Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsDifferentiate Accuracy From Precision
Differentiate Accuracy From Precision
Uploaded by
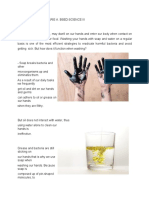
jessa marie marevilesThis document provides a table of specifications for a general physics exam covering the 1st quarter. It outlines 7 main learning competencies that will be assessed, including solving measurement problems, differentiating error types, and estimating uncertainties. For each competency, it specifies the item format that will be used (e.g. multiple choice, matching), the number of days and items allocated, and how items will be distributed across cognitive domains. It also lists subtopics in physics that will be covered, such as atomic/molecular physics, electricity/magnetism, and optics. In total, the exam will contain 50 multiple choice, matching, identification, and alternative test items assessing student understanding of general 1st quarter physics concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- IB Chemistry IA Eggshell LabDocument8 pagesIB Chemistry IA Eggshell LabNour Makarem0% (3)
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsTutor_KLNo ratings yet
- Calculus Table-of-SpecificationDocument1 pageCalculus Table-of-SpecificationJojie T. DeregayNo ratings yet
- Schedule PDFDocument1 pageSchedule PDFInconnuNo ratings yet
- Michael Creel - EconometricsDocument490 pagesMichael Creel - EconometricsJorge Guerrero NuñezNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus T1 2021 MATH 206 enDocument3 pagesCourse Syllabus T1 2021 MATH 206 enAmal Al-attasNo ratings yet
- MATH 117 Syllabus Fall 2019Document2 pagesMATH 117 Syllabus Fall 2019PerzivalNo ratings yet
- Eco No MetricsDocument312 pagesEco No MetricshalhoshanNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry (2020-1) SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesMATH119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry (2020-1) SYLLABUSMuratcan AkgünNo ratings yet
- EconometricsDocument310 pagesEconometricsHerwan GalinggingNo ratings yet
- Syllabus and Structure of MATH119Document4 pagesSyllabus and Structure of MATH119Fortune OputaNo ratings yet
- Calc 12 Exercise List 2012 13Document2 pagesCalc 12 Exercise List 2012 13Andrew FNo ratings yet
- Handout CHE F242Document6 pagesHandout CHE F242donasex652No ratings yet
- 2nd Six Weeks Calendar PLCDocument2 pages2nd Six Weeks Calendar PLCapi-291820023No ratings yet
- MATH 119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry: Online Online In-Class In-ClassDocument3 pagesMATH 119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry: Online Online In-Class In-ClassHussainNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1Document4 pagesMATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1mehmedjediNo ratings yet
- 769513Document196 pages769513Aman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1 - 2 2023-1Document3 pagesMATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1 - 2 2023-1Halil EmreNo ratings yet
- Pattern Classification: Second EditionDocument11 pagesPattern Classification: Second EditionR Gowri PrasadNo ratings yet
- Pattern Classification: Second EditionDocument11 pagesPattern Classification: Second EditionjojoNo ratings yet
- Math119-Course Syllabus and PolicyDocument5 pagesMath119-Course Syllabus and Policy19cerena03No ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS-Q1Document1 pageMathematics 10 TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS-Q1Ailen CeniaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Stat4351.501.07f Taught by Yuly Koshevnik (Yxk055000)Document5 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Stat4351.501.07f Taught by Yuly Koshevnik (Yxk055000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Math550 PDFDocument3 pagesMath550 PDFShelaRamosNo ratings yet
- HTTPS:/WWW Vidyalankar Org/gate/assets/docs/notes/maths PDFDocument354 pagesHTTPS:/WWW Vidyalankar Org/gate/assets/docs/notes/maths PDFIndra N PatelNo ratings yet
- Leigh Sutherland PHD 1997 (Uni of Soton E-Prints)Document301 pagesLeigh Sutherland PHD 1997 (Uni of Soton E-Prints)leighNo ratings yet
- Assignment Math 63 SummerDocument1 pageAssignment Math 63 SummerLi ChNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Course Outline 2020Document3 pagesNumerical Methods Course Outline 2020Abdiqani Mohamed AdanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Math 109 441Document3 pagesSyllabus Math 109 441Salman SaleemNo ratings yet
