific Ring of Fire – arc around the Pacific Ocean
4. Abyssopelagic – invertebrates or ‘The Abyss’ where many volcanoes and earthquakes are formed.
5. Hadalpelagic – ‘The Trench’
Absolute Dating – method that uses unstable elements
to determine the exact age of a rock.
Relative Dating – method of arranging geological
events and the rocks left behind in sequence without
providing for the actual age of rocks.
TECTONIC PROCESSES
1. Folding – two plates collide with each other
where some of the layers of rock which make up
the crust buckle and form folds; like
convergence.
a. Anticline – forms mountains & hills
b. Syncline – forms valleys
Continental Drift Theory – states that the continents 2. Faulting – blocks of rock fracture or break
drifted around the world and has once formed a giant apart; like transformation
landmass or supercontinent. a. Dip-slip – inclined fractures where the
blocks have mostly shifted vertically.
Pangaea – supercontinent or giant landmass that existed
b. Strike-slip – vertical fractures where the
during Paleozoic era until early Mesozoic era.
blocks have mostly moved horizontally.
Panthalassa – superocean that existed and surrounded
Pangaea.
Alfred Wegener – German polar researcher,
geophycist, and meteorologist. Was known for his work
on the continental drift theory. In his effort to defend his
work, he went to Greenland ice sheet where he died.
Tropical cyclones – typhoons (northwest pacific);
hurricanes (Atlantic and northeast region)
-storm system that characterized by rapid
spiraling storms, low pressure center, and intensely
strong winds.
o Tropical depression (45-62 km/hr)
o Storm (63-117 km/hr)
o Typhoon (118-239 km/hr)
o Super typhoon (240 km/hr or higher)
Geologic Time Scale – shows the correlation or relative
ages of rocks in all parts of the world and divided
Earth’s history into smaller blocks of time.
Hazards caused by Volcanic Eruptions
1. Lahars and floods
2. Lava flows and domes
BONUS QUESTIONS:
1. What is the connection between volcanic activity
and plate tectonics?
2. What is Bituminous Coal?
NOTE: This reviewer is not complete compared to the
lectures of this subject. You can only use this as a basis
during the study. Honestly, I don’t like this subject so if
you have some questions regarding with these topic to
me, I can’t assure you that I can give you a 100% of its
correct answer. Study hard!
You might also like
- Pre-Commissioning and CommissioningDocument9 pagesPre-Commissioning and CommissioningSaurabh Sharma100% (7)
- Earth and Life Science Reviewer PDFDocument16 pagesEarth and Life Science Reviewer PDFAndrea Detera83% (12)
- Geol 11 Reviewer For 1st LEDocument15 pagesGeol 11 Reviewer For 1st LEFrettyDavidNo ratings yet
- Grade-11 W1-Earth and Life Science-ModuleDocument5 pagesGrade-11 W1-Earth and Life Science-ModuleLeslie Mermelo100% (1)
- Rotational DynamicsDocument28 pagesRotational DynamicsCindy-chan Delfin100% (1)
- Earth Science Reviewer UniverseDocument8 pagesEarth Science Reviewer UniverseSophia GarciaNo ratings yet
- PDF Earth and Life Science Reviewerpdf CompressDocument16 pagesPDF Earth and Life Science Reviewerpdf CompressReysha Mae BagayawaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesEarth ScienceANGEL GWYNET RIEGONo ratings yet
- Earth Sci Lesson 1Document7 pagesEarth Sci Lesson 1kylematthewbalajayocaslaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reviewer Module 8-12 Nalay KuwanggggDocument6 pagesEarth Science Reviewer Module 8-12 Nalay Kuwanggggdm arriesgadoNo ratings yet
- Earth SciDocument9 pagesEarth SciJay ParkNo ratings yet
- Theories Behind The Origin of The UniverseDocument25 pagesTheories Behind The Origin of The UniverseslayNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science (NS001) WK1-8 - REVIEWERDocument12 pagesEarth and Life Science (NS001) WK1-8 - REVIEWERAleiah Tyrese PobleteNo ratings yet
- Sci01 ReviewerDocument11 pagesSci01 ReviewerJairah Faith CammayoNo ratings yet
- SCI111Document7 pagesSCI111Ciana SacdalanNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument15 pagesEarth Sciencemaryteph298No ratings yet
- Earth Science W1 To W2Document6 pagesEarth Science W1 To W2razshellareignNo ratings yet
- Geology 11 NotesDocument14 pagesGeology 11 Notescarmellagabriel31No ratings yet
- Earth Science 1Document5 pagesEarth Science 1Juls LleverNo ratings yet
- RevengeDocument3 pagesRevengekou.takeda.2007No ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth and Life SciencemowielovesNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci Q1 CompilationDocument13 pagesEarth Sci Q1 CompilationPatricia Gabriell MulaNo ratings yet
- Cosmology 2016Document27 pagesCosmology 2016carolNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Universe: Big Bang TheoryDocument3 pagesFormation of The Universe: Big Bang TheoryJianna ClementeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer and Summary of ElsDocument16 pagesReviewer and Summary of ElsKyle Brian Talingting100% (1)
- Earth Science: Evolution of The Universe According To The BIG Bang TheoryDocument4 pagesEarth Science: Evolution of The Universe According To The BIG Bang TheoryJudylyn SakitoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesLecture 1-Earth and Life ScienceJunar SantiagoNo ratings yet
