Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anticoagulant Drugs (HEPARIN)
Anticoagulant Drugs (HEPARIN)
Uploaded by
KyrrielJimenoCeladaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Vitamin K (Phytonadione)Document1 pageVitamin K (Phytonadione)E75% (4)
- Drugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - KatzungDocument3 pagesDrugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - Katzungsarguss14100% (6)
- InstallationDirective C13 IvecoDocument60 pagesInstallationDirective C13 Ivecoblaktion0% (1)
- Pharmacology Hematologic SystemDocument19 pagesPharmacology Hematologic SystemCurtney PedriaNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument4 pagesDrug NameDothy MaboloNo ratings yet
- Medcard Warfarin (Coumadin)Document3 pagesMedcard Warfarin (Coumadin)Tricia SicbaldiNo ratings yet
- Anti CoagulantsDocument25 pagesAnti Coagulantsshoaib106muhammadNo ratings yet
- Blood Pharmacology by Dr. Mayur Sayta M 910444Document21 pagesBlood Pharmacology by Dr. Mayur Sayta M 910444funzz100% (1)
- Anticoagulants May BeDocument5 pagesAnticoagulants May BeAmmar magdyNo ratings yet
- Coagulants and AnticoagulantsDocument29 pagesCoagulants and AnticoagulantsfdamissieNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Blood CoagulationDocument51 pagesDrugs Affecting Blood CoagulationMoxie Macado100% (1)
- Drugs Used in Disorders of CoagulationDocument61 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of CoagulationDUEÑAS, MARIELNo ratings yet
- Drug IneractionDocument25 pagesDrug IneractionarunNo ratings yet
- L8 Anti Coagulant DrugsDocument10 pagesL8 Anti Coagulant DrugsamanabduwahabNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Anti Coagulatants: Presented By:-Mr - Gorishankar Nursing Tutor (Tantia University)Document10 pagesAnti Coagulatants: Presented By:-Mr - Gorishankar Nursing Tutor (Tantia University)yogesh kumarNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantsKeerthana KNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat VaskularDocument23 pagesAntiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat Vaskularmonyet65No ratings yet
- Coagulation Related DrugsDocument20 pagesCoagulation Related DrugsshehranNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Hematologic DrugsDocument51 pagesPharmacology - Hematologic DrugsBenjamin Joel Breboneria100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Drugs Chart NursingDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Drugs Chart NursingSraddha PatelNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Affect in Blood Coagulation: Prajogo WibowoDocument44 pagesDrugs Used To Affect in Blood Coagulation: Prajogo WibowoIda Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Null 57Document159 pagesNull 578gxrxks6sqNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant TherapyDocument41 pagesAnticoagulant Therapyryan yovanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 LiyanaDocument36 pagesPertemuan 7 LiyanaLiyana SafitriNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Rosalinda FerrerDocument6 pagesDRUG STUDY - Rosalinda Ferrer40-GALOLO ANDREA PAULINENo ratings yet
- Cardiac DrugsDocument4 pagesCardiac DrugsIbrahem Al100% (2)
- Drug Study - Vitamin KDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Vitamin KJustin Ancog100% (1)
- AnticogulantDocument3 pagesAnticogulantWan TokNo ratings yet
- 9 - Anticoagulant Drugs (Final)Document17 pages9 - Anticoagulant Drugs (Final)wllmaanka4No ratings yet
- Anticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet DrugsDocument63 pagesAnticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet Drugsruchipickle100% (1)
- Drug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Kate PedzNo ratings yet
- PhytomenadioneDocument3 pagesPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- Drug Study-Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Tranexamic Acidecasantos595No ratings yet
- Drugs For Coagulation Disorders: Coagulant DrugDocument6 pagesDrugs For Coagulation Disorders: Coagulant DrugApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Paytonctrujillo - Er Drugs Nursing PharmacologyDocument9 pagesPaytonctrujillo - Er Drugs Nursing PharmacologyTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Nclex Pharm ReviewDocument10 pagesNclex Pharm ReviewRuiqi YangNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Disorders of CougulationDocument8 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of CougulationAnonymous qatL0V6p2No ratings yet
