Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roller Head Lines
Roller Head Lines
Uploaded by
Muhammad ShofiyansyahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Test Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition Karin C Vanmeter Robert J HubertDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition Karin C Vanmeter Robert J HubertTammyEricksonfitq98% (45)
- SCR Guarding GuideDocument18 pagesSCR Guarding GuideAlvin100% (2)
- Extrusion Equipment: Tire and Rubber IndustryDocument36 pagesExtrusion Equipment: Tire and Rubber Industrythiagorep17No ratings yet
- Rheology and Processing 2016Document65 pagesRheology and Processing 2016Shailendra PatelNo ratings yet
- PB3603 1 Raymond Mechanical Air Separator PDFDocument4 pagesPB3603 1 Raymond Mechanical Air Separator PDFmiraNo ratings yet
- New RC Form (Including 3rd Party) - Latest DSPDocument2 pagesNew RC Form (Including 3rd Party) - Latest DSPAfiqah Marshall0% (3)
- FLSmidth Ball Mill For Cement GrindingDocument8 pagesFLSmidth Ball Mill For Cement GrindingRaj K SharmaNo ratings yet
- Composite Fabrication by Filament WindingDocument26 pagesComposite Fabrication by Filament WindingAVI_ROHININo ratings yet
- 3rd Session - Christain PfeifferDocument6 pages3rd Session - Christain PfeifferZarni AungNo ratings yet
- Methods, Processes and Equipment Involved in Manufacturing of PlasticDocument34 pagesMethods, Processes and Equipment Involved in Manufacturing of PlasticNiño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- Brush Seals: World Class Sealing TechnologyDocument12 pagesBrush Seals: World Class Sealing Technologyguichen wangNo ratings yet
- Multi Head ExtrusionDocument12 pagesMulti Head Extrusionsuoya14No ratings yet
- InterminglingDocument0 pagesInterminglingHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- ZE Twin-Screw ExtrudersDocument30 pagesZE Twin-Screw ExtrudersSimas Servutas100% (1)
- 3D Blow Molding Machines For Three-Dimensional, Convoluted PipesDocument8 pages3D Blow Molding Machines For Three-Dimensional, Convoluted PipesnnNo ratings yet
- 2015 3 CFI KrautwurstDocument3 pages2015 3 CFI Krautwurstanil kapadiaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Low Cost Filament Winding MachineDocument6 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Low Cost Filament Winding MachineAbdalla HamedNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraDocument37 pagesManufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraRais Alfiansyah TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Blown Film CoexDocument4 pagesBlown Film CoexTaeng SoshiNo ratings yet
- Kautex K3DDocument8 pagesKautex K3DAmitava DattaNo ratings yet
- Rotor SpinningDocument36 pagesRotor SpinningSiva Jagadish Kumar M0% (1)
- Centrifugal CastingDocument4 pagesCentrifugal CastingaerovinuNo ratings yet
- Solenoid PhysicsDocument4 pagesSolenoid PhysicsAl VlearNo ratings yet
- Insulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin RichDocument9 pagesInsulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin Richrifal1990No ratings yet
- OC PultrusionDocument29 pagesOC PultrusionalmakmenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plastics Processing CIPET.Document55 pagesIntroduction To Plastics Processing CIPET.Pranav DNo ratings yet
- Study On Fiber Feeding Mechanism For Direct Extrusion Compression ProcessDocument5 pagesStudy On Fiber Feeding Mechanism For Direct Extrusion Compression ProcessInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Bekum Industrial Packagung ENDocument8 pagesBekum Industrial Packagung ENخبراء التصنيع الدوائي-اليمنNo ratings yet
- HBF Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesHBF Brochure PDFArif GfcNo ratings yet
- R. Panigrahi: View Article AnalyticsDocument18 pagesR. Panigrahi: View Article AnalyticsNakib Ibna BasharNo ratings yet
- YLB Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant: Henan Sinoroader Heavy Industry CorporationDocument14 pagesYLB Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant: Henan Sinoroader Heavy Industry CorporationMohammad Daoud100% (1)
- Twin Screw Extruders Optimization: MATERIALE PLASTICE December 2009Document6 pagesTwin Screw Extruders Optimization: MATERIALE PLASTICE December 2009Uneeb NoorNo ratings yet
- Plastics Topics Introduction To ExtrusionDocument15 pagesPlastics Topics Introduction To ExtrusionIshah ahamed KaziNo ratings yet
- Bombas AllweilerDocument14 pagesBombas AllweilerCARLOS ANDRES CARVAJAL SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraDocument37 pagesManufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraRais Alfiansyah TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Magotteaux - XLIFT PaperDocument11 pagesMagotteaux - XLIFT PaperHamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Filament Winding: Serkan CUBUK E6704Document17 pagesFilament Winding: Serkan CUBUK E6704Charaf Leo100% (1)
