Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P & ID - Wikipedia
P & ID - Wikipedia
Uploaded by
Dineshkumar SOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P & ID - Wikipedia
P & ID - Wikipedia
Uploaded by
Dineshkumar SCopyright:
Available Formats
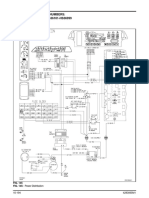
Piping and instrumentation diagram
A piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) is a detailed diagram in the process industry which
shows the piping and process equipment together with the instrumentation and control devices.
Superordinate to the P&ID is the process flow diagram (PFD) which indicates the more general flow of plant
processes and the relationship between major equipment of a plant facility.
Contents
Contents and function
Identification and reference designation
Symbols of chemical apparatus and equipment
See also
External links
Contents and function
A piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) is defined as follows:
1. A diagram which shows the interconnection of process equipment and
the instrumentation used to control the process. In the process
industry, a standard set of symbols is used to prepare drawings of
processes. The instrument symbols used in these drawings are
generally based on International Society of Automation (ISA) Standard
S5.1
2. The primary schematic drawing used for laying out a process control
installation. Example of a single industrial
control loop; showing continuously
They usually contain the following information: modulated control of process flow.
Mechanical equipment, including:
Pressure vessels, columns, tanks, pumps, compressors, heat
exchangers, furnaces, wellheads, fans, cooling towers, turbo-
expanders, pig traps (see 'symbols' below)
Bursting discs, restriction orifices, strainers and filters, steam traps,
moisture traps, sight-glasses, silencers, flares and vents, flame
arrestors, vortex breakers, eductors
Process piping, sizes and identification, including:
Pipe classes and piping line numbers Piping and instrumentation diagram
Flow directions of pump with storage tank. Symbols
according to EN ISO 10628 and EN
Interconnections references
62424.
Permanent start-up, flush and bypass lines
Pipelines and flowlines
Blinds and spectacle blinds
Insulation and heat tracing
Process control instrumentation and designation (names, numbers, unique tag identifiers), including:
Valves and their types and identifications (e.g. isolation, shutoff, relief and safety valves, valve
interlocks)
Control inputs and outputs (sensors and final elements, interlocks)
Miscellaneous - vents, drains, flanges, special fittings,
sampling lines, reducers and swages
Interfaces for class changes
Computer control system
Identification of components and subsystems delivered by
others
P&IDs are originally drawn up at the design stage from a
combination of process flow sheet data, the mechanical process
equipment design, and the instrumentation engineering design.
During the design stage, the diagram also provides the basis for
the development of system control schemes, allowing for
further safety and operational investigations, such as a Hazard A more complex example of a P&ID.
and operability study (HAZOP). To do this, it is critical to
demonstrate the physical sequence of equipment and systems,
as well as how these systems connect.
P&IDs also play a significant role in the maintenance and modification of the process after initial build.
Modifications are red-penned onto the diagrams and are vital records of the current plant design.
They are also vital in enabling development of;
Control and shutdown schemes
Safety and regulatory requirements
Start-up sequences
Operational understanding.
P&IDs form the basis for the live mimic diagrams displayed on graphical user interfaces of large industrial
control systems such as SCADA and distributed control systems.
Identification and reference designation
Based on STANDARD ANSI/ISA S5.1 and ISO 14617-6, the P&ID is used for the identification of
measurements within the process. The identifications consist of up to 5 letters. The first identification letter is
for the measured value, the second is a modifier, 3rd indicates passive/readout function, 4th - active/output
function, and the 5th is the function modifier. This is followed by loop number, which is unique to that loop.
For instance FIC045 means it is the Flow Indicating Controller in control loop 045. This is also known as the
"tag" identifier of the field device, which is normally given to the location and function of the instrument. The
same loop may have FT045 - which is the flow transmitter in the same loop.
