Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bangladesh Expectations
Bangladesh Expectations
Uploaded by
Monirul IslamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bangladesh Expectations
Bangladesh Expectations
Uploaded by
Monirul IslamCopyright:
Available Formats
2018 Health SDG Profile: Bangladesh
Bangladesh Last updated October, 2018
GDP per capita² Current health expenditure
Population (000s)¹ Urban population¹ Poverty² (Current US$) as share of GDP³
(ppp<< $1.90
(ppp $1.90 aaday)
day)
166 368 35.9% 18.5 1516.5 3.0%
Monitoring the health SDG goal: Indicators of overall progress
Life expectancy
100
Life expectancy at birth⁴ provides an indication of overall mortality of a
73 country's population. In Bangladesh, from 2000 (65.3 years) to 2016 (72.7
Age (years)
65 63
56 years), the life expectancy at birth has improved by 7.4 years.
50
Healthy life expectancy⁴ reflects overall health of the country's population.
In Bangladesh, from 2000 (56.3 years) to 2016 (63.3 years), healthy life
0 expectancy has improved by 7.0 years.
2000 2007 2015 2016
Life expectancy at birth Healthy life expectancy
Universal health coverage: At the centre of the health goal
The goal of universal health coverage (UHC) is that all people and communities receive the health care they need, without suffering financial
hardship. Monitoring UHC requires measuring health service coverage and financial protection (SDG target 3.8).
HEALTH SERVICE COVERAGE FINANCIAL PROTECTION
A summary measure of essential health services coverage, a
composite service coverage index, is used:16 indicators are derived Financial protection is measured through two indicators:
from four main areas of work: (1) reproductive, maternal, newborn (1) impoverishment, and (2) catastrophic health expenditure.
and child health; (2) infectious diseases; (3) noncommunicable
diseases; (4) service capacity, access and health security. Impoverishment: 3.4% or approximately 5 234 000 people are
being pushed into poverty because of out-of-pocket health
Reproductive, maternal, newborn and child health Latest available data (2010-2017) spending³.
Coverage (%)
100 97
62 Catastrophic expenditure on health: 13.9% of people spent more
42
50 37 than 10% of their household's total expenditure on health care³.
0
Family planning
coverage⁵
Pregnancy care⁵ Care seeking
behaviour suspected
Child immunization
coverage (DTP3)⁶
Out-of-pocket expenditure³ Public spending on health³ is
pneumonia⁵ In most cases, high determined by the capacity of the
Infectious diseases percentage of out-of-pocket government to raise revenues and
expenditure out of the total allocate it to health.
Coverage (%)
100
62 health expenditure is
50 36
47
associated with low financial
0
16
protection.
Tuberculosis HIV antiretroviral Insecticide-treated Access to basic
treatment coverage⁷ therapy coverage⁸ bednets/indoor sanitation¹⁰
residual spray
coverage for malaria
prevention⁹ 5.7%
Noncommunicable diseases 5.7%
Coverage (%)
100 90
75
65
2.8%
50
0
Prevalence of normal Tobacco non-use¹¹ Prevalence of normal Cervical cancer
blood pressure in fasting glucose level¹¹ screening 72% GDP 2015
population¹⁰
Service capacity, access and health security Estimated total government expenditure, 2015
or latest available year
Coverage (%)
100 78
65 Out-of-pocket expenditure, as % of the Estimated government expenditure on health,
health expenditure (2015) 2015 or latest available year
50 33
19
0
Health security: IHR Access to essential Density of hospital Heath worker density,
compliance¹⁰ medicines¹⁴ beds¹⁵, expressed as expressed as % of
% of global threshold, new global threshold, This profile provides an overview of the current status
18/10 000¹² 44.5/10 000¹³
of achieving better health towards the 13 targets
UHC services coverage index of essential health services under the Sustainable Development Goal #3 (SDG3):
To provide a summary measure of UHC services coverage index Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
coverage, an index of national 100 All 25 SDG3 indicators plus other selected health-related
service coverage is computed by indicators are presented where data is available.
