Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem Bonding Notes Ch7 2019
Chem Bonding Notes Ch7 2019
Uploaded by
Kevin Weathers0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document discusses different types of chemical bonds and their properties:
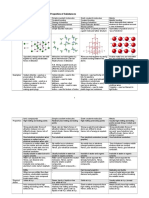
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between ions, forming ionic compounds that are typically hard, brittle solids with high melting points.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, forming molecules. Covalent compounds can be solids, liquids or gases and have lower melting points than ionic compounds.
- Metallic bonds involve delocalized or freely moving valence electrons between positive metal ions. Metallic compounds are typically good conductors and exist as solids.
Original Description:
notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of chemical bonds and their properties:
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between ions, forming ionic compounds that are typically hard, brittle solids with high melting points.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, forming molecules. Covalent compounds can be solids, liquids or gases and have lower melting points than ionic compounds.
- Metallic bonds involve delocalized or freely moving valence electrons between positive metal ions. Metallic compounds are typically good conductors and exist as solids.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesChem Bonding Notes Ch7 2019
Chem Bonding Notes Ch7 2019
Uploaded by
Kevin WeathersThe document discusses different types of chemical bonds and their properties:
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between ions, forming ionic compounds that are typically hard, brittle solids with high melting points.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, forming molecules. Covalent compounds can be solids, liquids or gases and have lower melting points than ionic compounds.
- Metallic bonds involve delocalized or freely moving valence electrons between positive metal ions. Metallic compounds are typically good conductors and exist as solids.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
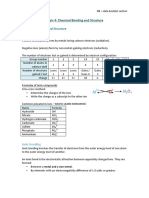
Chemical Bonds Ionic Covalent Metallic
Chemical Compound made of Compound made of Compound made
Structure network of ions molecules or diatomic of
called formula units molecules Atoms in metals
(alloys)
Valence Transfer of Polar bonds: Share Valence electrons
electrons oppositely valence electrons are delocalized or
(outermost charged valence equally free to move
energy level) electrons Nonpolar Bonds:
Unequal sharing of
electrons
Bonding Consist of Positive Consist of molecules Consist of only
ion: cation (metal) made of nonmetals metals
Negative ion: anion
(nonmetal)
Properties Malleable, ductile, Brittle, Soft, and Dull Same as ionic
Hard, and Lustrous Low melting point
High melting point Low boiling point
High boiling point
Conductivity good conductor of poor conductor of good conductor of
electricity in aqueous electricity electricity
form (nonelectrolyte/
(electrolyte) dimmer)
States of matter Mostly solids Solids, liquids, or gases Mostly solids
Aqueous in the liquid
state
Binary Full name of metal *Numerical prefixes n/a for this class
Nomenclature and –ide suffix on *No mono on 1 st
the nonmetal element
-ide suffix at the end
Polyatomic Use criss-cross **Special rules for n/a
nomenclature method w/ cation and acids and other covalent
anion compounds
Writing Formulas of Simple Organic Compounds:
Straight-Chain Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons with a
single chain between each molecule
Formula: simple alkanes (CnH2n+2)
Table 21.2 p. 751 List the 1st Ten of the Alkane Series
Alkenes: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons with one or more
double covalent bonds between carbon atoms in a chain
Formula: simple alkenes (CnH2n)
Alkynes: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons that contain one or
more triple bonds between carbon atoms in a chain
Formula: simple alkynes (CnH2n-2)
Alcohol: An organic compound in which a hydroxyl group
replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon
Formula: alcohols (CH3-OH)
You might also like
- Chemistry of Drug Fasttrack PDFDocument271 pagesChemistry of Drug Fasttrack PDFBudhi PrasetiaNo ratings yet
- Grade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionDocument65 pagesGrade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionMoun Lynn Sythu100% (3)
- CHM214 PS1-CFMonarquiaDocument12 pagesCHM214 PS1-CFMonarquiacfmonarquiaNo ratings yet
- Core Chem Bonding Intro PresDocument43 pagesCore Chem Bonding Intro PresSHEILA MARIE CORTADO - UNDANNo ratings yet
- Electron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingDocument50 pagesElectron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingJoan Clarice CorlaNo ratings yet
- N 10 02 Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesN 10 02 Chemical BondingShivNo ratings yet
- 02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingDocument10 pages02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingShreyash ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Chem BondingDocument40 pagesChem BondingMark AhronNo ratings yet
