Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
220 viewsAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short Term
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short Term
Uploaded by
Francis Xavier S. MendezThe nursing assessment identified a client with signs of fluid volume deficit due to blood loss including decreased red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. The short term plan was to stabilize the client's vital signs within 1-2 hours through nursing interventions and assess skin signs, output, and consciousness. The long term goals were to maintain normal blood counts and vital signs within 1-2 days and ensure all goals were met after 2 days of treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Musical Acoustics PDFDocument26 pagesMusical Acoustics PDFGino Mendoza0% (1)
- Normas NES M1019Document12 pagesNormas NES M1019Margarita Torres FloresNo ratings yet
- Perfect Score Score Questions ChecklistDocument4 pagesPerfect Score Score Questions ChecklistPaul Jackson0% (2)
- NCP Pain HypertensionDocument3 pagesNCP Pain HypertensionEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Tissue PerfusionKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- SAS - Session-24-Research 1Document5 pagesSAS - Session-24-Research 1ella retizaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan CapDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For InfectionBianca MaeNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Calcium)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Calcium)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs RefDocument61 pagesRenal Fabs RefREBECCANo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationDocument1 pageCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationJess GoNo ratings yet
- NCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Document2 pagesNCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Arnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ineffective ProtectionDocument7 pagesIneffective Protectionapi-283822730No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Casepres NCPDocument6 pagesCasepres NCPdencio1992No ratings yet
- NCP SeratroDocument2 pagesNCP SeratroKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cva Verb1Document2 pagesAssessment Cva Verb1JhiLy 사랑의 케빈 우No ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- I. LearningsDocument5 pagesI. LearningsMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- NCP .Postoperative.Document5 pagesNCP .Postoperative.Jerome GazmenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Document1 pageTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- NCP KateDor NewDocument6 pagesNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Context: NCM 116 RleDocument1 pageContext: NCM 116 RleTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocument2 pagesJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument6 pagesNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- SDL 1Document2 pagesSDL 1Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- NCP DM Group 6Document4 pagesNCP DM Group 6Jeffrey Calicdan BucalaNo ratings yet
- AAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPDocument2 pagesAAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPMoi ValdozNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNKristina Marie Parulan RnNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- NCP LupusDocument5 pagesNCP LupusMarwin OditaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Managment of Chest Tubes: by Alice Leung RN, BSN, PCCNDocument55 pagesNursing Managment of Chest Tubes: by Alice Leung RN, BSN, PCCNFrancis Xavier S. Mendez0% (1)
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) : CausesDocument11 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) : CausesFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: NCM 114 Clinical LABORATORY Case Study: Covid-19 October 15, 2021Document62 pagesGeriatric Nursing: NCM 114 Clinical LABORATORY Case Study: Covid-19 October 15, 2021Francis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Teenage PregnancyDocument10 pagesTeenage PregnancyFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
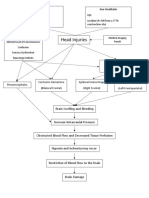
