Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
463 viewsDermatology Questions
Dermatology Questions
Uploaded by
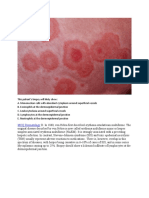
Muziki Wa KiafrikaThe patient has a linear pruritic vesicular rash on their forearm, which is most consistent with a type IV hypersensitivity reaction like contact dermatitis. A 9-year-old boy hospitalized for cellulitis has skin denudation from splitting of the epidermis at the stratum granulosum, consistent with scalded skin syndrome. A 27-year-old man has recurrent, intensely pruritic vesicles symmetrically distributed on his trunk, and electron microscopy shows granular deposition of IgA and complement at the dermoepidermal junction, consistent with dermatitis herpetiformis which is associated with celiac sprue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Prometric Exam March 2020Document250 pagesPrometric Exam March 2020Sally dossNo ratings yet
- Med Dermatology Questions-75Document67 pagesMed Dermatology Questions-75Khalifa AL-Wishahi75% (4)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASDocument183 pagesQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- Dermatology MCQ FRCPDocument101 pagesDermatology MCQ FRCPhesham90% (20)
- TS Vaccine Stability Table PDFDocument17 pagesTS Vaccine Stability Table PDFDimitrios DalagiorgosNo ratings yet
- Photodermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Derma MCQ Ch01Document20 pagesDerma MCQ Ch01Rasha Dabbagh75% (4)
- Derma Exam 2013 (2Document18 pagesDerma Exam 2013 (2Lamyaa M. Elmubarak100% (1)
- Skin Tumor MCQDocument73 pagesSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- Oral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersDocument29 pagesOral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersMedo JTNo ratings yet
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Document672 pagesETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (2)
- Dermatology QuizDocument7 pagesDermatology QuizFaddy OrahaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology QuizDocument10 pagesDermatology QuizSyed Ali Haider0% (1)
- Genodermatosis MCQsDocument152 pagesGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Full Report - ELISA LatestDocument8 pagesFull Report - ELISA LatestNik AmirNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Icthyosis With KeyDocument7 pagesMcqs of Icthyosis With KeysaleemNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesDermatology MCQNiwashiny CnyNo ratings yet
- Dermat Questions 252Document72 pagesDermat Questions 252Srirupa BiswasNo ratings yet
- Grand Test May 6 Question PaperDocument48 pagesGrand Test May 6 Question PaperSonalNo ratings yet
- Dermatopathology Q - ADocument55 pagesDermatopathology Q - AKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (7)
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Pics MCQSDocument22 pagesPics MCQStania100% (1)
- Part I 2016 - Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesPart I 2016 - Dermatology MCQEmma Dawod100% (1)
- Prometric Book 2nd EditionDocument207 pagesPrometric Book 2nd Editionsajitha100% (2)
- Dermatology Written Exam 2007Document6 pagesDermatology Written Exam 2007Abdullah Matar BadranNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Finals (Sept. 2014)Document14 pagesDermatology Finals (Sept. 2014)Paz VidaNo ratings yet
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsDocument25 pages101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Top Dermatology Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesTop Dermatology Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersMuha RajNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQ With AnswersDocument27 pagesDermatology MCQ With Answershesham0% (1)
- DermatologyDocument3 pagesDermatologyDrkhslid890% (1)
- DermatologyDocument121 pagesDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- MCQ Dermatosurg Neel Chap 24-25Document78 pagesMCQ Dermatosurg Neel Chap 24-25DurgaMadhab TripathyNo ratings yet
- Dermatoven MCQDocument30 pagesDermatoven MCQS2 GIZI FKUI 2020No ratings yet
- End Round of Dermatology, MCQsDocument20 pagesEnd Round of Dermatology, MCQsMuhdZaeed100% (2)
- Dermatology LE1 PDFDocument17 pagesDermatology LE1 PDFCearlene GalleonNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument17 pagesDermatologyEbn Seena75% (4)
- KEY: Certain, Pretty Sure, Possible: 18 Years Old/female CameDocument8 pagesKEY: Certain, Pretty Sure, Possible: 18 Years Old/female Camefairodz salapudinNo ratings yet