- Nursing Chemistry ChapDocument22 pagesNursing Chemistry ChapJ.K HomerNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Covalent BondDocument55 pages3.2 Covalent Bond陈凯雯No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LNDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding LNCenjie Niña Hayag SongcalNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer (Chemical Bonding) 3Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer (Chemical Bonding) 3Yohan Kleir PuruggananNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Reviewer - CHEMISTRYDocument2 pages2nd Quarter Reviewer - CHEMISTRYKate Ashley CailingNo ratings yet
- 02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingDocument9 pages02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 5 Study GuideDocument3 pagesChemistry Test 5 Study GuideLeanne RoseNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument64 pagesChemical BondangelieshaynnmtalagtagNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument6 pagesChemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersH.sNo ratings yet
- CH 22 Chemical BondingDocument12 pagesCH 22 Chemical BondingeherrerahghsNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 1st Quarter - Week Three Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructureDocument5 pagesGrade 12 1st Quarter - Week Three Chemical Bonds and Lewis Structurenicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Chemical Bonding and Structure PDFDocument13 pagesTopic 4 Chemical Bonding and Structure PDFSveta StepanovaNo ratings yet
- X Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24Document35 pagesX Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24zilkag47No ratings yet
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Chemistry The Ionic Bond Model: Two Fundamental ConceptsDocument2 pagesChemistry The Ionic Bond Model: Two Fundamental ConceptsPATRICIA GAIL PONo ratings yet
- Specialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoDocument5 pagesSpecialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Structure 2.1Document16 pagesStructure 2.1nehasri.sagineeduNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument3 pagesBondingJudy SherifNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec Notes CompletedDocument36 pagesChem Lec Notes Completedaliaaplarisan647No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 1-4 2 NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 4 1-4 2 NotesKarelene SotoNo ratings yet
- Covalent Ionic: Forms MoleculesDocument1 pageCovalent Ionic: Forms Moleculesash100% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesChemical BondingJenifer TaniaNo ratings yet
- 4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondDocument71 pages4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondEren Micaella100% (1)
- IB Chemistry HL 20-22 VocabularyDocument5 pagesIB Chemistry HL 20-22 VocabularySchmidt JakeNo ratings yet
- FaziraRazak - Chemical BondingDocument71 pagesFaziraRazak - Chemical BondingaieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular GeometryDocument211 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometryonline purchaseNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis EditedDocument32 pagesElectrolysis Editedqa795907No ratings yet
- Bonding - Covalent N Metallic BondDocument22 pagesBonding - Covalent N Metallic Bondwadheea.thaufeeqNo ratings yet
- 002 Ch02 Chemistry v2020 PDFDocument4 pages002 Ch02 Chemistry v2020 PDFshahidabubaker19No ratings yet
- Earth & Science (Learning Portfolio)Document7 pagesEarth & Science (Learning Portfolio)triviaNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document12 pagesScience 9Catherine Yorong PedranoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quarter 2Document12 pagesScience 9 Quarter 2Catherine Yorong PedranoNo ratings yet
- IMFA and Chemical BondingDocument137 pagesIMFA and Chemical BondingEnna SertNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 3Document77 pagesScience 9 Week 3Eliseo MuyaNo ratings yet
- Chemıcal BondsDocument10 pagesChemıcal BondsDesirie MarceloNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- C2 Revision Slides V3 Questions MS HDocument35 pagesC2 Revision Slides V3 Questions MS HNeen NaazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Chemistry 1C Engr. Albert S. Revilla InstructorDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding Chemistry 1C Engr. Albert S. Revilla Instructorgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Periodic Properties and Variations of PropertiesDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Periodic Properties and Variations of PropertiesSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument39 pagesIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 1 TEDocument5 pagesElectrolysis 1 TETom TommmaNo ratings yet
