Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap5
Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap5
Uploaded by
PK ChunCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Buff Dudes Mobility Band Workout PlanDocument80 pagesBuff Dudes Mobility Band Workout PlanLeandro Aisa75% (8)
- PTA3 PokedexDocument790 pagesPTA3 PokedexAllan ZistchmelNo ratings yet
- Design A New Style Suspension Linkage and Frame For A Full Suspension Mountain Bike For Banshee BikesDocument52 pagesDesign A New Style Suspension Linkage and Frame For A Full Suspension Mountain Bike For Banshee Bikeskeithmscott100% (3)
- Sequence and SeriesDocument34 pagesSequence and SeriesAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 ProgressionsDocument6 pages12 ProgressionschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Sequence, Series & ProgressionsDocument49 pagesSequence, Series & Progressionsadarshjha1812No ratings yet
- Progression Theory Module-1Document19 pagesProgression Theory Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Jee Mainsample Chapter Maths 11 Sequences and Series PDFDocument44 pagesJee Mainsample Chapter Maths 11 Sequences and Series PDFAditya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Allen: 6. Arithmetic ProgressionDocument3 pagesAllen: 6. Arithmetic ProgressionRitesh MalikNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths N Ch. 2Document5 pages10 Maths N Ch. 2clementjamesmannasNo ratings yet
- ProgressionsDocument8 pagesProgressionsAayush DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Maths Bridge Course Material - 23-24 (16 04 23)Document33 pages3 - Maths Bridge Course Material - 23-24 (16 04 23)Sasi SasiNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics ProgressionDocument23 pages10 Mathematics ProgressionKumarNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression - Short NotesDocument2 pagesArithmetic Progression - Short Noteschanmol12024No ratings yet
- Math - Series & SequencesDocument4 pagesMath - Series & Sequenceshelixate100% (4)
- Series Outline. Subtopic 1 Arithmetic Progressions (A.Ps) : Thiscanbe Writtenas (n+1)Document10 pagesSeries Outline. Subtopic 1 Arithmetic Progressions (A.Ps) : Thiscanbe Writtenas (n+1)Kateu victorNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: Chapter - 4Document13 pagesSequences and Series: Chapter - 4AnupNo ratings yet
- Ntse Mathematics SynopsisDocument32 pagesNtse Mathematics SynopsissrilathaNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: Chapter - 4Document13 pagesSequences and Series: Chapter - 4Ayush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sequence Finite Sequence Infinite Sequence Series: For ExampleDocument2 pagesSequence Finite Sequence Infinite Sequence Series: For ExampleNaresh bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sequences and SeriesDocument40 pagesSequences and SeriesExtra Marks100% (2)
- Mathematics Formulas CompleteDocument28 pagesMathematics Formulas CompleteMark Lester LindoNo ratings yet
- Sequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Document1 pageSequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Jaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionDocument3 pagesArithmetic ProgressionFarhad HossainNo ratings yet
- 0278 MathematicsDocument30 pages0278 MathematicsZarex BorjaNo ratings yet
- 8 Sequences and SeriesDocument37 pages8 Sequences and Seriestusharfiitjee80No ratings yet
- (6665) Sheet 1 Sequence and Series BDocument61 pages(6665) Sheet 1 Sequence and Series BSourabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionsDocument10 pagesArithmetic ProgressionsSiri SBNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series PDFDocument2 pagesSequence and Series PDFscribdNo ratings yet
- 03 Sequence - SeriesDocument19 pages03 Sequence - Seriesabenav05No ratings yet
- 11 - Sequences and Series NotesDocument20 pages11 - Sequences and Series NotesPranab PhagetraNo ratings yet
- 6322deec814cca0018591b2d - ## - Chapter 03 - Sequence and Series - Module PDFDocument39 pages6322deec814cca0018591b2d - ## - Chapter 03 - Sequence and Series - Module PDFAhaan ParasharNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SeriesDocument31 pagesSequence and SeriesSiddhanth VengaliNo ratings yet
- DGT Sequence and SeriesDocument60 pagesDGT Sequence and SeriesRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument8 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets Getmarks ApppranjalpandeyspNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionDocument6 pagesArithmetic ProgressionLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets Quizrrshivam tirmanwarNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series: 1 SequencesDocument7 pagesSequence and Series: 1 SequencesF20BA020Hafsa YounasNo ratings yet
- Progressions A.P, G.PDocument13 pagesProgressions A.P, G.PAnanth SureshNo ratings yet
- Concept Map APDocument1 pageConcept Map APApoorva Eliza JohnNo ratings yet
- 08 Sequence Series Revision Notes QuizrrDocument38 pages08 Sequence Series Revision Notes QuizrrDivyansh KaraokeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1SequenceSeriesiDocument7 pagesWorksheet 1SequenceSeriesiPhysics A1No ratings yet
- SNS SheetsDocument59 pagesSNS SheetsMOHD SARFARAZNo ratings yet
- Class-X Arithmetic ProgressionDocument34 pagesClass-X Arithmetic Progressionchintesh mehtaNo ratings yet
- @StudyTime - Channel Maths-7 PDFDocument8 pages@StudyTime - Channel Maths-7 PDFSipra PaulNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progressons (Part-1)Document16 pagesArithmetic Progressons (Part-1)shambhaviNo ratings yet
- Sequences-Series - Arithmetics and GeometricsDocument10 pagesSequences-Series - Arithmetics and GeometricsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 10.series and SequencesDocument7 pages10.series and SequencesWhatyoudoingNo ratings yet
- Class-X Arithmetic ProgressionDocument34 pagesClass-X Arithmetic ProgressionA. R.S TECHNo ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrShivek SinghalNo ratings yet
- 10 Series and SequencesDocument7 pages10 Series and Sequencespatrick clarkeNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Sequence and SeriesDocument18 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Sequence and SeriesAnweshMishraNo ratings yet
- APGP Series AP GP HP Progressions Handbook by CKDocument31 pagesAPGP Series AP GP HP Progressions Handbook by CKசரவணக்குமார் .பNo ratings yet
- 1979 15erdosDocument19 pages1979 15erdosvahidmesic45No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - SequenceDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 1 - SequenceZuriati SalehaNo ratings yet
- MAA HL Formula Booklet ExamDocument13 pagesMAA HL Formula Booklet Examnathan.kimNo ratings yet
- Sequence & Series (@BrilliantsAcademy)Document37 pagesSequence & Series (@BrilliantsAcademy)AHMMED AHMMEDNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus 86 122 PDFDocument37 pagesPre Calculus 86 122 PDFKheza SuravillaNo ratings yet
- Resource 1109Document2 pagesResource 1109jalpanapaul7430006148No ratings yet
- Harmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)From EverandHarmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)No ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap7Document17 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap7PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap4Document16 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap4PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2Document22 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2PK ChunNo ratings yet
- KSSM 3 in 1 f3 中文参考资料+配版练习 辅助本 ansDocument8 pagesKSSM 3 in 1 f3 中文参考资料+配版练习 辅助本 ansPK ChunNo ratings yet
- 2009 KS3 Maths Level 3-5 Paper 3 Calculator AllowedDocument28 pages2009 KS3 Maths Level 3-5 Paper 3 Calculator AllowedPK ChunNo ratings yet
- KS3 Mathematics SAT 2010 MarkschemeDocument96 pagesKS3 Mathematics SAT 2010 MarkschemePK ChunNo ratings yet
- Rohn #80 290' Guyed - Proposed Antenna - H MODDocument1 pageRohn #80 290' Guyed - Proposed Antenna - H MODJohn Neil MitraNo ratings yet
- AJSSM Children's Readiness For Learning Front Crawl Swimming by B A Blanksby, H E Parker, S Bradley and V OngDocument6 pagesAJSSM Children's Readiness For Learning Front Crawl Swimming by B A Blanksby, H E Parker, S Bradley and V Ongvohm28No ratings yet
- Fallout - Game DesignDocument17 pagesFallout - Game DesignAnonymous HNBHPdSbj100% (1)
- As Ve Sa Su Me Ra Ke: NavamsaDocument1 pageAs Ve Sa Su Me Ra Ke: NavamsaAstroAnudeepNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of RunningDocument19 pagesBiomechanics of RunningJaviera Paz VegaNo ratings yet
- Minor ClassificationDocument28 pagesMinor Classificationnofiya yousufNo ratings yet
- Psoas RehabDocument7 pagesPsoas Rehabmtemei4414No ratings yet
- CD NoDocument2 pagesCD Nohighlander_77No ratings yet
- Character Sheets MoonDocument4 pagesCharacter Sheets MoonGabriel Othero VedolinNo ratings yet
- 30 Natural Ways To Help Treat Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument12 pages30 Natural Ways To Help Treat Polycystic Ovary SyndromeArun AchalamNo ratings yet
- Mazda Bt50 WL C & We C Wiring Diagram f198!30!05l121Document1 pageMazda Bt50 WL C & We C Wiring Diagram f198!30!05l121staff055100% (1)
- Group 10 Steering Valve: 1. StructureDocument2 pagesGroup 10 Steering Valve: 1. StructureالمهندسوليدالطويلNo ratings yet
- 2023 ERCS Finding List A2-5Document4 pages2023 ERCS Finding List A2-5Khine ZinNo ratings yet
- Faction: Steppes TribesDocument5 pagesFaction: Steppes TribesBorchNo ratings yet
- Calgary Barbell 16 Week (Revised) LB + KGsDocument15 pagesCalgary Barbell 16 Week (Revised) LB + KGsMAJ FALLATANo ratings yet
- Rear Axle Shaft DesignDocument11 pagesRear Axle Shaft DesignSandeep Chauhan75% (4)
- Formula R1 Racing - Explosionszeichnungen Und Adapter PDFDocument9 pagesFormula R1 Racing - Explosionszeichnungen Und Adapter PDFIBC_TobiNo ratings yet
- Choose The CORRECT Words Present SimpleDocument2 pagesChoose The CORRECT Words Present SimpleAgustín EchevarríaNo ratings yet
- Codex Imperial Guard FAQ 5th EditionDocument3 pagesCodex Imperial Guard FAQ 5th EditionJohn McLeishNo ratings yet
- 4 Hour BodyDocument536 pages4 Hour BodyHa Ri85% (13)
- Effect of Weight On Stall SpeedDocument2 pagesEffect of Weight On Stall Speedpp2076No ratings yet
- X-Plorers RPG (Illustrated)Document40 pagesX-Plorers RPG (Illustrated)deathbydoughnut100% (1)
- Sargodha 5th Class Result 2014Document396 pagesSargodha 5th Class Result 2014DMO OFFICENo ratings yet
- Assistive DevicesDocument3 pagesAssistive DevicesKarina Bianca ColladoNo ratings yet
- Women's Health Australia - May 2017Document148 pagesWomen's Health Australia - May 2017Lucia Carolina Velasco Lopez100% (2)
- 5.56 NATO Duplication LoadsDocument4 pages5.56 NATO Duplication Loadswatch_sutNo ratings yet
- Ko and Dame Endgames Under Area Scoring: PrefaceDocument64 pagesKo and Dame Endgames Under Area Scoring: PrefaceFrédéric VieiraNo ratings yet
Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap5
Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap5
Uploaded by
PK ChunCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap5
Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap5
Uploaded by
PK ChunCopyright:
Available Formats
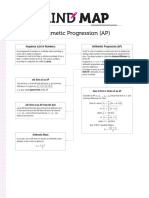
5 Progressions
Janjang
Arithmetic Progressions
5.1 Janjang Aritmetik Textbook
pg. 128 – 138
SMART Notes
d.