- 11Document3 pages11faresaltaii100% (2)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument42 pagesMCQ Dermatologydraik71100% (5)
- اسئلة الجلدية لهيئة التخصصات السعودية PDFDocument24 pagesاسئلة الجلدية لهيئة التخصصات السعودية PDFDrhisham AttiaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQ With ExplinationsDocument46 pagesDermatology MCQ With Explinationshesham100% (1)
- Final Dermatology ExamDocument37 pagesFinal Dermatology ExamheshamNo ratings yet
- Derma CD McqsDocument22 pagesDerma CD McqsheshamNo ratings yet
- Geno MCQDocument60 pagesGeno MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDocument92 pagesBasic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (17)
- Dermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2Document56 pagesDermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2hesham50% (2)
- MCQs Ch07-45651100rdzDocument27 pagesMCQs Ch07-45651100rdzKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (2)
- MCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)Document17 pagesMCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)R Ratheesh100% (9)
- Derma MCQ Ch01 PDFDocument20 pagesDerma MCQ Ch01 PDFShah NawazNo ratings yet
- June 2022 - Dermatology - 10 McqsDocument8 pagesJune 2022 - Dermatology - 10 McqsAhmed ShihataNo ratings yet
- Dermatology OSCE Pictures 1Document208 pagesDermatology OSCE Pictures 1medt80No ratings yet
- Immunedermatology MCQsDocument73 pagesImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- MCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Document31 pagesMCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dinesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Dermatology RecertificatDocument8 pagesDermatology RecertificatKhalifa AL-WishahiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam One Answered 2.. All 3 VersionsDocument21 pagesFinal Exam One Answered 2.. All 3 Versionsh8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- 1-Dermatological Case PresentationDocument41 pages1-Dermatological Case Presentationnaimat007No ratings yet
- Bollous MCQDocument21 pagesBollous MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- Pediatric Dermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPediatric Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed89% (18)
- Etas MCQ 2015..2Document605 pagesEtas MCQ 2015..2sajithaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 QbankDocument10 pagesGroup 1 QbankBatch ElysianNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank ProceduresDocument33 pagesBlood Bank Proceduresninadroy2844100% (20)
- Polymyalgia RheumaticaDocument27 pagesPolymyalgia RheumaticaBima Anugrah KusumaNo ratings yet
- DR ZauteaDocument56 pagesDR Zauteadvo aizawlNo ratings yet
- Func - Samplebooklet - Libro Gratis de Muestra Pivot PointDocument81 pagesFunc - Samplebooklet - Libro Gratis de Muestra Pivot PointRaquel100% (1)
- MCQ HematologyDocument12 pagesMCQ Hematologymohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateThamizhan Cyber SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Transfusion RXNsDocument67 pagesTransfusion RXNsSuha Abdullah100% (1)
- Case Study For Beta Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-All)Document15 pagesCase Study For Beta Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-All)Shakira HashimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transfusion MedicineDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Transfusion MedicineSamantha BuiNo ratings yet
- Recall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTDocument4 pagesRecall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTRafael CayananNo ratings yet
- Pro-Lab: E.COLI 0157Document2 pagesPro-Lab: E.COLI 0157api-3742158No ratings yet
- Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesDocument2 pagesTumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesFika Ayu SafitriNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLearning ObjectivesjmcvicenteNo ratings yet
- Bardac 208M - APIC CSPA PosterDocument1 pageBardac 208M - APIC CSPA PosterDyaniNo ratings yet
- Employee Health Policy TemplateDocument4 pagesEmployee Health Policy Templatebromberg.alexaNo ratings yet
- Daniel Santiago Rincón PinzónDocument2 pagesDaniel Santiago Rincón PinzónYANDRA YINNETH RINCON PINZONNo ratings yet
- SINAS IDAI 2023 Flyer 2 Hal OK (PUTIH-Merah) - 281222Document2 pagesSINAS IDAI 2023 Flyer 2 Hal OK (PUTIH-Merah) - 281222izdihar rahmadindaNo ratings yet
