Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TQM Explanation: Other Design Method 1. Product Life Cycle
TQM Explanation: Other Design Method 1. Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
danicamae berongaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TQM Explanation: Other Design Method 1. Product Life Cycle
TQM Explanation: Other Design Method 1. Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
danicamae berongaCopyright:
Available Formats
TQM EXPLANATION
OTHER DESIGN METHOD
1. PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
- Product Life Cycle describes the stages of a product from launch to being discontinued. It is a
strategy tool that helps companies plan for new product development and refine existing products.
Like for example Typewriter, in late 19th century first judt nila nga gigamit is ang typewriter mao na
ang ilang technology sauna nga maka help improve sa ilang writing. But then as time pass by
magkadugay magka evolve judt na ang product manggawas na ang mga computers, laptops and even
smartphones so mahitabo atung typewriters magkagamay na ang iyang demand, so ang ending ma
phase out na cya. Even if ma phase out ang usa ka product naa man puy mupuli nga new and improve
product by using product life cycle companies will learn kung kanus a sila need mag reinvent or pivot
their product in a new direction.
2. Complementary Products
- Complementary good can be a product or service that is sold separately that adds value to another.
In other words, they are two or more goods that are used together. For example, Petrol and Cars.
Ang sakyanan dba dli mo andar ug way gas. So ang gas ug ang sakyanan need nila ang usag usa
para mo work. And with that kung mo taas and demand sa usa ka product mao pudt ang sa usa.
Mostly sa mga companies mao ning gigamit na method to increase sales both product.
3. DESIGN PRODUCTS THAT WORK
- When designing products, always remember that you are designing for people. before you design a
product First you should know what are the needs and wants of your consumers. Because kitang mga
consumer dba mo tan aw man judt tas product nga gamit kaayu ofcourse ikaw nga mudesign ug
product dapat e make sure nmu nga useful sad na imung gibaligya kay the more nga ma ka feel ug
satisfaction ang customers the more mo taas ang demand sa imuhang product.
4. DESIGN FOR THE MANUFACTURE METHOD
- Design for manufacturability is the general engineering practice of designing products in such a way
that they are easy to manufacture. Since ikaw nga nagdesign sa imung product dapat usa sa imung
goal is successful ang process sa pagbuhat sa imung desired designed product. To make that effective,
design your product for ease of manufacturing with an end goal of making a better product at a lower
cost. This is done by simplifying, optimizing and refining the product design.
5. DESIGN FOR MAINTABILITY
- Design for Maintainability (DfM) is the practice of integrating operations and maintenance
considerations into project planning and design to achieve effectiveness, safety, and economy of
maintenance tasks during the lifespan of a facility. So when you design a product d.i one of most
important is ang pagmaintain sa quality sa product dapat ang imung product is sayun rasad cya
mareplacesan sa iyang component parts not just sayun but also safe rapudt. Since maintainability
is designed in, it is important to specify both reliability and maintainability targets
early in the design cycle.
DESIGNING FOR RELIABILITY
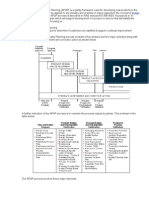
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic, proactive method for evaluating a
process to identify where and how it might fail and to assess the relative impact of different failures, in
order to identify the parts of the process that are most in need of change. Having Failure Modes and
Effects Analysis there will be Improvement of safety, quality and reliability, Improvement of a
company's image, Increased user satisfaction, Reduction in product development cost and Record of
actions taken
Where FMEA can be applied
Where? So in Concept, Process, Design, Service and in Equipment
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis can be applied
1. When a process, product, or service is being designed or redesigned, after quality function
deployment (QFD) ang QFD d.i is a is a focused methodology for carefully listening to the voice of
the customer and then effectively responding to those needs and expectations.
2. When an existing process, product, or service is being applied in a new way
3. Before developing control plans for a new or modified process
4. When improvement goals are planned for an existing process, product, or service
5. When analyzing failures of an existing process, product, or service
6. Periodically throughout the life of the process, product, or service
How FMEA works
So as Failure Modes and Effects Analysis also documents current knowledge and actions about the
risks of failures, for use in continuous improvement. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis pudt d.i is
gina use during sa pag design to prevent failures. Ig human ana gina use pudt na cya for control,
before and during ongoing operation of the process. So how Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
works d.i?