Coverage (%)
averaging service coverage values
50
across the 16 tracer indicators. The 50
UHC coverage index ranges from
0% to 100%, with 100% implying full
coverage across a range of 0
services. UHC services coverage index
Equity : Leave no one behind
Variation by geography Variation by income Variation by education
Under five mortality⁵ Antenatal care coverage⁵ Stunting⁵
100 100 100
Mortality Rate
Percentage
Percentage
50 50 50
0
0 0
2000 2005 2010 2015
2000 2005 2010 2015 2000 2005 2010 2015
Sanitation¹⁰ Contraceptive (modern) prevalence rate⁵ Full Immunization⁵
100 100 100
Percentage
Percentage
Percentage
50 50 50
0 0 0
2000 2005 2010 2015 2000 2005 2010 2015 2000 2005 2010 2015
Rural
Quintile 5 (richest) No education Primary school
Urban
Quintile 1 (poorest) Secondary school+
SDGs emphasis on equity
SDG target 17.18 emphasizes the need for disaggregated data. By 2020, enhance capacity-building support to developing countries to
increase significantly the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data disaggregated by income, gender, age, race, location and other
characteristics relevant in national contexts.
Strengthening civil registration and vital statistics (CRVS)
Birth registration¹⁵ Cause of death¹⁶
Death registration¹⁵
100 100
87.2
85.4
85.9
100
85.2
86.4
85.0
87.4
84.2
Percentage
Percentage
Percentage
50.0
50 50
50
0
0 0
2000 2005 2010 2015
2000 2005 2010 2015 2000 2005 2010 2015
SDGs emphasis on mortality statistics
More reliable vital statistics on births, deaths and causes of death from civil registration and vital statistics (CRVS) systems are required for
reporting on 14 health-related SDG mortality indicators. Understanding better what people are dying from can lead to stronger health policies
and plans, and improve monitoring of the health-related SDGs.
SDG 3: Health targets
Maternal and child mortality (SDG target 3.1, 3.2)
Births attended by skilled health personnel⁵ Child mortality¹⁸
Maternal mortality ratio¹⁷
100 150
750
MMR [100 000 live births ]
MR [1000 live births]
Coverage (%)
100 88
500
399
50 42
250 32 50
43
176 34
18
20
0 0
0
2000 2005 2010 2015 2000 2005 2010 2015 2016
2007 2011 2014
Children under-five Neonatal
2018 Health SDG Profile: Bangladesh
Communicable diseases (SDG target 3.3)
TB incidence⁷ Malaria incidence⁹ Regional
New HIV infections among Indicators Year Bangladesh
adults 15 to 49 years⁸ 20 estimate
500
Number of people
Malaria IR [1000 pop. at risk]
TB incidence [100 000 pop.]
requiring
HIV IR [1000 uninfected pop.]
400 15
interventions 2016 47,484,224 671,797,672
0.4 300 against neglected
225 221 10 tropical diseases⁴
200
0.2
5 3.9
100
0.02 1.6
0.0
0.01 0 0
2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
Malaria incidence is calculated for
confirmed malaria cases
Noncommunicable diseases and injuries
SDG Regional Total alcohol per capita (age 15+ years)
Indicators Year Bangladesh consumption⁴
target estimate
9
Mortality between 30 and 70 years
of age from cardiovascular
3.4.1 2016 21.6 23.1
diseases, cancer, diabetes or
chronic respiratory diseases⁴ (%)
Suicide mortality rate⁴ 6
3.4.2 2016 5.9 13.2
(per 100 000 population)
Litres
Total alcohol per capita (age 15+
3.5.2 2016 <0.05 4.5
years) consumption⁴
Mortality rate from road traffic 3
3.6.1 2013 13.6 17
injuries⁴ (per 100 000 population)
Sexual and reproductive health
Proportion of married or in-union 0.0 0.0
women of reproductive age who 0
3.7.1 2014 72.5 75.1
have their need for family planning 2003 2008 2010 2015 2016
satisfied with modern methods⁵ (%)
Adolescent birth rate (per 1000 women
Adolescent birth rate¹⁹ (per 1000 aged 15 to 19 years)¹⁹