- The Design of A Small-Scale Plastic Extruder MachiDocument4 pagesThe Design of A Small-Scale Plastic Extruder MachiKARUPPUCHAMY GNo ratings yet
- Subscribe To Deepl Pro To Edit This Document.: Vi - 4 - The Filamentary DepotDocument10 pagesSubscribe To Deepl Pro To Edit This Document.: Vi - 4 - The Filamentary DepotSoufianeNo ratings yet
- Single-Screw Extruders and Barrier ScrewsDocument17 pagesSingle-Screw Extruders and Barrier ScrewsAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unipump: Close Coupled Sewage PumpDocument24 pagesUnipump: Close Coupled Sewage PumpHiago GasparNo ratings yet
- ملخصDocument8 pagesملخصAkram AbdulkaremNo ratings yet
- Handling Systems ALUMINIUMDocument35 pagesHandling Systems ALUMINIUMAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Rubber Injection MouldingDocument10 pagesPractical Guide To Rubber Injection Mouldingسعید اینانلوNo ratings yet
- Latest Technology of Mill DiaphragmsDocument17 pagesLatest Technology of Mill DiaphragmsISLAM I. Fekry100% (5)
- Extruder Times 9Document16 pagesExtruder Times 9skimmer05No ratings yet
- Shot PeeningDocument32 pagesShot PeeningRahul KadbeNo ratings yet
- Grinding and Classifying Technology For Slag: Replacement Factors DryingDocument6 pagesGrinding and Classifying Technology For Slag: Replacement Factors DryingGerman Gabriel Anaya Vega100% (1)
- Aeb 1FDocument12 pagesAeb 1FGustavo ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Variations On The Yankee Dryer: Magnus Högman Valmet ABDocument55 pagesMinimizing Variations On The Yankee Dryer: Magnus Högman Valmet ABApitNo ratings yet
- Yogi Exim ExtrusionDocument11 pagesYogi Exim ExtrusionRaj Kumar GiriNo ratings yet
- Processing Technology: Processing of Polymer Melts Made in GermanyDocument24 pagesProcessing Technology: Processing of Polymer Melts Made in GermanyRobel MTNo ratings yet
- Ball Mill For Cement GrindingDocument5 pagesBall Mill For Cement GrindingNkosilozwelo Sibanda100% (1)
- HD National Foam - MCSDocument4 pagesHD National Foam - MCSJavier Hinojosa Garrido LeccaNo ratings yet
- 98 en Single Screw ExtrudersDocument17 pages98 en Single Screw ExtrudersAlvaro Fernando Reyes CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Polycom High-Pressure Grinding RollDocument8 pagesPolycom High-Pressure Grinding RolltonyNo ratings yet
- MQ 54486Document114 pagesMQ 54486Muhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- Damping Behaviour of Dynamically Cured Butyl Rubber/polypropylene BlendsDocument8 pagesDamping Behaviour of Dynamically Cured Butyl Rubber/polypropylene BlendsMuhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- NL9262 PDFDocument1 pageNL9262 PDFMuhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document12 pagesChapter 07Muhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- 0 6 B 0 8 B - 1 0 B - 1 2 B - 1 6 B: BS Standard Roller ChainsDocument1 page0 6 B 0 8 B - 1 0 B - 1 2 B - 1 6 B: BS Standard Roller ChainsMuhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai: CircularDocument5 pagesUniversity of Mumbai: CircularDhiraj Sanjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Versatile DC Motor PWM Speed ControllerDocument5 pagesVersatile DC Motor PWM Speed ControllerinvictusNo ratings yet
- Agro Prom ServiceDocument1 pageAgro Prom ServiceDmitriyNo ratings yet
- SAM-12 Instruction ManualDocument176 pagesSAM-12 Instruction Manualpoquimon100% (1)
- Booths AlgorithmDocument3 pagesBooths AlgorithmNARENDRAKUMARREDDYNo ratings yet
- A+490m+-+04++ Qtq5me0Document6 pagesA+490m+-+04++ Qtq5me0tehOnipisNo ratings yet
- Spring Animations PlaygroundDocument12 pagesSpring Animations PlaygroundBalen SarkoNo ratings yet
- EasyPlusTM TitratorDocument12 pagesEasyPlusTM TitratorSales - Khushboo ScientificNo ratings yet
- MaxDocument19 pagesMaxWaltencir SoutoNo ratings yet
- EEPROM 24C256 - Atmel PDFDocument20 pagesEEPROM 24C256 - Atmel PDFValdir DerlannNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security Gouvernance & AssuranceDocument31 pagesCloud Security Gouvernance & Assurancebaye omar SoceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FinalDocument83 pagesChapter 2 FinalSana SaleemNo ratings yet
- Ir5800c PM PDFDocument456 pagesIr5800c PM PDFojawarikNo ratings yet
- Etc 4420Document4 pagesEtc 4420mileniumtemucoNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter - Lesson 1: Plan and Prepare Maintenance ProceduresDocument9 pagesThird Quarter - Lesson 1: Plan and Prepare Maintenance ProceduresJohnny Virtz100% (1)
- Week 9Document79 pagesWeek 9svNo ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument71 pagesInequalitieskrissypaintyNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Systems (MCQS)Document9 pagesTelecommunication Systems (MCQS)Aqsa LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Database Fundamentals: INFM 603 - Information Technology and Organizational ContextDocument35 pagesDatabase Fundamentals: INFM 603 - Information Technology and Organizational ContextGilbert RozarioNo ratings yet