- Nasser Soltani Study of Mixed Mode Stress Intensity Factor Using The ExperimentaDocument144 pagesNasser Soltani Study of Mixed Mode Stress Intensity Factor Using The ExperimentaIrynaNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Board Batch-2021-22: S.No. Unit - Term-1 No. of Classes 1 11 2 8 3 9 4 9 Unit - Term-2 5 2Document2 pagesClass 12th Board Batch-2021-22: S.No. Unit - Term-1 No. of Classes 1 11 2 8 3 9 4 9 Unit - Term-2 5 2Aditya MithunNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Experimental Methods and Instrumentation For Chemical Engineers PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Experimental Methods and Instrumentation For Chemical Engineers PDFmichael.harryman140100% (26)
- STAT 336-Course Outline - 2023-2024Document4 pagesSTAT 336-Course Outline - 2023-2024Kena JesusNo ratings yet
- SPSS Viskositas WordDocument5 pagesSPSS Viskositas WordIka YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Math002 Syl 232Document2 pagesMath002 Syl 232nabhanbinyaqub05No ratings yet
- TOS-Template RasDocument2 pagesTOS-Template RasRassel Jay GumbocNo ratings yet
- MTH141 Syllabus-CalDocument4 pagesMTH141 Syllabus-CaltucchelNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies:: Parameter Statistic Parameter StatisticDocument5 pagesLearning Competencies:: Parameter Statistic Parameter StatisticSheryn Joy BadiNo ratings yet
- Autput Penelitian: StatisticsDocument3 pagesAutput Penelitian: StatisticsririNo ratings yet
- STA 220 Syllabus Spring 2018-1Document3 pagesSTA 220 Syllabus Spring 2018-1Anass BNo ratings yet
- 2 Quarter Exam-Table of SpecificationDocument1 page2 Quarter Exam-Table of SpecificationBianca Isabel GayanesNo ratings yet
- Math 104: Calculus, Part I. (4h. 1 C.u.)Document2 pagesMath 104: Calculus, Part I. (4h. 1 C.u.)BreyonnaMorganNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Basic College Mathematics An Applied Approach Canadian 1st Edition by Aufmann Lockwood and Milburn ISBN 0176562087 9780176562083Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Basic College Mathematics An Applied Approach Canadian 1st Edition by Aufmann Lockwood and Milburn ISBN 0176562087 9780176562083ernesto.medina346100% (20)
- PROBABILITY & STATISTICS - Final Examination: Dinah Fe T. OlitanDocument5 pagesPROBABILITY & STATISTICS - Final Examination: Dinah Fe T. OlitanDinah Fe Tabaranza-OlitanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Microarray Gene Expression Data - M. Lee (KluwerDocument398 pagesAnalysis of Microarray Gene Expression Data - M. Lee (KluwerciuckyNo ratings yet
- 2022 CHM 171 SyllabusDocument2 pages2022 CHM 171 SyllabusNat GariNo ratings yet
- College of Science Department of Mathematics Course Syllabus: Statistical Methods Spring Semester 2020/2021Document3 pagesCollege of Science Department of Mathematics Course Syllabus: Statistical Methods Spring Semester 2020/2021G. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Data Science For Genomics PDFDocument89 pagesDwnload Full Data Science For Genomics PDFthomas.higgins735100% (25)
- (Download PDF) Micromechanics With Mathematica 1St Edition Nomura Seiichi Ebook Online Full ChapterDocument53 pages(Download PDF) Micromechanics With Mathematica 1St Edition Nomura Seiichi Ebook Online Full Chapteraratzspokes100% (7)
- Apstat - Module 2022 EditionDocument129 pagesApstat - Module 2022 EditionJAEZAR PHILIP GRAGASINNo ratings yet
- 2TOSDocument3 pages2TOSRito MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Math 5Document8 pagesThird Periodical Test in Math 5Fatima RosalNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument268 pages02 WholeMarco BernardesNo ratings yet
- TextbookDocument355 pagesTextbookKaylin LeeNo ratings yet
- G.K. Publications (P) Ltd. - GATE 2022 - Electronics and Communication Engineering - Guide-GK Publications Pvt. Ltd. (2021)Document847 pagesG.K. Publications (P) Ltd. - GATE 2022 - Electronics and Communication Engineering - Guide-GK Publications Pvt. Ltd. (2021)Lakshay Madaan100% (2)
- Fulltext ThesisDocument210 pagesFulltext ThesisSalimNo ratings yet
- QUANTITATIVEDocument252 pagesQUANTITATIVEEdgar RodNo ratings yet
- Statistical Foundations For EconometricDocument413 pagesStatistical Foundations For EconometricAli Cüneyt ÇetinNo ratings yet
- Dacio TOSDocument1 pageDacio TOSMaria Famela DacioNo ratings yet
- Data Science For Genomics 1St Edition Amit Kumar Tyagi Full ChapterDocument51 pagesData Science For Genomics 1St Edition Amit Kumar Tyagi Full Chapterrachele.lewis625100% (5)