3.7.2 2016 78 33
women aged 15 to19 years)
Mortality due to environmental pollution 126
Mortality rate attributed to
household and ambient air 3.9.1 2016 149 164
pollution⁴ (per 100 000 population) 100
Mortality rate attributed to exposure
78
Proportion
to unsafe WASH services⁴ 3.9.2 2016 11.9 15.4
(per 100 000 population)
Mortality rate attributed to
unintentional poisoning⁴ 3.9.3 2016 0.3 1.8 50
(per 100 000 population)
Tobacco use
Tobacco use among persons (15+
3.a.1 2017 25.2 -
yrs) and older - Female²⁰ 0
2007 2011 2014
Tobacco use among persons (15+
3.a.1 2017 46.0 - Total NCD Mortality¹⁰
yrs) and older - Male²⁰
1000
Essential medicines and vaccines
Total NCD Mortality rate (per 100 000)
Proportion of the population with
access to affordable medicines and - 750
3.b.1 2014 65
vaccines on a sustainable basis¹⁴
Total net official development
assistance to medical research and 500
3.b.2 2016 1.25 -
basic health per capita¹⁴
Health workforce 250
Health worker density¹³
3.c.1 2017 8.3 -
(per 10 000 population)
0
National and global health risks
2000 2005 2010 2015
International Health Regulations
3.d.1 2017 78 73 Female Male
Core Capacity Index⁴
Note: A dash (-) implies relevant data are not available
2018 Health SDG Profile: Bangladesh
Country Other health-related SDGs
Bangladesh
General government health expenditure Prevalence of children under 5 years of age who
are stunted⁵
SDG Regional
Indicators Year Bangladesh 100
target estimate
General government health expenditure as
1.a 2015 2.8 9.3
% of general government expenditure⁴
Proportion (%)
Child nutrition 50.6
50
Children under 5 years who are stunted⁴ 2.2.1 2014 36.1 33.8 36.1
Children under 5 years who are wasted⁴ 2.2.2 2014 14.3 15.3
Children under 5 years who are 0
2.2.3 2014 1.4 5.3
overweight⁴
2004 2007 2011 2014
Drinking water services and sanitation
Proportion of population using improved Prevalence of children under 5 years of age who
6.1 2015 56 - are wasted⁵
drinking water sources⁴
50
Proportion of population using improved
6.2 2015 - -
sanitation⁴
Clean household energy
Proportion (%)
Proportion of population with primary
7.1 2016 18 - 25
reliance on clean fuel⁴
Ambient air pollution 14.5 14.3
Air pollution level in cities⁴ (PM 2.5)
11.6.2 2016 58.6 -
(µg/m³)
0
Natural disasters
2004 2007 2011 2014
Number of deaths by disaster⁴ Prevalence of children under 5 years who are
13.1.2 2016 <0.1 0.3
( per 100 000 people) overweight⁵
Homicide and conflicts 15
Mortality rate due to homicide⁴
16.1.1 2016 2.9 4
(per 100 000 population) Proportion (%)
Estimated direct deaths from major
16.1.2 2011-16 < 0.1 0.1
conflicts⁴ (per 100 000 population) 8
Birth registration
Birth registration coverage¹⁵ 16.9.1 2016 85.9 -
1.4
Cause-of-death data 0
0.9
Completeness of cause-of-death data¹⁶ 2004 2007 2014
17.19.2 2016 50 10
(%)
Note: A dash (-) implies relevant data are not available
1. World population prospects: the 2017 revision. New York: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division; 2017
(http://esa.un.org/wpp/, accessed 9 July 2018).
2. World urbanization prospects: the 2018 revision. New York: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division; 2018
(https://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/DataQuery/, accessed 9 July 2018).
3. Global health expenditure database. Geneva: World Health Organization; June 2016 (http://apps.who.int/nha/database, accessed 9 July 2018).
4. World health statistics 2018: monitoring health for the SDGs. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
(http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2018/en/, accessed 9 July 2018).