- How To Apply Ration Card in Tamilnadu - TNPSC PortalDocument3 pagesHow To Apply Ration Card in Tamilnadu - TNPSC PortalMukesh100% (1)
- Media Information LiteracyDocument32 pagesMedia Information LiteracyCaranay BillyNo ratings yet
- Ug NXDocument4 pagesUg NX816623No ratings yet
- Seating Arrangement Mid-SemDocument15 pagesSeating Arrangement Mid-SemKaran DesaiNo ratings yet
- Learning To See To See: Value Stream MappingDocument19 pagesLearning To See To See: Value Stream MappingMakiNo ratings yet
- Poem 2009: 2 Ifip WG 8.1 Working Conference OnDocument1 pagePoem 2009: 2 Ifip WG 8.1 Working Conference OnRitu SharmaNo ratings yet
- ResuDocument2 pagesResumanaswinipaboluNo ratings yet
Roller Head Lines
Roller Head Lines
Uploaded by
Muhammad ShofiyansyahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roller Head Lines
Roller Head Lines
Uploaded by
Muhammad ShofiyansyahCopyright:
Available Formats
Roller head lines
Roller head lines for the production der to remove volatile components from the
compound.
of technical rubber sheets When compounds have to be cleaned of
impurities or inadequately mixed constitu-
T. C. Pohl, M. Meinert* ents of the compound prior to forming, this
is achieved with the aid of a strainer process,
in which the compound is forced through
Roller head lines have been used for many years for the production of sheets for
a fine-mesh screen. The straining can take
technical rubber articles. Typical products include sheet goods, tank linings, conveyor
belts, V-belts, printing sheets, wear protection panels, preliminary pressing products, place at various process stages:
shoe soles, pneumatic springs and many more. Standard systems can rarely be used
for these production processes; the roller head lines must be specially designed and 1. Directly after the mixing process with an
tailor-made to the relevant customer requirements. extruder-gear pump combination
2. After storage and before extrusion by
means of an independent gear extruder
3. During extrusion and before the preform
1. Introduction used for almost every type of compound. head.
With the wide range of compounds avail-
Roller head lines have been used for able, the selection of the individual line A cold-feed gear extruder before the
many years for the production of sheets for components requires both experience and extruder enables the greatest process win-
technical rubber articles. Typical products extensive knowledge of the handling of the dow in terms of output, melt homogeneity
include sheet goods, tank linings, conveyor relevant compound. and maximum permissible processing tem-
belts, V-belts, printing sheets, wear protec- perature. The rubber compound is strained
tion panels, preliminary pressing products, through the volumetric transport in the gear
shoe soles, pneumatic springs and many 2. Extruder technology pump under minimum shear load (fig. 5).
more (fig. 1).
The cold-feed extruder, sometimes
In contrast to multiple-roller calender equipped with a vacuum zone for venting 3. Preform head (WBK)
lines, in the roller head principle the calender of the compound, has established itself as
gap is fed with compound from an extruder the preferred system for the production of The optimum feeding of the roller gap
with a preform head. Due to the preliminary technical rubber articles. Hot-feed extrud- is achieved if the thickness and width of
forming of the cross-section in the preform ers in combination with mills are used for the compound fed can be adjusted to the
head, rubber sheets up to a thickness range compounds which are difficult to plastify, sheet to be calendered. This requirement is
of 20 mm can be produced without bubbles such as compounds based on natural rub- fulfilled by the preform head. The distribu-
(fig. 1-3). ber or those with a high material feedback tion of the compound is carried out by the
proportion (fig. 3). so-called fishtail contour in the preform
Modern roller head lines offer a high head. Easily replaceable extrusion dies are
level of automation and rationalisation The state-of-the-art technology for roller mounted at the end of the preform head.
possibilities in comparison to convention- head lines today is the cold-feed pin-type The thickness is adjusted with the aid of
ally fed calenders. It should be emphasised extruder. Pins in the extrusion barrel serve the different outlet heights of the extru-
in particular that roller head lines can be to distribute the flow and thus ensure good sion dies. The different flow characteristics
distribution and uniform material tempera- of the various compounds can be compen-
ture. sated for by profiling of the extrusion dies.