1. Give each component in the system a unique qualifier
2. List all functions each part of the system performs
3. List the one or two failure modes for each function
4. Describe the effect of each failure mode of the component
5. Determine whether the failure will result in a hazard
6. Estimate the relative likelihood of occurrence for each failure on a 10 point scale.
7. Estimate the ease with which the failure may be detected
8. Use the estimates from steps 5,6 and 7 to identify the highest risks
9. Decide what action will be taken to eliminate or reduce the likelihood
So mao na cya noh oh how Failure Method and Effects Analysis works.
Next we have, Fault Tree Analysis is An analytic tool which graphically renders the combination of
faults that lead to the failure of a system
by using Fault Tree Analysis the failures root can be identified using a diagram. It
can also be used to explore a single failure or systematically examine a group of components,
which makes it a versatile tool for a root cause analysis. Ang root cause analysis is a set of tools
that examines errors in security, manufacturing, internal processes, assets or systems. In short, FTA
evaluates the probability of the undesirable outcome and then helps to identify opportunities to reduce
the likelihood of occurrence.
Next we have, Failure modes, Effects and Critically Analysis (FMECA)
So if sa FMEA kay ang role is to identify potential problems and basically, nga makahelp detect
errors or failures that may affect a product's quality. Ang FMECA d.i is not only identify but also
investigate potential failure modes and their causes. Compared to FMEA, FMECA looks at
potential problems in more detail and yields more accurate results. But before ma apply ang
FMECA mas una judt dapat ma perform ang FMEA kay mao manay una mo provide sa detailed
insights about each product or process. These processes are interconnected and complement each
other, allowing for a more robust analysis. So in FMECA there is.....
PRODUCT TRACEABILITY
allows you to track your inventory movements from end-to-end, meaning you can track products to
where they were shipped, or back through their operational steps. Not just for products that have a
short shelf life, but for products that will become outdated due to technological advancements. product
traceability systems will help you improve production efficiency and product quality control, as you’ll
have real-time visibility to understand where along your production is causing problems, such
as bottlenecks in production.
You might also like
- Determining The Optimal Level of Product AvailabilityDocument75 pagesDetermining The Optimal Level of Product AvailabilityTakarial l0% (1)
- Proceeding From The Seminar On Development of Modular ProductsDocument179 pagesProceeding From The Seminar On Development of Modular Productselnegroleo2No ratings yet
- Incoterms QuizDocument4 pagesIncoterms QuizGicille Morales100% (1)
- Tcs InterviewDocument10 pagesTcs InterviewYogi GowdaNo ratings yet
- Hazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Document14 pagesHazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Ihadz CleverleyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document13 pagesAssignment 4api-331731429No ratings yet
- FMEA A Complete Guide To Identifying and Preventing Risks in Your CompanyDocument42 pagesFMEA A Complete Guide To Identifying and Preventing Risks in Your CompanyGabriel Domé100% (1)
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument7 pagesFailure Mode Effect AnalysisRewati KumarNo ratings yet
- Cause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationDocument3 pagesCause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationAlain DoniNo ratings yet
- Lembar Jawaban: Ujian Akhir Semester Online SEMESTER GENAP 2019/2020 Fakultas BisnisDocument4 pagesLembar Jawaban: Ujian Akhir Semester Online SEMESTER GENAP 2019/2020 Fakultas BisnisOlivia SandyNo ratings yet
- T5 FmeaDocument11 pagesT5 Fmeahasovod464No ratings yet
- Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis of A Centrifugal Oil Cleaner and Plan For Validation of The DfmeaDocument8 pagesDesign Failure Mode Effect Analysis of A Centrifugal Oil Cleaner and Plan For Validation of The DfmeaEfren RodríguezsNo ratings yet
- Stqa Julydefaulter 2019 20solDocument6 pagesStqa Julydefaulter 2019 20solAniket LamgeNo ratings yet
- 1 Explain The Significance, Methodology and Advantages of SMED Technique AnswerDocument3 pages1 Explain The Significance, Methodology and Advantages of SMED Technique AnswerArjun SNo ratings yet