Column 3 Column 5
Column 1 (Measured Column 4 (Output/active
Letter Column 2 (Modifier) (Readout/passive (Function
value) function)
function) modifier)
A Analysis Alarm
B Burner, combustion User choice User choice User choice
User's choice (usually
C Control Close
conductivity)
User's choice (usually
D Difference Deviation
density)
E Voltage Sensor
F Flow rate Ratio
User's choice (usually
G Gas Glass/gauge/viewing
gaging/gauging)
H Hand High
I Current Indicate
J Power Scan
K Time, time schedule Time rate of change Control station
L Level Light Low
Middle /
M User's choice
intermediate
User's choice (usually
N User choice User choice User choice
torque)
O User's choice Orifice Open
P Pressure Point/test connection
Q Quantity Totalize/integrate Totalize/integrate
R Radiation Record Run
Safety (Non SIS
S Speed, frequency Switch Stop
(S5.1))
T Temperature Transmit
U Multivariable Multifunction Multifunction
Vibration, mechanical
V Valve or damper
analysis
W Weight, force Well or probe
User's choice (usually Accessory devices,
X X-axis Unclassified Unclassified
on-off valve as XV) unclassified
Y Event, state, presence Y-axis Auxiliary devices
Z-axis or Safety Actuator, driver or
Z Position, dimension Instrumented unclassified final control
System element
For reference designation of any equipment in industrial systems the standard IEC 61346 (Industrial systems,
installations and equipment and industrial products — Structuring principles and reference designations)
can be applied. For the function Measurement the reference designator B is used, followed by the above listed
letter for the measured variable.
For reference designation of any equipment in a power station the KKS Power Plant Classification System can
be applied.
Symbols of chemical apparatus and equipment
Below are listed some symbols of chemical apparatus and equipment normally used in a P&ID, according to
ISO 10628 and ISO 14617.
Symbols of chemical apparatus and equipment
Thermally Jacketed Cooled or
Pipe
insulated pipe pipe heated pipe
Vacuum
Flexible Hydraulic
Pump pump or
connection pump
compressor
Fan Axial fan, MK, Radial fan Dryer
Jacketed
Pressurized Pressurized
mixing Half pipe
horizontal vertical
vessel mixing vessel
vessel vessel
(autoclave)
Packed
Plate column Furnace Cooling tower
column
Plate & frame
Heat Coil heat
Cooler heat
exchanger exchanger
exchanger
Double Fixed straight U shaped
Spiral heat
pipe heat tubes heat tubes heat
exchanger
exchanger exchanger exchanger
Covered Curved gas Funnel or
(Air) filter
gas vent vent tundish
Pressure
Steam trap Viewing glass reducing Valve
valve
Manual
Gate valve Control valve Check valve
valve
Needle Diaphragm
Butterfly valve Ball valve
valve valve
Check Back draft Bag Gas bottle
valve damper
Globe
Pinch valve Plug valve Relief valve
valve
Rupture Centrifugal Reciprocating
Turboexpander
disc pump pump
See also
Instrumentation in petrochemical industries
External links
Commons:Category:Chemical engineering symbols - A list of P&ID symbols in SVG format
Learn How to Read P&ID Drawings – A Complete Guide (https://hardhatengineer.com/how-to-read-pid-pef
s-drawings/)
Interpreting Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams-Symbology (https://www.aiche.org/chenected/2010/09/int
erpreting-piping-and-instrumentation-diagrams-symbology/)
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Piping_and_instrumentation_diagram&oldid=1055512254"
This page was last edited on 16 November 2021, at 08:25 (UTC).