- IgA NephropathyDocument6 pagesIgA NephropathySyed AlmaazNo ratings yet
- Public Assesment Report VAXIGRIP TETRA NH - INITIALDocument5 pagesPublic Assesment Report VAXIGRIP TETRA NH - INITIALShelly NataniaNo ratings yet
- Rajat GoswamiDocument2 pagesRajat GoswamiNM KPTNo ratings yet
- Subacute PLEVADocument3 pagesSubacute PLEVAArya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and EpistaxisDocument17 pagesTonsillitis and EpistaxisAllaine Grace CanoNo ratings yet
- Me Pediatrics Ntruhs Previous Question Papers Chapter WiseDocument11 pagesMe Pediatrics Ntruhs Previous Question Papers Chapter WiseNarendra AnnaladasuNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections - What Are Bacterial Infections - Treatment and CausesDocument4 pagesBacterial Infections - What Are Bacterial Infections - Treatment and CausesFarwa AnisNo ratings yet
- Letter To Gov. Sununu From NH College TownsDocument2 pagesLetter To Gov. Sununu From NH College TownsportsmouthheraldNo ratings yet
- ACTINOMYCETESDocument22 pagesACTINOMYCETESDaniel WaweruNo ratings yet
- Children 07 00162Document5 pagesChildren 07 00162Camille MalilayNo ratings yet
- Study Stack - M (ASCP) EXAM Table Review PDFDocument9 pagesStudy Stack - M (ASCP) EXAM Table Review PDF장주연100% (2)
Dermatology Questions
Dermatology Questions
Uploaded by
Muziki Wa Kiafrika0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
463 views3 pagesThe patient has a linear pruritic vesicular rash on their forearm, which is most consistent with a type IV hypersensitivity reaction like contact dermatitis. A 9-year-old boy hospitalized for cellulitis has skin denudation from splitting of the epidermis at the stratum granulosum, consistent with scalded skin syndrome. A 27-year-old man has recurrent, intensely pruritic vesicles symmetrically distributed on his trunk, and electron microscopy shows granular deposition of IgA and complement at the dermoepidermal junction, consistent with dermatitis herpetiformis which is associated with celiac sprue.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient has a linear pruritic vesicular rash on their forearm, which is most consistent with a type IV hypersensitivity reaction like contact dermatitis. A 9-year-old boy hospitalized for cellulitis has skin denudation from splitting of the epidermis at the stratum granulosum, consistent with scalded skin syndrome. A 27-year-old man has recurrent, intensely pruritic vesicles symmetrically distributed on his trunk, and electron microscopy shows granular deposition of IgA and complement at the dermoepidermal junction, consistent with dermatitis herpetiformis which is associated with celiac sprue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
463 views3 pagesDermatology Questions
Dermatology Questions
Uploaded by
Muziki Wa KiafrikaThe patient has a linear pruritic vesicular rash on their forearm, which is most consistent with a type IV hypersensitivity reaction like contact dermatitis. A 9-year-old boy hospitalized for cellulitis has skin denudation from splitting of the epidermis at the stratum granulosum, consistent with scalded skin syndrome. A 27-year-old man has recurrent, intensely pruritic vesicles symmetrically distributed on his trunk, and electron microscopy shows granular deposition of IgA and complement at the dermoepidermal junction, consistent with dermatitis herpetiformis which is associated with celiac sprue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1. Pt. has linear pruritic vesicular rash on forearm.
Which of the following is
mediated by type IV hypersensitivity reaction and is most likely dx?
a. Bullous pemphigoid
b. Contact dermatitis
c. Dermatitis herpetiformis
d. Discoid lupus erythematous
e. Urticaria
2. 9 y/o boy, hospitalized for cellulitis, exhibits denudation of the skin
resulting from splitting of epidermis at stratum granulosum. Which of the
following is most likely dx?
a. Impetigo
b. Melasma
c. Scalded skin syndrome
d. Tinea corporis
e. Vitiligo
3. 27 y/o man presents with recurrent episodes of intensely pruritic vesicles
symmetrically distributed on his trunk. On EM, granular deposition of IgA
and complement is noted at dermoepidermal junction. Which of the
following underlying conditions predisposes patients to the described skin
disorder?
a. Celiac sprue
b. Lactase deficiency
c. Tropical sprue
d. UC
e. Whipple disease
4. Biopsy of a skin lesion shows marked intercellular edema that splays apart
adjacent cells, leaving only thin dark lines between the cells. What is this
process called?