- How To Recognize Effective CAPAs and A Culture of Quality (Caso #3)Document9 pagesHow To Recognize Effective CAPAs and A Culture of Quality (Caso #3)A. MorilloNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesTotal Quality Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: Manufacturing SciencesDocument15 pagesTerm Paper: Manufacturing SciencesArpit BajajNo ratings yet
- Publisher Namespringer, London Print Isbn978-1-84882-471-3 Online Isbn978-1-84882-472-0 Ebook PackagesDocument3 pagesPublisher Namespringer, London Print Isbn978-1-84882-471-3 Online Isbn978-1-84882-472-0 Ebook PackagesEva WatiNo ratings yet
- TQM Reviewe1Document4 pagesTQM Reviewe1Angel Mae SalvadorNo ratings yet
- C. For Students - Session 8 PDFDocument13 pagesC. For Students - Session 8 PDFSairah Camille ArandiaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document41 pagesAssignment 5api-288019990No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Quarter 2Document43 pagesLesson 2 Quarter 2John Paul GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Synthesis ReportDocument6 pagesSynthesis ReportMark Paul AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- Are The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapDocument4 pagesAre The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapSergio Cristobal Bonilla CegadorNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 3 PDDDocument30 pages3 Chapter 3 PDDdesnetselomonNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993Document5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993JeevanNo ratings yet
- Se NotesDocument4 pagesSe NotesYashavanth B ANo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagmentDocument11 pagesTotal Quality ManagmentAvisekh KumarNo ratings yet
- Production Management Lecture NotesDocument172 pagesProduction Management Lecture NotesVinoth Heartkiller71% (7)
- Defination of POMDocument9 pagesDefination of POMShen MetzNo ratings yet
- Study Report: ObservationsDocument8 pagesStudy Report: ObservationsjanarthananNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 1 Oct 2022 - OPM545 - FinalDocument7 pagesASSIGNMENT 1 Oct 2022 - OPM545 - FinalMuhammad Syafiq AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariNo ratings yet
- FMEA StepsDocument8 pagesFMEA Stepsmn1938No ratings yet
- 4th Unit 16mDocument24 pages4th Unit 16mIfthisam banuNo ratings yet
- Industrial ManagementDocument10 pagesIndustrial ManagementHimanshu GautamNo ratings yet
- IGNOU MBA MS-05 Solved AssignmentDocument16 pagesIGNOU MBA MS-05 Solved AssignmenttobinsNo ratings yet
- TQM Presentation by Group 1: Hriday Bora Vishnu Tej Neelanjan Ghosh Mohit TarwayDocument50 pagesTQM Presentation by Group 1: Hriday Bora Vishnu Tej Neelanjan Ghosh Mohit Tarwaysiddhartha tulsyanNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Green BeltDocument23 pagesSix Sigma Green BeltSharjeel ShahidNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide to FMEA : A Proactive Approach to Failure AnalysisFrom EverandPractical Guide to FMEA : A Proactive Approach to Failure AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Core Tools PDFDocument3 pagesCore Tools PDFR.BalasubramaniNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Secret : Product Development and Intelligent Manufacturing For Flexible Automation With Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1From EverandManufacturing Secret : Product Development and Intelligent Manufacturing For Flexible Automation With Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1No ratings yet
- TQM Seatwork #2Document25 pagesTQM Seatwork #2Heart OgatisNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Failure Modes and Effects Analysis Template: A Benchmarking and Improvements ToolDocument4 pagesHow To Use The Failure Modes and Effects Analysis Template: A Benchmarking and Improvements ToolsahirlyesNo ratings yet
- Why We Should Test Our CodeDocument2 pagesWhy We Should Test Our Codemgajbhe1No ratings yet
- Visual Inspection Standards FOR Powder Coated PARTSDocument13 pagesVisual Inspection Standards FOR Powder Coated PARTSManuNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of Total Quality Managemnt: Submitted By: Sujata Dalvi 10009Document32 pagesPhilosophies of Total Quality Managemnt: Submitted By: Sujata Dalvi 10009Nitin ChauhanNo ratings yet
- PDM Lab ManualDocument155 pagesPDM Lab ManualCAD With RaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FMEADocument57 pagesIntroduction To FMEAypo41956No ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument185 pagesTotal Quality ManagementRussell GaylaNo ratings yet