- Anticoagulant PresentationDocument29 pagesAnticoagulant Presentationrozha100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY Week 4Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 4Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants ParamedDocument20 pagesAnticoagulants ParamedManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- Anti CoagulantsDocument37 pagesAnti CoagulantsMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- 50 Emergency DrugsDocument70 pages50 Emergency DrugsderizNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Group 7Document33 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Group 7Jann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- CardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)Document1 pageCardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Patient: Mrs. T. P. Diagnosis: Perineal Relaxation, Uterine Prolapse, With RectoceleDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Name of Patient: Mrs. T. P. Diagnosis: Perineal Relaxation, Uterine Prolapse, With RectoceleKristina Garces HuertasNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument4 pagesHeparinTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Document WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesDocument WPS OfficeWenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Route Warfarin Coumadin AnticoagulantsDocument1 pageGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Route Warfarin Coumadin AnticoagulantsChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- Euro Pharma FurosemideDocument2 pagesEuro Pharma Furosemideashleiy17No ratings yet
- Emrgency Drugs: Submitted By: Fernandez, Ana Maria Francesca M. RLE Group B7Document35 pagesEmrgency Drugs: Submitted By: Fernandez, Ana Maria Francesca M. RLE Group B7chin41686No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Interactions TableDocument2 pagesInteractions TableKulfi BarfiNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 pageAnticoagulants Drug TableNicole HoNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On: HeparinDocument8 pagesA Drug Study On: HeparinRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- AntiarrhythmiaDocument29 pagesAntiarrhythmiaDRx Raju ChandranNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument20 pagesReviewerKC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Pain Medication (SALICYLATES ASPIRIN)Document2 pagesPain Medication (SALICYLATES ASPIRIN)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Pain Medication (NON SELECTIVES NSAID)Document1 pagePain Medication (NON SELECTIVES NSAID)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs (DECONGESTANTS)Document1 pageRespiratory Drugs (DECONGESTANTS)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Cardiacvascular Drugs (Antiarrhythmic Drugs Nitrates Nitroglycerin)Document1 pageCardiacvascular Drugs (Antiarrhythmic Drugs Nitrates Nitroglycerin)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- CardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)Document1 pageCardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Abella, Cadotdot, Celada, Dominguez, Ellacer, OmarDocument32 pagesEpistaxis: Abella, Cadotdot, Celada, Dominguez, Ellacer, OmarKyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Akinlo and Asaolo, 2012 PDFDocument9 pagesAkinlo and Asaolo, 2012 PDFJason KurniawanNo ratings yet
- FEG Token Litepaper v2.1Document15 pagesFEG Token Litepaper v2.1TelorNo ratings yet
- Allemande (Allemand, Almain, Alman, Almond) : 1. 16th-Century AllemandesDocument5 pagesAllemande (Allemand, Almain, Alman, Almond) : 1. 16th-Century AllemandesAndrés OrtizNo ratings yet
- CPESC Scope of PracticeDocument3 pagesCPESC Scope of Practicealphapinnacle techNo ratings yet
- People vs. PradesDocument2 pagesPeople vs. PradesMayr TeruelNo ratings yet
- Ds 457Document24 pagesDs 457Angel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Health Talk ExcerciseDocument5 pagesHealth Talk ExcerciseNyalen Hakom100% (1)