Different product widths are achieved by
The performance optimum between ho- means of easily replaceable insert parts.
mogeneity and output can be adjusted by The cleaning of the preform head is partic-
the screw geometry, the pin configuration ularly easy, since both halves of the head are
* Dr. Tim C. Pohl or the set temperatures of the screw and the swung open when changing compound. By
General Manager Rubber Machinery Division barrel. The selection of the screw geometry this means, the compound is released from
Dipl.-Ing. Martin Meinert is based on the type of material to be pro- the flow channel when opening the head
Engineering: Calenders for Rubber cessed, and can be adapted to the customer’s halves (fig. 6).
Project Management: Rubber Machinery Division requirements (fig. 4).
info@troester.de The roller head process is characterised
Cold-feed extruders are also used in medi- particularly by its ability to achieve very
Troester GmbH & Co KG Hannover, Germany cal technology as vacuum extruders in or- accurate thickness tolerances. The influ-
18 RFP 1/2008 – Volume 3
Roller head lines
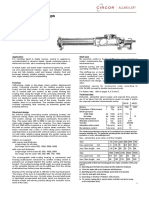
Fig. 1: Line for the production of wear- and corrosion-protection linings Fig. 2: Line for the production of films for pressure expansion vessels,
conveyor belts and medical products
Extruder: QSM 200/k – 16 D Sheet width: 600 to 2200 mm Extruder: QSM 120/k – 16 D Sheet width: 250 to 1700 mm
Extrusion head: WBK 200/2200 Sheet thickness: 0.5 to 15 mm Extrusion head: WBK 120/1350 Sheet thickness: 0.3 to 10 mm
Calender: KDI 700x2400 Speed: max. 25 m/min Calender: KDI 600x1800 Speed: max. 10 m/min
Fig. 3: Line for the production of semi-finished products for seals/gaskets Fig. 4: Line for the production of narrow sheets / Mini roller-head system
Extruder: QSM 150/k – 12 D Sheet width: 500 to 950 mm Extruder: QSM 90/k – 14 D Sheet width: 50 to 300 mm
Extrusion head: WBK 150/1050 Sheet thickness: 0.9 to 1.5 mm Extrusion head: WBK 90/270 Sheet thickness: 0.3 to 5 mm
Calender: KDI 400x1300 Speed: max. 10 m/mins Calender: KDI 200x350 Speed: max. 45 m/min
Fig. 5: Gear extruder and vacuum extruder in cascade arrangement Fig. 6: Line for the production of tank linings, carriageway marking film
Extruder: QSM 150/k – 16 D Sheet width: 250 to 1270 mm
Extrusion head: WBK 150/1400 Sheet thickness: 0.5 to 25.4 mm
Calender: KDI 500x1550 Speed: max. 30 m/min
RFP 1/2008 – Volume 3 19
Roller head lines
ence of the calender gap on the achiev- impermissible stress is placed on the com- 4. Calender technology
able tolerances is particularly great at low pound. This requires accurate material dis-
sheet thicknesses. In contrast, the influence tribution over the complete width at the The calibration of the material sheet takes
of the calender gap is reduced at greater head outlet. place in the calender gap. The number of cal-
thicknesses, and the thickness tolerance of ender rollers is determined according to the
the material sheet is determined largely by In order to achieve this, flow channels process task. Two or three-roller calenders
the material distribution after the extru- today are designed with the aid of FEM can be used (fig. 8).
sion preform head. The production of elastic (finite element method) flow calculations.
NR compounds with a thickness of over 10 The illustration in figure 7 shows such a In order to be able to produce a plane
mm places particular demands on the roller calculation result. The particular challenge parallel sheet with accurate thickness
head system. On the one hand, the roller in this case, and the necessary experience, tolerances, the roller head calender is
gap has no great influence, while on the lies in optimising the flow kinetics of the equipped with one or more of the follow-
other, reset forces in the transverse direc- peripheral area. ing devices for compensation of the roller
tion adversely affect the sheet tolerances. deflection:
In this case, the design of the flow channels For the optimum design of the flow
is particularly important. The channels in channel therefore, the rheological prop- • Crowning on one or more calender rollers
the preform head must be designed so that erties of the compounds must be known • Crossing of one calender roller
the reset forces are minimised, although no in advance. • Roller bending of the calender rollers.
