Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parasitology Babesia SPP Cat
Parasitology Babesia SPP Cat
Uploaded by
Irina AtudoreiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parasitology Babesia SPP Cat
Parasitology Babesia SPP Cat
Uploaded by
Irina AtudoreiCopyright:
Available Formats
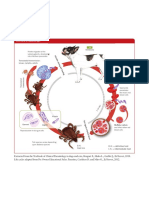
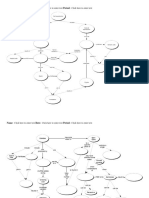
Life cycle of Babesia spp.
Kinete migrates to the
salivary glands, developing I.H.
into infective sporozoites Vertebrate
Infe
ctio
Transstadial transmission:
nd
larvae, nymphs, adults
urin
g tic
k fe
edin
g
transmission
Transovarial
Sporozoite
penetrates
the host’s red
blood cells
ays
4d
7–1
Kinete
Tick
Gamont Zygote
inges
Multiply, rupture
and infect other red
ts inf
Reproduction in tick gut cells blood cells
ected
blood
Tick species varies depending D.H.
upon Babesia species Hard tick D.H. = definitive host
I.H. = intermediate host
Extracted from the Textbook of Clinical Parasitology in dogs and cats, Beugnet F., Halos L., Guillot J., Ed Servet, 2018.
Life cycles adapted from Pet Owner Educational Atlas. Parasites, Carithers D. and Miro G., Ed Servet, 2012.
You might also like
- Cell Final ExamDocument8 pagesCell Final ExamJorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, DevelopingDocument1 pageLife Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, DevelopingIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of RHDDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of RHDshmily_0810No ratings yet
- Blood SmearsDocument4 pagesBlood SmearsAmor KourdouliNo ratings yet
- PlasmodiumDocument13 pagesPlasmodiumDAVID TERRONESNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium: Asexual Growth and Sexual Development in The Haematopoietic Niche of The HostDocument13 pagesPlasmodium: Asexual Growth and Sexual Development in The Haematopoietic Niche of The HostEzme VázquezNo ratings yet
- Virus Chart For Med MicroDocument2 pagesVirus Chart For Med MicroAndie RaczNo ratings yet
- 64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)Document6 pages64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)sourajeetsahoo2610No ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology-AmebiasisDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology-AmebiasisHajirNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 224 ToxoplasmosisDocument15 pagesCapitulo 224 ToxoplasmosisEdsonPerezNo ratings yet
- MB Rickettsiaceae PassDocument2 pagesMB Rickettsiaceae PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument70 pagesUntitledAhmad QuraanNo ratings yet
- Sporozoa TableDocument2 pagesSporozoa TableJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis (Plu - ZoonosessDocument8 pagesZoonosis (Plu - Zoonosess6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Disease: ElephantiasisDocument1 pageAnalysis of Disease: ElephantiasisAkash YadavNo ratings yet
- Broad Fish Tapeworm Pork Tapeworm Beef Tapeworm Dwarf Tapeworm Rat Tapeworm Dog or Cat Tapeworm, Pumpkin Seed Tapeworm Dog Tapeworm, Hydatid Tapeworm Common Rat TapewormDocument1 pageBroad Fish Tapeworm Pork Tapeworm Beef Tapeworm Dwarf Tapeworm Rat Tapeworm Dog or Cat Tapeworm, Pumpkin Seed Tapeworm Dog Tapeworm, Hydatid Tapeworm Common Rat TapewormSteven CaragNo ratings yet
- Erythropoiesis - Development and Differentiation - Dzierzak - 2013Document16 pagesErythropoiesis - Development and Differentiation - Dzierzak - 2013angeles delgado marquinaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Ms Sara KhanDocument37 pagesForm 4 Biology Ms Sara KhanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Helminthic Infection 3Document13 pagesIntestinal Helminthic Infection 3gf5kxqgnx9No ratings yet
- Parasitology SimplifiedDocument18 pagesParasitology SimplifiedAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- Revisão ToxoplasmoseDocument12 pagesRevisão ToxoplasmoseRosana BritoNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFNatalie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument168 pagesUntitledIcaro KashamuraNo ratings yet
- Haematology Part 1Document152 pagesHaematology Part 1Sai praveen DasariNo ratings yet
- Best HandMade Notes of INHERITANCE ChapterDocument12 pagesBest HandMade Notes of INHERITANCE Chapterhbadhani11No ratings yet
- 18.sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument25 pages18.sexual and Asexual ReproductionAubrey Cissé MwakayeNo ratings yet
- Clocks An Rulers in Life... and Synthetic BiologyDocument133 pagesClocks An Rulers in Life... and Synthetic BiologySaúlNo ratings yet
- SdarticleDocument2 pagesSdarticlegorpimcgorpersenNo ratings yet
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 pagesAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniNo ratings yet
- AP Bio CH 10 15 16Document16 pagesAP Bio CH 10 15 16Hiba NajjarNo ratings yet
- Mycology SimplifiedDocument8 pagesMycology Simplifiedvishuvishu8648No ratings yet
- Table of HML Infections - Numbers-Feuil1Document3 pagesTable of HML Infections - Numbers-Feuil1naazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Hematology - Red Blood CellsDocument1 pageHematology - Red Blood CellsChewyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Sep 2021Document14 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sep 2021Sanju SNo ratings yet