- METRIX AUTOCOMP - Company ProfileDocument2 pagesMETRIX AUTOCOMP - Company ProfileVaibhav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: ProjectDocument4 pagesTotal Quality Management: Projectfaaiz yousufNo ratings yet
- Submarine Cable Installation ContractorsDocument19 pagesSubmarine Cable Installation Contractorswiji_thukulNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureHesti hasanNo ratings yet
- Medications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationDocument1 pageMedications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationrubymayNo ratings yet
- Phantom Turbo 6000Document22 pagesPhantom Turbo 6000Manos LoukianosNo ratings yet
- Importing Google Earth Data Into A GISDocument15 pagesImporting Google Earth Data Into A GISJONAMNo ratings yet
- 3rdquarter Week7 Landslide and SinkholeDocument4 pages3rdquarter Week7 Landslide and SinkholeNayeon IeeNo ratings yet
- Disaster Mana BooksDocument20 pagesDisaster Mana BooksSupraja_Prabha_8353No ratings yet
- Requirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Document17 pagesRequirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Chandrashekhar KuriNo ratings yet
- The Sophia Sun: in This Issue..Document32 pagesThe Sophia Sun: in This Issue..Gi3iBq7uAANo ratings yet
- GCC - Lesson Plan 2020Document35 pagesGCC - Lesson Plan 2020henaNo ratings yet
- Technical InstructionsDocument6 pagesTechnical InstructionsSadinjana LakshanNo ratings yet
- Green Hills Engineering CollegeDocument18 pagesGreen Hills Engineering CollegeNoor BanoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Strain in RocksDocument2 pagesMeasuring Strain in Rocksdarebusi1No ratings yet
- Damper Valve - Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageDamper Valve - Technical Data SheetPinakin PatelNo ratings yet
- Taylor's Scientific ManagementDocument7 pagesTaylor's Scientific Managementsipanjegiven0% (1)
- What To Expect After Getting The Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 VaccineDocument2 pagesWhat To Expect After Getting The Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 Vaccineoz fmc3No ratings yet
- Faccenter Recording GradesDocument9 pagesFaccenter Recording GradessubcribedNo ratings yet
- Calculus III and IV - SodinDocument164 pagesCalculus III and IV - Sodintom-manor-1138No ratings yet
- Japanese TrifectaDocument9 pagesJapanese TrifectaJustin Lloyd FloroNo ratings yet
- People Vs OandasanDocument2 pagesPeople Vs OandasanAdoha Lei T Blanco100% (1)
Anticoagulant Drugs (HEPARIN)
Anticoagulant Drugs (HEPARIN)
Uploaded by
KyrrielJimenoCeladaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anticoagulant Drugs (HEPARIN)
Anticoagulant Drugs (HEPARIN)
Uploaded by
KyrrielJimenoCeladaCopyright:
Available Formats
ANTICOAGULANT DRUGS: PHARMACOLOGY
HEPARIN
November 02, 2020
Transcribers: Celada, Kyrriel J.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
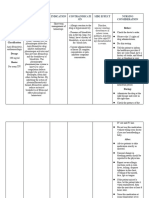
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTICS ADVERSE REACTIONS
⎯ Heparin: Venous thromboembolism, ⎯ Bleeding
Disseminated intravascular coagulation and ⎯ Bruising
Acute myocardial infarction ⎯ Hematoma formation
⎯ Warfarin: thromboembolism ⎯ Necrosis of the skin
⎯ Antiplatelet: Several indications ⎯ Thrombocytopenia
PHARMACOKINETIC IMPLEMENTATION
⎯ Heparin: Continuous IV infusion ⎯ Carefully and regularly monitor PTT.
⎯ Warfarin: Oral anticoagulants Anticoagulation is present when PTT values
⎯ Antiplatelet: Oral- 1-2 hours and IV – 15-20 are 11 /2 to 2 times the control values.
minutes ⎯ Don’t administer heparin IM; avoid IM
injections of any anticoagulant, if possible.
⎯ Keep protamine sulfate available to treat
PHARMACODYNAMICS severe bleeding caused by the drug.
⎯ Notify the prescriber about serious or
⎯ Heparin: Inhibits the formation of thrombin
persistent adverse reactions.
and fibrin by activating antithrombin III
⎯ Maintain bleeding precautions throughout
⎯ Warfarin: Alters the ability of the liver to
therapy.
synthesize vitamin and K–dependent
⎯ Administer IV solutions using an infusion
clotting factors
pump, as appropriate.
⎯ Antiplatelet: Aspirin inhibits clot formation
⎯ Avoid excessive IM injection of other drugs,
by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandin
to minimize the risk of hematoma.
