Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 4 - Audit in Automated Environment
Chap 4 - Audit in Automated Environment
Uploaded by
Tejas jogadeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 4 - Audit in Automated Environment
Chap 4 - Audit in Automated Environment
Uploaded by
Tejas jogadeCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.
in
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 1
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
Chapter 4
Audit in an Automated Environment
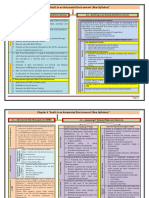
"Marks Distribution of Past Exams (New Syllabus)"
6
4
Marks
0
May-18 Nov-18 May-19 Nov-19 May-20 Nov-20 May-21 -
Series1 4 4 5 4
*From May 2019, Marks are given only for subjective questions.
4.1 – Meaning and Components of Automated Environment
Q.1 A real-time environment is a type of automated environment in which
business operations and transactions are initiated, processed and
recorded immediately as they happen without delay. It has several
critical IT components that enable anytime, anywhere transactions to
take place. You are required to name the components and its example of
real-time environment. [MTP-Oct. 18, RTP-Nov. 18]
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 2
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
Answer: Components and Example of real Time Environment:
• Real Time Environment is a type of automated environment in
which business operations and transactions are initiated,
processed and recorded on a real-time basis, i.e. immediately on
their occurrence.
• Examples of Such environments are Airlines and Railway
Reservations, CORE Banking,
E-Commerce, ERP etc.
• Real Time Environment facilitates anytime, anywhere
transactions to take place. For this purpose, it is essential to have
the systems, networks and applications available during all times.
IT Components required in Real Time Environment:
1. Applications like ERP, Core Banking Etc.
2. Middleware like web servers
3. Networks like WAN, Internet hosting.
4. Hardware like Data centers, storage devices, power supply etc.
4.2 – Auditing in an Automated Environment
Q.2 SA 315 requires the auditor to obtain an understanding of the entity and
its environment as a part of Risk Assessment procedure to identify and
assess Risk of Material Misstatements. List the areas of which auditor is
required to obtain understating in an automated environment.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 3
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
Or
Write a short note on: Understanding and documenting automated
environment. [RTP-May 20]
Answer: Understanding of Automated Environment
As required by SA 315, auditor is required to obtain an understanding
of the entity and its environment as a part of Risk Assessment
procedure to identify and assess Risk of Material Misstatements. In an
automated environment, auditor is required to obtain an understating
of the following:
1. Applications being used by the entity;
2. IT infrastructure components for each of the application;
3. Organisation structure and governance;
4. Policies, procedures and processes followed;
5. IT risks and controls.
As required by SA 230, auditor is required to document the
understanding of a company automated environment.
Q.3 In a controls-based audit, the audit approach can be classified into three
broad phases comprising of planning, execution, and completion. In this
approach, the considerations of automated environment will be relevant
at every phase. Comment. [RTP-May 18, MTP-Aug. 18]
Or
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 4
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
“The audit cycle consists of Planning, Execution and Completion. The
automation in processing of business transactions has considerations to
be weighed by auditor at every phase of this cycle” – Enumerate the focal
points of such considerations when auditing in automated environment.
[Nov. 18-New Syllabus (4 Marks)]
Or
In a controls-based audit, the audit approach can be classified into three
broad phases comprising of planning, execution, and completion. You are
required to briefly explain the relevant considerations for every phase in
above audit approach in case of an automated environment.
[Nov. 19 – New Syllabus (4 Marks)]
Answer: Considerations of automated environment in different stages of
Audit:
Stages of Audit Considerations
A. Planning Stage
1. Risk • Consider risk arising from use of IT
Assessment systems.
• Identify significant accounts and
disclosures.
• Identify likely sources of
misstatement.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 5
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
2. Understanding 1. Document understanding of business
of the Business processes using Flowcharts /
Narratives.
2. Prepare Risk and Control Matrices.
3. Understand design of controls by
performing walkthrough of end-to-
end process.
