Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ε e y ' y '' y: Calculus & analysis symbols
ε e y ' y '' y: Calculus & analysis symbols
Uploaded by
AubreyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MAT1332 NotesDocument106 pagesMAT1332 Notespeonyvu05No ratings yet
- Satellite Platform DesignDocument533 pagesSatellite Platform DesignHoujou100% (4)
- Energy Engineering Project ProposalDocument10 pagesEnergy Engineering Project ProposalRenan John CanasNo ratings yet
- CO-1 Course Material (15-12-17)Document27 pagesCO-1 Course Material (15-12-17)Bhargav BhargavNo ratings yet
- Metco Anti Bond 10 148Document2 pagesMetco Anti Bond 10 148Remco Van Den Berg100% (2)
- Splice JointsDocument2 pagesSplice JointsManoj ManoharanNo ratings yet
- SINN Catalog English 2010 2011Document96 pagesSINN Catalog English 2010 2011Abhijoy PaulNo ratings yet
- CAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFDocument16 pagesCAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFJimmy Teh0% (1)
- Calculus SymbolsDocument1 pageCalculus Symbolspcr123No ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument2 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListJohn BondNo ratings yet
- Algebraic SymbolDocument2 pagesAlgebraic SymbolAman YadavNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument23 pagesIntegral Calculusfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet
- 補充習題 - error correctedDocument2 pages補充習題 - error corrected洪碩辰No ratings yet
- A Proposed Hamiltonian Whose Eigenvalues Are The Zeros of The Riemann Zeta FunctionDocument11 pagesA Proposed Hamiltonian Whose Eigenvalues Are The Zeros of The Riemann Zeta FunctionJose Javier GarciaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols: When 2x 4, Then X 2Document2 pagesAlgebra Symbols: When 2x 4, Then X 2AubreyNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument2 pagesAlgebraColeen Jhoy SieteNo ratings yet
- Isra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111Document26 pagesIsra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111syeda zainabNo ratings yet
- Daryl Lalangan Gavino Bsba FM 1B Teacher: Joymarie Tayaban Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument5 pagesDaryl Lalangan Gavino Bsba FM 1B Teacher: Joymarie Tayaban Mathematics in The Modern WorldDARYL GAVINONo ratings yet
- The Xi Function Xi (1/2+is) Evaluated As A Functional Determinant of A Differential OperatorDocument13 pagesThe Xi Function Xi (1/2+is) Evaluated As A Functional Determinant of A Differential Operatoreljose1234No ratings yet
- BananesDocument16 pagesBananesxalove3892No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document13 pagesLecture 2James Karen100% (1)
- Applications-Of-Integration For Engineering, FileDocument36 pagesApplications-Of-Integration For Engineering, Filemoxima3638No ratings yet
- CH 3 Differentiation - RulesDocument19 pagesCH 3 Differentiation - Rulesserhataydin451No ratings yet
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDocument11 pagesAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- Deq19 02 First Order DEDocument58 pagesDeq19 02 First Order DE陳浚維No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Michael S. G. ForhNo ratings yet
- Calc 1 Chapter 4 PT 2Document9 pagesCalc 1 Chapter 4 PT 2freakysnatchNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Differentiation 87feb5ef 43ac 403a A959 5cca046c23f7Document54 pagesUnit 4 Differentiation 87feb5ef 43ac 403a A959 5cca046c23f7dande3359No ratings yet
- 0 A Cal1 191 Endterm Review 01Document2 pages0 A Cal1 191 Endterm Review 01GIANG LẠI THUNo ratings yet
- Lectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsDocument7 pagesLectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsLaluNo ratings yet
