Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsChapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
target iit2019The document defines key concepts related to databases including data, information, databases, database systems, and their components. It discusses how databases are organized and structured. It also provides examples of common database applications and defines the main components of a database system as data, hardware, software, and users.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Steps To Create and Deploy Our YOLO Model On AWS SagemakerDocument3 pagesSteps To Create and Deploy Our YOLO Model On AWS SagemakerAnupam PoddarNo ratings yet
- Key Technical Topics in A System Conversion To SAP S4HANADocument23 pagesKey Technical Topics in A System Conversion To SAP S4HANARafael RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Open Source SoftwareDocument11 pagesOpen Source SoftwareMohammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Wallix Academy: Certified Training CoursesDocument7 pagesWallix Academy: Certified Training CoursesShahram SametNo ratings yet
- KEP SERVER Cimplicity Connectivity GuideDocument10 pagesKEP SERVER Cimplicity Connectivity Guidegirish23monuNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DBMS NotesDocument102 pagesUnit-1 DBMS Notessonudhakad173No ratings yet
- DBMSDocument52 pagesDBMSjjs17No ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument28 pages1 IntroductionYubaraj MallaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 2Document31 pagesUnit 1 Part 2Shreyansh 1485No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basics of DBMS EDocument35 pagesUnit 1 Basics of DBMS EVijay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Dbms Basic ConceptsDocument47 pagesDbms Basic ConceptsSâürãbh KùmårNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument33 pagesBasic Conceptskiller GamingNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument15 pagesDatabase Management SystemsDIWAKAR UNo ratings yet
- Intro To Database Systems & DBMSDocument17 pagesIntro To Database Systems & DBMSgurungeNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DBMS NotesDocument85 pagesUnit-1 DBMS NotesRoshan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DBMS RM2Document30 pagesDBMS RM2PavanreddyNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument52 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptsPuru RajNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction To DatabaseDocument31 pagesUnit I - Introduction To DatabaseGaurav Patni100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Information System & I.T. FundamentalsDocument182 pagesChapter 2: Information System & I.T. FundamentalsAnkx Gagan JaitewaliaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1Document31 pagesDBMS Unit-1Sai ShaikNo ratings yet
- To DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDocument14 pagesTo DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDulal SahanaNo ratings yet
- To DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDocument14 pagesTo DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDulal SahanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To DataBase SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To DataBase Systemsprathameshm.cs21No ratings yet
- Databases and Database Users: Dr. Ali ObaidiDocument27 pagesDatabases and Database Users: Dr. Ali ObaidiVidhi GovilNo ratings yet
- File Systems and DatabasesDocument25 pagesFile Systems and DatabasesZapish SaeedNo ratings yet
- Good Database Design Will Get You Through PoorDocument50 pagesGood Database Design Will Get You Through PoorKofiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management System: Topic 1Document12 pagesIntroduction To Database Management System: Topic 1King JazzNo ratings yet
- DBS NotesDocument85 pagesDBS NotesOmary HajiNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument29 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptssaloniNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument29 pagesDBMS Basic Conceptsraspberry piNo ratings yet
- Database Design & ManagementDocument45 pagesDatabase Design & ManagementyohoNo ratings yet
- Dbms 1Document70 pagesDbms 1mailforsv259No ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document47 pagesDBMS Unit 1Faisal Nazir (ANDY)No ratings yet
- The Database EnvironmentDocument16 pagesThe Database EnvironmentWahab MansoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Introduction & ER Model)Document31 pagesUnit 1 (Introduction & ER Model)Madhu RayaproluNo ratings yet