Fig. 7: FEM flow simulation of a preform head for different distributor geometries Fig. 9: Line for production of semi-finished products
for the pharmaceutical industry
Fig. 8: Line for production of semi-finished products for V-belt manufacture Extruder: GS-Vak 90/k-16 D-m/Spw Sheet width: 120 to 1200 mm
Extrusion head: WBK 90/1050 Sheet thickness: 0.5 to 25.4 mm
Calender: KDI 400x1300 Speed: max. 15 m/min
Fig. 10: Comparison of types of cooling section
(cooling medium temperature = 20 °C, ambient air = 35 °C,
extrusion temperature = 100 °C, average winding temperature = 40 °C)
50
45 Drum cooling section with 3 x 2 drums
40 Air cooling section 4 x 10 m
Line speed [m/min]
35 Air cooling section 4 x 5 m
30 Water spray cooling 6 m
25
20
15
10
5
Extruder: QSM 200/k – 16 D Sheet width 800 to 1500 mm 0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Extrusion head: WBK 200/1650 Sheet thickness: 0.3 to 3 mm
Calender: KTI 600x1800 Speed: max. 30 m/min Product thickness [mm]
20 RFP 1/2008 – Volume 3
Roller head lines
The crowning of the calender rollers and ing drums are very effective in the case of matic process regulation. The optimum de-
the crossing device form part of the stand- low sheet thicknesses. In the case of higher sign of the user interfaces, both on the PLC
ard equipment of a roller head calender. The sheet thicknesses, the cooling characteris- screen and on the PC screen, provides ergo-
roller bending device of the calender rollers tics are determined largely by the heat con- nomic system operation for the operator. The
is used for high-viscosity rubber compounds, duction in the rubber compound. In this display language can also be switched to the
which are formed into thin sheets. case, the dwell time in the cooling section relevant national language. Due to the se-
must be increased. This can be achieved for lected hardware of the system controls, very
Modern roller head calenders are also example by a multilayer air cooling section. high system availability is ensured.
equipped with a hydraulic roller adjustment This also enables self-threading, which is
device, which enables accurate position- not possible with drum cooling. During the project planning and com-
ing of the calender rollers. This also ena- missioning of the system, the controls are
bles the monitoring of the maximum gap Within the roller head line, it is particular- adapted and optimised to the relevant cus-
force, which ensures reliable protection of ly important that the material is transported tomer requirements, in order to be able
the rollers against breakage resulting from carefully. The transfer points between the to operate the system with short product
overloads. individual conveyor belts are designed with change times and optimum start-up tech-
the aid of dancers and head rollers so that nology. The graphic process visualisation
Roller head calenders comply with the the material sheet is not subjected to tensile and the disposition and recipe management
latest safety regulations, and in addition stress and thereby deformed. represent further essential elements for ef-
to various emergency-off circuits, are also ficient production. For the evaluation of
equipped with programme-controlled moni- Winding can be carried out using contact past production, the production planner and
toring of the brake device for the drive of winders or centre winders. In combination process engineer are provided with online
the calender rollers (fig. 9). with a cross-cutter, the cross-cutting, the and historical trend displays of the differ-
residual winding, the replacement of the ent process parameters, production report-
winder and the winding take place fully au- ing and evaluation, and statistical process
5. Downstream tomatically (fig. 11). The centre winders are control. These process data are available not
following equipment equipped with an edge control device for only on the system itself, but can also be
the material and the liner. The liner is also made available to other computers of the
After the forming of the sheet, it must unwound under tensile force control. customer by networking via Intranet or In-
be cooled down to the winding tempera- ternet, enabling either centralised or decen-
ture. The diagram (fig. 10) shows the re- tralised data storage.
lationship between sheet thickness, line 6. Line control and regulation
speed and the type of cooling. Cooling With the aid of remote maintenance,
drum assemblies, each with two drums, are An essential component of a modern roller Troester engineers can monitor every sys-
frequently used in roller head lines. Cool- head line is the line control with fully auto- tem worldwide, provide assistance and if
Fig. 11: Centre winder with cross-cutter Fig. 12: Line for production of semi-finished products for pneumatic spring
components for the automotive industry
Extruder: QSM 90/k - 12 D Sheet width: 60 to 250 mm
Extrusion head: WBK 90/270 Sheet thickness: 0.25 to 1 mm
Calender: KDI 150x350 Speed: max. 37 m/min
RFP 1/2008 – Volume 3 21
Roller head lines
necessary carry out programme modifica- 7. Summary 8. Literature
tions. This ensures quick reaction times fol-
lowing system stoppages and rapid resump- Standard systems can rarely be used for the [1] H.-F. Ramm, E. Seidler: Automation Options for
tion of production. production of technical rubber goods; this Calenders and Extruders, Tire Technology Inter-
must be carried out instead with roller head national 1995
Maintenance personnel are provided with lines specially designed and tailor-made to the [2] G. Targiel, H. Klein: Herstellen großer Kaut-
an online maintenance management system, relevant customer requirements. All the re- schukbahnen im Einfach- und Doublierver-
which draws attention at the relevant time quirements can be fulfilled thanks to the wide fahren, Kautschuk + Gummi Kunststoffe 50th
to what maintenance work must be carried range of extruder designs and sizes available, Issue, 1/97
out. The system also provides information with screw diameters of up to 250 mm, and
on which auxiliary materials are needed for the corresponding calender equipment with
this purpose, and displays instructions for roller diameters from 80 –700 mm.
the performance of the work (fig. 12).