5. Bangladesh demographic and health survey 2014. Dhaka, Bangladesh, and Rockville, Maryland, USA: NIPORT, Mitra and Associates, and ICF International;
2014(https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR311/FR311.pdf, accessed 9 July 2018).
6. WHO vaccine-preventable diseases: monitoring system. 2018 global summary. Geneva: World Health Organization(http://apps.who.int/immunization_monitor-
ing/globalsummary/countries?countrycriteria%5Bcountry%5D%5B%5D=TLS&commit=OK, accessed 9 July 2018).
7. Global tuberculosis report 2017.Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017(http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/259366/9789241565516, accessed 9 July
2018).
8. UNAIDS 2016 estimates for coverage of people receiving ART. (http://aidsinfo.unaids.org, accessed 9 July 2018).
9. Global malaria report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017 (http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2017/en/, accessed 9 July 2018).
10. Global health observatory. Geneva: World Health Organization (http://www.who.int/gho/en/, accessed 9 July 2018).
11. CVD vs Tobacco factsheet http://www.searo.who.int/entity/ncd_tobacco_surveillance/documents/ban_wntd_18/en/ - accessed 20 June 2018.
12. World health statistics 2013. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2013. (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/82058/WHO_HIS_HSI_13.1_eng.pdf,
accessed 9 July 2018).
13. Decade for health workforce strengthening in the South-East Asia Region 2015—2024: Second review of progress, 2018. New Delhi: World Health Organization;
2018.
14. Saha, Tulshi. Bangladesh Service provision Assessment Survey 1999-2000. Calverton, Maryland: National Institute of Population Research and Training (NIPORT),
Mitra and Associates, and ORC Macro; 2002 (https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/SPA2/SPA2.pdf, accessed 9 July 2018).
15. Report on Bangladesh Sample Vital Statistics 2013-2014, 2017-2018. Dhaka: Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (https://www.bbs.gov.bd). The figure reported is
based on sentinal sites only not representing the whole country. Further, please note that Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey, 2014 reported birth registration
coverage as 20.2%.
16. CRVS regional action framework reporting 2013-2017. Bangkok: United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific; 2018 (unpublished
document).
17. Trends in maternal mortality: 1990 to 2015 http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/monitoring/maternal-mortality-2015/en/ - accessed 9 July 2018).
18. Levels & trends in child mortality: report 2015: estimates developed by the UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. New York (NY), Geneva and
Washington (DC): UNICEF, World Health Organization, World Bank, United Nation; 2015 (http://www.childinfo.org/, accessed 9 July 2018).
19. United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017). World Fertility Data 2017
http://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/theme/fertility/index.shtml - accessed 20 June 2018
20. Fact sheet : CVD Vs Tobacco, Department of non-communicable diseases
2018 Health SDG Profile: Bangladesh
You might also like
- Public Health Nursing Population Centered 9th Edition Stanhope Lancaster Test BankDocument14 pagesPublic Health Nursing Population Centered 9th Edition Stanhope Lancaster Test BankMichael SingletonNo ratings yet
- National Objectives For HealthDocument85 pagesNational Objectives For HealthJesserene SorianoNo ratings yet
- 2018 Health SDG Profile: IndonesiaDocument4 pages2018 Health SDG Profile: Indonesiadedek latifNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: 2019 Health SDG Profi Le: IndonesiaDocument4 pagesIndonesia: 2019 Health SDG Profi Le: IndonesiafabianrichieNo ratings yet