- 02.advantages of Database ApproachDocument14 pages02.advantages of Database ApproachMadhuNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument45 pagesDatabasewaqas08No ratings yet
- Information Technology: Chapter TwoDocument56 pagesInformation Technology: Chapter TwoĒrmias ÁlemayehuNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BCSE302L TH CH2023240502444 Reference Material I 08-01-2024 MODULE 1Document165 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCSE302L TH CH2023240502444 Reference Material I 08-01-2024 MODULE 1sarvesh.vitchennaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesUnit 1.1 Introductionranaji181223No ratings yet
- Unit1 - FinalDocument71 pagesUnit1 - FinalRoshan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CUAP DBMS Notes Unit11Document31 pagesCUAP DBMS Notes Unit11sahil rajNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lec1Document22 pagesDBMS Lec1ZainNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document37 pagesLect 1MitNo ratings yet
- Module 1 DBMSDocument96 pagesModule 1 DBMSreddytejaswini0431No ratings yet
- DBMS NotesDocument10 pagesDBMS NotesRagav RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Database SystemsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Database SystemskrisNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SudhaDocument129 pagesModule 1 SudhaRupith Kumar .NNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionMarkapuri Santhoash kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Databases and Database UsersDocument25 pagesUnit 1: Databases and Database UsersVarun RameshNo ratings yet
- 6 IntroductionDocument44 pages6 IntroductionAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument61 pagesDBMSsangiwenmoyoNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument61 pagesDBMSShubham MehtaNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument61 pagesDBMSvikrant kumarNo ratings yet
- DbmsDocument12 pagesDbmsmanicheese100% (1)
- Unit 1: Introduction: Dhanashree HuddedarDocument26 pagesUnit 1: Introduction: Dhanashree HuddedarArchit AnandNo ratings yet
- Components of Database Management System: What Is DBMS?Document14 pagesComponents of Database Management System: What Is DBMS?Rajvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Database Management System 1: E-Module inDocument30 pagesDatabase Management System 1: E-Module inJanah Andrea RiveraNo ratings yet
- Database System Background PDFDocument40 pagesDatabase System Background PDFNandanNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems-Chapter 1: Dr. M. Brindha Assistant Professor Department of CSE NIT, Trichy-15Document26 pagesDatabase Management Systems-Chapter 1: Dr. M. Brindha Assistant Professor Department of CSE NIT, Trichy-15Rashika KhannaNo ratings yet
- DBMS (Part 1)Document57 pagesDBMS (Part 1)Harsh WaghelaNo ratings yet
- Guide To DatabasesDocument47 pagesGuide To DatabasesAnne RosalesNo ratings yet
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocument35 pagesFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramJan Reinhart PerezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database / RdbmsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Database / RdbmsMaria PanesNo ratings yet
- THE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)From EverandTHE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- A Brief History of Microsoft WindowsDocument20 pagesA Brief History of Microsoft Windowsyoo IjinNo ratings yet
- Fospha Big Data Visualisations ReactDocument15 pagesFospha Big Data Visualisations ReactDaniel Garcia AcostaNo ratings yet
- Name: Ismael Antonio Liriano Rodriguez Enrollment: 1-20-4078 Answer These QuestionsDocument7 pagesName: Ismael Antonio Liriano Rodriguez Enrollment: 1-20-4078 Answer These QuestionsIsmael LirianoNo ratings yet
- Capterra Software Buying GuideDocument15 pagesCapterra Software Buying Guidesai kumarNo ratings yet
- YozologDocument2 pagesYozologHeruNo ratings yet
- Vcenter Orchestrator Plugin Development - Best PracticesDocument28 pagesVcenter Orchestrator Plugin Development - Best PracticesAshish PichaNo ratings yet
- MS AX Installation GuideDocument153 pagesMS AX Installation GuideAlain Ternet100% (1)
- Practical Training ReportDocument24 pagesPractical Training Reporthairi.faizal.sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 7 QuizFitri-ssiNo ratings yet
- NYTECH BIAA Keynote 09 15 10Document42 pagesNYTECH BIAA Keynote 09 15 10Manoj Kumar JenaNo ratings yet