LSR India Roadshow About Momentive
Momentive, Engel and Elmet will together Contact: (Information, registration) Momentive Performance Materials was
present a cross-country roadshow to rubber V. Ramesh (Country Manager, created from the sale of GE Advanced Ma-
and plastics producers in the Indian market. Engel India) terials and its former joint ventures, GE
Taking place from 25 –27 February 2008 in E-mail engel@vnsl.com Bayer Silicones and GE Toshiba Silicones to
the automotive hubs Pune, Delhi and Chen- Tel. +91 22 2847 9851 Apollo Management, L.P. in December 2006.
nai, this series of events will allow manu- Fax +91 22 2847 9854 The company is the world’s second-largest
facturers to discuss the latest advances in producer of silicones and silicone deriva-
LSR technology directly with experts in the Ashutosh Mantri (Market Development tives and a global leader in the development
areas of raw materials (Momentive), moulds, Manager, Momentive) and manufacture of products derived from
coldrunner-blocks, pumps and turnkey sys- E-mail ashutosh.mantri@momentive.com quartz and advanced ceramics.
tems (Elmet), and LSR injection moulding Tel. +91 22 4005 9350-55
machines and systems (Engel). Fax +91 22 4005 9356 About Engel
The roadshow will give access to expertise
across the entire LSR value chain and the lat- As an individual brand, Engel is the big-
est LSR solutions. gest manufacturer of injection moulding
Jointly led by representatives of the three Advantages of LSR manufacturing machines in the world. The Engel group
organising companies the discussions will fo- include: currently offers all technology modules for
cus on a broad range of LSR topics, includ- plastics processing from a single source:
ing self-bonding technology, self-bleeding • fast cycle time though platinum injection moulding machines for thermo-
products, liquid fluorosilicone elastomers, catalysed addition curing system plastics and elastomers, tools and auto-
applications, machines and machine tech- • flash-less and trim-free parts matic systems. The group has 8 production
nology, local support, and LSR pumping and directly from the machine, no facilities in Europe, North America and Asia
mixing units. Each programme will be fol- de-flashing or manual trimming (China, Korea), own branches in 17 coun-
lowed by a cocktail reception and individual • process can run fully automated tries, and representations in more than 70
24 hours/day
discussions. countries. The company is based in Schwert-
• wasteless manufacturing: through
berg, Austria.
cold-runner technology no waste
Schedule: (daily at 5 p.m.)
material
Pune 25 February 2008 • long flow length, low injection About Elmet
Delhi 26 February 2008 pressure, moulding of highly complex
Chennai 27 February 2008 parts possible Elmet is a specialist in the field of elas-
Speakers: • available materials for consumer tomer moulding technology by means of
Oliver Franssen (Global Marketing goods, automotive, industrial goods, designing, manufacturing and automation
Manager Automotive, Momentive) electrical connectors etc. of LSR, 2K, HTV and rubber injection moulds;
Paul Fattinger • supplied materials are ready-to-use standardised valve gate cold decks, LSR dos-
(Global R & D Manager, Elmet) and are easy to pigment within the ing systems, LIM peripheral devices and com-
Leo Praher (Global Sales Manager process plete turn-key production systems. The com-
LSR/LIM Machines, Engel) pany is located in Oftering, Austria.
22 RFP 1/2008 – Volume 3
You might also like
- Test Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition Karin C Vanmeter Robert J HubertDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition Karin C Vanmeter Robert J HubertTammyEricksonfitq98% (45)
- SCR Guarding GuideDocument18 pagesSCR Guarding GuideAlvin100% (2)
- Extrusion Equipment: Tire and Rubber IndustryDocument36 pagesExtrusion Equipment: Tire and Rubber Industrythiagorep17No ratings yet
- Rheology and Processing 2016Document65 pagesRheology and Processing 2016Shailendra PatelNo ratings yet
- PB3603 1 Raymond Mechanical Air Separator PDFDocument4 pagesPB3603 1 Raymond Mechanical Air Separator PDFmiraNo ratings yet
- New RC Form (Including 3rd Party) - Latest DSPDocument2 pagesNew RC Form (Including 3rd Party) - Latest DSPAfiqah Marshall0% (3)
- FLSmidth Ball Mill For Cement GrindingDocument8 pagesFLSmidth Ball Mill For Cement GrindingRaj K SharmaNo ratings yet
- Composite Fabrication by Filament WindingDocument26 pagesComposite Fabrication by Filament WindingAVI_ROHININo ratings yet
- 3rd Session - Christain PfeifferDocument6 pages3rd Session - Christain PfeifferZarni AungNo ratings yet