- Cestodes - TableDocument5 pagesCestodes - TableJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 01 PDFDocument1 page01 PDFRishikanta NameirakpamNo ratings yet
- Nematodes & Cestodes TableDocument20 pagesNematodes & Cestodes TableAbby SiervoNo ratings yet
- Pically, The Esicmaa Microscopica: ParasitesDocument1 pagePically, The Esicmaa Microscopica: ParasitesFghu GhujiNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument1 pageMalariaSonny Dizon PareñasNo ratings yet
- 11th STD - Class-3 (ZMP Sir) - Chemical Coordination and Integration - NotesDocument18 pages11th STD - Class-3 (ZMP Sir) - Chemical Coordination and Integration - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Intro+Clini+Blood Film Malaria Balsam 2Document66 pagesIntro+Clini+Blood Film Malaria Balsam 2DaxNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology RevisionDocument4 pagesBacteriology RevisionVenkat TNo ratings yet
- Biol 23Document820 pagesBiol 23defnedemircayNo ratings yet
- Trematodes and RicktesiosisDocument2 pagesTrematodes and RicktesiosisDeepankar SrigyanNo ratings yet
- Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Disease: Where Is The Risk?: CommentaryDocument4 pagesPsoriasis and Cardiovascular Disease: Where Is The Risk?: CommentarySaifuddin HaswareNo ratings yet
- Cell ReproductionConceptMapfillableDocument2 pagesCell ReproductionConceptMapfillableJanet NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Rhetoric of Confess10N: CenturyDocument8 pagesThe Rhetoric of Confess10N: CenturyMNo ratings yet
- Note 18 May 2024Document4 pagesNote 18 May 2024Ahmed Mohamed HelalNo ratings yet
- Animals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)Document5 pagesAnimals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)krisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument6 pagesHepatitis BCarmen MargoNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument19 pagesTrematodesCamilove EricNo ratings yet
- Preceptors: Prof. Rita Sood Prof. Padma M.V. Dr. Rohit Bhatia Speaker: Swastik AgrawalDocument77 pagesPreceptors: Prof. Rita Sood Prof. Padma M.V. Dr. Rohit Bhatia Speaker: Swastik AgrawalIqbal AbdillahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cestodes and Minor CestodesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Cestodes and Minor CestodesJustin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Hours: PlanceDocument1 pageHours: PlanceSayandeep DuttaNo ratings yet
- Repro On AninimalDocument32 pagesRepro On AninimalAnush GaikwadNo ratings yet
- 9 ThyroidDocument3 pages9 Thyroidfekid37444No ratings yet
- Pro To ZoologyDocument9 pagesPro To Zoologytxhj82xcnmNo ratings yet
- MB Spirochaete PassDocument2 pagesMB Spirochaete PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes: RE, Vic Ed . NE, at A ADocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes: RE, Vic Ed . NE, at A APatricia NerNo ratings yet
- (A) Hydra (B) RedwoodsDocument6 pages(A) Hydra (B) Redwoodsエアーア ラシブNo ratings yet
- Marvellous Repossessions: The Tempest, Globalization and The Waking Dream of ParadiseFrom EverandMarvellous Repossessions: The Tempest, Globalization and The Waking Dream of ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition Physical and Sensory PropertiDocument13 pagesChemical Composition Physical and Sensory PropertiIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Wcms 400598Document76 pagesWcms 400598Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health Perceptions in Work-Related TranDocument20 pagesSafety and Health Perceptions in Work-Related TranIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Bread MetDocument32 pagesBread MetIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- ACRP DesignCompetition 2ndplace ManagementDocument54 pagesACRP DesignCompetition 2ndplace ManagementIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- AdvanceDocument11 pagesAdvanceIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Bread Consumption and Waste of Households in UrbanDocument15 pagesBread Consumption and Waste of Households in UrbanIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Belts For The Airport Industry: Helping AchieveDocument6 pagesBelts For The Airport Industry: Helping AchieveIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- 101-112 18946 UchrońskiDocument12 pages101-112 18946 UchrońskiIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Policies For Information Security & PrivacyDocument166 pagesPolicies For Information Security & PrivacyIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract Joao CoutoDocument10 pagesExtended Abstract Joao CoutoIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- The Main Characteristics of Travel Agencies in Montenegro: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2012Document8 pagesThe Main Characteristics of Travel Agencies in Montenegro: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2012Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- A Typology of Tourism Related Web Sites: Its Theoretical Background and ImplicationsDocument37 pagesA Typology of Tourism Related Web Sites: Its Theoretical Background and ImplicationsIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Research