4. Process wide considerations for Entity
Level Controls, Segregation of Duties.
B. Executing Stage
3. Assessing Consider aspects related to
Entity Level • understanding and review of IT
Controls Governance.
• Segregation of duties,
• Review of General IT Controls &
Application Controls.
4. Assessing Consider aspects relating to Risks and
Process Level Controls with each process, sub-process
Controls and activity.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 6
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
C. Reporting Stage
5. Testing of Consider the evaluation of control
Reports & deficiencies using Data Analytics.
Information
produced by
the entity at
completion
stage
“ICAI Examiner Comments”
It appeared that the examinees were not aware about the topic consequently they
answered in general terms.
4.3 – Enterprise Risk Management
Q.4 The volatility, unpredictability and pace of fast changes that exists in the
automated environment today is far greater than in the past and
consequently it throws more risks to business which requires them to
have a need to continuously manage such risks. State various risks which
an enterprise may have to face and manage. [May 19 (5 Marks)]
Answer: Risks which an enterprise may face and manage:
Businesses today operate in a dynamic environment. The volatility,
unpredictability and pace of changes that exist in the business
environment today is far greater than in the past. Some of the reasons
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 7
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
for this dynamic environment include globalisation, use of
technology, new regulatory requirements, etc. Because of this
dynamic environment the associated risks to business have also
increased and companies have a need to continuously manage risks.
Examples of risks include:
1. Market Risks;
2. Regulatory & Compliance Risks;
3. Technology & Security Risks;
4. Financial Reporting Risks;
5. Operational Risks;
6. Credit Risk;
7. Business Partner Risk;
8. Product or Project Risk; and
9. Environmental Risks.
Q.5 Briefly describe the various stages of a Risk Assessment process.
Answer: Stages in a Risk Assessment Process:
Risk Assessment Process is the most critical component of Enterprise
Risk Management. The entity’s risk assessment process forms the
basis for how management determines the risks to be managed.
Steps involved in Risk Assessment Process
Step 1 - Define Business Objectives and Goals.
Step 2 - Identify events that affect achievement of business objectives.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 8
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
Step 3 - Assess likelihood and impact.
Step 4 - Respond and mitigate risks.
Step 5 - Assess Residual Risks.
Q.6 Write short note on: Enterprise Risk Management.
Answer: Enterprise Risk Management (ERM):
• ERM is a formal program that is implemented across an enterprise
for enabling risk management. In many countries, companies are
required to have a formal ERM Program as a statutory requirement.
• In India, Sec. 134(3) of Companies Act, 2013 requires the Board of
Directors to include in their report a statement indicating
development and implementation of a risk management policy for
the company including identification therein of elements of risk, if
any, which in the opinion of the Board may threaten the existence
of the company.
• The most common framework that is suitable for implementing an
effective ERM is the COSO Enterprise Risk Management –
Integrated Framework developed by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organisations (COSO) in 2004 and subsequently updated in 2016
to address the changes in business environment.
• Besides COSO framework, another widely available framework is
the ISO 31000 Risk Management standard published by the
International Organization for Standardization.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 9
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
4.4 – Assessing IT Related Risks and Controls
Q.7 Write short note on: General IT Controls.
Answer: General IT Controls:
General IT-controls are policies and procedures that relate to many
applications and support the effective functioning of application
controls.
They apply to mainframe, mini frame, and end-user environments.
General IT-controls that maintain the integrity of information and
security of data commonly include controls over the following:
1. Data centre and network operations.
2. System software acquisition, change and maintenance.
3. Program change.
4. Access security.
5. Application system acquisition, development, and maintenance.
Q.8 Describe application controls and give three examples of automated
application controls.
Answer: Application Controls:
• Application controls are manual or automated procedures that
typically operate at a business process level and apply to the
processing of individual applications.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 10
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
• Application controls can be preventive or detective in nature and
are designed to ensure the integrity of the accounting records.