- Methods, Processes and Equipment Involved in Manufacturing of PlasticDocument34 pagesMethods, Processes and Equipment Involved in Manufacturing of PlasticNiño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- Brush Seals: World Class Sealing TechnologyDocument12 pagesBrush Seals: World Class Sealing Technologyguichen wangNo ratings yet
- Multi Head ExtrusionDocument12 pagesMulti Head Extrusionsuoya14No ratings yet
- InterminglingDocument0 pagesInterminglingHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- ZE Twin-Screw ExtrudersDocument30 pagesZE Twin-Screw ExtrudersSimas Servutas100% (1)
- 3D Blow Molding Machines For Three-Dimensional, Convoluted PipesDocument8 pages3D Blow Molding Machines For Three-Dimensional, Convoluted PipesnnNo ratings yet
- 2015 3 CFI KrautwurstDocument3 pages2015 3 CFI Krautwurstanil kapadiaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Low Cost Filament Winding MachineDocument6 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Low Cost Filament Winding MachineAbdalla HamedNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraDocument37 pagesManufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraRais Alfiansyah TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Blown Film CoexDocument4 pagesBlown Film CoexTaeng SoshiNo ratings yet
- Kautex K3DDocument8 pagesKautex K3DAmitava DattaNo ratings yet
- Rotor SpinningDocument36 pagesRotor SpinningSiva Jagadish Kumar M0% (1)
- Centrifugal CastingDocument4 pagesCentrifugal CastingaerovinuNo ratings yet
- Solenoid PhysicsDocument4 pagesSolenoid PhysicsAl VlearNo ratings yet
- Insulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin RichDocument9 pagesInsulation System Comparison VPI Versus Resin Richrifal1990No ratings yet
- OC PultrusionDocument29 pagesOC PultrusionalmakmenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plastics Processing CIPET.Document55 pagesIntroduction To Plastics Processing CIPET.Pranav DNo ratings yet
- Study On Fiber Feeding Mechanism For Direct Extrusion Compression ProcessDocument5 pagesStudy On Fiber Feeding Mechanism For Direct Extrusion Compression ProcessInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Bekum Industrial Packagung ENDocument8 pagesBekum Industrial Packagung ENخبراء التصنيع الدوائي-اليمنNo ratings yet
- HBF Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesHBF Brochure PDFArif GfcNo ratings yet
- R. Panigrahi: View Article AnalyticsDocument18 pagesR. Panigrahi: View Article AnalyticsNakib Ibna BasharNo ratings yet
- YLB Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant: Henan Sinoroader Heavy Industry CorporationDocument14 pagesYLB Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant: Henan Sinoroader Heavy Industry CorporationMohammad Daoud100% (1)
- Twin Screw Extruders Optimization: MATERIALE PLASTICE December 2009Document6 pagesTwin Screw Extruders Optimization: MATERIALE PLASTICE December 2009Uneeb NoorNo ratings yet
- Plastics Topics Introduction To ExtrusionDocument15 pagesPlastics Topics Introduction To ExtrusionIshah ahamed KaziNo ratings yet
- Bombas AllweilerDocument14 pagesBombas AllweilerCARLOS ANDRES CARVAJAL SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraDocument37 pagesManufacture of Composites: Submitted To - S.S GodaraRais Alfiansyah TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Magotteaux - XLIFT PaperDocument11 pagesMagotteaux - XLIFT PaperHamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Filament Winding: Serkan CUBUK E6704Document17 pagesFilament Winding: Serkan CUBUK E6704Charaf Leo100% (1)
- The Design of A Small-Scale Plastic Extruder MachiDocument4 pagesThe Design of A Small-Scale Plastic Extruder MachiKARUPPUCHAMY GNo ratings yet
- Subscribe To Deepl Pro To Edit This Document.: Vi - 4 - The Filamentary DepotDocument10 pagesSubscribe To Deepl Pro To Edit This Document.: Vi - 4 - The Filamentary DepotSoufianeNo ratings yet
- Single-Screw Extruders and Barrier ScrewsDocument17 pagesSingle-Screw Extruders and Barrier ScrewsAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unipump: Close Coupled Sewage PumpDocument24 pagesUnipump: Close Coupled Sewage PumpHiago GasparNo ratings yet
- ملخصDocument8 pagesملخصAkram AbdulkaremNo ratings yet
- Handling Systems ALUMINIUMDocument35 pagesHandling Systems ALUMINIUMAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Rubber Injection MouldingDocument10 pagesPractical Guide To Rubber Injection Mouldingسعید اینانلوNo ratings yet
- Latest Technology of Mill DiaphragmsDocument17 pagesLatest Technology of Mill DiaphragmsISLAM I. Fekry100% (5)
- Extruder Times 9Document16 pagesExtruder Times 9skimmer05No ratings yet