- Single Piece FlowDocument8 pagesSingle Piece FlowUchral TseNo ratings yet
- FMEA Flier Dietz PDFDocument3 pagesFMEA Flier Dietz PDFMayurNo ratings yet
- BSA 385 Frequent Shopper Program, Part IDocument7 pagesBSA 385 Frequent Shopper Program, Part IAnthony KleinNo ratings yet
- Som Assignment-2Document17 pagesSom Assignment-2Saurav RanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Process Industry: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Document26 pagesIntroduction To Process Industry: Condition Monitoring and Maintenance (MT-362)Engr.shamiNo ratings yet
- Sandhya Assignment3Document13 pagesSandhya Assignment3api-298023080No ratings yet
- All Tools in OneDocument38 pagesAll Tools in Oneom_3334No ratings yet
- R.Hariharan, Lect / EeeDocument31 pagesR.Hariharan, Lect / EeeJinto AntonyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ENTRP 101Document16 pagesChapter 5 ENTRP 101rhyshryroch royerasNo ratings yet
- Explain Quality Circles and Its Importance? Explain How CAD and CIM Aid in Reducing The Concept To Market TimeDocument7 pagesExplain Quality Circles and Its Importance? Explain How CAD and CIM Aid in Reducing The Concept To Market TimeRohit KpNo ratings yet
- MS 05Document8 pagesMS 05Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- OgdclDocument9 pagesOgdclSun RayNo ratings yet
- Wharton Executive Development ProgramDocument8 pagesWharton Executive Development ProgramRoge C. MabagNo ratings yet
- PRDocument430 pagesPRJohnNo ratings yet
- Commodity Derivatives 1Document29 pagesCommodity Derivatives 1Bibhudatta MishraNo ratings yet
- Erp AssignmentDocument4 pagesErp AssignmentRutaba TahirNo ratings yet
- Ed SyllabusDocument4 pagesEd SyllabusVenkatesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Degussa Ag Hocus FocusDocument88 pagesDegussa Ag Hocus FocusVNNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing Communication and Sales ManagementDocument128 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communication and Sales ManagementGobind Singh BhariNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Services: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services: Multiple Choice QuestionsttoraddoraNo ratings yet
- MRF Limited - Rating Report: Strategic Business and Risk Analysis - Project (EPGP - 06)Document4 pagesMRF Limited - Rating Report: Strategic Business and Risk Analysis - Project (EPGP - 06)CH NAIRNo ratings yet
- International Marketing: Lecturer: DR - Dinh Tien Minh Class: B01EDocument12 pagesInternational Marketing: Lecturer: DR - Dinh Tien Minh Class: B01EMỹ NgàNo ratings yet
- The Very Best of 5SDocument32 pagesThe Very Best of 5SxyalfaxyzNo ratings yet
- Boston Matrix - MOBDocument4 pagesBoston Matrix - MOBK YacintheNo ratings yet
- Labour Laws Question BankDocument5 pagesLabour Laws Question BankSumant KumarNo ratings yet
- Internship OutlineDocument2 pagesInternship OutlineManh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Face WashDocument3 pagesFace WashJagruti SontakkeNo ratings yet
- What Is Six Sigma and Which Company Uses The System Overview of Six SigmaDocument1 pageWhat Is Six Sigma and Which Company Uses The System Overview of Six SigmaBarby AngelNo ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument4 pagesSynopsispirdada100% (1)
- ADDENDUM TO COC DBKL 230A (Rev.1-2010) PDFDocument3 pagesADDENDUM TO COC DBKL 230A (Rev.1-2010) PDFAbdul Aziz BurokNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper Class 8 Mathematics Chapter: Profit and LossDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper Class 8 Mathematics Chapter: Profit and LossAadiNo ratings yet
- 1943 Caminito de La Cruz Combined ReportDocument21 pages1943 Caminito de La Cruz Combined ReportValerie LopezNo ratings yet
- Account Statement: Aarush SinghDocument1 pageAccount Statement: Aarush SinghRakibul IslamNo ratings yet
- Jzanzig - Acc 512 - Chapter 12Document27 pagesJzanzig - Acc 512 - Chapter 12lehvrhon100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 - Wharton MBA Career ManagementDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Wharton MBA Career Managementjoes100% (1)
- Thesis On Life Insurance Corporation of IndiaDocument8 pagesThesis On Life Insurance Corporation of Indiamaritzapetersonpaterson100% (2)
- Mis Question PaperDocument4 pagesMis Question PaperddeekshitadharaniNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure TemplateDocument7 pagesWork Breakdown Structure TemplateShinểşţaŕ IñfanţaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument5 pagesReviewerJeline E LansanganNo ratings yet