- For Sped - Science ActivityDocument16 pagesFor Sped - Science ActivityMarineilNo ratings yet
- EarthSci Module 2.1 Theories About The Formation of The UniverseDocument8 pagesEarthSci Module 2.1 Theories About The Formation of The UniversePia Cassandra GamboaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument20 pagesEarth ScienceAfidah CamarNo ratings yet
- Universe Solar System PPT EDRAIZADocument19 pagesUniverse Solar System PPT EDRAIZACelestine LunaNo ratings yet
- Unit I. Origin and Structure of The Earth Lesson 1: The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument8 pagesUnit I. Origin and Structure of The Earth Lesson 1: The Universe and The Solar SystemMonica RiveraNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 1 Earth Life ScienceDocument5 pagesDLP Week 1 Earth Life ScienceAien Chloe FranciscoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCINCES Lec#01Document32 pagesPHYSICAL SCINCES Lec#01Zain Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- ELSCI NOTES Theories To MineralsDocument19 pagesELSCI NOTES Theories To Mineralsejqc proNo ratings yet
- Earthsci PrelimsDocument6 pagesEarthsci PrelimsKrisha DimailigNo ratings yet
- Geography - Microsoft OneNote OnlineDocument5 pagesGeography - Microsoft OneNote OnlineRicha SinghNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci Unit 1Document3 pagesEarth Sci Unit 1KhrysNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 1st SemDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Science 1st SemAngelica Ross de LunaNo ratings yet
- Geography English MediumDocument84 pagesGeography English MediumRajan shahNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument2 pagesOrigin of The UniverseLeonie LanzadoNo ratings yet
- Els ReviewerDocument3 pagesEls ReviewerNicole SandovalNo ratings yet
- Origin and Branches of Earth ScienceDocument9 pagesOrigin and Branches of Earth ScienceJon Meynard TavernerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Geology: Lesson 2: The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument10 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Geology: Lesson 2: The Universe and The Solar SystemGerard GalangNo ratings yet
- GEO01 - Week 3 (CO1) - Formation of The Earth's Solar SystemDocument58 pagesGEO01 - Week 3 (CO1) - Formation of The Earth's Solar SystemMatte Raven AngNo ratings yet
- Meteorology, Oceanography, and Astronomy.: Earth Science The Big BangDocument4 pagesMeteorology, Oceanography, and Astronomy.: Earth Science The Big BangKaryl AarientosNo ratings yet
- Notes in Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesNotes in Earth and Life ScienceRachel Hanh AbaloNo ratings yet
- Abalo - Notes in Science (1st Sem)Document19 pagesAbalo - Notes in Science (1st Sem)Rachel Hanh AbaloNo ratings yet
- Elsc Earth and Life Science First QuarterDocument2 pagesElsc Earth and Life Science First QuarteraliahandreamarquezNo ratings yet
- Earth Science HUMSS 11Document4 pagesEarth Science HUMSS 11Hannah VergaraNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences 2 Weeks Lessons PDFDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Sciences 2 Weeks Lessons PDFDanabelle PasionNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth ScienceJehan AlimatarNo ratings yet
- ELSEE NotesDocument6 pagesELSEE NotesfelizNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument26 pagesOrigin of The UniverseDoreen Guevarra Ollanas100% (2)
- Physical Geology QAB1013: The EarthDocument25 pagesPhysical Geology QAB1013: The EarthtambahkenalanNo ratings yet
- Geology LectureDocument4 pagesGeology LectureGabriel Christopher MembrilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 SlideDocument23 pagesLesson 1 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- First Le ReviewerDocument10 pagesFirst Le ReviewerGerard GalangNo ratings yet
- Primordial Atom, Which Described As The Cosmic Egg.: Origin & Structure of Earth Earth & Life Science 11 - First QuarterDocument5 pagesPrimordial Atom, Which Described As The Cosmic Egg.: Origin & Structure of Earth Earth & Life Science 11 - First QuarterHelace SentinaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Handout ELSDocument7 pages1st Quarter Handout ELSClifford Tubana100% (1)
- EARTHANDLIFEDocument10 pagesEARTHANDLIFEStephanie PorioNo ratings yet
- Nostradamus Volume 12 of 17: And Explanations of Afterlife ExperiencesFrom EverandNostradamus Volume 12 of 17: And Explanations of Afterlife ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluid 2023-06-07 11 - 57 - 27Document1 pageProperties of Fluid 2023-06-07 11 - 57 - 27Argueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- RSW CMT Portland CementDocument6 pagesRSW CMT Portland CementArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Weir and Gates 2023-06-07 12 - 05 - 00Document8 pagesWeir and Gates 2023-06-07 12 - 05 - 00Argueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Rectilinear Motion 2023-06-07 12 - 07 - 37Document5 pagesRectilinear Motion 2023-06-07 12 - 07 - 37Argueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- The Internet PDFDocument2 pagesThe Internet PDFArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Mechanics IntroductionDocument10 pagesMechanics IntroductionArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Raymond CatellDocument12 pagesRaymond CatellArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Immanuel KantDocument25 pagesImmanuel KantArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument17 pagesEARTHQUAKEArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Nature of Literature: Vista 1: TraditionalismDocument4 pagesNature of Literature: Vista 1: TraditionalismArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Literary Element Used in Creative Non-FictionDocument6 pagesLiterary Element Used in Creative Non-FictionArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1560771052138Document28 pagesOrca Share Media1560771052138Argueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- LIT First Quarter ReviewerDocument16 pagesLIT First Quarter ReviewerArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- FINALS ELS Made Easy 1Document9 pagesFINALS ELS Made Easy 1Argueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Literature Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesLiterature Finals ReviewerArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- EAPP Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesEAPP Finals ReviewerArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- ELS PrelimsDocument10 pagesELS PrelimsArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- English 2 Reviewer Reading and Writing ReadingDocument10 pagesEnglish 2 Reviewer Reading and Writing ReadingArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer II Mid QPDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer II Mid QPRambabuDaraNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 2216-05 Standard Test Methods For Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass PDFDocument7 pagesASTM D 2216-05 Standard Test Methods For Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass PDFHamza QayyumNo ratings yet
- Hyrolysis of AL Dross To Achieve Zero Hazardous WasteDocument9 pagesHyrolysis of AL Dross To Achieve Zero Hazardous WasteXantos YulianNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Sheet 5 Energy ADocument19 pagesHydraulics Sheet 5 Energy AMohamed H AliNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Valerie Ivanna WenNo ratings yet
- Arson Module in PrelimDocument19 pagesArson Module in PrelimHan WinNo ratings yet
- 2 Environmental PollutionDocument10 pages2 Environmental Pollutionlula byNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Variable Speed Wind Turbine Voltage Regulation Model Using MATLAB/SimulinkDocument5 pagesSimulation of Variable Speed Wind Turbine Voltage Regulation Model Using MATLAB/SimulinkWiem Jmei MansourNo ratings yet
- Summative TEstDocument14 pagesSummative TEstxoxkakidoxoxNo ratings yet
- Course Objective QuestionDocument243 pagesCourse Objective Questionahmish kabbaxeNo ratings yet
- Technical Note A FORTRAN Program For Calculating The Evaporation Rates in Diesel Engine Fuel SpraysDocument5 pagesTechnical Note A FORTRAN Program For Calculating The Evaporation Rates in Diesel Engine Fuel Spraysim19rahulNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gas Reduction Strategy 2020 2022Document2 pagesGreenhouse Gas Reduction Strategy 2020 2022te fannyNo ratings yet
- 2024 Processes Involving Ideal GasesDocument17 pages2024 Processes Involving Ideal GasesncayiyanaminentleNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Heating and Fire in Coal Mines: SciencedirectDocument13 pagesSpontaneous Heating and Fire in Coal Mines: SciencedirectTamil VananNo ratings yet
- Basic Definitions & Terminology in Soil MechanicsDocument7 pagesBasic Definitions & Terminology in Soil MechanicspkNo ratings yet
- Rmi Breakthrough BatteriesDocument84 pagesRmi Breakthrough BatteriesNAVDEEP100% (1)
- § ¤ Ёп 9Document6 pages§ ¤ Ёп 9Dilnaz BaimuratovaNo ratings yet
- Why Is Water Important in Life? WhatDocument4 pagesWhy Is Water Important in Life? Whataro0j100% (1)
- LIQUIDO-06 Quiz 1Document1 pageLIQUIDO-06 Quiz 1Krexia Mae L. LiquidoNo ratings yet
- Energy: Sources, Conversion, Conservation and SustainabilityDocument37 pagesEnergy: Sources, Conversion, Conservation and SustainabilityRicardoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Module 1: University of Rizal SystemDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Module 1: University of Rizal SystemJMNo ratings yet
- Eco RightDocument84 pagesEco RightJesse RobertNo ratings yet
- Plant LifeDocument19 pagesPlant Lifesheena2sa100% (3)
- ENPHYS30 1 Work and EnergyDocument35 pagesENPHYS30 1 Work and Energychlorine169No ratings yet
- NWPDocument31 pagesNWPmrafikmNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Air Around UsDocument3 pagesClass 7 - Air Around Usmamta sehrawat100% (1)
- Simulation and Analysis of Highspeed Modular Flywheel Energy Storage Systems Using MATLAB SimulinkDocument6 pagesSimulation and Analysis of Highspeed Modular Flywheel Energy Storage Systems Using MATLAB Simulinkgunasekaran sNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 TestDocument4 pagesTopic 5 TestGenevieve LawrenceNo ratings yet