- Chatterjee & HadiDocument30 pagesChatterjee & HadiGaurav AtreyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Statistics Through Resampling Methods and Microsoft Office ExcelFrom EverandIntroduction to Statistics Through Resampling Methods and Microsoft Office ExcelNo ratings yet
- Soap and Alcohol WorksDocument5 pagesSoap and Alcohol Worksjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Moddule 4Document11 pagesModdule 4jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Science Behind SoapDocument2 pagesScience Behind Soapjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 7Document5 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 7jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 6.Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 6.jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 5Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Mareviles NatSci Module-2Document4 pagesMareviles NatSci Module-2jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLearning Objectivesjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- NatScie Mod-4Document5 pagesNatScie Mod-4jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Weekly Accomplishment Report (July 25, 2022)Document18 pagesWeekly Accomplishment Report (July 25, 2022)jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Mareviles NatSci Mod-5Document5 pagesMareviles NatSci Mod-5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Mareviles - NatSci - Module 3Document3 pagesMareviles - NatSci - Module 3jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro MF. LessonPlanDocument7 pagesCentro MF. LessonPlanjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Scientific Notation and UnitsDocument49 pagesScientific Notation and Unitsjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty Analysis of Thermocouple MeasurementsDocument82 pagesUncertainty Analysis of Thermocouple MeasurementsgardenergardenerNo ratings yet
- Surveying: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument84 pagesSurveying: Polytechnic University of The Philippinesacurvz2005No ratings yet
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: MeasurementsDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: MeasurementsFaith Asdf100% (3)
- Viscosity of Sulphuric Acid PDFDocument13 pagesViscosity of Sulphuric Acid PDFSanthosh MohanNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- CC140 WSDocument4 pagesCC140 WShudasalhadinNo ratings yet
- ISRO Previous Paper 2007Document11 pagesISRO Previous Paper 2007Kshitija50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Physical Quantity and MeasurementDocument65 pagesChapter 1 - Physical Quantity and MeasurementSyfull musicNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingDocument5 pagesGenphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingRonilo Rivera CaringalNo ratings yet
- Sensor Deviations: Transfer Function AccuracyDocument1 pageSensor Deviations: Transfer Function AccuracyseqNo ratings yet
- Problems and Errors in Measurements by PugazhDocument10 pagesProblems and Errors in Measurements by PugazhFameNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Units of Measurements and Theory of ErrorsDocument16 pagesChapter Two Units of Measurements and Theory of ErrorsAMANUEL WORKUNo ratings yet
- Chapt 6 - Statistic DataDocument82 pagesChapt 6 - Statistic Dataski3013No ratings yet
- Phy 433 Experiment 2Document5 pagesPhy 433 Experiment 2Airin RosliNo ratings yet
- Errors in Measurements: Lesson 3.2Document41 pagesErrors in Measurements: Lesson 3.2Xhanynne CocoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Unit: 9th GradeDocument28 pagesPhysical Quantities and Unit: 9th GradeAlexanderNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest1Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest1Jasmin Soriano100% (1)
- Experiment 1 The Determination of Gravitational AccelerationDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 The Determination of Gravitational AccelerationTorong VNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Errors in LevellingDocument12 pagesTopic 3 Errors in LevellingBdsm JapaneseNo ratings yet
- Y9 Science End of Year Exam Support Sheet 2023Document5 pagesY9 Science End of Year Exam Support Sheet 2023elliemariselamurphyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument MechanicDocument58 pagesMultiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument Mechanicمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- Error Lecture PPT 1Document13 pagesError Lecture PPT 1habteNo ratings yet
- ExperimentosDocument680 pagesExperimentosGerardo Lopez100% (4)