• Accordingly, application controls relate to procedures used to
initiate, record, process and report transactions or other financial
data. These controls help ensure that transactions occurred, are
authorised, and are completely and accurately recorded and
processed.
• Examples of Application controls include the following:
1. Edit checks and Validation of input data,
2. Sequence Number checks.
3. Limit Checks.
4. Reasonable Checks.
5. Mandatory Data Fields.
Q.9 Identify the controls which are automated, manual or IT dependent
manual for the below mentioned cases?
(i) Price master configured in the sales master can only be edited by
authorised personnel in the system.
(ii) Invoice cannot be booked in SAP in case Purchase orders are not
approved.
(iii) Inventory ageing report is pulled out from the system based on which
provisioning is calculated after analyzing the future demand by the
inventory personnel and approved by the controller.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 11
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
(iv) All invoices are signed by warehouse personnel before the goods are
dispatched to the customer.
(v) Credit limit is assigned to the customer and goods cannot be sold in
excess of credit limit configured in the system.
(vi) All changes to the credit limit is approved manually by sales
manager.
(vii) Ageing report is pulled out from SAP based on which provisioning is
calculated by accounting personnel and approved by financial
controller.
(viii)PO, GRN (Good received note) and invoice are matched by the system
before it is posted in the financial records. [MTP-April 18]
Answer: Identification of Controls:
(i) Automated control as there is inbuilt control which allows
editing in sales master by only authorised personnel.
(ii) Automated control as there is inbuilt control which doesn’t
allow approval of invoice in case of non approval of purchase
order.
(iii) IT dependent manual control as inventory ageing report is
pulled out from the system after which provision for inventory
is manually approved.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 12
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
(iv) Manual control as sign off is required to be done for the invoice
before the dispatch of the goods.
(v) Automated control as there is inbuilt control that doesn’t allow
goods to be sold if credit limit assigned to the customer has been
crossed.
(vi) Manual control as sign off is required for every change to the
credit limit.
(vii) IT dependent manual control as ageing report is relied upon for
calculation of provisioning for debtors.
(viii) Automated control as PO, GRN and invoice is matched by the
system before recording of the invoice to the vendor account.
4.5 – Evaluating Controls at Entity Level and Process Level
Q.10 Distinguish between: Direct Entity Level Controls and Indirect Entity
Level Controls.
Or
While evaluating the risks and controls at entity level, the Auditor should
take cognizance of the prevalent direct and indirect entity level controls
operating in the entity. Explain what they pertain to with few examples.
[May 18 (4 Marks)]
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 13
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
Answer: Direct Entity Level Controls (ELCs) and Indirect Entity Level
Controls:
Direct ELCs
Direct ELCs operate at a level of business process to prevent, detect
or correct a misstatement in a timely manner. Examples of Direct
ELCs are:
• Business performance reviews;
• Monitoring of effectiveness of control by Internal Audit function.
Indirect ELCs
Indirect ELCs do not relate to any specific business process,
transaction or account balance and therefore, cannot prevent,
detect or correct misstatements.
Indirect ELCs contribute indirectly to the effective operation of
direct ELCs. Examples of Indirect ELCs are:
• Company code of conduct;
• Human resource policies;
• Job roles & responsibilities.
“ICAI Examiner Comments”
It seems that examinees were unaware of the topic. Very few examinees could
comprehend and explain Direct ELCs and indirect ELCs with examples. Some examinees
misunderstood the question and explained wrongly the types of audit Risk Viz., Inherent
Risk, Control Risk, Detection Risk.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 14
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
4.6 – Data Analytics
Q.11 What is Data Analytics. When auditing in an automated environment,
auditors can apply the concepts of data analytics for several aspects of
an audit. State those aspects.