- Cap 3.3ADocument7 pagesCap 3.3AJohanna I. De Jesus MatosNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 The Integral Calculus 2019Document22 pagesLecture Notes 1 The Integral Calculus 2019Crystel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Rules (Differential Calculus)Document3 pagesDifferentiation Rules (Differential Calculus)md. mofasser ahamed shaibalNo ratings yet
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBankDocument12 pages1551 FinalExam ProblemBankPedro TNo ratings yet
- Vector True False PracticeDocument4 pagesVector True False PracticeSivakumar RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesDifferentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024SAMRIDH SAHANo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Alevel Maths WORDDocument14 pagesPeriodic Table Alevel Maths WORDSahar QuadriNo ratings yet
- MATH 115: Lecture XXVIII NotesDocument3 pagesMATH 115: Lecture XXVIII NotesDylan C. BeckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Applications of DifferentiationDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Applications of Differentiationapi-3728615No ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document4 pagesLecture 02jua134No ratings yet
- 1821 BasicsDocument4 pages1821 Basicsrio leonNo ratings yet
- T2 - IntegrationDocument100 pagesT2 - IntegrationMahmudNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesDifferential Calculus Lecture NotesraulNo ratings yet
- PDF Solutions Manual To Accompany Fundamentals of Differential Equations 8Th Edition 9780321747730 Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument34 pagesPDF Solutions Manual To Accompany Fundamentals of Differential Equations 8Th Edition 9780321747730 Online Ebook Full Chaptermiguel.macchione583100% (5)
- Delta FunctionDocument9 pagesDelta FunctionPritam PalNo ratings yet
- WBMT2049-T2/WI2032TH - Numerical Analysis For ODE'sDocument23 pagesWBMT2049-T2/WI2032TH - Numerical Analysis For ODE'sJoost SchinkelshoekNo ratings yet
- Multiple Integration: Sphere 3Document5 pagesMultiple Integration: Sphere 3simon georgeNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralDocument36 pagesMultiple Integralericayaaamankwah1987No ratings yet
- Derivatives of Inverse Function - Problems and SolutionsDocument11 pagesDerivatives of Inverse Function - Problems and SolutionsYinkci Heart Entertainment StudioNo ratings yet
- Derivative Formulas To Memorize 150Document1 pageDerivative Formulas To Memorize 150PETERNo ratings yet
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument27 pagesImplicit DifferentiationWirtu BoranaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument2 pagesCalculusdissipog1932No ratings yet
- 화학수학 과제 - 220416 - 235359Document5 pages화학수학 과제 - 220416 - 235359cmc107No ratings yet
- 03 BasicDerivativeRulesDocument2 pages03 BasicDerivativeRulesRebeca Enrique-CifresNo ratings yet
- Ch8 TechniquesofIntegrationDocument21 pagesCh8 TechniquesofIntegrationMert AktarNo ratings yet
- 18 01 Fall 2005 Lecture 16 PDFDocument6 pages18 01 Fall 2005 Lecture 16 PDFAl VlearNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Numerical Integration: in This Chapter, You Will LearnDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Numerical Integration: in This Chapter, You Will LearnArvin 97No ratings yet
- Derivatives Of A Function Using The 5-Step Rule: dy dx = lim Δy Δx f (x+ Δx) −f (x) ΔxDocument7 pagesDerivatives Of A Function Using The 5-Step Rule: dy dx = lim Δy Δx f (x+ Δx) −f (x) ΔxRhembea Gardose FerasolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document13 pagesLecture 6Jitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lecture 006Document32 pages2013 Lecture 006eouahiauNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument72 pagesIntegralSachin5586No ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument5 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListDay WilsonNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument6 pagesTechniques of IntegrationFahrettin CakirNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Derivatives of Expo FunctionsDocument7 pagesModule 7 - Derivatives of Expo FunctionsLyka Soriano MopasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 PI Current Control of DC MotorDocument3 pagesExperiment No 3 PI Current Control of DC MotorMohammed Dyhia Ali100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Guided Wave UltrasonicsDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - Guided Wave UltrasonicsSabavoon FazliNo ratings yet
- 1301 Formula SheetDocument2 pages1301 Formula Sheetdivitimaniteja999786No ratings yet
- HYSTERESIS HEVIA: A New Routine To Generate Input Data For Inductors With HysteresisDocument10 pagesHYSTERESIS HEVIA: A New Routine To Generate Input Data For Inductors With HysteresisLuis Átila100% (1)
- Energy and Exergy Based Analysis of Hybrid Solar DryerDocument12 pagesEnergy and Exergy Based Analysis of Hybrid Solar DryerDeepika ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cigre TB 513Document172 pagesCigre TB 513Arogya Raju Pudhota100% (2)
- Properties of Water Lab 2012aDocument8 pagesProperties of Water Lab 2012aFatien VioLet's SmilezsiieNo ratings yet
- Wl12 b5681 SensorDocument18 pagesWl12 b5681 SensorFayber Campos100% (2)
- Analysis and Design of Flat Slab by Using Etabs Software: 1.1 GeneralDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flat Slab by Using Etabs Software: 1.1 GeneralMikeNo ratings yet
- Overfilled Arch BridgeDocument5 pagesOverfilled Arch BridgeTony OngNo ratings yet
- Steel Structure Lecture - TorsionDocument45 pagesSteel Structure Lecture - TorsionPatrick LeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFJoshua TesoroNo ratings yet
- Computational HydraulicsDocument130 pagesComputational HydraulicsPeter Riad100% (3)
- Cultivation of White Button MushroomDocument7 pagesCultivation of White Button MushroomLalzar ZovaNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment PowerpointDocument31 pagesLab Equipment PowerpointRiee Naxx RekaccNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument23 pagesPreviewpdfKeyitsmee 00100% (2)
- Thermodynamic Variables Path Function State Function I II IIIDocument42 pagesThermodynamic Variables Path Function State Function I II IIIadriannthehunkNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding PDFDocument329 pagesArc Welding PDFMEHMET TÜRKERNo ratings yet
- Sonlite Solar ProfileDocument47 pagesSonlite Solar ProfileMoses G. G NdovieNo ratings yet
- RFY - Annual Test Calendar (REVISED)Document1 pageRFY - Annual Test Calendar (REVISED)ali the gamer 270No ratings yet
- Edition 7 Arcing Faults in Medium and Low Voltage Switchgear PDFDocument12 pagesEdition 7 Arcing Faults in Medium and Low Voltage Switchgear PDFE.ANANDANNo ratings yet
- Some Properties of Corn Grains and Their Flours I: Physicochemical, Functional and Chapati-Making Properties of FloursDocument9 pagesSome Properties of Corn Grains and Their Flours I: Physicochemical, Functional and Chapati-Making Properties of FloursscrNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeDocument45 pagesInterpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeAnnisa RizqiaNo ratings yet
ε e y ' y '' y: Calculus & analysis symbols
ε e y ' y '' y: Calculus & analysis symbols
Uploaded by
AubreyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ε e y ' y '' y: Calculus & analysis symbols
ε e y ' y '' y: Calculus & analysis symbols
Uploaded by
AubreyCopyright:
Available Formats
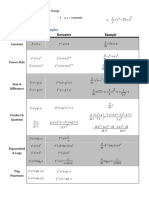
Calculus & analysis symbols
Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example
limit limit value of a function
represents a very small
ε epsilon
number, near zero
ε → 0
e constant / Euler's e = lim
e number e = 2.718281828...