- The Gartner Report: MS GuidesDocument19 pagesThe Gartner Report: MS GuidesJonathan SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Vernee M5 4G SmartphoneEnglish User ManualDocument25 pagesVernee M5 4G SmartphoneEnglish User ManualAna LuaNo ratings yet
- NSN CDR Call TypeDocument3 pagesNSN CDR Call TypeDarwin Noel MataroNo ratings yet
- YEP Pack Procedure - V1Document6 pagesYEP Pack Procedure - V1Vaclav MullerNo ratings yet
- Formality: Equivalence Checking and Interactive ECODocument6 pagesFormality: Equivalence Checking and Interactive ECOneerajbakshiNo ratings yet
- Mis13 Ch13 Case1 Ibm-BpmDocument3 pagesMis13 Ch13 Case1 Ibm-Bpm720i0180No ratings yet
- IaC Security - Lab GuideDocument32 pagesIaC Security - Lab GuideAndrew RyanNo ratings yet
- Anviz C2Slim QuickGuide EN 8.28.2018Document2 pagesAnviz C2Slim QuickGuide EN 8.28.2018AzMarNo ratings yet
- Databricks - Spark StreamingDocument55 pagesDatabricks - Spark StreamingSlavimirVesićNo ratings yet
- JavaProgrammingForBeginners PresentationDocument58 pagesJavaProgrammingForBeginners Presentationdeva priyan100% (1)
- Examtorrent: Best Exam Torrent, Excellent Test Torrent, Valid Exam Dumps Are Here Waiting For YouDocument6 pagesExamtorrent: Best Exam Torrent, Excellent Test Torrent, Valid Exam Dumps Are Here Waiting For Youmy pcNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument44 pagesDX DiagCatalin ROGAMERNo ratings yet
- 3BSE044222R101 - en Compact Control Builder AC 800M Version 5.0 Application Programming Introduction and DesignDocument158 pages3BSE044222R101 - en Compact Control Builder AC 800M Version 5.0 Application Programming Introduction and DesignraiNo ratings yet
- Igate and HA Into Proxmox v2 00Document15 pagesIgate and HA Into Proxmox v2 00cemaranet feedbackNo ratings yet
- Wondershare FilmoraDocument22 pagesWondershare FilmoraMa TetNo ratings yet
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
target iit20190 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views9 pagesThe document defines key concepts related to databases including data, information, databases, database systems, and their components. It discusses how databases are organized and structured. It also provides examples of common database applications and defines the main components of a database system as data, hardware, software, and users.
Original Description:
bvedcshxachd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key concepts related to databases including data, information, databases, database systems, and their components. It discusses how databases are organized and structured. It also provides examples of common database applications and defines the main components of a database system as data, hardware, software, and users.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views9 pagesChapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
target iit2019The document defines key concepts related to databases including data, information, databases, database systems, and their components. It discusses how databases are organized and structured. It also provides examples of common database applications and defines the main components of a database system as data, hardware, software, and users.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
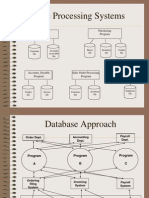
Chapter 1: Introduction
• Data: Known facts that can be recorded and
that have implicit meaning
• Information:-processing of data.
• Data Base:- Collection of related data.
• .Ex. the names, telephone numbers and
addresses of all the people you know. Database
are organized by fields, records and files
Benefits of database approach(Data base system)
over file system
• Redundancy can be reduced
• Inconsistency can be avoided
• Data can be shared
• Security restrictions can be applied
• Data independence can be provided
• Backup and Recovery.
• Data retrieval become efficient.
• Transactional Problem can be removed.
• Economic on scale
Database Applications:
– Banking: all transactions
– Airlines: reservations, schedules
– Universities: registration, grades
– Sales: customers, products, purchases
– Manufacturing: production, inventory,
orders, supply chain
– Human resources: employee records,
salaries, tax deductions
• Databases touch all aspects of our
lives
DEFINITION of
DATABASE
• Data Base is composed of a collection
of files that are linked in such a way
that information from one of the
files may be combined with
information from other files so that
a user may receive the exact
information needed.