1. Arithmetic progression (AP) is a sequence of numbers 3. The sum of the first n terms, S n , of an arithmetic
such that each term after the first is obtained by adding progression is
Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama, Sn, bagi suatu janjang
Bh
the previous one with a constant called common
aritmetik ialah
difference, d.
Janjang aritmetik (JA) ialah suatu jujukan nombor dengan n
Sn = [2a + (n – 1)d ]
keadaan setiap sebutan selepas sebutan pertama diperoleh 2
dengan menambah sebutan sebelumnya dengan suatu pemalar, or/ atau
.
iaitu beza sepunya, d.
dn
n
Sn = [a + l ] where l = last term
Term/ Sebutan T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 2 dengan keadaan l = sebutan terakhir
Sequence/ Jujukan 5 , 9 , 13 , 17 , 21 , …
S
Common difference of the above sequence:
Beza sepunya bagi jujukan di atas: Sn =
1
[2a + (n – 1)d]
2
d = T2 – T1 = T3 – T2 = T4 – T3 = T5 – T4 = …
gi 1
Sn = [a + a + (n – 1)d]
2
= 4 The last term/ Sebutan terakhir
an
1
2. The nth term, Tn, of an arithmetic progression is Sn = [a + l ]
2
Sebutan ke-n, Tn, bagi suatu janjang aritmetik ialah
Tn = a + (n – 1)d 4. The nth term, Tn, of an arithmetic progression can also be
l
found using Sn – Sn – 1.
Pe
where a = first term, d = common difference Sebutan ke-n, Tn, bagi suatu janjang aritmetik juga dapat dicari
dengan keadaan a = sebutan pertama, d = beza sepunya dengan menggunakan Sn – Sn – 1.
n
1. Determine whether each of the following sequences is an arithmetic progression. Give your justification. PL 2
Tentukan sama ada setiap jujukan yang berikut ialah janjang aritmetik atau bukan. Berikan justifikasi anda.
ta
Example
(a) 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , …
bi
7, 3, –1, –5, … 2 3 4 5
d1 = 1 – 1 = – 1
d1 = –5 – (–1) = –4 3 2 6
r
d2 = –1 – 3 = –4 d2 = – = – 1
1 1
ne
d3 = 3 – 7 = –4 4 3 12
An arithmetic progression because d1 = d2 = d3 = –4. d3 = – = – 1
1 1
5 4 20
Pe
Not an arithmetic progression because
d1 ≠ d2 ≠ d3.
(b) –2, 3, 8, 13, … (c) 2x + y, x, –y, –x – 2y, …
d1 = 3 – (–2) = 5 d1 = (–x – 2y) – (–y) = –x – y
d2 = 8 – 3 = 5 d2 = –y – x = –x – y
d3 = 13 – 8 = 5 d3 = x – (2x + y) = –x – y
An arithmetic progression because An arithmetic progression because
d1 = d2 = d3 = 5. d1 = d2 = d3 = –x – y.
65 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
2. For each of the following arithmetic progressions, determine the term stated in bracket. PL 3
Bagi setiap janjang aritmetik berikut, tentukan sebutan yang dinyatakan dalam kurungan.
Example (a) 3, 7, 11, 15, … [8th term/ sebutan ke-8]
ln x, ln 3x, ln 9x, ln 27x, … [5th term/ sebutan ke-5] a=3
a = ln x d=7–3=4
d = ln 3x – ln x = ln 3x = ln 3
x T8 = 3 + 7(4)
T5 = ln x + 4 ln 3 Tn = a + (n – 1)d = 31
= ln 34x = ln 81x
(b) –10, –13, –16, –19, … [16th term/ sebutan ke-16] (c) 2p, 3p , p, p , … [21th term/ sebutan ke-21]
2 2
d.
a = –10 a = 2p
d = –13 – (–10) = –3
d = 3p – 2p = – p
Bh
2 2
T16 = –10 + 15(–3)
= –55 T21 = 2p + 20 – p = 2p – 10p = –8p
1 2
2
.
dn
3. Determine the first term and the common difference of each of the following. PL 4
Tentukan sebutan pertama dan beza sepunya bagi setiap yang berikut.
Example
S
gi
In an arithmetic progression, the 4th and 8th terms are 16 and 56 respectively.
Dalam suatu janjang aritmetik, sebutan ke-4 dan ke-8 masing-masing ialah 16 dan 56.
an
Tn = a + (n – 1)d 2 – 1, 4d = 40
T4 = a + (4 – 1)d = 16 d = 10
a + 3d = 16 ………… 1 Substitute d = 10 into 1,
l
T8 = a + (8 – 1)d = 56 a + 3(10) = 16
Pe
a + 7d = 56 ………… 2 a = –14
\ The first term is –14 and the common difference
is 10.
n
(a) In an arithmetic progression, the 3rd and 8th terms (b) In an arithmetic progression, the 2 nd and 5th
ta
are –5 and 15 respectively. terms are x and 2y respectively.
Dalam suatu janjang aritmetik, sebutan ke-3 dan ke-8 Dalam suatu janjang aritmetik, sebutan ke-2 dan ke-5
bi
masing-masing ialah –5 dan 15. masing-masing ialah x dan 2y.
T3 = a + (3 – 1)d = –5
T2 = a + d = x ………… 1
r
a + 2d = –5 ……… 1
T5 = a + 4d = 2y ………… 2
ne
T8 = a + (8 – 1)d = 15
2 – 1, 3d = 2y – x
a + 7d = 15 ……… 2
d = 2y – x
2 – 1, 5d = 20 3
Pe
d = 4
Substitute d = 4 into 1, Substitute d = 2y – x into 1,
3
a + 2(4) = –5 2y – x
a = –13 a + = x
3
\ The first term is –13 and the common a = x – 2y – x
difference is 4. 3
= 4x – 2y
3
\ The first term is 4x – 2y and the common
3
difference is 2y – x .
3
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 66
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
4. Find the number of terms for each of the following arithmetic progressions. PL 4
Cari bilangan sebutan bagi setiap janjang aritmetik berikut.
Example (a) –7, 3, 13, …, 93 (b) 4p, 11p, 18p, …, 67p
43, 31, 19, …, –29
a = –7, a = 4p,
a = 43, d = 3 – (–7) = 10, d = 11p – 4p = 7p,
d = 31 – 43 = –12, Tn = 93 Tn = 67p
Tn = –29
93 = –7 + (n – 1)(10) 67p = 4p + (n – 1)(7p)
Tn = a + (n – 1)d n = 93 + 7 + 1 n = 67p – 4p + 1
–29 = 43 + (n – 1)(–12) 10 7p
= 11 = 10
n = –29 – 43 + 1
d.
–12
= 7
Bh
5. Each of the following shows three consecutive terms of an arithmetic progression. Find the value of p. PL 5
.
dn
Setiap yang berikut menunjukkan tiga sebutan berturutan dalam suatu janjang aritmetik. Cari nilai p.