- BS 7334-8-Measuring Instruments For BuildingDocument25 pagesBS 7334-8-Measuring Instruments For BuildinggadNo ratings yet
- Measurement Uncertainty CalculatorDocument4 pagesMeasurement Uncertainty Calculatordhani_isNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1Document11 pagesModule 1 Unit 1Kit LbjNo ratings yet
- 2012 Nyjc PH h1 p2 Promo SolnDocument13 pages2012 Nyjc PH h1 p2 Promo SolnDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- M&I 203 ErrorsDocument46 pagesM&I 203 ErrorsAhmed HusseinNo ratings yet
Differentiate Accuracy From Precision
Differentiate Accuracy From Precision
Uploaded by
jessa marie mareviles0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThis document provides a table of specifications for a general physics exam covering the 1st quarter. It outlines 7 main learning competencies that will be assessed, including solving measurement problems, differentiating error types, and estimating uncertainties. For each competency, it specifies the item format that will be used (e.g. multiple choice, matching), the number of days and items allocated, and how items will be distributed across cognitive domains. It also lists subtopics in physics that will be covered, such as atomic/molecular physics, electricity/magnetism, and optics. In total, the exam will contain 50 multiple choice, matching, identification, and alternative test items assessing student understanding of general 1st quarter physics concepts.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mareviles_REVISED TOS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a table of specifications for a general physics exam covering the 1st quarter. It outlines 7 main learning competencies that will be assessed, including solving measurement problems, differentiating error types, and estimating uncertainties. For each competency, it specifies the item format that will be used (e.g. multiple choice, matching), the number of days and items allocated, and how items will be distributed across cognitive domains. It also lists subtopics in physics that will be covered, such as atomic/molecular physics, electricity/magnetism, and optics. In total, the exam will contain 50 multiple choice, matching, identification, and alternative test items assessing student understanding of general 1st quarter physics concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesDifferentiate Accuracy From Precision
Differentiate Accuracy From Precision
Uploaded by
jessa marie marevilesThis document provides a table of specifications for a general physics exam covering the 1st quarter. It outlines 7 main learning competencies that will be assessed, including solving measurement problems, differentiating error types, and estimating uncertainties. For each competency, it specifies the item format that will be used (e.g. multiple choice, matching), the number of days and items allocated, and how items will be distributed across cognitive domains. It also lists subtopics in physics that will be covered, such as atomic/molecular physics, electricity/magnetism, and optics. In total, the exam will contain 50 multiple choice, matching, identification, and alternative test items assessing student understanding of general 1st quarter physics concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Table of Specifications in General Physicsn1, 1st Quarter
Learning Competencies Item Format No. of No. of Percent
Used Days Items of Item Placement Under Each Cognitive Domain
Items
Rem Und App Ana Eva Cre
1. Solve measurement problems
involving Multiple 3 3 7.5 1,2.3
Choice
conversion of units, expression
of
measurements in scientific
notation
2. Differentiate accuracy from Alternative 2 2 5 26,27
Test
precision
3. Differentiate random errors
from Matching 2 2 5 28,29
Type
systematic errors
4. Use the least count concept
to estimate Alternative 2 2 5 30,31
Test
errors associated with single
measurements
5. Estimate errors from multiple
measurements of a physical Identificatio 3 3 7.5 32,33,3
n 4
quantity
using variance
6. Estimate the uncertainty of a
derived Alternative 3 3 7.5 35,36,3
Test 7
quantity from the estimated
values and
uncertainties of directly
measured
quantities
7. Estimate intercepts and
slopes—and and Matching 3 3 7.5 38,39,4
Type 0
their uncertainties—in
experimental data
with linear dependence using
the
“eyeball method” and/or linear
regression formulae
7.1 Atomic and Molecular Physics Multiple 2 2 5 4,5
Choice
7.2 Electricity and Magnetism Matching 2 2 5 6,7
Type