Or
In an automated environment, the data stored and processed in systems
can be used to get various insights into the way business operates. This
data can be useful for preparation of management information system
(MIS) reports and electronic dashboards that give a high-level snapshot
of business performance. In view of above you are required to briefly
discuss the meaning of data analytics and example of circumstances
when auditing in an automated environment, auditors can apply the
concepts of data analytics. [RTP-May 19]
Answer: Data Analytics:
• Data analytics is an analytical process by which meaning
information is ggenerated and prepared from raw system data
using processes, tools, and techniques. In an automated
environment, various insights can be extracted from operational,
financial, and other forms of electronic data internal or external
to the organization
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 15
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
• The data so extracted is useful for preparation of management
information system (MIS) reports and electronic dashboards that
give a high-level snapshot of business performance. The data
analytics methods used in an audit are known as Computer
Assisted Auditing Techniques or CAATs.
Application of Data Analytics
In an automated environment, auditors can apply the concept of
data analytics for several aspects of an audit including the
following:
1. Preliminary Analytics;
2. Risk Assessment;
3. Control Testing;
4. Non-Standard Journal Analysis;
5. Evaluation of Deficiencies;
6. Fraud Risk assessment.
Q.12 “Generating and preparing meaningful information from raw system
data using processes, tools, and techniques is known as Data Analytics
and the data analytics methods used in an audit are known as Computer
Assisted Auditing Techniques or CAATs.” You are required to give a
suggested approach to get the benefit from the use of CAATs.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 16
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
Answer: Suggested approach to get the benefit from the use of CAATs:
A suggested approach to benefit from the use of CAATs is to follow
the steps given below:
Step 1: Understand Business Environment including IT;
Step 2: Define the Objectives and Criteria;
Step 3: Identify Source and Format of Data;
Step 4: Extract Data;
Step 5: Verify the Completeness and Accuracy of Extracted Data;
Step 6: Apply Criteria on Data Obtained;
Step 7: Validate and Confirm Results.
4.7 – Standards, Guidelines and Procedures – to be adhered to while auditing in
an automated environment
Q.13 When auditing in an automated environment the auditor should be
aware, adhere to and be guided by the various standards, guidelines and
procedures that may be relevant to both audit and the automated
environment. Briefly describe any four such standards.
Answer: Standards relevant to Audit and Automated Environment:
(i) Standards on Auditing (SA): AASB of ICAI issues various
standards which are required to be followed while auditing the
financial statements of an entity.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 17
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
(ii) Sec. 143(3)(i) of Companies Act, 2013: Section 143(3)(i)of
Companies Act 2013 requires statutory auditors to provide an
Independent Opinion on the Design and Operating Effectiveness
of Internal Financial Controls with reference to financial
statements of the company as at Balance Sheet date. For this
purpose, ICAI issued a Guidance Note on Audit of Internal
Financial Controls Over Financial Reporting which provides the
guidelines and procedures for reporting on IFC.
(iii) Section 404 of SOX Act, 2002: Section 404 of Sarbanes Oxley
Act of 2002 requires public listed companies to implement,
assess and ensure effectiveness of internal controls over
financial reporting. Auditors of such companies are required to
express an independent opinion on the design and operating
effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting (ICFR).
(iv) CoBIT: Control Objectives for Information and Related
Technologies is best practice IT Governance and Management
framework published by Information Systems Audit and Control
Association. It provides the required tools, resources and
guidelines that are relevant to IT governance, risk, compliance
and information security.
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 18
Chapter 1 – Quality control and Engagement Standards ©www.altclasses.in
(v) CSF: Cyber security Framework published by the National
Institute of Standards and Technology is one of the most popular
framework for improving critical infrastructure cyber security,
which provides a set of standards and best practices for
companies to manage cyber security risks.
