Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I On Exchange Chromatography
I On Exchange Chromatography
Uploaded by
soumi soumiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I On Exchange Chromatography
I On Exchange Chromatography
Uploaded by
soumi soumiaCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/303971533
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Poster · June 2016
CITATIONS READS
0 2,713
1 author:
Reza Yousefi
Shiraz University
226 PUBLICATIONS 2,052 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
The effectiveness of essential oils and extracts of Z. majdae and S. mirzayanii on Helicobacter pylori View project
Competitive binding affinity of two lanthanum(III) macrocycle complexes toward DNA and bovine serum albumin in water View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Reza Yousefi on 15 June 2016.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
P4
Ion-Exchange Chromatography
THE 2ND SUMMER SCHOOL
IN INTERDISCIPLINARY
SCIENCES
21-24 September 2009
Presenter:M.Taheri
Supervised by Dr.R.Yousefi (Assistant Professor of Biochemistry)
Co- Supervisor: Dr.H.R.Karbalaei (Assistant Professor of Biochemistry)
Department of Biology,College of Sience,Shiraz University,Shiraz 71454,Iran
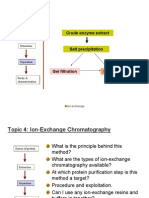
Ion Exchange Some biochemically useful ion exchangers Stepwise / Linear Elution
Chromatography (IEC)
Ion-exchange chromatography (or ion
chromatography) is a process that allows the
separation of ions and polar molecules based
on their charge. It can be used for almost any
kind of charged molecule including large
proteins, small nucleotides and amino acids.
IEC Techniques
Strong ion exchangers (like SP and
QAE) are ionized over a wide pH range
Weak ion exhangers (like DEAE or CM)
are useful over a limited pH range
Choice of resin/matrix depends on:
Principle is to separate on basis of – Scale of separation
charge “adsorption” – Molecular size of components
Positively charged proteins are – Isoelectric point of desired protein
reversibly adsorbed to immobilized – pH stability of the protein of interest
negatively charged beads/polymers
Selecting a resin and starting
Negatively charged proteins are
reversibly adsorbed to immobilized
positively charged beads/polymers
Schematic representation of cation
Important considerations
exchange chromatography
If a protein is most stable below its pI,
a cation exchanger should be used
If a protein is most stable above its pI,
an anion exchanger should be used
If stability of the protein is known to
be good over a wider pH range then
either type of ion exchanger can be Chromatofocusing
IEC Advantages used
Proteins bind to charged matrix in low salt
Has highest resolving power
Has highest loading capacity
Widespread applicability (almost
universal)
Most frequent chromatographic
technique for protein purification
Used in ~75% of all purifications
View publication stats
You might also like
- 02 01 Properties of Water Lab ReportDocument3 pages02 01 Properties of Water Lab ReportkyleaNo ratings yet
- Proposal On Construction and Installation of Water Treatment PlantDocument6 pagesProposal On Construction and Installation of Water Treatment PlantDolce Ncube100% (1)
- Ion Exchange ChromatographyDocument10 pagesIon Exchange ChromatographyJUDE serpesNo ratings yet
- Wa0020Document4 pagesWa0020ghuhgfg096No ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography: Cationic Exchangers Possess Negatively Charged Group, and TheseDocument6 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography: Cationic Exchangers Possess Negatively Charged Group, and TheseJylla AngwayNo ratings yet
- Li Et Al 2021 Progress in Tuning Emission of The Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (Esipt) Based FluorescentDocument7 pagesLi Et Al 2021 Progress in Tuning Emission of The Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (Esipt) Based Fluorescentd20vipsplayNo ratings yet
- Ion-Exchange Chromatography and Its ApplicationsDocument15 pagesIon-Exchange Chromatography and Its ApplicationslopejuNo ratings yet
- Liebana 2016Document10 pagesLiebana 2016JaancaarloDiiazNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentsajidajavaid640No ratings yet
- Acs Accounts 5b00072Document9 pagesAcs Accounts 5b00072veneta gizdakovaNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography PDFDocument14 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography PDFPromita MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Dragulescu Andrasi Et Al 2013 Activatable Oligomerizable Imaging Agents For Photoacoustic Imaging of Furin LikeDocument8 pagesDragulescu Andrasi Et Al 2013 Activatable Oligomerizable Imaging Agents For Photoacoustic Imaging of Furin LikenanoassemblyNo ratings yet
- Anajali ChromatographyDocument10 pagesAnajali ChromatographyAbhishek BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Seen in Diagnostic Laboratories: ElectrophoresisDocument5 pagesSeen in Diagnostic Laboratories: ElectrophoresisARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Iex of Biopharmaceuticals 1234Document15 pagesIex of Biopharmaceuticals 1234aa385864No ratings yet