and Clopidogrel inhibits platelet aggregation
by inhibiting platelet fibrinogen binding
DRUG INTERACTIONS
⎯ Oral anticoagulants
⎯ NSAIDs Iron dextran
⎯ Antihistamines
⎯ Digoxin
⎯ Nicotine
⎯ Nitroglycerin
⎯ Protamine sulfate
Page 1|1
You might also like
- Vitamin K (Phytonadione)Document1 pageVitamin K (Phytonadione)E75% (4)
- Drugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - KatzungDocument3 pagesDrugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - Katzungsarguss14100% (6)
- InstallationDirective C13 IvecoDocument60 pagesInstallationDirective C13 Ivecoblaktion0% (1)
- Pharmacology Hematologic SystemDocument19 pagesPharmacology Hematologic SystemCurtney PedriaNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument4 pagesDrug NameDothy MaboloNo ratings yet
- Medcard Warfarin (Coumadin)Document3 pagesMedcard Warfarin (Coumadin)Tricia SicbaldiNo ratings yet
- Anti CoagulantsDocument25 pagesAnti Coagulantsshoaib106muhammadNo ratings yet
- Blood Pharmacology by Dr. Mayur Sayta M 910444Document21 pagesBlood Pharmacology by Dr. Mayur Sayta M 910444funzz100% (1)
- Anticoagulants May BeDocument5 pagesAnticoagulants May BeAmmar magdyNo ratings yet
- Coagulants and AnticoagulantsDocument29 pagesCoagulants and AnticoagulantsfdamissieNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Blood CoagulationDocument51 pagesDrugs Affecting Blood CoagulationMoxie Macado100% (1)
- Drugs Used in Disorders of CoagulationDocument61 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of CoagulationDUEÑAS, MARIELNo ratings yet
- Drug IneractionDocument25 pagesDrug IneractionarunNo ratings yet
- L8 Anti Coagulant DrugsDocument10 pagesL8 Anti Coagulant DrugsamanabduwahabNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Anti Coagulatants: Presented By:-Mr - Gorishankar Nursing Tutor (Tantia University)Document10 pagesAnti Coagulatants: Presented By:-Mr - Gorishankar Nursing Tutor (Tantia University)yogesh kumarNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantsKeerthana KNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat VaskularDocument23 pagesAntiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat Vaskularmonyet65No ratings yet
- Coagulation Related DrugsDocument20 pagesCoagulation Related DrugsshehranNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Hematologic DrugsDocument51 pagesPharmacology - Hematologic DrugsBenjamin Joel Breboneria100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Drugs Chart NursingDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Drugs Chart NursingSraddha PatelNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Affect in Blood Coagulation: Prajogo WibowoDocument44 pagesDrugs Used To Affect in Blood Coagulation: Prajogo WibowoIda Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Null 57Document159 pagesNull 578gxrxks6sqNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant TherapyDocument41 pagesAnticoagulant Therapyryan yovanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 LiyanaDocument36 pagesPertemuan 7 LiyanaLiyana SafitriNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Rosalinda FerrerDocument6 pagesDRUG STUDY - Rosalinda Ferrer40-GALOLO ANDREA PAULINENo ratings yet
- Cardiac DrugsDocument4 pagesCardiac DrugsIbrahem Al100% (2)
- Drug Study - Vitamin KDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Vitamin KJustin Ancog100% (1)
- AnticogulantDocument3 pagesAnticogulantWan TokNo ratings yet
- 9 - Anticoagulant Drugs (Final)Document17 pages9 - Anticoagulant Drugs (Final)wllmaanka4No ratings yet
- Anticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet DrugsDocument63 pagesAnticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet Drugsruchipickle100% (1)
- Drug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Kate PedzNo ratings yet
- PhytomenadioneDocument3 pagesPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- Drug Study-Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Tranexamic Acidecasantos595No ratings yet
- Drugs For Coagulation Disorders: Coagulant DrugDocument6 pagesDrugs For Coagulation Disorders: Coagulant DrugApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Paytonctrujillo - Er Drugs Nursing PharmacologyDocument9 pagesPaytonctrujillo - Er Drugs Nursing PharmacologyTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Nclex Pharm ReviewDocument10 pagesNclex Pharm ReviewRuiqi YangNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Disorders of CougulationDocument8 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of CougulationAnonymous qatL0V6p2No ratings yet
- Anticoagulant PresentationDocument29 pagesAnticoagulant Presentationrozha100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY Week 4Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 4Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants ParamedDocument20 pagesAnticoagulants ParamedManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- Anti CoagulantsDocument37 pagesAnti CoagulantsMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- 50 Emergency DrugsDocument70 pages50 Emergency DrugsderizNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Group 7Document33 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Group 7Jann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- CardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)Document1 pageCardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Patient: Mrs. T. P. Diagnosis: Perineal Relaxation, Uterine Prolapse, With RectoceleDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Name of Patient: Mrs. T. P. Diagnosis: Perineal Relaxation, Uterine Prolapse, With RectoceleKristina Garces HuertasNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument4 pagesHeparinTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Document WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesDocument WPS OfficeWenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Route Warfarin Coumadin AnticoagulantsDocument1 pageGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Route Warfarin Coumadin AnticoagulantsChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- Euro Pharma FurosemideDocument2 pagesEuro Pharma Furosemideashleiy17No ratings yet