7.3 Electromagnetic Radiation Identificatio 2 2 5 8,9
n
7.4 Classical Mechanics Multiple 2 2 5 10,11
Choice
7.5 Crystallography Identificatio 2 2 5 12,13
n
7.6 Fluid Mechanics Identificatio 2 2 5 14,15
n
7.7 Lasers Multiple 2 2 5 16,17
Choice
7.8 Low Temperatuire Physics Multiple 2 2 5 18,19
Choice
7.9 Nuclear Physics Identificatio 3 3 7.5 20,21,2
n 2
7.10 Optics Matching 3 3 7.5 23,24,2
Type 5
(40)
Total 40 50 100%
Prepared by :
Jessa Marie A. Mareviles
Student, Educ 107, MWF 6:00-7:00
You might also like
- IB Chemistry IA Eggshell LabDocument8 pagesIB Chemistry IA Eggshell LabNour Makarem0% (3)
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsTutor_KLNo ratings yet
- Calculus Table-of-SpecificationDocument1 pageCalculus Table-of-SpecificationJojie T. DeregayNo ratings yet
- Schedule PDFDocument1 pageSchedule PDFInconnuNo ratings yet
- Michael Creel - EconometricsDocument490 pagesMichael Creel - EconometricsJorge Guerrero NuñezNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus T1 2021 MATH 206 enDocument3 pagesCourse Syllabus T1 2021 MATH 206 enAmal Al-attasNo ratings yet
- MATH 117 Syllabus Fall 2019Document2 pagesMATH 117 Syllabus Fall 2019PerzivalNo ratings yet
- Eco No MetricsDocument312 pagesEco No MetricshalhoshanNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry (2020-1) SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesMATH119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry (2020-1) SYLLABUSMuratcan AkgünNo ratings yet
- EconometricsDocument310 pagesEconometricsHerwan GalinggingNo ratings yet
- Syllabus and Structure of MATH119Document4 pagesSyllabus and Structure of MATH119Fortune OputaNo ratings yet
- Calc 12 Exercise List 2012 13Document2 pagesCalc 12 Exercise List 2012 13Andrew FNo ratings yet
- Handout CHE F242Document6 pagesHandout CHE F242donasex652No ratings yet
- 2nd Six Weeks Calendar PLCDocument2 pages2nd Six Weeks Calendar PLCapi-291820023No ratings yet
- MATH 119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry: Online Online In-Class In-ClassDocument3 pagesMATH 119 Calculus With Analytic Geometry: Online Online In-Class In-ClassHussainNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1Document4 pagesMATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1mehmedjediNo ratings yet
- 769513Document196 pages769513Aman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1 - 2 2023-1Document3 pagesMATH119 Course Syllabus and Policy v1 - 2 2023-1Halil EmreNo ratings yet
- Pattern Classification: Second EditionDocument11 pagesPattern Classification: Second EditionR Gowri PrasadNo ratings yet
- Pattern Classification: Second EditionDocument11 pagesPattern Classification: Second EditionjojoNo ratings yet
- Math119-Course Syllabus and PolicyDocument5 pagesMath119-Course Syllabus and Policy19cerena03No ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS-Q1Document1 pageMathematics 10 TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS-Q1Ailen CeniaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Stat4351.501.07f Taught by Yuly Koshevnik (Yxk055000)Document5 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Stat4351.501.07f Taught by Yuly Koshevnik (Yxk055000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Math550 PDFDocument3 pagesMath550 PDFShelaRamosNo ratings yet
- HTTPS:/WWW Vidyalankar Org/gate/assets/docs/notes/maths PDFDocument354 pagesHTTPS:/WWW Vidyalankar Org/gate/assets/docs/notes/maths PDFIndra N PatelNo ratings yet
- Leigh Sutherland PHD 1997 (Uni of Soton E-Prints)Document301 pagesLeigh Sutherland PHD 1997 (Uni of Soton E-Prints)leighNo ratings yet
- Assignment Math 63 SummerDocument1 pageAssignment Math 63 SummerLi ChNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Course Outline 2020Document3 pagesNumerical Methods Course Outline 2020Abdiqani Mohamed AdanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Math 109 441Document3 pagesSyllabus Math 109 441Salman SaleemNo ratings yet
- Nasser Soltani Study of Mixed Mode Stress Intensity Factor Using The ExperimentaDocument144 pagesNasser Soltani Study of Mixed Mode Stress Intensity Factor Using The ExperimentaIrynaNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Board Batch-2021-22: S.No. Unit - Term-1 No. of Classes 1 11 2 8 3 9 4 9 Unit - Term-2 5 2Document2 pagesClass 12th Board Batch-2021-22: S.No. Unit - Term-1 No. of Classes 1 11 2 8 3 9 4 9 Unit - Term-2 5 2Aditya MithunNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Experimental Methods and Instrumentation For Chemical Engineers PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Experimental Methods and Instrumentation For Chemical Engineers PDFmichael.harryman140100% (26)