- Shot PeeningDocument32 pagesShot PeeningRahul KadbeNo ratings yet
- Grinding and Classifying Technology For Slag: Replacement Factors DryingDocument6 pagesGrinding and Classifying Technology For Slag: Replacement Factors DryingGerman Gabriel Anaya Vega100% (1)
- Aeb 1FDocument12 pagesAeb 1FGustavo ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Variations On The Yankee Dryer: Magnus Högman Valmet ABDocument55 pagesMinimizing Variations On The Yankee Dryer: Magnus Högman Valmet ABApitNo ratings yet
- Yogi Exim ExtrusionDocument11 pagesYogi Exim ExtrusionRaj Kumar GiriNo ratings yet
- Processing Technology: Processing of Polymer Melts Made in GermanyDocument24 pagesProcessing Technology: Processing of Polymer Melts Made in GermanyRobel MTNo ratings yet
- Ball Mill For Cement GrindingDocument5 pagesBall Mill For Cement GrindingNkosilozwelo Sibanda100% (1)
- HD National Foam - MCSDocument4 pagesHD National Foam - MCSJavier Hinojosa Garrido LeccaNo ratings yet
- 98 en Single Screw ExtrudersDocument17 pages98 en Single Screw ExtrudersAlvaro Fernando Reyes CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Polycom High-Pressure Grinding RollDocument8 pagesPolycom High-Pressure Grinding RolltonyNo ratings yet
- MQ 54486Document114 pagesMQ 54486Muhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- Damping Behaviour of Dynamically Cured Butyl Rubber/polypropylene BlendsDocument8 pagesDamping Behaviour of Dynamically Cured Butyl Rubber/polypropylene BlendsMuhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- NL9262 PDFDocument1 pageNL9262 PDFMuhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document12 pagesChapter 07Muhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- 0 6 B 0 8 B - 1 0 B - 1 2 B - 1 6 B: BS Standard Roller ChainsDocument1 page0 6 B 0 8 B - 1 0 B - 1 2 B - 1 6 B: BS Standard Roller ChainsMuhammad ShofiyansyahNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai: CircularDocument5 pagesUniversity of Mumbai: CircularDhiraj Sanjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Versatile DC Motor PWM Speed ControllerDocument5 pagesVersatile DC Motor PWM Speed ControllerinvictusNo ratings yet
- Agro Prom ServiceDocument1 pageAgro Prom ServiceDmitriyNo ratings yet
- SAM-12 Instruction ManualDocument176 pagesSAM-12 Instruction Manualpoquimon100% (1)
- Booths AlgorithmDocument3 pagesBooths AlgorithmNARENDRAKUMARREDDYNo ratings yet
- A+490m+-+04++ Qtq5me0Document6 pagesA+490m+-+04++ Qtq5me0tehOnipisNo ratings yet
- Spring Animations PlaygroundDocument12 pagesSpring Animations PlaygroundBalen SarkoNo ratings yet
- EasyPlusTM TitratorDocument12 pagesEasyPlusTM TitratorSales - Khushboo ScientificNo ratings yet
- MaxDocument19 pagesMaxWaltencir SoutoNo ratings yet
- EEPROM 24C256 - Atmel PDFDocument20 pagesEEPROM 24C256 - Atmel PDFValdir DerlannNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security Gouvernance & AssuranceDocument31 pagesCloud Security Gouvernance & Assurancebaye omar SoceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FinalDocument83 pagesChapter 2 FinalSana SaleemNo ratings yet
- Ir5800c PM PDFDocument456 pagesIr5800c PM PDFojawarikNo ratings yet
- Etc 4420Document4 pagesEtc 4420mileniumtemucoNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter - Lesson 1: Plan and Prepare Maintenance ProceduresDocument9 pagesThird Quarter - Lesson 1: Plan and Prepare Maintenance ProceduresJohnny Virtz100% (1)
- Week 9Document79 pagesWeek 9svNo ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument71 pagesInequalitieskrissypaintyNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Systems (MCQS)Document9 pagesTelecommunication Systems (MCQS)Aqsa LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Database Fundamentals: INFM 603 - Information Technology and Organizational ContextDocument35 pagesDatabase Fundamentals: INFM 603 - Information Technology and Organizational ContextGilbert RozarioNo ratings yet
- How To Apply Ration Card in Tamilnadu - TNPSC PortalDocument3 pagesHow To Apply Ration Card in Tamilnadu - TNPSC PortalMukesh100% (1)
- Media Information LiteracyDocument32 pagesMedia Information LiteracyCaranay BillyNo ratings yet
- Ug NXDocument4 pagesUg NX816623No ratings yet
- Seating Arrangement Mid-SemDocument15 pagesSeating Arrangement Mid-SemKaran DesaiNo ratings yet
- Learning To See To See: Value Stream MappingDocument19 pagesLearning To See To See: Value Stream MappingMakiNo ratings yet
- Poem 2009: 2 Ifip WG 8.1 Working Conference OnDocument1 pagePoem 2009: 2 Ifip WG 8.1 Working Conference OnRitu SharmaNo ratings yet
- ResuDocument2 pagesResumanaswinipaboluNo ratings yet