Example (a) …, 2p, 4p + 9, 3p + 15, … (b) …, 2p – 1, 4p, 5p + 4, …
…, p + 4, 3p, 3p + 8, …
S
4p + 9 = (2p) + (3p + 15) 4p = (2p – 1) + (5p + 4)
2 2
3p = (p + 4) + (3p + 8)
2
gi
8p + 18 = 5p + 15 8p = 7p + 3
6p = 4p + 12 T + Tn + 1 3p = –3 p = 3
Tn = n – 1 ,
2 p = –1
an
2p = 12
Tn is known as the
p=6 arithmetic mean of
Tn – 1 and Tn + 1
l
Pe
6. Solve the following problems. PL 5
Selesaikan masalah berikut.
n
Example (a) Given 51 and 33 are the 2nd and 5th terms of
ta
–35, –31, –27, … are the first three terms in an an arithmetic progression respectively. Find
arithmetic progression. Find the smallest value of n the smallest value of n such that the nth term is
negative. Hence determine the term.
bi
such that the nth term is positive. Hence, determine
the term. Diberi 51 dan 33 masing-masing ialah sebutan ke-2 dan
–35, –31, –27, … ialah tiga sebutan pertama dalam suatu ke-5 bagi suatu janjang aritmetik. Cari nilai n yang terkecil
r
janjang aritmetik. Cari nilai n yang terkecil dengan keadaan dengan keadaan sebutan ke-n adalah negatif. Seterusnya,
ne
sebutan ke-n adalah positif. Seterusnya, tentukan sebutan ini. tentukan sebutan ini.
a = –35, d = –31 – (–35) = 4 and Tn . 0 (positive) a + d = 51 ……… 1
a + 4d = 33 ……… 2
Pe
Tn = a + (n – 1)d . 0 2 – 1, 3d = –18
–35 + (n – 1)(4) . 0 d = –6
(n – 1)(4) . 35
Substitute d = –6 into 1,
(n – 1) . 35 a + (–6) = 51
4
a = 57
n . 8.75 + 1
n . 9.75 Tn = a + (n – 1)d , 0
\ n = 10 57 + (n – 1)(–6) , 0
57 – 6n + 6 , 0
T10 = –35 + (10 – 1)(4) 6n . 63
=1 n . 10.5
\ n = 11
T11 = 57 + (11 – 1)(–6) = –3
67 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
7. Find the sum of the first n terms for each of the following arithmetic progressions. PL 3
Cari hasil tambah n sebutan pertama bagi setiap janjang aritmetik berikut.
Example
1, 6, 11, 16, … (the first 12 terms)
(12 sebutan pertama)
1
Sn = [2a + (n – 1)d]
a = 1, d = 6 – 1 = 5 2
Sn = n [2a + (n – 1)d]
where / dengan keadaan
2 Sn = sum of first nth terms / hasil tambah n sebutan pertama
a = first term / sebutan pertama
S12 = 12 [2(1) + (12 – 1)(5)]
1 2 d = common difference / beza sepunya
2
= 342
d.
(a) 4, 6, 8, 10, … (the first 10 terms) (b) –23, –16, –9, –2, … (the first 14 terms)
Bh
(10 sebutan pertama) (14 sebutan pertama)
a = 4, d = 6 – 4 = 2 a = –23, d = –16 – (–23) = 7
S10 = 10 [2(4) + (10 – 1)(2)]
1 2 S14 = 14 [2(–23) + (14 – 1)(7)]
1 2
.
2 2
dn
= 130 = 315
(c) 23, 17, 11, 5, … (the first 16 terms)
S (d) –15, –12, –9, –6, … (the first 15 terms)
gi
(16 sebutan pertama) (15 sebutan pertama)
a = 23, d = 17 – 23 = –6 a = –15, d = –12 – (–15) = 3
an
S16 = 16 [2(23) + (16 – 1)(–6)]
1 2 S15 = 15 [2(–15) + (15 – 1)(3)]
1 2
2 2
l
= –352 = 90
Pe
n
8. Find the sum of the terms in each of the following arithmetic progressions. PL 4
ta
Cari hasil tambah sebutan dalam setiap janjang aritmetik berikut.
Example
bi
2, –3, –8, …, –38
Use Sn = n [a + l ]
S9 = 9 [2 + (–38)]
r
a = 2, d = –3 – 2 = –5, Tn = –38 2
2 where l = last term
ne
–38 = 2 + (n – 1)(–5) To determine the number of = –162
terms, use Tn = a + (n – 1)d.
n = –38 – 2 + 1
–5
Pe
=9
(a) 15, 23, 31, 39, …, 255 (b) –52, –48, –44, …, 0
a = 15, d = 23 – 15 = 8, Tn = 255 a = –52, d = –48 – (–52) = 4, Tn = 0
255 = 15 + (n – 1)(8) 0 = –52 + (n – 1)(4)
n = 255 – 15 + 1 n = 0 + 52 + 1
8 4
= 31 = 14
S31 = 31 [15 + 255] S14 = 14 [–52 + 0]
2 2
= 4 185 = –364
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 68
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
9. The sequence –22, –14, –6, … is an arithmetic progression. Find the sum from the PL 4
Jujukan –22, –14, –6, … ialah suatu janjang aritmetik. Cari hasil tambah dari
Example
2 term to 8th term
nd
sebutan ke-2 hingga sebutan ke-8
a = –22, d = –14 – (–22) = 8 S8 = T1 + T2 + T3 + T4 + T5 + T6 + T7 + T8
S1 = T1
S8 = 8 [2(–22) + (8 – 1)(8)] = 48 ‘From 2nd term to 8th term’ means T2 is
2 included in the calculation, so
S1 = –22 ‘Dari sebutan ke-2 hingga sebutan ke-8’
bererti T2 diambil kira dalam pengiraan, jadi
The sum from the 2 term to 8 term
nd th
S2 → 8 = T2 + T3 + T4 + T5 + T6 + T7 + T8
= S8 – S1 Sm → n = Sn – Sm – 1 = S8 – S2 – 1
d.
= 48 – (–22)
= 70
Bh
(a) 3rd term to 10th term (b) 5th term to 15th term (c) 20th term to 40th term
sebutan ke-3 hingga sebutan ke-10 sebutan ke-5 hingga sebutan ke-15 sebutan ke-20 hingga sebutan ke-40
S10 = 10 [2(–22) + (10 – 1)(8)] S15 = 15 [2(–22) + (15 – 1)(8)] S40 = 40 [2(–22) + (40 – 1)(8)]
dn
2 2 2
= 140 = 510 = 5 360
S2 = T1 + T2
= –22 + (–14) S4 = 4 [2(–22) + (4 – 1)(8)] S19 = 19 [2(–22) + (19 – 1)(8)]
S
2 2
= –36 = –40 = 950
S3 → 10 = S10 – S2
gi
S5 → 15 = S15 – S4 S20 → 40 = S40 – S19
= 140 – (–36)
= 510 – (–40) = 5 360 – 950
= 176
= 550
an
= 4 410
l
10. For each of the following arithmetic progressions, the sum of the first n terms is given in the bracket. Find the
Pe
value of n. PL 4
Bagi setiap janjang aritmetik yang berikut, hasil tambah sebutan n pertama diberikan dalam kurungan. Cari nilai n.
Example (a) 21, 15, 9, … [21]
n
12, 18, 24, … [390]
ta
a = 21, d = 15 – 21 = –6, Sn = 21
a = 12, d = 18 – 12 = 6, Sn = 390 Sn = n [2(21) + (n – 1)(–6)] = 21
2
bi
Sn = n [2(12) + (n – 1)(6)] = 390 n (48 – 6n) = 21
2 n (18 + 6n) = 390 2
24n – 3n2 – 21 = 0
r
2
9n + 3n2 – 390 = 0 n2 – 8n + 7 = 0
ne
n2 + 3n – 130 = 0 (n – 1)(n – 7) = 0
(n + 13)(n – 10) = 0 \ n ≠ 1, n = 7
\ n ≠ –13, n = 10
Pe
(b) –36, –32, –28, … [–168] (c) –10, –15, –20, … [–595]
a = –36, d = –32 – (–36) = 4, Sn = –168 a = –10, d = –15 – (–10) = –5, Sn = –595
Sn = n [2(–36) + (n – 1)(4)] = –168 Sn = n [2(–10) + (n – 1)(–5)] = –595
2 n (–76 + 4n) = –168 2 n (–15 – 5n) = –595
2 2
–38n + 2n2 + 168 = 0
– n – 5 n2 + 595 = 0
15
n2 –19n + 84 = 0 2 2
(n – 12)(n – 7) = 0 n2 + 3n – 238 = 0
\ n = 12 or n = 7 (n – 14)(n + 17) = 0
\ n ≠ –17, n = 14
69 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
11. Solve each of the following. PL 5
Selesaikan setiap yang berikut.
Example (a) The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic
The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progression is given by Sn = 1 + 4n2. Find the 11th
progression is given by Sn = 3 – 8n. Find the first term term.
and the common difference. Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama suatu janjang aritmetik
Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama suatu janjang aritmetik diberi diberi oleh Sn = 1 + 4n2. Cari sebutan ke-11.
oleh Sn = 3 – 8n. Cari sebutan pertama dan beza sepunya.
S10 = 1 + 4(10)2 T11 = S11 – S10
a = T1 = S1 = 3 – 8(1) = –5 = 401 = 485 – 401
= 84
Tn = Sn – Sn – 1 d = T2 – T1 S11 = 1 + 4(11)2
= 485
d.