COMPONENTS OF
DATABASE SYSTEM
• A database system is composed of
four components;
• Data
• Hardware
• Software
• Users
• Data -. A data is known as the rowfact which is stored in
computers memory and used by the user.
• Data may be of different types.
• User Data - It consists of a table(s) of data called
Relation(s) where Column(s) are called fields of attributes
and rows are called Records for tables. A Relation must be
structured properly.
• Metadata - A description of the structure of the database
is known as Metadata. It basically means "data about data".
System Tables store the Metadata which includes.
• - Number of Tables and Table Names
• - Number of fields and field Names
• - Primary Key Fields
• 2. Hardware - The hardware consists of the secondary storage
devices such as magnetic disks (hard disk, zip disk, floppy disks),
optical disks (CD-ROM), magnetic tapes etc. on which data is
stored together with the Input/Output devices (mouse, keyboard,
printers), processors, main memory etc. which are used for storing
and retrieving the data in a fast and efficient manner.
• 3. Software - The Software part consists of DBMS which
acts as a bridge between the user and the database or in
other words, software that interacts with the users,
application programs, and database and files system of a
particular storage media (hard disk, magnetic tapes etc.) to
insert, update, delete and retrieve data. For performing
these operations such as insertion, deletion and updating, we
can either use the Query Languages like SQL, QUEL or
application software's such as Visual basic etc.
• 4. Users - Users are those persons who
need the information from the database to
carry out their primary business
responsibilities i.e. Personnel, Staff,
Clerical, Managers, Executives etc. On the
basis of the job and requirements made by
them they are provided access to the
database totally or partially.
• The various types of users which can
access the database are:-
• • Database Administrators (DBA)
• • Database Designers
• • End Users
• • Application Programmers
DBMS
• Database Management System
(DBMS): DBMS is the software that
interprets and processes user’s
requests to retrieve information
from a database. Figure shows that a
DBMS serves as an interface b/w the
users & the database.
Queries
Operating
DBMS Data
System
C/C++ Base
You might also like
- Steps To Create and Deploy Our YOLO Model On AWS SagemakerDocument3 pagesSteps To Create and Deploy Our YOLO Model On AWS SagemakerAnupam PoddarNo ratings yet
- Key Technical Topics in A System Conversion To SAP S4HANADocument23 pagesKey Technical Topics in A System Conversion To SAP S4HANARafael RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Open Source SoftwareDocument11 pagesOpen Source SoftwareMohammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Wallix Academy: Certified Training CoursesDocument7 pagesWallix Academy: Certified Training CoursesShahram SametNo ratings yet
- KEP SERVER Cimplicity Connectivity GuideDocument10 pagesKEP SERVER Cimplicity Connectivity Guidegirish23monuNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DBMS NotesDocument102 pagesUnit-1 DBMS Notessonudhakad173No ratings yet
- DBMSDocument52 pagesDBMSjjs17No ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument28 pages1 IntroductionYubaraj MallaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 2Document31 pagesUnit 1 Part 2Shreyansh 1485No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basics of DBMS EDocument35 pagesUnit 1 Basics of DBMS EVijay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Dbms Basic ConceptsDocument47 pagesDbms Basic ConceptsSâürãbh KùmårNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument33 pagesBasic Conceptskiller GamingNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument15 pagesDatabase Management SystemsDIWAKAR UNo ratings yet