- Head Injuries: Brain Swelling and BleedingDocument23 pagesHead Injuries: Brain Swelling and BleedingFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Document1 pageTheoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Francis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Document4 pagesTheoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Francis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Trial in AbsentiaDocument12 pagesTrial in AbsentiaNahid hossainNo ratings yet
- Al Ajurumiyah Hamzayusuf - TextDocument46 pagesAl Ajurumiyah Hamzayusuf - TextBest channelNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuouseewuanNo ratings yet
- Email Writing by Syeda Narjis FatimaDocument38 pagesEmail Writing by Syeda Narjis FatimaBadar MughairaNo ratings yet
- Welspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Document4 pagesWelspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Digest Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument25 pagesCase Digest Extinguishment of ObligationsLyneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- PGDRD Mail Assignment 26 Feb PalitDocument8 pagesPGDRD Mail Assignment 26 Feb PalitDeepak PandeyNo ratings yet
- List Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021Document11 pagesList Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021minhyun hwangNo ratings yet
- Informative Essays TopicsDocument9 pagesInformative Essays Topicsb725c62j100% (2)
- Web-2012-Allison 250-C18 T63-T700 Gas Turbine EngineDocument4 pagesWeb-2012-Allison 250-C18 T63-T700 Gas Turbine Enginekillerghosts666No ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and StandardsDocument12 pagesElectrical Symbols and StandardsSanjay KNo ratings yet
- Dermatology TreatmentsDocument6 pagesDermatology TreatmentsMayar MostafaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Segmentation Targeting Positioning FINAL PDFDocument13 pagesModule 3 Segmentation Targeting Positioning FINAL PDFLusiana Lie100% (1)
- Phd:304 Lab Report Advanced Mathematical Physics: Sachin Singh Rawat 16PH-06 (Department of Physics)Document12 pagesPhd:304 Lab Report Advanced Mathematical Physics: Sachin Singh Rawat 16PH-06 (Department of Physics)sachin rawatNo ratings yet
- T-Systems CPNI Policy Statement - Final 022717 PDFDocument2 pagesT-Systems CPNI Policy Statement - Final 022717 PDFFederal Communications Commission (FCC)No ratings yet
- Security and Privacy Issues: A Survey On Fintech: (Kg71231W, Mqiu, Xs43599N) @pace - EduDocument12 pagesSecurity and Privacy Issues: A Survey On Fintech: (Kg71231W, Mqiu, Xs43599N) @pace - EduthebestNo ratings yet
- Guiberon Well Service SytemsDocument66 pagesGuiberon Well Service SytemsRonald LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Asco Power Transfer Switch Comparison Features-3149 134689 0Document2 pagesAsco Power Transfer Switch Comparison Features-3149 134689 0angel aguilarNo ratings yet
- Notes On HAMDocument89 pagesNotes On HAMCletus Paul100% (1)
- Edo Mite GenealogiesDocument23 pagesEdo Mite GenealogiesPeace Matasavaii LeifiNo ratings yet
- ECON7002: Unemployment and InflationDocument65 pagesECON7002: Unemployment and InflationNima MoaddeliNo ratings yet
- Russian General Speaks Out On UFOsDocument7 pagesRussian General Speaks Out On UFOsochaerryNo ratings yet
- Plyometric Training - Part I by Juan Carlos SantanaDocument2 pagesPlyometric Training - Part I by Juan Carlos SantanaPedro SilvaNo ratings yet
- Drill #1 With RationaleDocument12 pagesDrill #1 With RationaleRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IslamDocument22 pagesHuman Rights in IslamNoor AliNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentRamana VaralaNo ratings yet
- OutDocument318 pagesOutBet HalNo ratings yet
- Test Method For DDF ProjectDocument13 pagesTest Method For DDF ProjectrantosbNo ratings yet
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short Term
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short Term
Uploaded by
Francis Xavier S. Mendez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
220 views2 pagesThe nursing assessment identified a client with signs of fluid volume deficit due to blood loss including decreased red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. The short term plan was to stabilize the client's vital signs within 1-2 hours through nursing interventions and assess skin signs, output, and consciousness. The long term goals were to maintain normal blood counts and vital signs within 1-2 days and ensure all goals were met after 2 days of treatment.