T2 = S2 – S1 = –8 – (–5)
= [3 – 8(2)] – (–5) = –3
= –8
Bh
(b) The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic (c) The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic
progression is given by Sn = 2 – 5n + n2. Find the progression is given by Sn = 4n – n2. Find Tn – 1 in
.
5 term and the common difference.
th
terms of n. HOTS Applying
dn
Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama suatu janjang aritmetik Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama suatu janjang aritmetik
diberi oleh Sn = 2 – 5n + n2. Cari sebutan ke-5 dan beza diberi oleh Sn = 4n – n2. Cari Tn – 1 dalam sebutan n.
sepunya.
S
Sn – 1 = 4(n – 1) – (n – 1)2
S5 = 2 – 5(5) + (5)2 = 2 = (n – 1)(4 – n + 1)
gi
S4 = 2 – 5(4) + (4)2 = –2 = (n – 1)(5 – n)
\ T5 = S5 – S4 = 2 – (–2) = 4 Sn – 2 = 4(n – 2) – (n – 2)2
= (n – 2)(4 – n + 2)
an
S6 = 2 – 5(6) + (6)2 = 8 = (n – 2)(6 – n)
T6 = S6 – S5 = 8 – 2 = 6
Tn – 1 = Sn – 1 – Sn – 2
\ d = T6 – T5 = 6 – 4 = 2
l
= (n – 1)(5 – n) – (n – 2)(6 – n)
Pe
= (5n – n2 – 5 + n) – (6n – n2 – 12 + 2n)
= 7 – 2n
n
ta
12. Solve each of the following. PL 5 Daily Application
bi
Selesaikan setiap yang berikut.
Example
r
ne
Chong borrows RM8 000 from a financial institution and promises to return the amount borrowed in 12
instalments with a total interest of RM400. The payment of the instalments is such that every subsequent
instalment is RM50 more than the previous one. How much is the starting and last instalments?
Pe
Chong meminjam sejumlah RM8 000 daripada sebuah institusi kewangan dan berjanji akan membayar balik dalam 12 ansuran
dengan faedah sejumlah RM400. Pembayaran ansuran dibuat dengan keadaan setiap ansuran berikut adalah RM50 lebih daripada
ansuran sebelumnya. Berapakah bayaran ansuran pertama dan terakhir? HOTS Applying
S12 = 8 000 + 400 = 8 400, Total to pay
n = 12, d = 50 = Amount borrowed
+ interest incurred T12 = 425 + (12 – 1)(50)
8 400 = 12 [2a + (12 – 1)(50)] = 975
2
1 400 = 2a + 550 Hence, the last instalment is RM975.
2a = 850
a = 425
Hence, the first instalment is RM425.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 70
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
(a) Supermarket A displays the can drinks in the form of a pyramid. 41 cans in the bottom-most row, 37
cans in the next row, followed by 33 cans and so on for the rows above the previous row. HOTS Analysing
Pasar Raya A menyusunkan minumum tin dalam bentuk piramid. 41 tin berada pada baris terbawah, 37 tin berada pada baris
seterusnya diikuti dengan 33 tin dan seterusnya dengan corak yang sama bagi baris yang seterusnya.
(i) Find the number of cans at the 8th row./ Cari bilangan tin pada baris ke-8.
(ii) How many rows are there, if there is 25 cans on the topmost row?
Berapakah bilangan baris yang ada, jika terdapat 25 tin pada baris teratas?
(iii) If the process carried on, determine/ Jika proses diteruskan, tentukan
(a) the number of possible rows, / bilangan baris yang mungkin,
(b) the number of cans on the topmost row, / bilangan tin pada baris teratas,
(c) the total number of cans in the display. / jumlah bilangan tin dalam susunan itu.
41, 37, 33, … (iii) (a) Tn . 0
a = 41, d = 37 – 41 = –4 41 + (n – 1)(–4) . 0
d.
(i) T8 = 41 + (8 – 1)(–4) 4n , 45
= 13 n , 11.25
Bh
\ 11 rows are possible.
(ii) Tn = 25
(b)
T11 = 41 + (11 – 1)(–4)
41 + (n – 1)(–4) = 25
=1
4n = 20
.
n = 5 S11 = 11 (41 + 1)
dn
(c)
\ 5 rows 2
= 231
Geometric Progressions
S
gi
5.2 Janjang Geometri Textbook
pg. 139 – 149
an
SMART Notes
l
Pe
1. Geometric progression (GP) is a sequence of or/ atau
numbers such that each term after the first is obtained a(1 – r n)
by multiplying the previous one by a constant called Sn = ,r,1
1–r
common ratio, r.
n
Janjang geometri (JG) ialah suatu jujukan nombor dengan
keadaan setiap sebutan selepas sebutan pertama diperoleh
ta
dengan mendarab sebutan sebelumnya dengan suatu pemalar, a(rn – 1)
Sn = , r . 1
iaitu nisbah sepunya, r. r–1
If r , 1, then r n – 1 , 0 as r n , 1.
Term/ Sebutan T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
bi
Jika r , 1, maka r n – 1 , 0 kerana r n , 1.
Sequence/ Jujukan 2 , 6 , 18 , 54 , 162 , … Sn =
–a(r n – 1)
=
a(1 – r n)
–(r – 1) 1–r
r
Common ratio of the above sequence:
ne
Nisbah sepunya bagi jujukan di atas:
4. The nth term, Tn, of a geometric progression can also be
T T T T found using Sn – Sn – 1.
r = 2 = 3 = 4 = 5 = …
T1 T2 T3 T4 Sebutan ke-n, Tn, bagi suatu janjang geometri juga dapat dicari
= 3 dengan menggunakan Sn – Sn – 1.
Pe
2. The nth term, Tn, of a geometric progression is 5. In a geometric progression where –1 , r , 1, as n
Sebutan ke-n, Tn, bagi suatu janjang geometri ialah approaches infinity (n → ∞), rn approaches zero (r n → 0),
thus 1 – r n ≈ 1. So, when –1 , r , 1 and as n increases
Tn = arn – 1 without limit, the sum to infinity is
where a = first term, r = common ratio Dalam suatu janjang geometri dengan –1 , r , 1, apabila n
dengan keadaan a = sebutan pertama, d = nisbah sepunya mendekati infiniti (n → ∞), r n mendekati sifar (r n → 0), maka
1 – r n ≈ 1. Jadi, apabila –1 , r , 1 dan n bertambah tanpa had,
3. The sum of the first n terms, S n , of a geometric hasil tambah hingga ketakterhinggaan ialah
progression is
Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama, S n, bagi suatu janjang a
Sn =
geometri ialah 1–r
a(r n – 1)
Sn = ,r.1
r–1
71 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
13. Determine whether each of the following sequences is a geometric progression. Give your justification. PL 1
Tentukan sama ada setiap jujukan yang berikut ialah janjang geometri atau bukan. Berikan justifikasi anda.
Example (a) 1, –3, 9, –27, …
x – 2k, 2x – 4k, 4x – 8k, 8x – 16k, … r1 = –27 = –3
9
r1 = 2x – 4k = 2(x – 2k) = 2
x – 2k x – 2k r2 = 9 = –3
4x – 8k 4(x – 2k) = 2 –3
r2 = =
2x – 4k 2(x – 2k) r3 = –3 = –3
1
r3 = 8x – 16k = 8(x – 2k) = 2 A geometric progression because r1 = r2 = r3 = –3.
4x – 8k 4(x – 2k)
A geometric progression because r1 = r2 = r3 = 2.
d.
(b) 20, 2x, 2x + 1, 2x + 2, … (c) loga x, loga x2, loga x3, loga x 4, …
r1 = 20 = 2 = 2x loga x 4 4 loga x
x x
= 4
Bh
r1 = =
2 1 loga x 3 3 loga x 3
2 x+1
(2 x
)(2) loga x 3
3 loga x
r2 = x =
2 2x
=2 r2 = = = 3
loga x 2 2 loga x 2
.
2 x+2
r3 = x + 1 = (2 x
)(22
) =2 loga x 2
2 loga x
dn
2 (2x)(2) r3 = = =2
loga x loga x
Not a geometric progression because r1 ≠ r2 and
r1 ≠ r3. Not a geometric progression because r1 ≠ r2 ≠ r3.
