Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statement:: L J J M J M
Statement:: L J J M J M
Uploaded by
GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLOOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statement:: L J J M J M
Statement:: L J J M J M
Uploaded by
GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLOCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery SOLUTION MANUAL 2-20-1
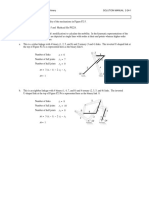
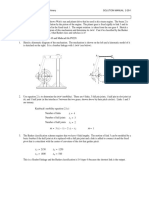
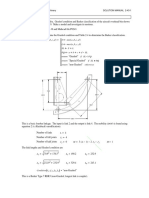
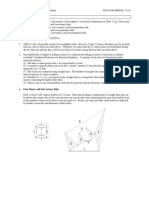
PROBLEM 2-20
Statement: Make kinematic sketches, define the types of all the links and joints, and determine the mobility of
the mechanisms shown in Figure P2-3.
Solution: See Figure P2-3 and Mathcad file P0220.
1. Use equation 2.1c (Kutzbach's modification) to calculate the mobility.
a. Number of links L
12
C
Number of full joints J1
15
6
Number of half joints J2
0 7
B 8
M
3
( L 1) 2
J1 J 2 M 3 5
4
9
Link 2 is a quaternary, link 7 is pentagonal, and the 2
remainder are binary. All joints are full. There are 3 10
1 11
translating joints and 12 pin joints. The main boom (link 2)
is rotated about fixed pivot A by hydraulic cylinder 3-4. A 12
The secondary boom (link 7) is rotated about the main 3
boom at pivot B by hydraulic cylinder 5-6. The bucket is
the output link of a fourbar (links 7,10,11, and 12). Its
position is controlled by hydraulic cylinder 8-9 acting on
the input link (10).
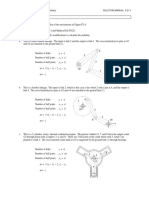
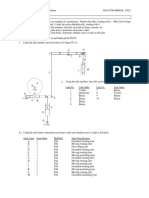
b. Number of links L
9
Number of full joints J1
11 9
Number of half joints J2
0 8 6
M
3
( L 1) 2
J1 J 2 M 2
5 4 3
Link 1 is ternary, link 7 is pentagonal, and the remainder are 7 1
binary. All joints are full. There are 2 translating joints and 2
9 pin joints. The basic linkage (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6) is a
Stephenson's sixbar. Hydraulic cylinder 5-6 is the input to
the basic linkage and controls the position of the main
boom (link 3). The bucket position is determined by
hydraulic cylinder 8-9.
You might also like
- Robert L. Norton Design of Machinery SOLUTIONS MANUAL PDFDocument5 pagesRobert L. Norton Design of Machinery SOLUTIONS MANUAL PDFAb25% (4)
- 1.6 MVA Dry Transformer DesignDocument21 pages1.6 MVA Dry Transformer DesignJemal MusaNo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-24Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-24GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-8Document4 pagesStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-8Dio ChanNo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-7Document2 pagesStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-7GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-21Document3 pagesStatement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-21GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Homework 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesHomework 1 SolutionMrinmoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-27Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-27GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-9Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-9GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-8Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-8GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-34Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-34GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-14Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-14GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: Problem 2-1Document2 pagesStatement:: Problem 2-1GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: Problem 2-1Document2 pagesStatement:: Problem 2-1Gustavo CopplaNo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-30Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-30GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-13Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-13GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-36Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-36GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-28Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-28GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Solution manual for Design of Machinery: An Introduction to the Synthesis and Analysis of Mechanisms and Machines Norton 5th Edition download pdf full chapterDocument27 pagesSolution manual for Design of Machinery: An Introduction to the Synthesis and Analysis of Mechanisms and Machines Norton 5th Edition download pdf full chaptermanukasukk100% (3)
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Machine Design 5th Edition 013335671xDocument2 pagesSolutions Manual To Accompany Machine Design 5th Edition 013335671xantonybestin94No ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-35Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-35GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method: Beam AnalysisDocument10 pagesFinite Element Method: Beam AnalysisZaffira RahmanNo ratings yet