Article Management Model On Electronic Commerce Data Based On Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesResearch Article Management Model On Electronic Commerce Data Based On Cloud ComputingIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, DevelopingDocument1 pageLife Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, DevelopingIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Horizons - Economics: Andreea Marin-Pantelescu, Laura - Cristina MANIUDocument4 pagesKnowledge Horizons - Economics: Andreea Marin-Pantelescu, Laura - Cristina MANIUIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Sorted Stone Circles On Svalbard - An Analog Study For Mars: January 2019Document3 pagesSorted Stone Circles On Svalbard - An Analog Study For Mars: January 2019Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Female Reproductive SystemDocument73 pagesChapter 17 Female Reproductive SystemIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Review: Parasitic Diseases of Dogs and Cats in The Tropics.: January 2011Document21 pagesReview: Parasitic Diseases of Dogs and Cats in The Tropics.: January 2011Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Background: (CITATION Soh19 /L 1033)Document4 pagesTheoretical Background: (CITATION Soh19 /L 1033)Kimberly McleanNo ratings yet
- D20rha25 2013-1Document2 pagesD20rha25 2013-1Icmi KadarsihNo ratings yet
- SchistosomiasisDocument93 pagesSchistosomiasisJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- EarthwormDocument24 pagesEarthwormAlakesh Coldplay KalitaNo ratings yet
- Final Results Report: Curative Labs Inc. 3330 New York Ave NE Washington, DC 20002Document1 pageFinal Results Report: Curative Labs Inc. 3330 New York Ave NE Washington, DC 20002Aidan NicholsNo ratings yet
- Sequencing DNA: Nobel in Chemistry 1958, Structure of Insulin Nobel in Chemistry, DNA SequencingDocument16 pagesSequencing DNA: Nobel in Chemistry 1958, Structure of Insulin Nobel in Chemistry, DNA SequencingAaron CzikNo ratings yet
- Cross-Specialization Training For Grades 7-10 Science TeachersDocument13 pagesCross-Specialization Training For Grades 7-10 Science TeachersJen DescargarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Care in ALL Management 29th August-InvitaionDocument2 pagesComprehensive Care in ALL Management 29th August-InvitaionMuhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Food Chain Food Web Wordsearch Answer KeyDocument1 pageFood Chain Food Web Wordsearch Answer KeyAlexander RussellNo ratings yet
- Manual Quick ChangeDocument20 pagesManual Quick Changerodolphalb100% (3)
- Early Embryology, Fate Determination, and Patterning in DrosophilaDocument40 pagesEarly Embryology, Fate Determination, and Patterning in DrosophilaJoyae ChavezNo ratings yet
- Plant Biochemistry - Lecture Notes, Study Materials and Important Questions AnswersDocument8 pagesPlant Biochemistry - Lecture Notes, Study Materials and Important Questions AnswersBrainKart Com100% (1)
- MCI FMGE Previous Year Solved Question Paper 2002Document32 pagesMCI FMGE Previous Year Solved Question Paper 2002Girdhari Ram SauNo ratings yet
- Kenneth J. Wurdack and Charles C. DavisDocument20 pagesKenneth J. Wurdack and Charles C. DavisAldo A. Vela0% (1)
- Biology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesBiology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersmisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- Genetically Food ResearchDocument8 pagesGenetically Food ResearchVeronica YamatNo ratings yet
- Interspecies Trait Genetics Reveals Association of Adcy8 With Mouse Avoidance Behavior and A Human Mood DisorderDocument8 pagesInterspecies Trait Genetics Reveals Association of Adcy8 With Mouse Avoidance Behavior and A Human Mood DisorderAnnetrude de MooijNo ratings yet
- Yeast Autolysis in Sparkling Wine - A Review, SUBDocument9 pagesYeast Autolysis in Sparkling Wine - A Review, SUBoscardannstrom5431No ratings yet
- BIoregulation & Biosafety4Document7 pagesBIoregulation & Biosafety4Ayu ArrahmahNo ratings yet
- Zoology Assignment #1Document5 pagesZoology Assignment #1Decemei CuaboNo ratings yet
- Science Magazine 5700 2004-11-19Document134 pagesScience Magazine 5700 2004-11-19WillimSmithNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Roben CasiongNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 Combined PacopDocument103 pagesMod 6 Combined PacopJacosby WorcestershireNo ratings yet
- Biology BDocument12 pagesBiology Bspiyush.ranjansahooNo ratings yet
- Application of Engineering in Biology: DR Nishu Goyal Department of Chemical Engineering, UPESDocument7 pagesApplication of Engineering in Biology: DR Nishu Goyal Department of Chemical Engineering, UPESchirag malavNo ratings yet
- Successional Changes in CommunitiesDocument4 pagesSuccessional Changes in CommunitiesSofia Christel JavierNo ratings yet
- Ib Sehs Topic 13: Exercise and Immunity HL OnlyDocument6 pagesIb Sehs Topic 13: Exercise and Immunity HL OnlyOmar El-BourinyNo ratings yet
- A-P CHAPTER 1 The Human OrganismDocument19 pagesA-P CHAPTER 1 The Human OrganismMONIQUE VELASCO100% (1)
- Nad / Nadp: 3. Coenzyme Q / UbiquinoneDocument4 pagesNad / Nadp: 3. Coenzyme Q / UbiquinoneNicole ChanNo ratings yet