S
gi
14. For each of the following geometric progressions, determine the common ratio. PL 2
Bagi setiap janjang geometri berikut, tentukan nisbah sepunya.
an
Example (a) 2k, 6k2, 18k3, 54k4, …
–3, 12, –48, 192, …
l
12 –48 192
r = 6k = 3k
2
r= = = = – 4
Pe
–3 12 –48
r = 12 = –4 2k
–3
1 1 1
(b) 2 , – 2 , 2 , – 2 , … (c) e8x, e6x, e4x, e2x, … x x x
(d) ln p x, ln p 2 , ln p 4 , ln p 8 , …
3 9 27 81
n
r = e8x = e6x – 8x = e–2x
6x
1 x (ln p)
r=– ÷ =– 1
2 2 1
x
1 2
ta
ln p 2
= 2 = 1
9 3 3 e
r=
ln px x ln p 2
bi
15. For each of the following geometric progressions, determine the term stated in bracket. PL 3
r
Bagi setiap janjang geometri berikut, tentukan sebutan yang dinyatakan dalam kurungan.
ne
Example
(a) 1 , –1, 4, … (b) 2 , 1, 3 , …
1 , 2 , 4 , … 4 3 2
3 15 75 [5th term/ sebutan ke-5] [9th term/ sebutan ke-9]
Pe
[5th term/ sebutan ke-5] a = 1 , r = –1 ÷ 1 = – 4
4 4 a = 2, r = 1 ÷ 2 = 3
a = 1, r = 2 ÷ 1 = 2 1
3 3 2
3 15 3 5 T5 =
4 1 2
(–4)4 = 64
2 3
1 21 2 = 2 187
8
T5 = ar5 – 1 = 1 2 = 16
1 21 2 T9 =
4
3 5 1 875 3 2 128
(c) 1, 52x, 54x, … (d) 2, –4k2, 8k4, … (e) p, p , p , …
2 3
[8th term/ sebutan ke-8] [7th term/ sebutan ke-7] 5 25
[6th term/ sebutan ke-6]
a = 1, r = 52x
a = 2, r = –4k = –2k2
2
a = p, r = p ÷ p = p
2
T8 = (1)(52x)7 = 514x 2 5 5
p p 6
1 2
5
T7 = (2)(–2k2)6 = 128k12 T6 = (p) =
5 3 125
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 72
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
16. Find the number of terms for each of the following geometric progressions. PL 4
Cari bilangan sebutan bagi setiap janjang geometri berikut.
Example
Alternative Method
12, 4, 4 , …, 4 1 = 1 n – 1
3 243
729 1 2 3
a = 12, r = 4 = 1 , Tn = 4 1 = log10 1 1 2
n–1
12 3 243 log10
729 3
Tn = ar n – 1
log10 1 = (n – 1) log10 1
1 2
4 = 12 1 1 2
n–1
729 3
243 3 1
log10
1 1
1 2
n–1
= 729
n – 1 = =6
729 3
log10 1
d.
6
3
1 = 1
1 2 1 2
n–1
3 3 \ n = 7
Bh
n = 7
(a) 20, – 4, 4 , …, – 4 (b) 18, 27, 81 , …, 2 187 (c) –12, 24, –48, …, –3 072
5 15 625 2 16
.
a = 20, a = 18, a = –12,
dn
r = – 4 = – 1 , r = 27 = 3 , r = 24 = –2,
20 5 18 2 –12
Tn = – 4 Tn = – 2 187 Tn = –3 072
S
15 625 16
–3 072 = (–12)(–2)n – 1
4 = 20 – 1 n – 1 2 187 = 18 3
1 2 1 2
n–1
– 256 = (–2)n – 1
15 625 5 16
gi 2
(–2)8 = (–2)n – 1
1 1 243 3
1 2 1 2
n–1 n–1
– = – = n = 9
78 125 5 32 2
an
1 = – 1 3 = 3
1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2
n–1 5 n–1
– 7
5 5 2 2
n = 8 n = 6
l
Pe
n
17. Each of the following shows some information of a geometric progression. Determine the first term and the
ta
common ratio of the geometric progression. PL 4
Setiap yang berikut menunjukkan maklumat suatu janjang geometri. Tentukan sebutan pertama dan nisbah sepunya janjang geometri
bi
tersebut.
Example (a) –48 and –12 are the 5th term and 7th term
r
respectively
ne
1 and –128 are the 2 term and 9 term respectively
nd th
1 dan –128 masing-masing ialah sebutan ke-2 dan ke-9 –48 dan –12 masing-masing ialah sebutan ke-5 dan ke-7
T5 = ar4 = –48 …… 1
Pe
Tn = arn – 1
T2 = ar = 1 …………… 1 T7 = ar6 = –12 …… 2
T9 = ar8 = –128 ……… 2 2 ÷ 1, r2 = 1
4
2 ÷ 1, r7 = –128 r = 1
r = –2 2
Substitute r = –2 into 1, Substitute r = 1 into 1,
a(–2) = 1 2
1
1 2
4
a = – 1 a
2
= –48
2 a = –768
\ The first term is – 1 and the common ratio is –2. \ The first term is –768 and the common ratio
2
is 1 .
2
73 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
(b) 32 is the fourth term and it is half of the first (c) 4x3 and –128x8 are the 3rd term and 8th term
term. respectively.
32 ialah sebutan ke-empat dan adalah separuh daripada 4x3 dan –128x8 masing-masing ialah sebutan ke-3 dan ke-8.
sebutan pertama.
T3 = ar2 = 4x3 …… 1
T4 = 1 a = 32 T8 = ar7 = –128x8 …… 2
2
a = 64
2 ÷ 1, r5 = –32x5
T4 = ar = 323
r = –2x
64r3 = 32 Substitute r = –2x into 1,
a(–2x)2 = 4x3
r3 = 1
2 a = x
1
\ The first term is x and the common ratio is
r = 1 3 1 2
d.
2 –2x.
\ The first term is 64 and the common ratio
Bh
1
is 1 3 . 1 2
2
.
18. Find the sum of the first n terms for each of the following geometric progressions. PL 3
dn
Cari hasil tambah n sebutan pertama bagi setiap janjang geometri berikut.
Example (a) 324, 216, 144, 96, … (b) 0.4, 1.6, 6.4, 25.6, …
S
3, –6, 12, –24, … (the first 5 terms) (the first 7 terms)
(the first 6 terms) (5 sebutan pertama) (7 sebutan pertama)
gi
(6 sebutan pertama)
a = 324, r = 216 = 2
a = 0.4, r = 1.6 = 4
r,1
324 3 r.1
a = 3, r = –6 = –2 r,1 0.4
an
3 Sn = a(1 – r n
)
Sn = a(rn
– 1)
a(1 – r n
) 1–r
Sn = r–1
324 1 – 2
3 1 24
5
1–r 0.4(4 7
– 1)
l
3 S7 =
S6 = 3[1 – (–2) ]
6
S5 = 4–1
Pe
1 – (–2) 1– 2 = 2 184.4
= –63 3
= 844
n
ta
19. Find the sum of the terms in each of the following geometric progressions. PL 4
Cari hasil tambah sebutan dalam setiap janjang geometri berikut.
bi
Example 1
(a) 27, 9, 3, …,
r
1, 5, 25, …, 78 125 6 561
ne
a = 27, r = 9 = 1 , Tn = 1
a = 1, r = 5, Tn = 78 125 27 3 6 561
To determine the number
Tn = ar n – 1 1 = 27 1 n – 1
of terms, use Tn = arn – 1
1 2
Pe
78 125 = 1(5)n – 1 6 561 3
1 1
1 2
n – 1
l og10 78 125 = (n – 1) log10 5 =
3 177 147
log10 78 125
n – 1 =
log10 5 (n – 1) log10 1 = log10 1
3 177 147
n – 1 = 7 n = 12
n = 8
27 1 – 1 3 1 2 4
12
Sn = a(r – 1)
n
Use this formula as
r–1 r=5.1 S12 = 3
1(58
– 1) 1– 1
S8 =
5–1 3
= 97 656 = 40.50
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 74
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
(b) 2, –1, 1 , …, 1 (c) – 4, 8, –16, …, 2 048
2 128
a = 2, r = – , Tn = 1
1 a = – 4, r = 8 = –2, Tn = 2 048
2 128 – 4
2 048 = (–4)(–2)n – 1
1 = 2 – 1 1 2
n – 1
(–2)n – 1 = –512
128 2 = (–2)9
1 1
1 2
n–1
– = n = 10
2 256
= – 1 1 2
8
S10 = – 4[1 – (–2) ]
10
2
1 – (–2)
n = 9
= 1 364
21– – 1 3 1 24
9
d.
S9 =
1– – 1 1 2
2
Bh
= 171
128
.
dn
20. Calculate the sum of specific number of consecutive terms in a geometric progression. PL 4
Hitung hasil tambah sebutan tertentu yang berturutan bagi suatu janjang geometri.
Example (a) Given the first term of a geometric progression is
S
Given the first term of a geometric progression is 1 –2 and its common ratio is 1 . Calculate the sum
3 4
and its common ratio is 1 . Calculate the sum from
gi from the 2nd term to 6th term.
the 3rd term to 8th term. 3 Diberi sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang geometri ialah
1 1
an
Diberi sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang geometri ialah dan –2 dan nisbah sepunya ialah . Hitung hasil tambah dari
3 4
1 sebutan ke-2 hingga sebutan ke-6.
nisbah sepunya ialah . Hitung hasil tambah dari sebutan ke-3
3
hingga sebutan ke-8.
l
a = –2, r = 1
a=r= 1
Pe
4
3 The sum from the 2nd term to 6th term
The sum from the 3rd term to 8th term = S6 – S1
= S8 – S2 Sm → n = Sn – Sm – 1
(–2) 1 – 1
n
3 1 24
6
1 1– 1 1 1– 1 4
3 1 24 3 1 24
8 2
= – (–2)
ta
1
= 3 3 – 3 3 1–
1 1 4
1– 1– 1 365
3
bi
3 =– – (–2)
3 280 512
= – 4
6 561 9 = – 341
r
512
= 364
ne
6 561
(b) Given the first term of a geometric progression (c) Given the first term of a geometric progression is
Pe
is 1 and its common ratio is 3. Calculate the sum 2 and its common ratio is –2. Calculate the sum
from the 4th term to 7th term. from the 3rd term to 7th term.