(1+1/x)x , x→∞
derivative - Lagrange's
y ' derivative
notation
(3x3)' = 9x2
y '' second derivative derivative of derivative (3x3)'' = 18x
y(n) nth derivative n times derivation (3x3)(3) = 18
derivative - Leibniz's
derivative
notation
d(3x3)/dx = 9x2
second derivative derivative of derivative d2(3x3)/dx2 = 18x
nth derivative n times derivation
derivative by time -
time derivative
Newton's notation
time second derivative derivative of derivative
derivative - Euler's
Dx y derivative
notation
Dx2y second derivative derivative of derivative
partial derivative ∂(x2+y2)/∂x = 2x
∫ integral opposite to derivation ∫ f(x)dx
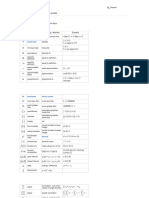
Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example
integration of function of
∫∫ double integral
2 variables
∫∫ f(x,y)dxdy
integration of function of
∫∫∫ triple integral
3 variables
∫∫∫ f(x,y,z)dxdydz
closed contour / line
∮ integral
∯ closed surface integral
∰ closed volume integral
[a,b] =
[a,b] closed interval
{x | a ≤ x ≤ b}
(a,b) =
(a,b) open interval
{x | a < x < b}
i imaginary unit i ≡ √-1 z = 3 + 2i
z* complex conjugate z = a+bi → z*=a-bi z* = 3 - 2i
z complex conjugate z = a+bi → z = a-bi z = 3 - 2i
real part of a complex
Re(z) number z = a+bi → Re(z)=a Re(3 - 2i) = 3
imaginary part of a
Im(z) complex number z = a+bi → Im(z)=b Im(3 - 2i) = -2
absolute
| z | value/magnitude of a |z| = |a+bi| = √(a2+b2) |3 - 2i| = √13
complex number
argument of a complex The angle of the radius arg(3 + 2i) =
arg(z) number in the complex plane 33.7°
gradient / divergence
∇ nabla / del
operator ∇f (x,y,z)
Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example
vector
unit vector
x * y convolution y(t) = x(t) * h(t)
Laplace transform F(s) = {f (t)}
Fourier transform X(ω) = {f (t)}
δ delta function
∞ lemniscate infinity symbol
You might also like
- MAT1332 NotesDocument106 pagesMAT1332 Notespeonyvu05No ratings yet
- Satellite Platform DesignDocument533 pagesSatellite Platform DesignHoujou100% (4)
- Energy Engineering Project ProposalDocument10 pagesEnergy Engineering Project ProposalRenan John CanasNo ratings yet
- CO-1 Course Material (15-12-17)Document27 pagesCO-1 Course Material (15-12-17)Bhargav BhargavNo ratings yet
- Metco Anti Bond 10 148Document2 pagesMetco Anti Bond 10 148Remco Van Den Berg100% (2)
- Splice JointsDocument2 pagesSplice JointsManoj ManoharanNo ratings yet
- SINN Catalog English 2010 2011Document96 pagesSINN Catalog English 2010 2011Abhijoy PaulNo ratings yet
- CAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFDocument16 pagesCAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFJimmy Teh0% (1)
- Calculus SymbolsDocument1 pageCalculus Symbolspcr123No ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument2 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListJohn BondNo ratings yet
- Algebraic SymbolDocument2 pagesAlgebraic SymbolAman YadavNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument23 pagesIntegral Calculusfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet
- 補充習題 - error correctedDocument2 pages補充習題 - error corrected洪碩辰No ratings yet
- A Proposed Hamiltonian Whose Eigenvalues Are The Zeros of The Riemann Zeta FunctionDocument11 pagesA Proposed Hamiltonian Whose Eigenvalues Are The Zeros of The Riemann Zeta FunctionJose Javier GarciaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols: When 2x 4, Then X 2Document2 pagesAlgebra Symbols: When 2x 4, Then X 2AubreyNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument2 pagesAlgebraColeen Jhoy SieteNo ratings yet
- Isra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111Document26 pagesIsra Univesitry: Calculus & Analytial Geometry: Chapter # 05 Derivatives: MTCA-111syeda zainabNo ratings yet
- Daryl Lalangan Gavino Bsba FM 1B Teacher: Joymarie Tayaban Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument5 pagesDaryl Lalangan Gavino Bsba FM 1B Teacher: Joymarie Tayaban Mathematics in The Modern WorldDARYL GAVINONo ratings yet
- The Xi Function Xi (1/2+is) Evaluated As A Functional Determinant of A Differential OperatorDocument13 pagesThe Xi Function Xi (1/2+is) Evaluated As A Functional Determinant of A Differential Operatoreljose1234No ratings yet