--------------------------
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg
Page 19
You might also like
- H&M HRMDocument38 pagesH&M HRMjanvi 20No ratings yet
- PRC Memorandum Circular No. 03 (Hazard Pay Clarifiation On Risk Factor)Document1 pagePRC Memorandum Circular No. 03 (Hazard Pay Clarifiation On Risk Factor)ABI Alco QANo ratings yet
- Auditing Rpa SystemDocument40 pagesAuditing Rpa SystemPalak AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Search PDF Books Com Ion Behaviour L M Prasad PDFDocument3 pagesSearch PDF Books Com Ion Behaviour L M Prasad PDFAarti GuptaNo ratings yet
- External AuditDocument84 pagesExternal Auditvishnupriya14450% (2)
- 1 Auditing Standards, Statements and Guidance Notes - An Overview PDFDocument24 pages1 Auditing Standards, Statements and Guidance Notes - An Overview PDFnavyaNo ratings yet
- Gui Ideonr Risk Bas Sed Inte Ernal Au Udit Pla N: Discl AimerDocument205 pagesGui Ideonr Risk Bas Sed Inte Ernal Au Udit Pla N: Discl AimerJaswanth PatangeNo ratings yet
- Automated System in BankingDocument60 pagesAutomated System in BankingMewati GaneshNo ratings yet
- Tally FeaturesDocument69 pagesTally FeaturesSudhakar Ganjikunta0% (1)
- Online Banking System: Functional Specification For User Login ModuleDocument7 pagesOnline Banking System: Functional Specification For User Login ModuleV A Prem KumarNo ratings yet
- Complete Mba Project 1Document47 pagesComplete Mba Project 1sachingaubaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Mercantile BankDocument39 pagesInternship Report On Mercantile BankIubianNo ratings yet
- KMB-401 Project Management (Mba - Iv Sem) Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesKMB-401 Project Management (Mba - Iv Sem) Important QuestionsNeha PalNo ratings yet
- Bcom 6 Sem Imp Questions - All SubsDocument5 pagesBcom 6 Sem Imp Questions - All SubsAbdul RaheemNo ratings yet
- Project Report Human Resource ManagementDocument72 pagesProject Report Human Resource ManagementThe KnightsNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 - Introduction To AuditingDocument19 pagesTOPIC 1 - Introduction To AuditingLANGITBIRUNo ratings yet
- Mobile Banking - ICICI BANK1Document64 pagesMobile Banking - ICICI BANK1ashfaq shaikhNo ratings yet
- Mba 301Document26 pagesMba 301Akash skills100% (1)
- The Auditing ProfessionDocument10 pagesThe Auditing Professionmqondisi nkabindeNo ratings yet
- Immersion Project Gropu No 22Document82 pagesImmersion Project Gropu No 22patel dhruvNo ratings yet
- Important Questions of Information Technology BBA & B.Com With AnswersDocument60 pagesImportant Questions of Information Technology BBA & B.Com With AnswersRishit GoelNo ratings yet
- Detect Phishing Website by Using Machine LearningDocument4 pagesDetect Phishing Website by Using Machine Learningeditor ijeratNo ratings yet
- Risk MGTDocument92 pagesRisk MGTJeetu RajaiNo ratings yet
- IntenshipDocument38 pagesIntenshiplovely siva100% (1)
- Mba Bcss ManualDocument4 pagesMba Bcss Manualleelachowdary1No ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior and DevelopmentDocument22 pagesOrganizational Behavior and Developmentወዲ ተስፋይ ገብረዮሱስNo ratings yet
- IFC PPT AhmedabadDocument57 pagesIFC PPT AhmedabadPrashant JainNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial Statement: Project Report OnDocument36 pagesAnalysis of Financial Statement: Project Report OnMayur KundarNo ratings yet
- General Banking, Loans and Advances Sonali BankDocument91 pagesGeneral Banking, Loans and Advances Sonali BankFahim0% (1)
- Best Manager Event (Ideas) : 1. Shark TankDocument3 pagesBest Manager Event (Ideas) : 1. Shark TankANKUR PUROHITNo ratings yet