- Kenya OnePagerDocument1 pageKenya OnePagerPrateek Golecha StudentNo ratings yet
- Alliancehpsr KenyaabridgedprimasysDocument12 pagesAlliancehpsr Kenyaabridgedprimasysdisposable101No ratings yet
- Health CareDocument12 pagesHealth CareAli SherNo ratings yet
- Module 1 CHN 1Document15 pagesModule 1 CHN 1Danz KieNo ratings yet
- Taiwan Health Profile MOHWDocument2 pagesTaiwan Health Profile MOHWAmalia MollyNo ratings yet
- Regional Profile 2023Document74 pagesRegional Profile 2023Griffith MirallesNo ratings yet
- NalgondanggggDocument4 pagesNalgondanggggmadara uNo ratings yet
- Importance of Population Health - PresentationDocument9 pagesImportance of Population Health - PresentationzpNo ratings yet
- Equatorial Guinea: Health SituationDocument2 pagesEquatorial Guinea: Health SituationRila Vita SariNo ratings yet
- Rewa-Madhya Pradesh PDFDocument4 pagesRewa-Madhya Pradesh PDFdileepkkvvNo ratings yet
- Prioritizing Health - A Prescription For ProsperityDocument1 pagePrioritizing Health - A Prescription For ProsperityLaura LaynezNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Kesiapan Pelaksanaan Program inDocument16 pagesEvaluasi Kesiapan Pelaksanaan Program inYudhistiraGilangPerdanaNo ratings yet
- 8-Point Action Agenda - The Medium-Term Strategy of The Health Sector For 2023-2028Document19 pages8-Point Action Agenda - The Medium-Term Strategy of The Health Sector For 2023-2028RURAL HEALTH CENTER TAMBLER BAWINGNo ratings yet
- NCD PIR 2023 TemplateDocument26 pagesNCD PIR 2023 TemplateroseannurakNo ratings yet
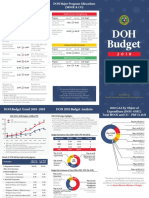
- DOH Budget (2018)Document2 pagesDOH Budget (2018)Hannah Rachel UlepNo ratings yet
- USAID IHP FY2021 Quarter 1 Report - SUMMARY - EN051321 - Submit02Document12 pagesUSAID IHP FY2021 Quarter 1 Report - SUMMARY - EN051321 - Submit02Jonathan KanzaNo ratings yet
- Document From Elle Final2Document18 pagesDocument From Elle Final2georgeNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Pelaksanaan Pendataan Program Indonesia Sehat Dengan Pendekatan KeluargaDocument16 pagesEvaluasi Pelaksanaan Pendataan Program Indonesia Sehat Dengan Pendekatan KeluargaAsmira YeddiNo ratings yet
- Catastrophic Health Spending in Europe: Equity and Policy Implications of Different Calculation MethodsDocument11 pagesCatastrophic Health Spending in Europe: Equity and Policy Implications of Different Calculation MethodsKev AdvanNo ratings yet
- On The World Health Organisation's Measurement of Health InequalitiesDocument6 pagesOn The World Health Organisation's Measurement of Health Inequalitiesujangketul62No ratings yet
- DOH 8-Point Action Agenda - The Medium-Term Strategy of The Health Sector For 2023-2028Document21 pagesDOH 8-Point Action Agenda - The Medium-Term Strategy of The Health Sector For 2023-2028ithran khoNo ratings yet
- EconomicBurden LBP IndiaDocument11 pagesEconomicBurden LBP Indiacvissa1964No ratings yet
- SSP032 M5 SDG3Document23 pagesSSP032 M5 SDG3Henry Darius NamocNo ratings yet
- Alliancehpsr Thailandabridgedprimasys PDFDocument12 pagesAlliancehpsr Thailandabridgedprimasys PDFIrvan AlfianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Integrated Universal Child Grant in Bihar-IndiaDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - Integrated Universal Child Grant in Bihar-Indialychandy1986No ratings yet
- Health Status of IndiaDocument10 pagesHealth Status of IndiaSutapa PawarNo ratings yet
- GER Bangladesh EngDocument12 pagesGER Bangladesh Engfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet
- Ccsbrief GRD EngDocument2 pagesCcsbrief GRD EngLexy AnnNo ratings yet
- Ccsbrief GRD EngDocument2 pagesCcsbrief GRD EngLexy AnnNo ratings yet