- STAT 336-Course Outline - 2023-2024Document4 pagesSTAT 336-Course Outline - 2023-2024Kena JesusNo ratings yet
- SPSS Viskositas WordDocument5 pagesSPSS Viskositas WordIka YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Math002 Syl 232Document2 pagesMath002 Syl 232nabhanbinyaqub05No ratings yet
- TOS-Template RasDocument2 pagesTOS-Template RasRassel Jay GumbocNo ratings yet
- MTH141 Syllabus-CalDocument4 pagesMTH141 Syllabus-CaltucchelNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies:: Parameter Statistic Parameter StatisticDocument5 pagesLearning Competencies:: Parameter Statistic Parameter StatisticSheryn Joy BadiNo ratings yet
- Autput Penelitian: StatisticsDocument3 pagesAutput Penelitian: StatisticsririNo ratings yet
- STA 220 Syllabus Spring 2018-1Document3 pagesSTA 220 Syllabus Spring 2018-1Anass BNo ratings yet
- 2 Quarter Exam-Table of SpecificationDocument1 page2 Quarter Exam-Table of SpecificationBianca Isabel GayanesNo ratings yet
- Math 104: Calculus, Part I. (4h. 1 C.u.)Document2 pagesMath 104: Calculus, Part I. (4h. 1 C.u.)BreyonnaMorganNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Basic College Mathematics An Applied Approach Canadian 1st Edition by Aufmann Lockwood and Milburn ISBN 0176562087 9780176562083Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Basic College Mathematics An Applied Approach Canadian 1st Edition by Aufmann Lockwood and Milburn ISBN 0176562087 9780176562083ernesto.medina346100% (20)
- PROBABILITY & STATISTICS - Final Examination: Dinah Fe T. OlitanDocument5 pagesPROBABILITY & STATISTICS - Final Examination: Dinah Fe T. OlitanDinah Fe Tabaranza-OlitanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Microarray Gene Expression Data - M. Lee (KluwerDocument398 pagesAnalysis of Microarray Gene Expression Data - M. Lee (KluwerciuckyNo ratings yet
- 2022 CHM 171 SyllabusDocument2 pages2022 CHM 171 SyllabusNat GariNo ratings yet
- College of Science Department of Mathematics Course Syllabus: Statistical Methods Spring Semester 2020/2021Document3 pagesCollege of Science Department of Mathematics Course Syllabus: Statistical Methods Spring Semester 2020/2021G. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Data Science For Genomics PDFDocument89 pagesDwnload Full Data Science For Genomics PDFthomas.higgins735100% (25)
- (Download PDF) Micromechanics With Mathematica 1St Edition Nomura Seiichi Ebook Online Full ChapterDocument53 pages(Download PDF) Micromechanics With Mathematica 1St Edition Nomura Seiichi Ebook Online Full Chapteraratzspokes100% (7)
- Apstat - Module 2022 EditionDocument129 pagesApstat - Module 2022 EditionJAEZAR PHILIP GRAGASINNo ratings yet
- 2TOSDocument3 pages2TOSRito MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Math 5Document8 pagesThird Periodical Test in Math 5Fatima RosalNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument268 pages02 WholeMarco BernardesNo ratings yet
- TextbookDocument355 pagesTextbookKaylin LeeNo ratings yet
- G.K. Publications (P) Ltd. - GATE 2022 - Electronics and Communication Engineering - Guide-GK Publications Pvt. Ltd. (2021)Document847 pagesG.K. Publications (P) Ltd. - GATE 2022 - Electronics and Communication Engineering - Guide-GK Publications Pvt. Ltd. (2021)Lakshay Madaan100% (2)
- Fulltext ThesisDocument210 pagesFulltext ThesisSalimNo ratings yet
- QUANTITATIVEDocument252 pagesQUANTITATIVEEdgar RodNo ratings yet
- Statistical Foundations For EconometricDocument413 pagesStatistical Foundations For EconometricAli Cüneyt ÇetinNo ratings yet
- Dacio TOSDocument1 pageDacio TOSMaria Famela DacioNo ratings yet
- Data Science For Genomics 1St Edition Amit Kumar Tyagi Full ChapterDocument51 pagesData Science For Genomics 1St Edition Amit Kumar Tyagi Full Chapterrachele.lewis625100% (5)
- Chatterjee & HadiDocument30 pagesChatterjee & HadiGaurav AtreyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Statistics Through Resampling Methods and Microsoft Office ExcelFrom EverandIntroduction to Statistics Through Resampling Methods and Microsoft Office ExcelNo ratings yet