Original Description:
Original Title
NCP-BLOOD-LOSS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing assessment identified a client with signs of fluid volume deficit due to blood loss including decreased red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. The short term plan was to stabilize the client's vital signs within 1-2 hours through nursing interventions and assess skin signs, output, and consciousness. The long term goals were to maintain normal blood counts and vital signs within 1-2 days and ensure all goals were met after 2 days of treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
220 views2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short Term
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short Term
Uploaded by
Francis Xavier S. MendezThe nursing assessment identified a client with signs of fluid volume deficit due to blood loss including decreased red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. The short term plan was to stabilize the client's vital signs within 1-2 hours through nursing interventions and assess skin signs, output, and consciousness. The long term goals were to maintain normal blood counts and vital signs within 1-2 days and ensure all goals were met after 2 days of treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
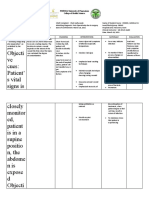
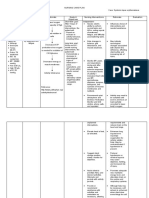
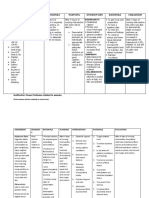
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE SHORT TERM INDEPENDENT SHORT TERM
- Fluid volume -Within 1-2 hours After 2 hours of
Deficit related to of nursing 1. Assess vital 1. To determine if nursing
blood loss intervention the signs. intravascular fluid intervention the
evidenced by client’s vital signs deficit exists. clients vital sign is
decrease RBC, will be in normal in normal range
hemoglobin, range such as as evidenced by
OBJECTIVE hematocrit & HR: 130 bpm to 2. Assess skin 2. Changes in HR: 100bpm and
-RBC: 3.29 10^6 platelet count. 100 bpm; color and moisture, these signs BP:110/80 mmHg
u/L BP:130/90 to urinary output, indicate blood
-Hemoglobin: 110/80 mmHg level of loss affecting LONG TERM
10.4b g/dL consciousness systemic
-Hematocrit: 31 % LONG TERM circulation. After 2 days of
-Platelet count: Within 1-2 days nursing
112 10^3 u/L of Nursing 3. Review 3. For baseline interventions the
-HR: 130 bpm Intervention the Laboratory data data and goals had been
-BP: 130/90 patient will such as CBC comparison completely met
maintain a before and after as evidenced by
normal blood blood transfusion the client
count as well as maintaining a
normal heart rate DEPENDENT normal blood
and blood 4. Administer anti- 4. To promote count and vital
pressure. coagulant clotting time and signs.
medications as prevent bleeding.
prescribed.
5. Provide blood 5. Increase
transfusion as oxygen capacity
prescribed. of blood and
blood
replacement
You might also like
- Musical Acoustics PDFDocument26 pagesMusical Acoustics PDFGino Mendoza0% (1)
- Normas NES M1019Document12 pagesNormas NES M1019Margarita Torres FloresNo ratings yet
- Perfect Score Score Questions ChecklistDocument4 pagesPerfect Score Score Questions ChecklistPaul Jackson0% (2)
- NCP Pain HypertensionDocument3 pagesNCP Pain HypertensionEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Tissue PerfusionKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- SAS - Session-24-Research 1Document5 pagesSAS - Session-24-Research 1ella retizaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan CapDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For InfectionBianca MaeNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Calcium)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Calcium)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs RefDocument61 pagesRenal Fabs RefREBECCANo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationDocument1 pageCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationJess GoNo ratings yet
- NCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Document2 pagesNCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Arnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ineffective ProtectionDocument7 pagesIneffective Protectionapi-283822730No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Casepres NCPDocument6 pagesCasepres NCPdencio1992No ratings yet
- NCP SeratroDocument2 pagesNCP SeratroKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cva Verb1Document2 pagesAssessment Cva Verb1JhiLy 사랑의 케빈 우No ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- I. LearningsDocument5 pagesI. LearningsMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- NCP .Postoperative.Document5 pagesNCP .Postoperative.Jerome GazmenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Document1 pageTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- NCP KateDor NewDocument6 pagesNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Context: NCM 116 RleDocument1 pageContext: NCM 116 RleTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocument2 pagesJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument6 pagesNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- SDL 1Document2 pagesSDL 1Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- NCP DM Group 6Document4 pagesNCP DM Group 6Jeffrey Calicdan BucalaNo ratings yet
- AAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPDocument2 pagesAAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPMoi ValdozNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNKristina Marie Parulan RnNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- NCP LupusDocument5 pagesNCP LupusMarwin OditaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Managment of Chest Tubes: by Alice Leung RN, BSN, PCCNDocument55 pagesNursing Managment of Chest Tubes: by Alice Leung RN, BSN, PCCNFrancis Xavier S. Mendez0% (1)
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) : CausesDocument11 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) : CausesFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: NCM 114 Clinical LABORATORY Case Study: Covid-19 October 15, 2021Document62 pagesGeriatric Nursing: NCM 114 Clinical LABORATORY Case Study: Covid-19 October 15, 2021Francis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Teenage PregnancyDocument10 pagesTeenage PregnancyFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries: Brain Swelling and BleedingDocument23 pagesHead Injuries: Brain Swelling and BleedingFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Document1 pageTheoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Francis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Document4 pagesTheoretical Framework References (PDF Books)Francis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Trial in AbsentiaDocument12 pagesTrial in AbsentiaNahid hossainNo ratings yet
- Al Ajurumiyah Hamzayusuf - TextDocument46 pagesAl Ajurumiyah Hamzayusuf - TextBest channelNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuouseewuanNo ratings yet
- Email Writing by Syeda Narjis FatimaDocument38 pagesEmail Writing by Syeda Narjis FatimaBadar MughairaNo ratings yet
- Welspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Document4 pagesWelspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Digest Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument25 pagesCase Digest Extinguishment of ObligationsLyneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- PGDRD Mail Assignment 26 Feb PalitDocument8 pagesPGDRD Mail Assignment 26 Feb PalitDeepak PandeyNo ratings yet
- List Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021Document11 pagesList Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021minhyun hwangNo ratings yet
- Informative Essays TopicsDocument9 pagesInformative Essays Topicsb725c62j100% (2)
- Web-2012-Allison 250-C18 T63-T700 Gas Turbine EngineDocument4 pagesWeb-2012-Allison 250-C18 T63-T700 Gas Turbine Enginekillerghosts666No ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and StandardsDocument12 pagesElectrical Symbols and StandardsSanjay KNo ratings yet
- Dermatology TreatmentsDocument6 pagesDermatology TreatmentsMayar MostafaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Segmentation Targeting Positioning FINAL PDFDocument13 pagesModule 3 Segmentation Targeting Positioning FINAL PDFLusiana Lie100% (1)
- Phd:304 Lab Report Advanced Mathematical Physics: Sachin Singh Rawat 16PH-06 (Department of Physics)Document12 pagesPhd:304 Lab Report Advanced Mathematical Physics: Sachin Singh Rawat 16PH-06 (Department of Physics)sachin rawatNo ratings yet
- T-Systems CPNI Policy Statement - Final 022717 PDFDocument2 pagesT-Systems CPNI Policy Statement - Final 022717 PDFFederal Communications Commission (FCC)No ratings yet
- Security and Privacy Issues: A Survey On Fintech: (Kg71231W, Mqiu, Xs43599N) @pace - EduDocument12 pagesSecurity and Privacy Issues: A Survey On Fintech: (Kg71231W, Mqiu, Xs43599N) @pace - EduthebestNo ratings yet
- Guiberon Well Service SytemsDocument66 pagesGuiberon Well Service SytemsRonald LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Asco Power Transfer Switch Comparison Features-3149 134689 0Document2 pagesAsco Power Transfer Switch Comparison Features-3149 134689 0angel aguilarNo ratings yet
- Notes On HAMDocument89 pagesNotes On HAMCletus Paul100% (1)
- Edo Mite GenealogiesDocument23 pagesEdo Mite GenealogiesPeace Matasavaii LeifiNo ratings yet
- ECON7002: Unemployment and InflationDocument65 pagesECON7002: Unemployment and InflationNima MoaddeliNo ratings yet
- Russian General Speaks Out On UFOsDocument7 pagesRussian General Speaks Out On UFOsochaerryNo ratings yet
- Plyometric Training - Part I by Juan Carlos SantanaDocument2 pagesPlyometric Training - Part I by Juan Carlos SantanaPedro SilvaNo ratings yet
- Drill #1 With RationaleDocument12 pagesDrill #1 With RationaleRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IslamDocument22 pagesHuman Rights in IslamNoor AliNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentRamana VaralaNo ratings yet
- OutDocument318 pagesOutBet HalNo ratings yet
- Test Method For DDF ProjectDocument13 pagesTest Method For DDF ProjectrantosbNo ratings yet