Diberi sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang geometri ialah Diberi sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang geometri ialah
1 dan nisbah sepunya ialah 3. Hitung hasil tambah dari 2 dan nisbah sepunya ialah –2. Hitung hasil tambah dari
sebutan ke-4 hingga sebutan ke-7. sebutan ke-3 hingga sebutan ke-7.
a = 1, r = 3 a = 2, r = –2
The sum from the 4th term to 7th term The sum from the 3rd term to 7th term
= S7 – S3 = S7 – (T1 + T2)
= 1(3 – 1) – 1(3 – 1)
7 3
= 2[1 – (–2) ] – [2 + 2(–2)]
7
3–1 3–1 1 – (–2)
= 1 093 – 13 = 86 – (–2)
= 1 080 = 88
75 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
21. For each of the following geometric progressions, determine the sum to infinity if exist. PL 3
Bagi setiap janjang geometri berikut, tentukan hasil tambah hingga ketakterhinggaan jika wujud.
Example
(ii) 18, 12, 8, …
(i) – 1 , –1, –2, …
2
a = – 1 , r = –1 ÷ – 1 = 2 . 1 a = 18, r = 12 = 2 , 1
2 2 1 2
18 3
Since r . 1, the sum to infinity cannot be Since r , 1, the sum to infinity can be
determined. determined.
S∞ = a
1–r
In a geometric progression, the sum to infinity can 18
be determined when –1 < r < 1. =
1– 2
d.
Dalam suatu janjang geometri, hasil tambah hingga
ketakterhinggan dapat ditentukan apabila –1 < r < 1. 3
= 54
Bh
(a) 8, –12, 18, … (b) –2, 1, 1 , …
2
a = 8, r = –12 = – 3 , –1 a = –2, r = – 1 . –1
.
8 2 2
dn
Since r < –1, the sum to infinity cannot be Since r . –1, the sum to infinity can be
determined. determined.
–2
S∞ = =– 4
S
1 3
1– – 12 2
gi
an
22. Find the sum to infinity for each of the following geometric progressions. PL 3
Cari hasil tambah hingga ketakterhinggaan bagi setiap janjang geometri yang berikut.
Example
(a) –5, 1, – 1 , … (b) 4, 2, 1, … (c) –8, – 4 , – 2 , …
l
Pe
5 5 25
3, 3 , 3 , …
2 4
a = –5, r = – 1 a = 4, r = 2 = 1 a = –8,
5 4 2
a = 3, r = 3 ÷ 3 = 1 –5 S∞ =
4 r = – 4 ÷ (–8) = 1
2 2 S∞ = 5 10
n
1– 1
3 1– – 1 1 2 –8 80
S∞ = a = =6 5
2 S∞ = =–
ta
1–r 1– 1 25 = 8 1– 1 9
2 = – 10
6
bi
23. Solve the following problems.
r
PL 4
ne
Selesaikan masalah berikut.
Example
The sum of the first two terms of a geometric progression is 9 and the sum to infinity is 8 . Find the possible
Pe
40 35
values of the first term and the common ratio of the geometric progression.
9 8
Hasil tambah dua sebutan pertama suatu janjang geometri ialah dan hasil tambah hingga ketakterhinggaan ialah . Cari nilai-
40 35
nilai yang mungkin bagi sebutan pertama dan nisbah sepunya janjang geometri tersebut.
a + ar = 9 1 ÷ 2, (1 + r)(1 – r) = 9 ÷ 8 Substitute the values of r into 1,
40 40 35
a= 9 ÷ 1+ 1 = 1
1 2
a(1 + r) = 9 …… 1 1 – r2 = 63 40 8 5
40 64
a = 8 …… 2 r = 1
2 a= 9 ÷ 1+ – 1 =
3 1 24 9
1 – r 35 64 40 8 35
\ r = 1 or r = – 1 \ r = 1 , a = 1 ; r = – 1, a = 9
8 8 8 5 8 35
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 76
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
(a) The sum of the first three terms of a geometric progression is – 13 and the sum to infinity is – 8 . Find
8 5
the first term and the common ratio of the geometric progression.
13 8
Hasil tambah tiga sebutan pertama suatu janjang geometri ialah – dan hasil tambah hingga ketakterhinggaan ialah – .
8 5
Cari sebutan pertama dan nisbah sepunya janjang geometri tersebut.
S3 = – 13 1 ÷ 2, (1 – r3) = – 13 ÷ – 8 1 2 Substitute r = – 1 into 2,
8 8 5 4
a(1 – r 3
) 13 65 a 8
= – …… 1 1 – r =
3 = –
5
1–r 8 64 1– – 1
1 2
a = – 8 …… 2 r = – 1
3 4
1–r 5 64 a = –2
\ r = – 1
4 \ r = – 1 , a = –2
4
d.
Bh
24. Express each of the following recurring decimals as a fraction in its simplest form. PL 4
Ungkapkan setiap perpuluhan berulang berikut sebagai satu pecahan dalam bentuk yang paling ringkas.
Example
.
dn
0.727272… Alternative Method
= 0.72 + 0.0072 + 0.000072 + …
Let/ Katakan x = 0.727272… …… 1
= 0.72 Use S∞ = a
S
1 × 100, 100x = 72.7272… …… 2
1 – 0.01 1–r
0.72 a = 0.72, r = 0.01 2 – 1, 99x = 72
=
0.99
gi x = 8
11
= 8
an
11
(a) 0.222… (b) 0.00931931931… (c) 3.0111…
= 0.2 + 0.02 + 0.002 + … = 0.00931 + 0.00000931 = 3 + (0.01 + 0.001
l
Pe
= 0.2 + 0.00000000931 + … + 0.0001 + …)
1 – 0.1
= 0.00931 = 3 + 0.01
= 0.2 1 – 0.001 1 – 0.1
0.9 0.00931 0.01
n
= =3+
= 2 0.999 0.9
ta
9
= 931 = 3 or 271
1
99 900 90 90
r bi
25. Solve each of the following. PL 5 Daily Application
ne
Selesaikan setiap yang berikut.
Example
The value of a new car is RM50 000. If the value of the car depreciates 5% each year, find HOTS Analysing
Pe
Nilai sebuah kereta baru ialah RM50 000. Jika nilai kereta itu menyusut 5% setiap tahun, cari
(i) the value of the car in the 8th year, / nilai kereta itu pada tahun ke-8,
(ii) the number of years when the value of the car is / bilangan tahun apabila nilai kereta itu ialah
(a) RM30 000
(b) half of the original price / separuh daripada nilai asalnya
a = 50 000, (ii) (a) Tn = 30 000 (ii) (b) Tn = 50 000 ÷ 2
r = 1 – 0.05 = 0.95 50 000(0.95) = 30 000
n–1 50 000(0.95)n – 1 = 25 000
(i) T8 = 50 000(0.95)8 – 1 (0.95)n – 1 = 0.6 (0.95)n – 1 = 0.5
= RM34 916.86 log10 0.6 log10 0.5
n – 1 = n – 1 =
log10 0.95 log10 0.95
= 9.96 = 13.5
n = 10.96 years n = 14.5 years
77 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
(a) Faiz joined a new company in the year 2018 and he was offered an annual salary of RM36 000 for the
year 2018 with an increase of 7% yearly thereafter. HOTS Analysing
Faiz menyertai sebuah syarikat baru pada tahun 2018 dan ditawarkan gaji tahunan RM36 000 bagi tahun 2018 dengan
kenaikan 7% setiap tahun berikutnya.
(i) Determine his annual salary in the 5th year.
Tentukan gaji tahunannya pada tahun ke-5.
(ii) In which year he will start receive a monthly salary of more than RM4 200?
Pada tahun yang keberapa dia akan mula menerima gaji bulanan yang lebih daripada RM4 200?
(iii) If he saves 10% of his annual salary every year, how much is the savings after 10 years in the
company?
Jika dia menyimpan 10% daripada gaji tahunannya setiap tahun, berapakah simpanannya selepas berkhidmat 10 tahun
dengan syarikat tersebut?
d.
a = 36 000, r = 1 + 0.07 = 1.07 (iii) Annual salary: 36 000, 38 520, 41 216.40, …
(i) T5 = 36 000(1.07)4 Savings: 3 600, 3 852, 4 121.64, …
Bh
= RM47 188.66 r = 1.07, a = 3 600, n = 10
S10 = 3 600(1.07 – 1)
10
(ii) Tn = 12 × RM4 200 = RM50 400
36 000(1.07)n – 1 . 50 400 1.07 – 1
(1.07)n – 1 . 1.4 = RM49 739.21
.
dn
log10 1.4
n – 1 .
log10 1.07
n – 1 . 4.97
S
n . 5.97
\ in the 6th year
gi
an
(b) A ball is dropped from a tall building of height 100 m. Each time it hits the ground, it bounces 95% of
the previous height. HOTS Analysing
l
Sebiji bola dijatuhkan daripada sebuah bangunan yang setinggi 100 m. Setiap kali menyentuh tanah, bola itu akan melantun
Pe
95% daripada ketinggian sebelumnya.
(i) What is the height, in m, of the ball after the 5th bounce?
Berapakah ketinggian, dalam m, bola itu selepas lantunan ke-5?