- Soap and Alcohol WorksDocument5 pagesSoap and Alcohol Worksjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Moddule 4Document11 pagesModdule 4jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Science Behind SoapDocument2 pagesScience Behind Soapjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 7Document5 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 7jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 6.Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 6.jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 5Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Mareviles NatSci Module-2Document4 pagesMareviles NatSci Module-2jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLearning Objectivesjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- NatScie Mod-4Document5 pagesNatScie Mod-4jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Weekly Accomplishment Report (July 25, 2022)Document18 pagesWeekly Accomplishment Report (July 25, 2022)jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Mareviles NatSci Mod-5Document5 pagesMareviles NatSci Mod-5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Mareviles - NatSci - Module 3Document3 pagesMareviles - NatSci - Module 3jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Centro MF. LessonPlanDocument7 pagesCentro MF. LessonPlanjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Scientific Notation and UnitsDocument49 pagesScientific Notation and Unitsjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty Analysis of Thermocouple MeasurementsDocument82 pagesUncertainty Analysis of Thermocouple MeasurementsgardenergardenerNo ratings yet
- Surveying: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument84 pagesSurveying: Polytechnic University of The Philippinesacurvz2005No ratings yet
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: MeasurementsDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: MeasurementsFaith Asdf100% (3)
- Viscosity of Sulphuric Acid PDFDocument13 pagesViscosity of Sulphuric Acid PDFSanthosh MohanNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- CC140 WSDocument4 pagesCC140 WShudasalhadinNo ratings yet
- ISRO Previous Paper 2007Document11 pagesISRO Previous Paper 2007Kshitija50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Physical Quantity and MeasurementDocument65 pagesChapter 1 - Physical Quantity and MeasurementSyfull musicNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingDocument5 pagesGenphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingRonilo Rivera CaringalNo ratings yet
- Sensor Deviations: Transfer Function AccuracyDocument1 pageSensor Deviations: Transfer Function AccuracyseqNo ratings yet
- Problems and Errors in Measurements by PugazhDocument10 pagesProblems and Errors in Measurements by PugazhFameNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Units of Measurements and Theory of ErrorsDocument16 pagesChapter Two Units of Measurements and Theory of ErrorsAMANUEL WORKUNo ratings yet
- Chapt 6 - Statistic DataDocument82 pagesChapt 6 - Statistic Dataski3013No ratings yet
- Phy 433 Experiment 2Document5 pagesPhy 433 Experiment 2Airin RosliNo ratings yet
- Errors in Measurements: Lesson 3.2Document41 pagesErrors in Measurements: Lesson 3.2Xhanynne CocoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Unit: 9th GradeDocument28 pagesPhysical Quantities and Unit: 9th GradeAlexanderNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest1Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest1Jasmin Soriano100% (1)
- Experiment 1 The Determination of Gravitational AccelerationDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 The Determination of Gravitational AccelerationTorong VNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Errors in LevellingDocument12 pagesTopic 3 Errors in LevellingBdsm JapaneseNo ratings yet
- Y9 Science End of Year Exam Support Sheet 2023Document5 pagesY9 Science End of Year Exam Support Sheet 2023elliemariselamurphyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument MechanicDocument58 pagesMultiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument Mechanicمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- Error Lecture PPT 1Document13 pagesError Lecture PPT 1habteNo ratings yet
- ExperimentosDocument680 pagesExperimentosGerardo Lopez100% (4)
- BS 7334-8-Measuring Instruments For BuildingDocument25 pagesBS 7334-8-Measuring Instruments For BuildinggadNo ratings yet
- Measurement Uncertainty CalculatorDocument4 pagesMeasurement Uncertainty Calculatordhani_isNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1Document11 pagesModule 1 Unit 1Kit LbjNo ratings yet
- 2012 Nyjc PH h1 p2 Promo SolnDocument13 pages2012 Nyjc PH h1 p2 Promo SolnDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- M&I 203 ErrorsDocument46 pagesM&I 203 ErrorsAhmed HusseinNo ratings yet