a. Acantholysis
b. Acanthosis
c. Hyperkeratosis
d. Parakeratosis
e. Spongiosis
5. 35 y/o presents to the physician with intensely pruritic skin lesions on his
axillary folds, nipples, waistband, wrists, interdigital spaces on the hand, and
genitalia. Linear burrows are apparent in affected areas. What is the dx?
a. Dermatitis herpetiformis
b. Lichen planus
c. Photosensitivity
d. Scabies
e. Seborrhea
6. 62 y/o presents with progressive, pruritic erythroderma, exfoliation, and
lymphadenopathy. Peripheral smear reveals T cells with cerebriform nuclei.
Which of the following is most likely dx?
a. Burkitt Lymphoma
b. Histiocytic lymphoma
c. Lymphoblastic lymphoma
d. Lymphocytic lymphoma
e. Sezary syndrome
7. 30 y/o woman has chronic, silver-white, scaly patches with an erythematous
border on the skin of her knees and elbows. What is cause of this condition?
a. Autoimmune disease
b. Bacterial dz
c. Fungal dz
d. Granulomatous dz
e. Large vessel vasculitis
8. From question 7, how can the dz be clinically identified?
a. KOH prep
b. Christmas tree distribution pattern bleeding
c. Removal of scale results in pinpoint bleeding (Auspitz sign)
d. Avulsion of epidermis on gentle pressure
e. Tzanck smear
9. 50 y/o woman presents with complaints of difficulty rising from a chair and
combing her hair. PE is remarkable for erythema and edema of cheeks,
eyelids, and backs of her hands. Lesions have a distinctive mauve color, and
mauve papules are noted on the knuckles. Approximately 30% of patients with
this disorder also may have what?
a. Abnormal circulating lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei
b. Bacillary bodies in macrophages in the lamina propria of the intestine
c. Flattening and blunting of villi in the jejunum
d. A mutation in a skeletal muscle protein
e. An underlying malignancy
10.A patient presents to dermatologist because of skin changes. Skin is
hyperpigmented and thickened and feels velvety. Multiple skin tags are
present. Changes are worst in the axillae, groin, and anogenital area, but are
very widespread. Somatic dysfunction is noted at T2-T8 bilaterally. This
patient should be specifically evaluated for which of the following diseases?
a. Hepatic cirrhosis
b. Lung Cancer
c. Polycystic renal disease
d. SLE
e. UC
11.Biopsy of a 4mm rough, tan, and slightly raised skin lesion on the face of a 65
y/o man demonstrates atypical basal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm but
persistent intercellular bridges. Stratum corneum is thickened, and
parakeratosis is present; the remainder of epidermis is thinned. Which of the
following features would also probably be seen in dermis?
a. Benign nevus cells
b. Blue-gray elastic fibers
c. Large numbers of spindle-shaped fibroblasts
d. Malignant nevus cells
e. Touton giant cells
12. A 65 y/o, fair skinned man develops scaly erythematous papules that have a
sandpaper texture on his forehead. A biopsy shows nuclear crowding,
hyperchromasia, and pleomorphism of the basal keratinocytes, with alteration
of the normal epidermal maturation. Hyperkeratosis is also present. Which of
the following neoplasms may arise from this lesion?
a. Basal Cell Carcinoma
b. Melanoma
c. Merkel Cell Carcinoma
d. Mycosis Fungoides
e. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
13.30 y/o man presents to dermatologist with silvery, scaling plaques on his
elbows and knees. His mother had been afflicted with the same condition in
the past. What is diagnosis?