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License;
additional terms may apply. By using this site, you
agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit
organization.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Eletrica MF 9690 E 9790Document43 pagesEletrica MF 9690 E 9790PABLO DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- Komatsu AcronymsDocument9 pagesKomatsu AcronymsEbrahim Sabouri100% (6)
- Penstock - WikipediaDocument2 pagesPenstock - WikipediaDineshkumar SNo ratings yet
- Gate DesignDocument2 pagesGate DesignDineshkumar SNo ratings yet
- WeldDocument4 pagesWeldDineshkumar SNo ratings yet
- How To Classify Oil TanksDocument4 pagesHow To Classify Oil TanksDineshkumar SNo ratings yet
- Actuator PDFDocument34 pagesActuator PDFEnar PauNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment No.1 ObjectivealiNo ratings yet
- Clarke-Providing Adequate Raw Water Supply To The Heat Exchanger Cooled Fire Pump EnginesDocument4 pagesClarke-Providing Adequate Raw Water Supply To The Heat Exchanger Cooled Fire Pump EnginesAnonymous CMS3dL1TNo ratings yet
- IMI Remosa ValvesDocument4 pagesIMI Remosa ValvesDhananjay B KNo ratings yet
- Psv-Screwed Type PDFDocument3 pagesPsv-Screwed Type PDFStanley PeterNo ratings yet
- Ccr100 Manual UsuarioDocument224 pagesCcr100 Manual UsuarioAndres RiveraNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Trueline VostokDocument15 pagesPowerpoint Trueline Vostokdocumentation5070No ratings yet
- Shutdown ValvesDocument2 pagesShutdown Valvesnazury2kNo ratings yet
- Actuation Price List: ACPL9000Document20 pagesActuation Price List: ACPL9000ShrikantNo ratings yet
- Rexroth 4WEH 4WH 10-32 Directional Valves RE24751Document40 pagesRexroth 4WEH 4WH 10-32 Directional Valves RE24751abilrajprNo ratings yet
- Lenkungskomponenten GB PDFDocument37 pagesLenkungskomponenten GB PDFFastcross HondaNo ratings yet
- Pentair Sand Filters PDFDocument42 pagesPentair Sand Filters PDFVISHALNo ratings yet
- P25 Bolted Plastic Pump: Engineering Operation MaintenanceDocument24 pagesP25 Bolted Plastic Pump: Engineering Operation MaintenanceAlvaro Muñoz BNo ratings yet
- Symphony 150 S (Ay15w6-T) My 2012 Motore-20120706-165718Document16 pagesSymphony 150 S (Ay15w6-T) My 2012 Motore-20120706-165718james1090100% (1)
- Telehandlers For: Agricultural and Construction ApplicationsDocument7 pagesTelehandlers For: Agricultural and Construction ApplicationsPankaj GargNo ratings yet
- Pressure Reducing Valve Watts Pr500Document4 pagesPressure Reducing Valve Watts Pr500Didik ListiawanNo ratings yet
- RMT DP Flow 3-Troubleshooting - Annubar - 485Document13 pagesRMT DP Flow 3-Troubleshooting - Annubar - 485Angel AvilaNo ratings yet
- Grader Case 800 Series B Vnafta PDFDocument20 pagesGrader Case 800 Series B Vnafta PDFtom souzaNo ratings yet
- Ansi Fci 70 2 2006Document11 pagesAnsi Fci 70 2 2006Jusebar ArisNo ratings yet
- Ambit ManiforlDocument6 pagesAmbit Maniforlmd_taheriNo ratings yet
- CV CalculationDocument23 pagesCV Calculationshivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- C200 - Engine GeneralDocument16 pagesC200 - Engine GeneralKada Ben youcefNo ratings yet
- ssII - Panel Muestreo Automatico para Vapor Liquidos - Sentry EquipmentDocument2 pagesssII - Panel Muestreo Automatico para Vapor Liquidos - Sentry EquipmentAlejandro VescovoNo ratings yet
- ASMA A330 PW RR Fleet PDFDocument2 pagesASMA A330 PW RR Fleet PDFManish ShAhNo ratings yet
- FMDS0307Document45 pagesFMDS0307Story LoveNo ratings yet
- Produts and List Prices 2004Document16 pagesProduts and List Prices 2004jonNo ratings yet
- SAIC-A-2009 Rev 2Document5 pagesSAIC-A-2009 Rev 2ரமேஷ் பாலக்காடுNo ratings yet
- Lift Axle Control Module: Technical Data MaterialDocument4 pagesLift Axle Control Module: Technical Data MaterialEric Grunst100% (1)