- Emrgency Drugs: Submitted By: Fernandez, Ana Maria Francesca M. RLE Group B7Document35 pagesEmrgency Drugs: Submitted By: Fernandez, Ana Maria Francesca M. RLE Group B7chin41686No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Interactions TableDocument2 pagesInteractions TableKulfi BarfiNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 pageAnticoagulants Drug TableNicole HoNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On: HeparinDocument8 pagesA Drug Study On: HeparinRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- AntiarrhythmiaDocument29 pagesAntiarrhythmiaDRx Raju ChandranNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument20 pagesReviewerKC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Pain Medication (SALICYLATES ASPIRIN)Document2 pagesPain Medication (SALICYLATES ASPIRIN)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Pain Medication (NON SELECTIVES NSAID)Document1 pagePain Medication (NON SELECTIVES NSAID)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs (DECONGESTANTS)Document1 pageRespiratory Drugs (DECONGESTANTS)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Cardiacvascular Drugs (Antiarrhythmic Drugs Nitrates Nitroglycerin)Document1 pageCardiacvascular Drugs (Antiarrhythmic Drugs Nitrates Nitroglycerin)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- CardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)Document1 pageCardiacVascular Drugs (ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CLASS IV CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS)KyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Abella, Cadotdot, Celada, Dominguez, Ellacer, OmarDocument32 pagesEpistaxis: Abella, Cadotdot, Celada, Dominguez, Ellacer, OmarKyrrielJimenoCeladaNo ratings yet
- Akinlo and Asaolo, 2012 PDFDocument9 pagesAkinlo and Asaolo, 2012 PDFJason KurniawanNo ratings yet
- FEG Token Litepaper v2.1Document15 pagesFEG Token Litepaper v2.1TelorNo ratings yet
- Allemande (Allemand, Almain, Alman, Almond) : 1. 16th-Century AllemandesDocument5 pagesAllemande (Allemand, Almain, Alman, Almond) : 1. 16th-Century AllemandesAndrés OrtizNo ratings yet
- CPESC Scope of PracticeDocument3 pagesCPESC Scope of Practicealphapinnacle techNo ratings yet
- People vs. PradesDocument2 pagesPeople vs. PradesMayr TeruelNo ratings yet
- Ds 457Document24 pagesDs 457Angel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Health Talk ExcerciseDocument5 pagesHealth Talk ExcerciseNyalen Hakom100% (1)
- METRIX AUTOCOMP - Company ProfileDocument2 pagesMETRIX AUTOCOMP - Company ProfileVaibhav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: ProjectDocument4 pagesTotal Quality Management: Projectfaaiz yousufNo ratings yet
- Submarine Cable Installation ContractorsDocument19 pagesSubmarine Cable Installation Contractorswiji_thukulNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureHesti hasanNo ratings yet
- Medications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationDocument1 pageMedications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationrubymayNo ratings yet
- Phantom Turbo 6000Document22 pagesPhantom Turbo 6000Manos LoukianosNo ratings yet
- Importing Google Earth Data Into A GISDocument15 pagesImporting Google Earth Data Into A GISJONAMNo ratings yet
- 3rdquarter Week7 Landslide and SinkholeDocument4 pages3rdquarter Week7 Landslide and SinkholeNayeon IeeNo ratings yet
- Disaster Mana BooksDocument20 pagesDisaster Mana BooksSupraja_Prabha_8353No ratings yet
- Requirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Document17 pagesRequirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Chandrashekhar KuriNo ratings yet
- The Sophia Sun: in This Issue..Document32 pagesThe Sophia Sun: in This Issue..Gi3iBq7uAANo ratings yet
- GCC - Lesson Plan 2020Document35 pagesGCC - Lesson Plan 2020henaNo ratings yet
- Technical InstructionsDocument6 pagesTechnical InstructionsSadinjana LakshanNo ratings yet
- Green Hills Engineering CollegeDocument18 pagesGreen Hills Engineering CollegeNoor BanoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Strain in RocksDocument2 pagesMeasuring Strain in Rocksdarebusi1No ratings yet
- Damper Valve - Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageDamper Valve - Technical Data SheetPinakin PatelNo ratings yet
- Taylor's Scientific ManagementDocument7 pagesTaylor's Scientific Managementsipanjegiven0% (1)
- What To Expect After Getting The Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 VaccineDocument2 pagesWhat To Expect After Getting The Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 Vaccineoz fmc3No ratings yet
- Faccenter Recording GradesDocument9 pagesFaccenter Recording GradessubcribedNo ratings yet
- Calculus III and IV - SodinDocument164 pagesCalculus III and IV - Sodintom-manor-1138No ratings yet
- Japanese TrifectaDocument9 pagesJapanese TrifectaJustin Lloyd FloroNo ratings yet
- People Vs OandasanDocument2 pagesPeople Vs OandasanAdoha Lei T Blanco100% (1)