a. Acne rosacea
b. Acne vulgaris
c. Pemphigus vulgaris
d. Pityriasis rosea
e. Psoriasis vulgaris
You might also like
- Prometric Exam March 2020Document250 pagesPrometric Exam March 2020Sally dossNo ratings yet
- Med Dermatology Questions-75Document67 pagesMed Dermatology Questions-75Khalifa AL-Wishahi75% (4)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASDocument183 pagesQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- Dermatology MCQ FRCPDocument101 pagesDermatology MCQ FRCPhesham90% (20)
- TS Vaccine Stability Table PDFDocument17 pagesTS Vaccine Stability Table PDFDimitrios DalagiorgosNo ratings yet
- Photodermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Derma MCQ Ch01Document20 pagesDerma MCQ Ch01Rasha Dabbagh75% (4)
- Derma Exam 2013 (2Document18 pagesDerma Exam 2013 (2Lamyaa M. Elmubarak100% (1)
- Skin Tumor MCQDocument73 pagesSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- Oral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersDocument29 pagesOral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersMedo JTNo ratings yet
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Document672 pagesETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (2)
- Dermatology QuizDocument7 pagesDermatology QuizFaddy OrahaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology QuizDocument10 pagesDermatology QuizSyed Ali Haider0% (1)
- Genodermatosis MCQsDocument152 pagesGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Full Report - ELISA LatestDocument8 pagesFull Report - ELISA LatestNik AmirNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Icthyosis With KeyDocument7 pagesMcqs of Icthyosis With KeysaleemNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesDermatology MCQNiwashiny CnyNo ratings yet
- Dermat Questions 252Document72 pagesDermat Questions 252Srirupa BiswasNo ratings yet
- Grand Test May 6 Question PaperDocument48 pagesGrand Test May 6 Question PaperSonalNo ratings yet
- Dermatopathology Q - ADocument55 pagesDermatopathology Q - AKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (7)
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Pics MCQSDocument22 pagesPics MCQStania100% (1)
- Part I 2016 - Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesPart I 2016 - Dermatology MCQEmma Dawod100% (1)
- Prometric Book 2nd EditionDocument207 pagesPrometric Book 2nd Editionsajitha100% (2)
- Dermatology Written Exam 2007Document6 pagesDermatology Written Exam 2007Abdullah Matar BadranNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Finals (Sept. 2014)Document14 pagesDermatology Finals (Sept. 2014)Paz VidaNo ratings yet
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsDocument25 pages101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Top Dermatology Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesTop Dermatology Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersMuha RajNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQ With AnswersDocument27 pagesDermatology MCQ With Answershesham0% (1)
- DermatologyDocument3 pagesDermatologyDrkhslid890% (1)
- DermatologyDocument121 pagesDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- MCQ Dermatosurg Neel Chap 24-25Document78 pagesMCQ Dermatosurg Neel Chap 24-25DurgaMadhab TripathyNo ratings yet
- Dermatoven MCQDocument30 pagesDermatoven MCQS2 GIZI FKUI 2020No ratings yet
- End Round of Dermatology, MCQsDocument20 pagesEnd Round of Dermatology, MCQsMuhdZaeed100% (2)
- Dermatology LE1 PDFDocument17 pagesDermatology LE1 PDFCearlene GalleonNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument17 pagesDermatologyEbn Seena75% (4)
- KEY: Certain, Pretty Sure, Possible: 18 Years Old/female CameDocument8 pagesKEY: Certain, Pretty Sure, Possible: 18 Years Old/female Camefairodz salapudinNo ratings yet
- 11Document3 pages11faresaltaii100% (2)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument42 pagesMCQ Dermatologydraik71100% (5)
- اسئلة الجلدية لهيئة التخصصات السعودية PDFDocument24 pagesاسئلة الجلدية لهيئة التخصصات السعودية PDFDrhisham AttiaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQ With ExplinationsDocument46 pagesDermatology MCQ With Explinationshesham100% (1)
- Final Dermatology ExamDocument37 pagesFinal Dermatology ExamheshamNo ratings yet
- Derma CD McqsDocument22 pagesDerma CD McqsheshamNo ratings yet
- Geno MCQDocument60 pagesGeno MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDocument92 pagesBasic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (17)
- Dermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2Document56 pagesDermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2hesham50% (2)
- MCQs Ch07-45651100rdzDocument27 pagesMCQs Ch07-45651100rdzKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (2)
- MCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)Document17 pagesMCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)R Ratheesh100% (9)
- Derma MCQ Ch01 PDFDocument20 pagesDerma MCQ Ch01 PDFShah NawazNo ratings yet
- June 2022 - Dermatology - 10 McqsDocument8 pagesJune 2022 - Dermatology - 10 McqsAhmed ShihataNo ratings yet
- Dermatology OSCE Pictures 1Document208 pagesDermatology OSCE Pictures 1medt80No ratings yet
- Immunedermatology MCQsDocument73 pagesImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- MCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Document31 pagesMCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dinesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Dermatology RecertificatDocument8 pagesDermatology RecertificatKhalifa AL-WishahiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam One Answered 2.. All 3 VersionsDocument21 pagesFinal Exam One Answered 2.. All 3 Versionsh8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- 1-Dermatological Case PresentationDocument41 pages1-Dermatological Case Presentationnaimat007No ratings yet
- Bollous MCQDocument21 pagesBollous MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- Pediatric Dermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPediatric Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed89% (18)
- Etas MCQ 2015..2Document605 pagesEtas MCQ 2015..2sajithaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 QbankDocument10 pagesGroup 1 QbankBatch ElysianNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank ProceduresDocument33 pagesBlood Bank Proceduresninadroy2844100% (20)
- Polymyalgia RheumaticaDocument27 pagesPolymyalgia RheumaticaBima Anugrah KusumaNo ratings yet
- DR ZauteaDocument56 pagesDR Zauteadvo aizawlNo ratings yet
- Func - Samplebooklet - Libro Gratis de Muestra Pivot PointDocument81 pagesFunc - Samplebooklet - Libro Gratis de Muestra Pivot PointRaquel100% (1)
- MCQ HematologyDocument12 pagesMCQ Hematologymohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateThamizhan Cyber SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Transfusion RXNsDocument67 pagesTransfusion RXNsSuha Abdullah100% (1)
- Case Study For Beta Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-All)Document15 pagesCase Study For Beta Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-All)Shakira HashimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transfusion MedicineDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Transfusion MedicineSamantha BuiNo ratings yet
- Recall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTDocument4 pagesRecall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTRafael CayananNo ratings yet
- Pro-Lab: E.COLI 0157Document2 pagesPro-Lab: E.COLI 0157api-3742158No ratings yet
- Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesDocument2 pagesTumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesFika Ayu SafitriNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLearning ObjectivesjmcvicenteNo ratings yet
- Bardac 208M - APIC CSPA PosterDocument1 pageBardac 208M - APIC CSPA PosterDyaniNo ratings yet
- Employee Health Policy TemplateDocument4 pagesEmployee Health Policy Templatebromberg.alexaNo ratings yet
- Daniel Santiago Rincón PinzónDocument2 pagesDaniel Santiago Rincón PinzónYANDRA YINNETH RINCON PINZONNo ratings yet
- SINAS IDAI 2023 Flyer 2 Hal OK (PUTIH-Merah) - 281222Document2 pagesSINAS IDAI 2023 Flyer 2 Hal OK (PUTIH-Merah) - 281222izdihar rahmadindaNo ratings yet
- IgA NephropathyDocument6 pagesIgA NephropathySyed AlmaazNo ratings yet
- Public Assesment Report VAXIGRIP TETRA NH - INITIALDocument5 pagesPublic Assesment Report VAXIGRIP TETRA NH - INITIALShelly NataniaNo ratings yet
- Rajat GoswamiDocument2 pagesRajat GoswamiNM KPTNo ratings yet
- Subacute PLEVADocument3 pagesSubacute PLEVAArya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and EpistaxisDocument17 pagesTonsillitis and EpistaxisAllaine Grace CanoNo ratings yet
- Me Pediatrics Ntruhs Previous Question Papers Chapter WiseDocument11 pagesMe Pediatrics Ntruhs Previous Question Papers Chapter WiseNarendra AnnaladasuNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections - What Are Bacterial Infections - Treatment and CausesDocument4 pagesBacterial Infections - What Are Bacterial Infections - Treatment and CausesFarwa AnisNo ratings yet
- Letter To Gov. Sununu From NH College TownsDocument2 pagesLetter To Gov. Sununu From NH College TownsportsmouthheraldNo ratings yet
- ACTINOMYCETESDocument22 pagesACTINOMYCETESDaniel WaweruNo ratings yet
- Children 07 00162Document5 pagesChildren 07 00162Camille MalilayNo ratings yet
- Study Stack - M (ASCP) EXAM Table Review PDFDocument9 pagesStudy Stack - M (ASCP) EXAM Table Review PDF장주연100% (2)