- BananesDocument16 pagesBananesxalove3892No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document13 pagesLecture 2James Karen100% (1)
- Applications-Of-Integration For Engineering, FileDocument36 pagesApplications-Of-Integration For Engineering, Filemoxima3638No ratings yet
- CH 3 Differentiation - RulesDocument19 pagesCH 3 Differentiation - Rulesserhataydin451No ratings yet
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDocument11 pagesAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- Deq19 02 First Order DEDocument58 pagesDeq19 02 First Order DE陳浚維No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Michael S. G. ForhNo ratings yet
- Calc 1 Chapter 4 PT 2Document9 pagesCalc 1 Chapter 4 PT 2freakysnatchNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Differentiation 87feb5ef 43ac 403a A959 5cca046c23f7Document54 pagesUnit 4 Differentiation 87feb5ef 43ac 403a A959 5cca046c23f7dande3359No ratings yet
- 0 A Cal1 191 Endterm Review 01Document2 pages0 A Cal1 191 Endterm Review 01GIANG LẠI THUNo ratings yet
- Lectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsDocument7 pagesLectures 07 & 08 - Calculus of VariationsLaluNo ratings yet
- Cap 3.3ADocument7 pagesCap 3.3AJohanna I. De Jesus MatosNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 The Integral Calculus 2019Document22 pagesLecture Notes 1 The Integral Calculus 2019Crystel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Rules (Differential Calculus)Document3 pagesDifferentiation Rules (Differential Calculus)md. mofasser ahamed shaibalNo ratings yet
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBankDocument12 pages1551 FinalExam ProblemBankPedro TNo ratings yet
- Vector True False PracticeDocument4 pagesVector True False PracticeSivakumar RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesDifferentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024SAMRIDH SAHANo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Alevel Maths WORDDocument14 pagesPeriodic Table Alevel Maths WORDSahar QuadriNo ratings yet
- MATH 115: Lecture XXVIII NotesDocument3 pagesMATH 115: Lecture XXVIII NotesDylan C. BeckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Applications of DifferentiationDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Applications of Differentiationapi-3728615No ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document4 pagesLecture 02jua134No ratings yet
- 1821 BasicsDocument4 pages1821 Basicsrio leonNo ratings yet
- T2 - IntegrationDocument100 pagesT2 - IntegrationMahmudNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesDifferential Calculus Lecture NotesraulNo ratings yet
- PDF Solutions Manual To Accompany Fundamentals of Differential Equations 8Th Edition 9780321747730 Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument34 pagesPDF Solutions Manual To Accompany Fundamentals of Differential Equations 8Th Edition 9780321747730 Online Ebook Full Chaptermiguel.macchione583100% (5)
- Delta FunctionDocument9 pagesDelta FunctionPritam PalNo ratings yet
- WBMT2049-T2/WI2032TH - Numerical Analysis For ODE'sDocument23 pagesWBMT2049-T2/WI2032TH - Numerical Analysis For ODE'sJoost SchinkelshoekNo ratings yet
- Multiple Integration: Sphere 3Document5 pagesMultiple Integration: Sphere 3simon georgeNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntegralDocument36 pagesMultiple Integralericayaaamankwah1987No ratings yet
- Derivatives of Inverse Function - Problems and SolutionsDocument11 pagesDerivatives of Inverse Function - Problems and SolutionsYinkci Heart Entertainment StudioNo ratings yet
- Derivative Formulas To Memorize 150Document1 pageDerivative Formulas To Memorize 150PETERNo ratings yet
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument27 pagesImplicit DifferentiationWirtu BoranaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument2 pagesCalculusdissipog1932No ratings yet
- 화학수학 과제 - 220416 - 235359Document5 pages화학수학 과제 - 220416 - 235359cmc107No ratings yet
- 03 BasicDerivativeRulesDocument2 pages03 BasicDerivativeRulesRebeca Enrique-CifresNo ratings yet
- Ch8 TechniquesofIntegrationDocument21 pagesCh8 TechniquesofIntegrationMert AktarNo ratings yet