- Organizational Study at ITI LTD, PalakkadDocument12 pagesOrganizational Study at ITI LTD, PalakkadVishnu S KumarNo ratings yet
- MBA 3rd SemDocument2 pagesMBA 3rd SemAdarsh NimborkarNo ratings yet
- Me - Rnsit NotesDocument71 pagesMe - Rnsit Notesantoshdyade100% (1)
- E-Commerce Project (MBA SEM II)Document201 pagesE-Commerce Project (MBA SEM II)shivam guptaNo ratings yet
- 3 Difference Between FA, CA & MADocument9 pages3 Difference Between FA, CA & MAamits3989No ratings yet
- The Future of Finance and Accounting:: Accelerating Digital Transformation in A Time of CrisisDocument45 pagesThe Future of Finance and Accounting:: Accelerating Digital Transformation in A Time of CrisisMarina SpasiuNo ratings yet
- Project On Bank AuditDocument33 pagesProject On Bank AuditShubham utekarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: NPTEL Online Certification Courses Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: NPTEL Online Certification Courses Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurSanjay100% (1)
- Mock Test 02 BST Sunil PandaDocument3 pagesMock Test 02 BST Sunil PandaHarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Auditing ProjectDocument15 pagesAuditing ProjectSasi Samhitha KNo ratings yet
- Audit AssigmentDocument11 pagesAudit AssigmentPooja JainNo ratings yet
- Report Delta AirlinesDocument13 pagesReport Delta Airlinesabu ubaidahNo ratings yet
- MBA 2nd Sem SyllabusDocument6 pagesMBA 2nd Sem SyllabusMohammad Ameen Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Bank of Baroda BankingApplicationDocument45 pagesBank of Baroda BankingApplicationprateekNo ratings yet
- Bharat QR ManualDocument3 pagesBharat QR ManualaishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Ty - Baf. Sem Vi Cost-1Document31 pagesTy - Baf. Sem Vi Cost-1Nilesh DaveNo ratings yet
- Scope of ManagementDocument40 pagesScope of ManagementDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process Automation Mini ProjectDocument34 pagesRobotic Process Automation Mini ProjectSipu100% (1)
- QMF Approved and CirculatedDocument78 pagesQMF Approved and CirculatedMuhammad Amir Usman100% (1)
- Project-Report-On-Working-Capital-Management-In-Hcl Important PDFDocument96 pagesProject-Report-On-Working-Capital-Management-In-Hcl Important PDFtanu srivastavaNo ratings yet
- MCom PI-2 Quantitative Techniques For BusinessDocument2 pagesMCom PI-2 Quantitative Techniques For BusinessMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Library Management System Assignment by Simon (BUBT)Document8 pagesLibrary Management System Assignment by Simon (BUBT)Simon Haque50% (2)
- MIS Structure Based On Physical ComponentsDocument2 pagesMIS Structure Based On Physical ComponentsSonia LawsonNo ratings yet
- Financial Strategy FormulationDocument7 pagesFinancial Strategy FormulationyaarbaileeNo ratings yet
- Project Report On "Cash Flow Statement at Thinknext Technologies Pvt. LTD"Document54 pagesProject Report On "Cash Flow Statement at Thinknext Technologies Pvt. LTD"Sat NamNo ratings yet
- 3rd CRMDocument18 pages3rd CRMShikhar Dixit100% (1)
- Hrpis - Unit 1 - SybmsDocument20 pagesHrpis - Unit 1 - SybmsYashNo ratings yet
- C6 Audit Question BankDocument12 pagesC6 Audit Question BankYash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Audit in An Automated Environment by CA - Pankaj GargDocument4 pagesChapter 4 - Audit in An Automated Environment by CA - Pankaj GargAnjali P ANo ratings yet
- Auditing Applications, Part 2: Tommie W. Singleton, PH.D., Cisa, Cgeit, Citp, Cpa, IsDocument4 pagesAuditing Applications, Part 2: Tommie W. Singleton, PH.D., Cisa, Cgeit, Citp, Cpa, IsJean Dumas MauriceNo ratings yet