- RMNCH ADocument41 pagesRMNCH AprivatejarjarbinksNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kesehatan MasyarakatDocument29 pagesJurnal Kesehatan MasyarakatAbdul HadiNo ratings yet
- Jamapediatrics Cao 2022 Oi 220026 1659113206.96349Document10 pagesJamapediatrics Cao 2022 Oi 220026 1659113206.96349Jack Eugene LiowNo ratings yet
- United Arab Emirates: Health SituationDocument2 pagesUnited Arab Emirates: Health SituationMohammed Yaser HussainNo ratings yet
- How Much Household Healthcare Expenditure PDFDocument16 pagesHow Much Household Healthcare Expenditure PDFluis.suarez8899No ratings yet
- BRM AssignmentDocument11 pagesBRM AssignmentSalman ButtNo ratings yet
- Gdi Annual Report 2019-20Document6 pagesGdi Annual Report 2019-20AbhishekAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Algérie: Situation de La SantéDocument2 pagesAlgérie: Situation de La SantéAmineNo ratings yet
- 2017 Global Health Care Outlook: Making Progress Against Persistent ChallengesDocument28 pages2017 Global Health Care Outlook: Making Progress Against Persistent ChallengesBrandon MeisterNo ratings yet
- Why UHC For India and How Can It Be AchievedDocument86 pagesWhy UHC For India and How Can It Be AchievedKeerthi Chowdary KoduruNo ratings yet
- Adesete Et Al1Document14 pagesAdesete Et Al1Abu WidaadNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Out of Pocket Costs in The Health Sector by An Average Household and Its Impact On The Economic Development of The Country (India) Research BackgroundDocument2 pagesThe Influence of Out of Pocket Costs in The Health Sector by An Average Household and Its Impact On The Economic Development of The Country (India) Research BackgroundSarcastic QueenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document35 pagesChapter 6Normayanti NurhadiNo ratings yet
- Physical Activity Levels Among The Adults of Majha Region of Punjab, India: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument12 pagesPhysical Activity Levels Among The Adults of Majha Region of Punjab, India: A Cross-Sectional StudyHarman DeepNo ratings yet
- Adulto Mayor y El Manejo GeriatricoDocument15 pagesAdulto Mayor y El Manejo GeriatricoMilton FabianNo ratings yet
- Impact of Stillbirths On International ComparisonsDocument9 pagesImpact of Stillbirths On International ComparisonsLays MarquesNo ratings yet
- Infant MortalityDocument2 pagesInfant MortalitydiakosvNo ratings yet
- Untitled PDFDocument2 pagesUntitled PDFkrissyNo ratings yet
- France and Saudi ArabiaDocument17 pagesFrance and Saudi ArabiaHajar HossamNo ratings yet
- Ebb PDFDocument12 pagesEbb PDFMonica TanNo ratings yet
- 03 Ijnh 09-JS-2023-11Document4 pages03 Ijnh 09-JS-2023-11Apacetech IluvbNo ratings yet
- NCDs and Effects of Vertical and Horizontal Health AidDocument18 pagesNCDs and Effects of Vertical and Horizontal Health AidSam CroweNo ratings yet
- Kusuma2017Impact CCT On Children Food ConsumptionDocument7 pagesKusuma2017Impact CCT On Children Food ConsumptionMuhammad dzaky AdzhanyNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument44 pagesFamily PlanningAparna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Adolescent HealthcareDocument10 pagesMaternal & Adolescent HealthcarechandrajoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Public Financing of Essential Maternal and ChildDocument9 pagesEffects of Public Financing of Essential Maternal and ChildSr Leticia EnujubaNo ratings yet