- 18 01 Fall 2005 Lecture 16 PDFDocument6 pages18 01 Fall 2005 Lecture 16 PDFAl VlearNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Numerical Integration: in This Chapter, You Will LearnDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Numerical Integration: in This Chapter, You Will LearnArvin 97No ratings yet
- Derivatives Of A Function Using The 5-Step Rule: dy dx = lim Δy Δx f (x+ Δx) −f (x) ΔxDocument7 pagesDerivatives Of A Function Using The 5-Step Rule: dy dx = lim Δy Δx f (x+ Δx) −f (x) ΔxRhembea Gardose FerasolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document13 pagesLecture 6Jitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lecture 006Document32 pages2013 Lecture 006eouahiauNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument72 pagesIntegralSachin5586No ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument5 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListDay WilsonNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument6 pagesTechniques of IntegrationFahrettin CakirNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Derivatives of Expo FunctionsDocument7 pagesModule 7 - Derivatives of Expo FunctionsLyka Soriano MopasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 PI Current Control of DC MotorDocument3 pagesExperiment No 3 PI Current Control of DC MotorMohammed Dyhia Ali100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Guided Wave UltrasonicsDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - Guided Wave UltrasonicsSabavoon FazliNo ratings yet
- 1301 Formula SheetDocument2 pages1301 Formula Sheetdivitimaniteja999786No ratings yet
- HYSTERESIS HEVIA: A New Routine To Generate Input Data For Inductors With HysteresisDocument10 pagesHYSTERESIS HEVIA: A New Routine To Generate Input Data For Inductors With HysteresisLuis Átila100% (1)
- Energy and Exergy Based Analysis of Hybrid Solar DryerDocument12 pagesEnergy and Exergy Based Analysis of Hybrid Solar DryerDeepika ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cigre TB 513Document172 pagesCigre TB 513Arogya Raju Pudhota100% (2)
- Properties of Water Lab 2012aDocument8 pagesProperties of Water Lab 2012aFatien VioLet's SmilezsiieNo ratings yet
- Wl12 b5681 SensorDocument18 pagesWl12 b5681 SensorFayber Campos100% (2)
- Analysis and Design of Flat Slab by Using Etabs Software: 1.1 GeneralDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flat Slab by Using Etabs Software: 1.1 GeneralMikeNo ratings yet
- Overfilled Arch BridgeDocument5 pagesOverfilled Arch BridgeTony OngNo ratings yet
- Steel Structure Lecture - TorsionDocument45 pagesSteel Structure Lecture - TorsionPatrick LeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFJoshua TesoroNo ratings yet
- Computational HydraulicsDocument130 pagesComputational HydraulicsPeter Riad100% (3)
- Cultivation of White Button MushroomDocument7 pagesCultivation of White Button MushroomLalzar ZovaNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment PowerpointDocument31 pagesLab Equipment PowerpointRiee Naxx RekaccNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument23 pagesPreviewpdfKeyitsmee 00100% (2)
- Thermodynamic Variables Path Function State Function I II IIIDocument42 pagesThermodynamic Variables Path Function State Function I II IIIadriannthehunkNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding PDFDocument329 pagesArc Welding PDFMEHMET TÜRKERNo ratings yet
- Sonlite Solar ProfileDocument47 pagesSonlite Solar ProfileMoses G. G NdovieNo ratings yet
- RFY - Annual Test Calendar (REVISED)Document1 pageRFY - Annual Test Calendar (REVISED)ali the gamer 270No ratings yet
- Edition 7 Arcing Faults in Medium and Low Voltage Switchgear PDFDocument12 pagesEdition 7 Arcing Faults in Medium and Low Voltage Switchgear PDFE.ANANDANNo ratings yet
- Some Properties of Corn Grains and Their Flours I: Physicochemical, Functional and Chapati-Making Properties of FloursDocument9 pagesSome Properties of Corn Grains and Their Flours I: Physicochemical, Functional and Chapati-Making Properties of FloursscrNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeDocument45 pagesInterpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeAnnisa RizqiaNo ratings yet