- Jenkins PDFDocument34 pagesJenkins PDFRobert ChenNo ratings yet
- Anion Exchange ChromatographyDocument19 pagesAnion Exchange ChromatographyTanzeela noureenNo ratings yet
- Proteomics Full LecturesDocument107 pagesProteomics Full LecturesPUBG Hacker100% (1)
- MOLBIO LEC 3.2 Gene Mutations PDFDocument8 pagesMOLBIO LEC 3.2 Gene Mutations PDFTy TriciaNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ChromatographyDocument29 pagesIon Exchange Chromatographysubodhgirdhar100% (6)
- Enzyme NPDocument18 pagesEnzyme NPRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Combined Chromatography and Mass SpectrometryDocument6 pagesChromatography: Combined Chromatography and Mass Spectrometrymoonaa070723No ratings yet
- Protein Purification and AnalysisDocument16 pagesProtein Purification and AnalysisSujan BoseNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Topic 4. Ion Exchange, Affinity - Theory, Instrumentation and Applications.Document25 pagesUnit 4 Topic 4. Ion Exchange, Affinity - Theory, Instrumentation and Applications.ashra sindhikkaaNo ratings yet
- Precision PH Sensor Based On WO Nano Fiber-Polymer Composites and Di Fferential AmplificationDocument6 pagesPrecision PH Sensor Based On WO Nano Fiber-Polymer Composites and Di Fferential Amplification18015 Asfia RifaNo ratings yet
- Bio ChromatographyDocument13 pagesBio Chromatographyvsvsuresh2099No ratings yet
- High Resolution Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis of ProteinsDocument15 pagesHigh Resolution Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis of ProteinsELIZABETHNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Separate Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument38 pagesTechniques To Separate Amino Acids and ProteinsDawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- Otra Ruta SX BZPDocument9 pagesOtra Ruta SX BZPFernando RSNo ratings yet
- ElectrophoresisDocument63 pagesElectrophoresisamolNo ratings yet
- Tissue Engineering 3Document12 pagesTissue Engineering 3Vidit NarayanNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography-IECDocument33 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography-IECnindiya20No ratings yet
- Kim Folger's Cell Membrane Diffusion 2008Document42 pagesKim Folger's Cell Membrane Diffusion 2008julie rainesNo ratings yet
- Cytochrome P460 Cofactor Maturation Proceeds Via PeroxideDependent Post-Translational ModificationDocument13 pagesCytochrome P460 Cofactor Maturation Proceeds Via PeroxideDependent Post-Translational ModificationYuzhuo WangNo ratings yet
- Ion 2022 WordDocument14 pagesIon 2022 Wordgovind ashokraoNo ratings yet
- 15 - Ding - Chemsocrev - Fluorescence and Colometric OligopyrroleDocument12 pages15 - Ding - Chemsocrev - Fluorescence and Colometric Oligopyrrolelenggah purwandariNo ratings yet
- GE IEXcolumnsDocument8 pagesGE IEXcolumnsRiri SyaviraNo ratings yet
- Can e Guner 2004Document12 pagesCan e Guner 2004Vithória Carolyna Trindade Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- 2014 A General Rate Model of Ionexchange Chromatography For Investigating Ionexchange Behavior and ScaleupDocument8 pages2014 A General Rate Model of Ionexchange Chromatography For Investigating Ionexchange Behavior and ScaleupJordan Hiles-BrownNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document4 pagesLecture 4angelNo ratings yet
- Kondo Et Al 2000 Conductivity and Solvation of Li Ions of Lipf6 in Propylene Carbonate SolutionsDocument5 pagesKondo Et Al 2000 Conductivity and Solvation of Li Ions of Lipf6 in Propylene Carbonate SolutionsLéya MateusNo ratings yet
- Nanopore SequencingDocument4 pagesNanopore SequencingRemjohn Aron MagtaasNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Indicators Based On BODIPYDocument43 pagesFluorescent Indicators Based On BODIPYAlex PolancoNo ratings yet
- Plenary: Column and Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPlenary: Column and Paper ChromatographyManila MedNo ratings yet
- Diferencias Esi+ y - Acs - Analchem.7b00096Document4 pagesDiferencias Esi+ y - Acs - Analchem.7b00096delvigoandresNo ratings yet
- Ionic Analytes Reversible Electrostatic Interactions With A ChargedDocument3 pagesIonic Analytes Reversible Electrostatic Interactions With A Chargedjuan mondaNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument6 pagesHPLCMohammad Khaier KaliliNo ratings yet
- Pnas 1119442109Document10 pagesPnas 1119442109Jakub HrycNo ratings yet
- Wu Et Al 2017 Light Induced Translocation of A Conjugated Polyelectrolyte in Cells From Fluorescent Probe To AnticancerDocument7 pagesWu Et Al 2017 Light Induced Translocation of A Conjugated Polyelectrolyte in Cells From Fluorescent Probe To Anticancernokikufubun72No ratings yet
- Membran Sel Dan Matriks EkstraselularDocument78 pagesMembran Sel Dan Matriks EkstraselularneviNo ratings yet