- Public Health Perspectives in Lactation: Pubhlth 310, Winter 2020. Carly Mccabe, M.SDocument27 pagesPublic Health Perspectives in Lactation: Pubhlth 310, Winter 2020. Carly Mccabe, M.Silikebooks1998No ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Membership in A Mutual Health Insurance Fund in The Thiès Region (Senegal) in 2023: ArticleDocument8 pagesFactors Associated With Membership in A Mutual Health Insurance Fund in The Thiès Region (Senegal) in 2023: ArticleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Doing the Right Thing: 'New' Building Zimbabwe's Health System: 'New' Building Zimbabwe's Health System: 'New Building: 'New Building' Zimbabwe's Health SystemFrom EverandDoing the Right Thing: 'New' Building Zimbabwe's Health System: 'New' Building Zimbabwe's Health System: 'New Building: 'New Building' Zimbabwe's Health SystemNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kinerja Bidan Dalam Pelayanan Nifas Di Kota SalatigaDocument11 pagesFaktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kinerja Bidan Dalam Pelayanan Nifas Di Kota SalatigaMirda MirdaNo ratings yet
- HR - Hipaa - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesHR - Hipaa - Answer KeyMokeshdharan RNo ratings yet
- Soriano, Cindy M: ContactDocument1 pageSoriano, Cindy M: ContactCindy SorianoNo ratings yet
- AFL-CIO Letter SurpriseBillingDocument2 pagesAFL-CIO Letter SurpriseBillingPeter SullivanNo ratings yet
- Premium Support in MedicareDocument4 pagesPremium Support in MedicareAi NurcahyaniNo ratings yet
- Final Research Proposal 1Document5 pagesFinal Research Proposal 1api-615502029No ratings yet
- Republic Act No 7875Document17 pagesRepublic Act No 7875Almira CayeNo ratings yet
- Perinatal GLDocument94 pagesPerinatal GLovidiuroscaNo ratings yet
- ظروف العمل وآثارها النفسية والجسدية على عمال الرعاية الصحيةDocument14 pagesظروف العمل وآثارها النفسية والجسدية على عمال الرعاية الصحيةabdelghanibichouess.19No ratings yet
- Journal of Infectious DiseaseDocument6 pagesJournal of Infectious DiseaseSoham SarangiNo ratings yet
- Job Application LetterDocument2 pagesJob Application LetterNovita SariNo ratings yet
- Penerapan Clinical Audit Untuk DokterDocument23 pagesPenerapan Clinical Audit Untuk DokterPratiwi DewiNo ratings yet
- Draft: The Principles of Infection Prevention and ControlDocument36 pagesDraft: The Principles of Infection Prevention and Controlandrel davidNo ratings yet
- Nurs FPX 4020 Assessment 4 Improvement Plan Tool KitDocument5 pagesNurs FPX 4020 Assessment 4 Improvement Plan Tool Kitjoohnsmith070No ratings yet
- Physician's Orders For Life-Sustaining TreatmentDocument2 pagesPhysician's Orders For Life-Sustaining Treatmentmarlon marlon JuniorNo ratings yet
- Ug Epidemiological Bulletin 2023Wk19Document8 pagesUg Epidemiological Bulletin 2023Wk19JACKLINE ONZIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Capitation in Provider ReimbursementDocument23 pagesChapter 6 - Capitation in Provider ReimbursementAdityaNo ratings yet
- Clarifying Your Strategic Planning AssumptionsDocument6 pagesClarifying Your Strategic Planning AssumptionsJihad Elias ChahlaNo ratings yet
- BCBSMDocument37 pagesBCBSMEjNo ratings yet
- National Clinical Guideline No. 5 Clinical Handover Nov2014Document306 pagesNational Clinical Guideline No. 5 Clinical Handover Nov2014Ahmad JuliadiNo ratings yet
- EmailsDocument31 pagesEmailsretihot169No ratings yet
- 5RequiredReadingList 8 21 08Document1 page5RequiredReadingList 8 21 08Sara NordNo ratings yet
- Online Discussion Forum 1Document2 pagesOnline Discussion Forum 1Brianna LeeNo ratings yet
- The Value of Healthcare AdministrationDocument3 pagesThe Value of Healthcare AdministrationKrizzella ShainaNo ratings yet
- Philhealth: Romeo R. Andaya, MD - MSCPD, PHD, Fpafp Chair, DPMCHDocument19 pagesPhilhealth: Romeo R. Andaya, MD - MSCPD, PHD, Fpafp Chair, DPMCHKatNo ratings yet
- Farmakoepidemiologi 1 OKDocument19 pagesFarmakoepidemiologi 1 OKFeby SupradonoNo ratings yet
- AHIMA World CongressDocument6 pagesAHIMA World Congressorpa iwaNo ratings yet
- Amelia Sung MAternity VSIM Guided ReflectionDocument2 pagesAmelia Sung MAternity VSIM Guided Reflectionmeisha thompsonNo ratings yet