- EE306#2Document6 pagesEE306#2Hasan ToubasiNo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-32Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-32GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Practice Sheet: Code Converters, Multiplexers, & Demultiplexers EET 1131 ReederDocument10 pagesUnit 8 Practice Sheet: Code Converters, Multiplexers, & Demultiplexers EET 1131 ReederCarlos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-31Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-31GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- KMPP 2023 2024 (Answer)Document13 pagesKMPP 2023 2024 (Answer)Afiqah AimanNo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-29Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-29GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- ADC0809 With CKT, Flow CodeDocument8 pagesADC0809 With CKT, Flow CodeBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- Sr. Grand Test Key and HintsDocument7 pagesSr. Grand Test Key and HintsM JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-56Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-56GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Generator (6HK1)Document2 pagesGenerator (6HK1)Oggy ToffyNo ratings yet
- Generator (6HK1) : SpecificationsDocument2 pagesGenerator (6HK1) : SpecificationsOggy ToffyNo ratings yet
- CPM Examples For Students-Lec 4Document9 pagesCPM Examples For Students-Lec 4sa3ody.911hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- EEE 51 Assignment 4Document3 pagesEEE 51 Assignment 4Anton GarciaNo ratings yet
- 4RUNNER 2006 Engine Control For 2UZ-FEDocument14 pages4RUNNER 2006 Engine Control For 2UZ-FEJamsyare MendozaNo ratings yet
- Anderson Bridge ExperimentDocument5 pagesAnderson Bridge Experimentsachin singh NegiNo ratings yet
- Agamoni, Mrunmayee, Prabhuti, Shalini, Suhrit - AAMM2Document14 pagesAgamoni, Mrunmayee, Prabhuti, Shalini, Suhrit - AAMM2SUHRIT BISWASNo ratings yet
- Ga02298 PertDocument7 pagesGa02298 PertiskandarbasiruddinNo ratings yet
- #MOCK JEE Main Practice Test-14 - Current & CapacitanceDocument6 pages#MOCK JEE Main Practice Test-14 - Current & CapacitanceVenkat VineshNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Switched Inductor-Capacitor Hybrid Buck-SEPIC Two-Input DC-DC ConverterDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Switched Inductor-Capacitor Hybrid Buck-SEPIC Two-Input DC-DC ConvertervijaNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Exercises: Manuel Alanis Miguel Charles Iram Lee Francisco Ramirez Francisco TreviñoDocument22 pagesLaplace Transform Exercises: Manuel Alanis Miguel Charles Iram Lee Francisco Ramirez Francisco TreviñoMihmidNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics For EEE Stream - BBEE103 - 203Document3 pagesBasic Electronics For EEE Stream - BBEE103 - 203dd0542469No ratings yet
- Network AnalysisDocument5 pagesNetwork AnalysisRudraksh MandhareNo ratings yet
- Usn 2 B V: UNIT-II and Any ONE Full Question From UNIT-III. Use of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Hand Book Is PermittedDocument6 pagesUsn 2 B V: UNIT-II and Any ONE Full Question From UNIT-III. Use of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Hand Book Is PermittedAkshay ArksaliNo ratings yet
- BBEE103 Set 1Document2 pagesBBEE103 Set 1Sachin K PNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6aDocument8 pagesLecture 6aJessa Clarisse CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- A High-Power DC-DC Converter Topology For Battery Charging ApplicationsDocument18 pagesA High-Power DC-DC Converter Topology For Battery Charging ApplicationsL CHNo ratings yet
- 6335-N17S-Slab Systems 17.1.21Document44 pages6335-N17S-Slab Systems 17.1.21satyaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Design of Machinery: An Introduction To The Synthesis and Analysis of Mechanisms and Machines Norton 5th EditionDocument25 pagesSolution Manual For Design of Machinery: An Introduction To The Synthesis and Analysis of Mechanisms and Machines Norton 5th Editionlawn.lights3zwi100% (23)
- 08 3 PhasetransfoDocument31 pages08 3 PhasetransfoJulie MartinNo ratings yet
- Revision 2021Document8 pagesRevision 2021abhishekash502No ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm: Aor Case Study AssignmentDocument8 pagesMinimum Spanning Tree Algorithm: Aor Case Study AssignmentRupam BiswasNo ratings yet
- DL 1612Document2 pagesDL 1612Gagan SLNo ratings yet
- Der Compressor V2 - Operating Values: Setting BiasDocument1 pageDer Compressor V2 - Operating Values: Setting Biasantonio martosNo ratings yet
- Project - CPM SolutionDocument2 pagesProject - CPM SolutionKawsar HossainNo ratings yet
- 2024-JEE Main-6 - SolutionsDocument16 pages2024-JEE Main-6 - Solutionssinglaanush18No ratings yet
- I B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations October 2021Document10 pagesI B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations October 2021AmarnathNo ratings yet
- Edc QB Final LatestDocument15 pagesEdc QB Final LatestrajeshadktNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsFrom EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-44Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-44GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-43Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-43GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-56Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-56GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Condition A B S Minab L Maxab SL S L PQ A B C D SL Return SL PQ If Return SL PQ If Return OtherwiseDocument1 pageCondition A B S Minab L Maxab SL S L PQ A B C D SL Return SL PQ If Return SL PQ If Return OtherwiseGUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-53Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-53GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-36Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-36GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-15Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-15GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-21Document3 pagesStatement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-21GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-7Document2 pagesStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-7GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- 4 D 3 1 E 5 4 G 7 I 6 1 J 8 7: StatementDocument1 page4 D 3 1 E 5 4 G 7 I 6 1 J 8 7: StatementGUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-30Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-30GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-18Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-18GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-32Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-32GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-28Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-28GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-23Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: PROBLEM 2-23GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-8Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-8GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-11Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-11GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-13Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-13GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-31Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-31GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement: Solution:: Problem 2-9Document1 pageStatement: Solution:: Problem 2-9GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-12Document4 pagesStatement:: PROBLEM 2-12GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-27Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-27GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-14Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-14GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-34Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-34GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: Inversions. How Many Distinct Inversions Does The Linkage in Row 4, Column 1 Have?Document1 pageStatement:: Inversions. How Many Distinct Inversions Does The Linkage in Row 4, Column 1 Have?GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- Statement:: PROBLEM 2-35Document1 pageStatement:: PROBLEM 2-35GUSTAVO VINICIUS VIEIRA MELLONo ratings yet
- GNG HoseDocument3 pagesGNG HoseMehdi SoltaniNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone BridgeDocument5 pagesWheatstone Bridgepm1511No ratings yet
- 2011 VRP PresentationDocument20 pages2011 VRP Presentationahs23No ratings yet
- MI LJ24 IA DatasheetDocument1 pageMI LJ24 IA DatasheetFco Javier Del ÁlamoNo ratings yet
- Alkalne - 9V 1604 - Alkaline 21 Ultra Plus AUP - Specifikacije Izdelka @WWW - Delko.siDocument6 pagesAlkalne - 9V 1604 - Alkaline 21 Ultra Plus AUP - Specifikacije Izdelka @WWW - Delko.si1qay1qayNo ratings yet
- APS-U2001 Manual de ServicioDocument24 pagesAPS-U2001 Manual de ServicioWilmer MaestreNo ratings yet
- Manifold CoplanarDocument5 pagesManifold CoplanarClaudio Salvador Vera AranedaNo ratings yet
- pr2 - Catalogo MG GensetDocument51 pagespr2 - Catalogo MG GensetrepelindNo ratings yet
- 110W Flexible Panel Spec SheetDocument1 page110W Flexible Panel Spec Sheetyvj_20006373No ratings yet
- Oversized Pressure Regulator Valve Kit: Renault/Peugot AL-4, DPODocument2 pagesOversized Pressure Regulator Valve Kit: Renault/Peugot AL-4, DPOEko hari PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Compressor BLDC Sensorless Control Based On MC56F82xxxDocument32 pagesRefrigerator Compressor BLDC Sensorless Control Based On MC56F82xxxJesus Almanzar SantosNo ratings yet
- Transformer Fuses Mind The Ga IEEE IASDocument8 pagesTransformer Fuses Mind The Ga IEEE IASkcirrenwodNo ratings yet
- Protection and SwitchgearDocument397 pagesProtection and SwitchgearRifky ZuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Manual Z300KDocument22 pagesManual Z300KHectorNo ratings yet
- Liebert Air Cooled Condenser User ManualDocument33 pagesLiebert Air Cooled Condenser User ManualDavid Soares100% (1)
- Makes ListDocument2 pagesMakes ListNagi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Posi Stop Plus Troubleshooting GuideDocument32 pagesPosi Stop Plus Troubleshooting GuideJesus AristizabalNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument8 pagesMajor ProjectDevansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Pressure Reducing Valve in Straightway Form DN 15 - 150Document6 pagesPressure Reducing Valve in Straightway Form DN 15 - 150Riza BagusNo ratings yet
- Activity4 ChanDocument25 pagesActivity4 Chanian jasper nathanNo ratings yet
- Driving Licence CategoriesDocument9 pagesDriving Licence CategoriesThe Best Coding EverNo ratings yet
- Imagine That Your House Is The Same As The Next PicturesDocument7 pagesImagine That Your House Is The Same As The Next PicturesJose Manuel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- LG MDD62 Service Manual PDFDocument69 pagesLG MDD62 Service Manual PDFIvan AsimovNo ratings yet
- A PDFDocument1 pageA PDFsarochimNo ratings yet
- V Protection Schemes2016Document71 pagesV Protection Schemes2016wistfulmemoryNo ratings yet
- Generator Operation ManualDocument31 pagesGenerator Operation Manuallliu yunNo ratings yet
- Standard Ac Induction MotorsDocument20 pagesStandard Ac Induction MotorsgalihatmojoNo ratings yet
- Seismic Vibration Detector SC100: Planning and Installation User GuideDocument32 pagesSeismic Vibration Detector SC100: Planning and Installation User GuideMartin DzNo ratings yet
- 324 Woodward, LS5 Specifications (37522, Rev A)Document4 pages324 Woodward, LS5 Specifications (37522, Rev A)Mohamed Abd ElazizNo ratings yet