(ii) After which bounce the height of the ball is less than 37 m?
n
Selepas lantunan yang keberapa ketinggian bola itu kurang daripada 37 m?
ta
(iii) Find the total distance covered, in m, when the ball stops to bounce.
Cari jumlah jarak yang dilalui, dalam m, apabila lantunan berhenti.
bi
a = 100 × 0.95 = 95, r = 0.95 (iii) S∞ = 95
1 – 0.95
r
(i) T5 = 95(0.95) 4
= 1 900
ne
= 77.38 m
Total distance covered
(ii) Tn , 37
= 2(1 900) + 100
Pe
95(0.95)n – 1 , 37
= 3 900 m
(0.95)n – 1 , 37
95
(n – 1)(log10 0.95) , log10 37 1 2
95
log10 37 1 2
n – 1 . 95
log10 0.95
n – 1 . 18.38
n . 19.38
\ after the 20th bounce
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 78
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
SPM Practice 5
6. Mat took 5 minutes to complete the first kilometre of 10 km
Paper 1 SPM
2016
run. He could not sustain his stamina for each subsequent
1
kilometre, he took more time compared to the time
1. It is given 4, 8, a, b and c are five consecutive terms of a 8
SPM geometric progression. he took for the previous kilometre. The participants who
2015
Diberi 4, 8, a, b dan c adalah lima sebutan berturutan suatu finished the run more than two hours are not qualified for
the state level run. Did Mat qualified? Show calculation to
janjang geometri. Cari nilai c.
support your answer.
[2]
Ans: c = 64 Mat mengambil masa 5 minit untuk menghabiskan kilometer
pertama dalam suatu acara larian 10 km. Dia tidak dapat
d.
2. In an arithmetic progression, the sum of the first four terms mengekalkan staminanya bagi setiap kilometer berikutnya, dia
SPM is 2 and the sixth term is –10. Find the first term and the mengambil 1 lebih masa berbanding dengan masa yang diambil
8
Bh
2015
common difference of the progression. untuk kilometer sebelumnya. Peserta-peserta yang menamatkan
Dalam suatu janjang aritmetik, hasil tambah empat sebutan larian melebihi dua jam tidak layak untuk acara larian peringkat
pertama ialah 2 dan sebutan keenam ialah –10. Cari sebutan negeri. Adakah Mat layak? Tunjukkan kiraan untuk menyokong
pertama dan beza sepunya janjang itu.
jawapan anda.
.
[3]
dn
[4]
Ans: a = 5, d = –3
Ans: Mat qualified for the state level run.
x–2
3. It is given that (x – 1), (7 – 2x) and 1 2
are three 7. It is given that the nth term of a geometric progression is
S
2
SPM SPM 5r n – 1
2016 consecutive terms of a geometric progression with a Tn = , r ≠ k. State
1
2017
4
common ratio of . Find
2
gi Diberi bahawa sebutan ke-n bagi suatu janjang geometri ialah
Tn = 5r , r ≠ k. Nyatakan
n–1
Diberi bahawa (x – 1), (7 – 2x) dan x – 2 ialah tiga sebutan
1 2 4
2
an
berturutan bagi suatu janjang geometri dengan nisbah sepunya (a) the value of k,
1 . Cari nilai k,
2 (b) the first term of the progression.
l
(a) the value of x, sebutan pertama bagi janjang itu.
Pe
nilai x, [2]
(b) the first term if (x – 1) is the 5th term of the Ans: (a) k = 1
progression.
5
(b)
sebutan pertama jika (x – 1) ialah sebutan ke-5 janjang itu. 4
n
[4]
ta
Ans: (a) x = 3 (b) 32
8. It is given that the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic
SPM n
4. It is given that m, 3 and n are the first three terms of a progression is Sn = [15 – 7n]. Find the nth term.
2017
2
bi
SPM geometric progression. Express in terms of n Diberi bahawa hasil tambah n sebutan pertama bagi suatu
2018
Diberi bahawa m, 3 dan n ialah tiga sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang aritmetik ialah Sn = n [15 – 7n]. Cari sebutan ke-n.
r
janjang geometri. Ungkapkan dalam sebutan n 2
[3]
ne
(a) the first term and the common ratio of the progression, Ans: 11 – 7n
sebutan pertama dan nisbah sepunya janjang itu,
(b) the sum to infinity of the progression. 9. The nth term of an arithmetic progression, Tn, is given by
Pe
hasil tambah sebutan hingga ketakterhinggaan janjang itu. 1
Tn = (6 + 5n). Find
[4] 3
9 n 27 Sebutan ke-n suatu janjang aritmetik, Tn, diberi oleh
Ans: (a) a = , r = (b)
n 3 n(3 – n) Tn = 1 (6 + 5n). Cari
3
5. A circle is divided to 5 sectors in such a way that the angles (a) the 15th term,
of the sectors are in an arithmetic progression. Given that sebutan ke-15,
the angle of the largest sector is 9 times the angle of the (b) the common difference.
smallest sector, find the angle of the largest sector. beza sepunya.
Suatu bulatan dibahagikan kepada 5 sektor dengan keadaan [4]
sudut-sudut bagi kesemua sektor adalah suatu janjang aritmetik. Ans: (a) 27
Diberi bahawa sudut sektor terbesar adalah 9 kali sudut sektor 5
(b)
terkecil, cari sudut sektor terbesar. 3
[3]
Ans: 129.6°
79 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
10. In an arithmetic progression, the 3rd term and the 17th term (c) the value of r, given that the rth term is the first
are 22 and –20 respectively. Find the 8th term. positive term of the progression.
Dalam suatu janjang aritmetik, sebutan ke-3 dan sebutan ke-17 nilai r, diberi bahawa sebutan ke-r adalah sebutan positif
masing-masing ialah 22 dan –20. Cari sebutan ke-8. pertama bagi janjang itu.
[3] [2]
Ans: 7 Ans: (a) –315
(b) a = –45, d = 3
(c) r = 17
11. Su has a wire with a length of 10.12 m. Su divided the wire
SPM into several pieces of different lengths. Each piece is bent
2018 3. At a certain day, a breeder has 3 500 chickens in his farm. He
to form a square. The diagram shows the first three squares SPM delivers 300 chickens every day to a wholesaler. The breeder
formed by Su. 2015
feeds the chickens before delivering. If the cost to feed a
Su mempunyai seutas dawai dengan panjang 10.12 m. Su chicken is RM0.50 per day, calculate the total cost until his
membahagikan dawai itu kepada beberapa bahagian yang
d.
remaining chickens are 500.
berlainan panjangnya. Setiap bahagian dibengkokkan untuk Pada suatu hari yang tertentu, seorang penternak mempunyai
membentuk satu segi empat sama. Rajah di bawah menunjukkan 3 500 ekor ayam di ladangnya. Dia menghantar 300 ekor
Bh
tiga segi empat sama yang pertama yang dibentuk oleh Su. ayam setiap hari kepada seorang pemborong. Penternak itu
11 cm akan memberi makan dahulu kepada ayamnya sebelum
penghantarannya. Jika kos memberi makan seekor ayam ialah
7 cm
RM0.50 sehari, hitung jumlah kos sehingga bilangan ayamnya
.
11 cm
dn
3 cm
berbaki 500 ekor.
7 cm
3 cm
[6]
Ans: RM11 000
S
How many squares can be formed by Su?
Berapa buah segi empat sama yang boleh dibentuk oleh Su? 4. The diagram shows part of a rectangular wall painted red,
gi
[3] SPM R, black, B and yellow, Y and so on in that order. The height
Ans: 11 2017
of the wall is 1.6 m. The side length of the first coloured
an
rectangle is 5 cm and the side length of each subsequent
coloured rectangle increases by 2 cm.
Paper 2 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan sebahagian daripada dinding
berbentuk segi empat tepat yang dicat dengan warna merah,
l
Pe
1. Given an arithmetic progression. R, hitam, B dan kuning, Y secara berselang seli. Tinggi dinding
Diberi suatu janjang aritmetik: ialah 1.6 m. Panjang sisi segi empat tepat berwarna yang
–12, –15, –18, … pertama ialah 5 cm dan panjang sisi bagi setiap segi empat tepat
(a) State the first term and the common difference. berwarna yang berikutnya bertambah sebanyak 2 cm.
n
Nyatakan sebutan pertama dan beza sepunya.
ta
[2]
(b) Find the sum of R B Y R B Y R
Cari hasil tambah bagi
bi
(i) the first six terms, / enam sebutan pertama,
(ii) the first seven terms, / tujuh sebutan pertama. It is given that the total number of the coloured rectangles
r
[4] is 48.
ne
(c) Use the answer in (b), find the 7th term. Diberi jumlah bilangan segi empat tepat berwarna ialah 48.
Gunakan jawapan dalam (b), cari sebutan ke-7. (a) Find/ Cari
[1]
Ans: (a) a = –12, d = –3 (i) the side length, in cm, of the last coloured
Pe
(b) (i) –117; (ii) –147 rectangle,
(c) –30 panjang sisi, dalam cm, bagi segi empat tepat
berwarna yang terakhir,
(ii) the total length, in cm, of the painted wall.
2. The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progression, Sn jumlah panjang, dalam cm, dinding yang dicat.
SPM 3n(n – 31)
is given by Sn = . Find [4]
2018
2
Hasil tambah n sebutan pertama bagi suatu janjang aritmetik, (b) Which coloured rectangle has an area of 14 880 cm2?