- Superior & Inferior Mesenteric Arteries Portal Vein & Its TributariesDocument19 pagesSuperior & Inferior Mesenteric Arteries Portal Vein & Its TributariesHevin GokulNo ratings yet
- Cuaderno de Actividades: Programa Nacional de InglésDocument5 pagesCuaderno de Actividades: Programa Nacional de InglésIselina RNo ratings yet
- Work Flow Plan - 4 (Supatsorn)Document7 pagesWork Flow Plan - 4 (Supatsorn)Calvin Van ChenNo ratings yet
- Swine ProductionDocument73 pagesSwine ProductionDUGONG PHNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - 1 Prof. Kalyan Chakravarti Department of Basic Courses Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Management - 1 Prof. Kalyan Chakravarti Department of Basic Courses Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurIvani KatalNo ratings yet
- Project Fianace 1Document46 pagesProject Fianace 17karswapnilNo ratings yet
- Importance of Psychology in Nursing PracticeDocument6 pagesImportance of Psychology in Nursing PracticeNan Nda Pradipta67% (3)
- AgarwalPackers - in QuotationDocument2 pagesAgarwalPackers - in Quotation9853318441No ratings yet
- Blue CampaignDocument2 pagesBlue CampaignDavid IbanezNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q3 Mapeh 4 Melc BasedDocument11 pagesPeriodical Test Q3 Mapeh 4 Melc BasedLEA ROSE ARREZANo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Continuous Band Sealer (Horizontal Orientation) Model No: FR-900SDocument5 pagesOperating Manual: Continuous Band Sealer (Horizontal Orientation) Model No: FR-900SRishi RaghaniNo ratings yet
- Craftsman Drill PressDocument26 pagesCraftsman Drill PressMilesFosseyNo ratings yet
- CLC 18-10Nb: A NB Stabilized 18Cr-10Ni Austenitic Stainless Steel (347 Grade)Document4 pagesCLC 18-10Nb: A NB Stabilized 18Cr-10Ni Austenitic Stainless Steel (347 Grade)PeterWayNo ratings yet
- Lesson1.2 Day3 Clean and Sanitize Kitchen PremisesDocument16 pagesLesson1.2 Day3 Clean and Sanitize Kitchen PremisesAliyah PlaceNo ratings yet
- High Performance Plastic Materials Guide Aug 2009Document8 pagesHigh Performance Plastic Materials Guide Aug 2009JeanMichelMNo ratings yet
- Jinny Choe Temp Mem CardDocument1 pageJinny Choe Temp Mem CardginauineNo ratings yet
- Soal Procedure Text 1Document8 pagesSoal Procedure Text 1Nina Sri AstutiNo ratings yet
- Pulse Power BU Understanding Common Mode NoiseDocument6 pagesPulse Power BU Understanding Common Mode NoiseÁrpád HimpliNo ratings yet
- Am I Crazy, or Is It My ShrinkDocument225 pagesAm I Crazy, or Is It My ShrinkTheFreeSpirit100% (5)
- CH17 Past Entry QuestionsDocument2 pagesCH17 Past Entry QuestionsKhanNo ratings yet
- B11 JiayiDocument1 pageB11 JiayiJumana AlSaadoonNo ratings yet
- Acetone Design ReviewDocument66 pagesAcetone Design ReviewEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Grading Structure GesDocument7 pagesGrading Structure Ges3944/95100% (1)
- Pedigree PPT (Biology)Document5 pagesPedigree PPT (Biology)Maxxdlc 16No ratings yet
- Gold Standard GuidelinesDocument16 pagesGold Standard GuidelinesCaio LeônidasNo ratings yet
- Maternity Benefit PolicyDocument2 pagesMaternity Benefit Policyshrija nairNo ratings yet
- Endress-Hauser Deltabar M PMD55 enDocument9 pagesEndress-Hauser Deltabar M PMD55 encristi_nc2upgNo ratings yet
- A Guide For Commercial Importers: Importing Into The United StatesDocument199 pagesA Guide For Commercial Importers: Importing Into The United Statescpears56No ratings yet
- Critically Evaluate Function of Ionisation ChamberDocument5 pagesCritically Evaluate Function of Ionisation ChamberMichelle LEINo ratings yet