- Endotoxin RemovalDocument4 pagesEndotoxin RemovalqhpuongNo ratings yet
- 10 1039@c1ob06020a PDFDocument7 pages10 1039@c1ob06020a PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure Prediction: Faruk Berat AkcesmeDocument44 pagesProtein Structure Prediction: Faruk Berat AkcesmeMišel VuittonNo ratings yet
- Bioinfo Mod 7Document9 pagesBioinfo Mod 7Amity BiotechNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Peptidyl-tRNA Mimics For Structural Biology ApplicationsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Peptidyl-tRNA Mimics For Structural Biology Applicationsarusha faheemNo ratings yet
- Adams J Am Chem Soc 2001Document14 pagesAdams J Am Chem Soc 2001vnq6gd6qbxNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument6 pagesHPLCHamza AliNo ratings yet
- HPLC PDFDocument6 pagesHPLC PDFEdilson Augosto NhanchengoNo ratings yet
- HPLCC KDocument6 pagesHPLCC Kfreskim.gashiNo ratings yet
- Ph-And Ion-Sensitive Polymers For Drug Delivery: ReviewDocument17 pagesPh-And Ion-Sensitive Polymers For Drug Delivery: ReviewadityaraomuchaNo ratings yet
- CellMembrane Grade 12Document50 pagesCellMembrane Grade 12Olayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Novel Developments in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical AnalysisFrom EverandNovel Developments in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical AnalysisNo ratings yet
- SDS 700076 Sharp Cutting OilsDocument7 pagesSDS 700076 Sharp Cutting OilsMukul SareenNo ratings yet
- Dollowi1: DME TWDocument13 pagesDollowi1: DME TWNishanth ViratNo ratings yet
- Smaw 1Document3 pagesSmaw 1OFFSHORE-ONSHORE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INCNo ratings yet
- CHM3201 Lab Report S2 2019-2020Document42 pagesCHM3201 Lab Report S2 2019-2020Halimatun MustafaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method For Validation of Ciprofloxacin SuspensionDocument2 pagesAnalytical Method For Validation of Ciprofloxacin SuspensionghazalaNo ratings yet
- Archivetemp01 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 1Document54 pagesArchivetemp01 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 1DOROTHY LING YU CHANG Moe0% (1)
- Model P-600 SIC AnalyzerDocument4 pagesModel P-600 SIC AnalyzerVasabinskiyNo ratings yet
- Paraquat Dichloride 24%SLDocument1 pageParaquat Dichloride 24%SLGarv singhNo ratings yet
- Technical and Economic Feasibility Analysis of An Industrial Plant For Producing Acrylo Nitril To Be Used For The Production of Acrylic Fiber PDFDocument95 pagesTechnical and Economic Feasibility Analysis of An Industrial Plant For Producing Acrylo Nitril To Be Used For The Production of Acrylic Fiber PDFMarvil Raul Cieza CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Carbonization of Water Lily Fibers and Coconut Husks As Charcoal PencilDocument17 pagesThe Carbonization of Water Lily Fibers and Coconut Husks As Charcoal PencilJohn Rey Laurente100% (1)
- Cementing OverviewDocument40 pagesCementing OverviewImanossNo ratings yet
- Rough PDF 1Document30 pagesRough PDF 1MURUGANNo ratings yet
- 6 - Axially Loaded ColumnsDocument11 pages6 - Axially Loaded ColumnsThe bestNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 PHSC Pre-Control Test 1 - 08 Mar 2024 - Sekhukhune EastDocument14 pagesGrade 12 PHSC Pre-Control Test 1 - 08 Mar 2024 - Sekhukhune Eastntokozomlotshwa10No ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument34 pagesChapter 11: Reactions of Alkyl HalidesHeena DuaNo ratings yet
- MaterialShelfLife PDFDocument1 pageMaterialShelfLife PDFSunil VermaNo ratings yet
- Final Project ReportDocument15 pagesFinal Project Reportwhãts brøNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Revision 2024Document4 pagesCoordination Compounds Revision 2024Soham GhodkhandeNo ratings yet
- Phytoplankton Community Structure in The River-Influenced Continental Margin of The Northern Gulf of MexicoDocument17 pagesPhytoplankton Community Structure in The River-Influenced Continental Margin of The Northern Gulf of MexicoZelfi IndrawatyNo ratings yet
- AeroChamber Plus® Flow-Vu® Official SiteDocument1 pageAeroChamber Plus® Flow-Vu® Official SiteJuan GomezNo ratings yet
- Microbiotes: La RevueDocument28 pagesMicrobiotes: La RevueAgnese ValentiniNo ratings yet
- 04 MSDS Arcel CT 126Document2 pages04 MSDS Arcel CT 126agusNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument38 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesdhonaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet SD Ferralium 255 SD50 BarDocument4 pagesDatasheet SD Ferralium 255 SD50 Barpranav kariaNo ratings yet
- 13 PDFDocument77 pages13 PDFwastequestNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification Sheet of ConveyorDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification Sheet of ConveyorRonak PanchalNo ratings yet
- PAG Activity For Biological MoleculesDocument19 pagesPAG Activity For Biological Moleculesahmedpadela84No ratings yet
- SB Drill Collar PDFDocument51 pagesSB Drill Collar PDFSiva GanaNo ratings yet