- Intro To Database Systems & DBMSDocument17 pagesIntro To Database Systems & DBMSgurungeNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DBMS NotesDocument85 pagesUnit-1 DBMS NotesRoshan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DBMS RM2Document30 pagesDBMS RM2PavanreddyNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument52 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptsPuru RajNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction To DatabaseDocument31 pagesUnit I - Introduction To DatabaseGaurav Patni100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Information System & I.T. FundamentalsDocument182 pagesChapter 2: Information System & I.T. FundamentalsAnkx Gagan JaitewaliaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1Document31 pagesDBMS Unit-1Sai ShaikNo ratings yet
- To DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDocument14 pagesTo DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDulal SahanaNo ratings yet
- To DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDocument14 pagesTo DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDulal SahanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To DataBase SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To DataBase Systemsprathameshm.cs21No ratings yet
- Databases and Database Users: Dr. Ali ObaidiDocument27 pagesDatabases and Database Users: Dr. Ali ObaidiVidhi GovilNo ratings yet
- File Systems and DatabasesDocument25 pagesFile Systems and DatabasesZapish SaeedNo ratings yet
- Good Database Design Will Get You Through PoorDocument50 pagesGood Database Design Will Get You Through PoorKofiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management System: Topic 1Document12 pagesIntroduction To Database Management System: Topic 1King JazzNo ratings yet
- DBS NotesDocument85 pagesDBS NotesOmary HajiNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument29 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptssaloniNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument29 pagesDBMS Basic Conceptsraspberry piNo ratings yet
- Database Design & ManagementDocument45 pagesDatabase Design & ManagementyohoNo ratings yet
- Dbms 1Document70 pagesDbms 1mailforsv259No ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document47 pagesDBMS Unit 1Faisal Nazir (ANDY)No ratings yet
- The Database EnvironmentDocument16 pagesThe Database EnvironmentWahab MansoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Introduction & ER Model)Document31 pagesUnit 1 (Introduction & ER Model)Madhu RayaproluNo ratings yet
- 02.advantages of Database ApproachDocument14 pages02.advantages of Database ApproachMadhuNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument45 pagesDatabasewaqas08No ratings yet
- Information Technology: Chapter TwoDocument56 pagesInformation Technology: Chapter TwoĒrmias ÁlemayehuNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BCSE302L TH CH2023240502444 Reference Material I 08-01-2024 MODULE 1Document165 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCSE302L TH CH2023240502444 Reference Material I 08-01-2024 MODULE 1sarvesh.vitchennaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesUnit 1.1 Introductionranaji181223No ratings yet
- Unit1 - FinalDocument71 pagesUnit1 - FinalRoshan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CUAP DBMS Notes Unit11Document31 pagesCUAP DBMS Notes Unit11sahil rajNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lec1Document22 pagesDBMS Lec1ZainNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document37 pagesLect 1MitNo ratings yet
- Module 1 DBMSDocument96 pagesModule 1 DBMSreddytejaswini0431No ratings yet
- DBMS NotesDocument10 pagesDBMS NotesRagav RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Database SystemsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Database SystemskrisNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SudhaDocument129 pagesModule 1 SudhaRupith Kumar .NNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionMarkapuri Santhoash kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Databases and Database UsersDocument25 pagesUnit 1: Databases and Database UsersVarun RameshNo ratings yet
- 6 IntroductionDocument44 pages6 IntroductionAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument61 pagesDBMSsangiwenmoyoNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument61 pagesDBMSShubham MehtaNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument61 pagesDBMSvikrant kumarNo ratings yet
- DbmsDocument12 pagesDbmsmanicheese100% (1)
- Unit 1: Introduction: Dhanashree HuddedarDocument26 pagesUnit 1: Introduction: Dhanashree HuddedarArchit AnandNo ratings yet