- Definitions PDFDocument9 pagesDefinitions PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 2020Document73 pagesChemical Bonding 2020HANNAH JULIA CAPUNGCONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Basic ChemistryClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 62761 - 2023 - 05 - 06 - 21 - 02Document40 pagesChemical Bonding - 62761 - 2023 - 05 - 06 - 21 - 02Tae KookNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Fulfils The Octet Arrangement Rule Ionic Bonds Metal Ion Donates Electrons Non-Metal Ion Accepts Electrons Cation Anion Concept MapDocument34 pagesChemical Bonds Fulfils The Octet Arrangement Rule Ionic Bonds Metal Ion Donates Electrons Non-Metal Ion Accepts Electrons Cation Anion Concept MapAnindita Effanti PutriNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals React To Form Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesMetals and Non-Metals React To Form Ionic CompoundsDarshanaK 728714No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 254 PDFDocument27 pagesChemical Bonding - 254 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Donate Electron Accept ElectronDocument2 pagesDonate Electron Accept ElectronPraveen Raj RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Covalent Network MoleculesDocument1 pageCovalent Network MoleculesGill CraigNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument284 pagesWelcome To: Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSachin NayakNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesMinistry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic ChemistryDocument50 pagesChemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic Chemistryyayooo200450% (2)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chapter 6-7 SG Answer Key 2014Document25 pagesChapter 6-7 SG Answer Key 2014Kevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds: Section 1Document8 pagesChemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds: Section 1Kevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- What Was The Byzantine Empire Like? (Please Read Below)Document3 pagesWhat Was The Byzantine Empire Like? (Please Read Below)Kevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Write The Definition of Executive Departments/Cabinet: 1) Read Each Scenario and With The Help ofDocument3 pagesVocabulary: Write The Definition of Executive Departments/Cabinet: 1) Read Each Scenario and With The Help ofKevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab - Magnisium Ribbon - Synthesize An Ionic CompoundDocument3 pagesChem Lab - Magnisium Ribbon - Synthesize An Ionic CompoundKevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- Sum Academy Chem 3Document5 pagesSum Academy Chem 3RAO UMAIRNo ratings yet
- Complexes With: BondingDocument4 pagesComplexes With: BondingAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Chemistry P1 2022 Set 1Document6 pagesAnswer Scheme Chemistry P1 2022 Set 1Tan JennyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Giant Covalent StructuresDocument3 pagesA Study On Giant Covalent StructuresNicholas TeyNo ratings yet
- Na PerDocument39 pagesNa PerHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- 2 AskelandDocument20 pages2 AskelandAlfredo ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Teoría Del Orbital MolecularDocument41 pagesTeoría Del Orbital MolecularEMMANUEL ALEJANDRO FERNANDEZ GAVIRIANo ratings yet
- Hydrogen BondingDocument1 pageHydrogen BondingOdette SnazelleNo ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 3 Atomic Structure: Assessment ObjectivesDocument30 pagesH2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 3 Atomic Structure: Assessment ObjectivesArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic BondingJohanna LipioNo ratings yet
- Lewis Theory of BondingDocument8 pagesLewis Theory of BondingJeto SantosNo ratings yet
- CMY 117 For VSEPR and Molecular GeometryDocument8 pagesCMY 117 For VSEPR and Molecular GeometryJack WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem. NotesDocument117 pagesOrganic Chem. NoteselcarlsansNo ratings yet
- Hybridization TarakkyDocument36 pagesHybridization TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- 9ch0 01 Rms 20230817Document35 pages9ch0 01 Rms 20230817sofia begumNo ratings yet
- Evaluation (GRADE 8)Document1 pageEvaluation (GRADE 8)Gel CabansagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding I The Covalent Bond Copyright © The McGraw-Hill CompaniesDocument87 pagesChemical Bonding I The Covalent Bond Copyright © The McGraw-Hill CompaniesRoll OutNo ratings yet
- TH1KDocument7 pagesTH1Kpinklimeblue6700No ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding - Grade 10Document13 pagesCovalent Bonding - Grade 10sashana stoddartNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesNeacle AlimonsurinNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument56 pagesBondingAngel Joy CATALAN (SHS)No ratings yet
- 3center and 2 Electron BondDocument20 pages3center and 2 Electron BondAmin GNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Physical Science Molecular PolarityDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Physical Science Molecular Polarityartjill printingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Periodic RelationshipsDocument42 pagesChapter 8 Periodic RelationshipsBRAYAN VELASQUEZ SOTELONo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures: Molecular Structure and BondingDocument83 pagesLewis Structures: Molecular Structure and Bondingحني اسفيانيNo ratings yet
- I6 VSEPR Effectoflonepairstheorysheet - 000Document2 pagesI6 VSEPR Effectoflonepairstheorysheet - 000Anuj MalaraNo ratings yet
- Basics of Organic Chemistry B Paaras Thakur @livedailyjeeDocument132 pagesBasics of Organic Chemistry B Paaras Thakur @livedailyjeeEluri YadaiahNo ratings yet
- Wades Rules 2Document5 pagesWades Rules 2ch_ymyaaNo ratings yet