- Components of Database Management System: What Is DBMS?Document14 pagesComponents of Database Management System: What Is DBMS?Rajvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Database Management System 1: E-Module inDocument30 pagesDatabase Management System 1: E-Module inJanah Andrea RiveraNo ratings yet
- Database System Background PDFDocument40 pagesDatabase System Background PDFNandanNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems-Chapter 1: Dr. M. Brindha Assistant Professor Department of CSE NIT, Trichy-15Document26 pagesDatabase Management Systems-Chapter 1: Dr. M. Brindha Assistant Professor Department of CSE NIT, Trichy-15Rashika KhannaNo ratings yet
- DBMS (Part 1)Document57 pagesDBMS (Part 1)Harsh WaghelaNo ratings yet
- Guide To DatabasesDocument47 pagesGuide To DatabasesAnne RosalesNo ratings yet
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocument35 pagesFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramJan Reinhart PerezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database / RdbmsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Database / RdbmsMaria PanesNo ratings yet
- THE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)From EverandTHE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- A Brief History of Microsoft WindowsDocument20 pagesA Brief History of Microsoft Windowsyoo IjinNo ratings yet
- Fospha Big Data Visualisations ReactDocument15 pagesFospha Big Data Visualisations ReactDaniel Garcia AcostaNo ratings yet
- Name: Ismael Antonio Liriano Rodriguez Enrollment: 1-20-4078 Answer These QuestionsDocument7 pagesName: Ismael Antonio Liriano Rodriguez Enrollment: 1-20-4078 Answer These QuestionsIsmael LirianoNo ratings yet
- Capterra Software Buying GuideDocument15 pagesCapterra Software Buying Guidesai kumarNo ratings yet
- YozologDocument2 pagesYozologHeruNo ratings yet
- Vcenter Orchestrator Plugin Development - Best PracticesDocument28 pagesVcenter Orchestrator Plugin Development - Best PracticesAshish PichaNo ratings yet
- MS AX Installation GuideDocument153 pagesMS AX Installation GuideAlain Ternet100% (1)
- Practical Training ReportDocument24 pagesPractical Training Reporthairi.faizal.sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 7 QuizFitri-ssiNo ratings yet
- NYTECH BIAA Keynote 09 15 10Document42 pagesNYTECH BIAA Keynote 09 15 10Manoj Kumar JenaNo ratings yet
- The Gartner Report: MS GuidesDocument19 pagesThe Gartner Report: MS GuidesJonathan SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Vernee M5 4G SmartphoneEnglish User ManualDocument25 pagesVernee M5 4G SmartphoneEnglish User ManualAna LuaNo ratings yet
- NSN CDR Call TypeDocument3 pagesNSN CDR Call TypeDarwin Noel MataroNo ratings yet
- YEP Pack Procedure - V1Document6 pagesYEP Pack Procedure - V1Vaclav MullerNo ratings yet
- Formality: Equivalence Checking and Interactive ECODocument6 pagesFormality: Equivalence Checking and Interactive ECOneerajbakshiNo ratings yet
- Mis13 Ch13 Case1 Ibm-BpmDocument3 pagesMis13 Ch13 Case1 Ibm-Bpm720i0180No ratings yet
- IaC Security - Lab GuideDocument32 pagesIaC Security - Lab GuideAndrew RyanNo ratings yet
- Anviz C2Slim QuickGuide EN 8.28.2018Document2 pagesAnviz C2Slim QuickGuide EN 8.28.2018AzMarNo ratings yet
- Databricks - Spark StreamingDocument55 pagesDatabricks - Spark StreamingSlavimirVesićNo ratings yet
- JavaProgrammingForBeginners PresentationDocument58 pagesJavaProgrammingForBeginners Presentationdeva priyan100% (1)
- Examtorrent: Best Exam Torrent, Excellent Test Torrent, Valid Exam Dumps Are Here Waiting For YouDocument6 pagesExamtorrent: Best Exam Torrent, Excellent Test Torrent, Valid Exam Dumps Are Here Waiting For Youmy pcNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument44 pagesDX DiagCatalin ROGAMERNo ratings yet
- 3BSE044222R101 - en Compact Control Builder AC 800M Version 5.0 Application Programming Introduction and DesignDocument158 pages3BSE044222R101 - en Compact Control Builder AC 800M Version 5.0 Application Programming Introduction and DesignraiNo ratings yet
- Igate and HA Into Proxmox v2 00Document15 pagesIgate and HA Into Proxmox v2 00cemaranet feedbackNo ratings yet
- Wondershare FilmoraDocument22 pagesWondershare FilmoraMa TetNo ratings yet