Sn diberi oleh Sn = 3n(n – 31) . Cari Hence, state the colour of that particular rectangle.
2 Segi empat tepat berwarna yang keberapa mempunyai
(a) the sum of the first 10 terms, keluasan 14 880 cm2? Seterusnya, nyatakan warna bagi
hasil tambah 10 sebutan pertama, segi empat tepat berkenaan.
[1]
(b) the first term and the common difference, [3]
sebutan pertama dan beza sepunya, Ans: (a) (i) 99 cm; (ii) 2 496 cm
[3] (b) 45th, yellow
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 80
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Chapter 5 Progressions
5. A total amount of RM74 477.00 will be given away in (c) How much the 6th lucky participant will receive?
cash in a lucky draw event. The first lucky participant will Berapakah wang yang akan diterima oleh peserta bertuah
receive RM111.00 and the last draw will be RM1 321.25. yang ke-6?
The amount of each draw after the first draw is obtained [2]
by adding a constant amount to the amount of the previous (d) What is the total amount received by
draw. Berapakah jumlah yang akan diterima oleh
Sejumlah RM74 477.00 akan diberikan secara tunai dalam (i) the first five lucky participants?
suatu cabutan bertuah. Peserta bertuah pertama akan menerima lima peserta bertuah pertama?
RM111.00 dan cabutan terakhir ialah RM1 321.25. Amaun (ii) the 10th to the 20th lucky participants?
setiap cabutan selepas cabutan pertama diperoleh melalui peserta bertuah ke-10 hingga ke-20?
penambahan satu amaun yang malar ke amaun cabutan [4]
sebelumnya. Ans: (a) 104
(a) How many lucky draw winners are there?
(b) RM11.75
Berapakah bilangan pemenang cabutan bertuah?
d.
(c) RM169.75
[2]
(d) (i) RM672.50; (ii) RM3 030.50
(b) Find the constant amount mentioned above.
Bh
Cari amaun yang malar yang dinyatakan di atas.
[2]
.
dn
HOTS Challenge
S
1. Find the number of the multiples of 7 between 80 and 259. HOTS Applying
Cari bilangan gandaan 7 di antara 80 dan 259.
gi
Answer Guide
an
Determine whether the sequence of the multiples of 7 is an arithmetic progression or a geometric progression.
Tentukan sama ada jujukan gandaan 7 ialah janjang aritmetik atau janjang geometri. Ans: 25
l
Pe
2. The numbers 1, q and r form an arithmetic progression and the numbers 1, q and r + 1 form a geometric progression. Find the
value of r where r is positive. HOTS Applying
Nombor-nombor 1, q dan r membentuk suatu janjang aritmetik dan nombor-nombor 1, q dan r + 1 membentuk suatu janjang geometri.
Cari nilai r dengan keadaan r adalah positif.
n
Answer Guide
ta
Use the concepts of common difference and common ratio.
Gunakan konsep beza sepunya dan nisbah sepunya. Ans: 3
bi
3. In a science exhibition, a volcanic eruption is demonstrated. The first eruption occurred 45 minutes after the exhibition opened.
r
The second eruption occurred 58 minutes after the exhibition opened and so on as shown below.
ne
Dalam suatu pameran sains, letusan gunung berapi didemonstrasikan. Letusan pertama berlaku 45 minit selepas pameran dibuka. Letusan
kedua berlaku 58 minit selepas pameran dibuka dan seterusnya seperti ditunjukkan di bawah.
Pe
45, 58, 71, 84, …
The exhibition has opened for 71 minutes. A tourist wishes to see the eruption and he takes 1 hour to reach the exhibition.
Upon reaching the exhibition, how long does he have to wait to see the next eruption? HOTS Analysing
Pameran itu telah dibuka selama 71 minit. Seorang pelancong ingin melihat letusan itu dan dia mengambil masa 1 jam untuk sampai ke
pameran itu. Selepas dia sampai, berapa lama dia perlu menunggu untuk melihat letusan itu?
Answer Guide
Determine first which eruption the tourist can see.
Tentukan dahulu letusan keberapa yang dapat dilihat oleh pelancong itu. Ans: 5 minutes
HOTS
81 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Answers
CHAPTER 5 Progressions 5. Let the smallest sector = T1 = a
and the largest sector = T5 = 9a
SPM Practice S5 = 360°
5
(a + 9a) = 360
n
Paper 1 Sn = 2 [a + l ]
2
10a = 144
1. a = 4, r = 8 = 2 a = 14.4
4
c = T5 Angle of the largest sector = 9 × 14.4
= ar 5–1
= 129.6°
= 4(2)4
d.
= 64
6. a = 5, r = 9
8
Bh
S10 = a[r – 1]
10
S4 = 4 [2a + (4 − 1)d] = 2
2. r–1
2
2a + 3d = 1 ......................a
5 9 –1
10
T6 = a + (6 – 1)d = −10 8 1 2
=
.
a + 5d = −10 ......................b 9 –1
dn
8
b × 2, 2a + 10d = −20 ......................c
= 89.89 minutes
c − a, 7d = −21
120 minutes 2 hours = 120 minutes
d = −3
S
Substitute d = −3 into a ∴ Mat qualified for the state level run.
2a + 3(−3) = 1
gi
2a = 10
7. Tn = arn – 1 = 5r , r ≠ 1
n–1
a = 5
4
an
(a) r ≠ 1, so k = 1
3. (a)
(7 – 2x)
= 1 (b) a = 5
4
l
(x – 1) 2
Pe
14 – 4x = x – 1
5x = 15 8. Tn = Sn – Sn – 1
x = 3 = n [15 – 7n] − n – 1 [15 – 7(n −1)]
2 2
n
T5 = ar5 – 1 = (x − 1)
(b) = 1 [15n – 7n2 – (n – 1)(22 – 7n)]
2
a 1 = 2
4
ta
2 1 2 = 1 [15n – 7n2 – (22n – 7n2 – 22 + 7n)]
a = 32 2
= 1 [−14n + 22]
bi
2
4. m, 3, n, … = 11 – 7n
(a) n = 3
r
3 m
ne
mn = 9
9. (a) T15 = 1 [6 + 5(15)]
a=m= 9 3
n = 27
Pe
r = n
3
(b) d = T15 − T14
(b) S∞ = a = 27 – 1 [6 + 5(14)]
1–r 3
9 = 27 – 76
3
n
= 5
1– n =
3
3
= × 3
9
n 3–n
27
=
n(3 – n)
1 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Answers
10. T3 = a + 2d = 22 .....................a 3. a = 3 500, d = −300, Tn = 500
T17 = a + 16d = −20 .....................b‚ Tn = a + (n – 1)d
b − a, 14d = −42 500 = 3 500 + (n – 1)(−300)
d = −3 300(n – 1) = 3 000
n – 1 = 10
Substitute d = −3 into a, n = 11
a + 2(−3) = 22
a = 28 Sn = n (a + l)
2
T8 = 28 + 7(−3) = 7
S11 = 11 (3 500 + 500)
2
11. Perimeter: 12 cm, 28 cm, 44 cm, … = 22 000
a = 12, d = 28 − 12 = 16 Total cost = 22 000 × RM0.50
Sn = 10.12 × 100 = RM11 000
n
[2(12) + (n − 1)(16)] = 1 012
d.
2 4. (a) (i) a = 5, d = 2, n = 48
n(12 + 8n – 8) = 1 012
4n + 8n2 = 1 012 Tn = a + (n − 1)d
Bh
n + 2n2 = 253 T48 = 5 + (48 – 1)(2)
2n + n – 253 = 0
2
= 99 cm
(n – 11)(2n + 23) = 0
∴ n = 11, n ≠ – 23 (ii) Sn = n (a + l)
2
.
2
dn
S48 = 48 (5 + 99)
2
Paper 2 = 2 496 cm
1. (a) a = −12, d = −15 − (−12) = −3
S
Tn × (1.6 × 100) = 14 880
(b)
(b) (i) S6 = 6 [2(−12) + (6 – 1)(−3)] Tn = 14 880
2 1.6 × 100
gi
= −117 5 + (n – 1)(2) = 93
(iii) S7 = 7 [2(−12) + (7 – 1)(−3)] n = 45
an
2
= −147 ∴ The 45th coloured rectangle has an area of 14 880 cm2.
The colour is yellow.
(c) T7 = S7 – S6
l
= −147 – (−117) 5. a = RM111.00,
Pe
= −30 l = Tn = RM1 321.25,
Sn = RM74 477.00
2. Sn = 3n(n – 31)
2 (a) Sn = n (a + l)
n
2
(a) S10 = 3(10)(10 – 31) 74 477.00 = n (111.00 + 1 321.25)
2
ta
2
= −315 n = 104
∴ There are 104 lucky draw winners.
bi
(b) T1 = S1 = 3(1)(1 – 31)
2
= −45 (b) Tn = a + (n − 1)d
r
1 321.25 = 111.00 + (104 – 1)d
S2 = 3(2)(2 – 31)
ne
d = RM11.75
2
= −87 ∴ The constant amount is RM11.75.
T2 = S2 – S1
Pe
(c) T6 = 111.00 + (6 – 1)(11.75)
= −87 – (−45)
= RM169.75
= −42
d = T2 – T1
= −42 – (−45) (d) (i) Sn = n [2a + (n − 1)d]
2
= 3
S5 = 5 [2(111.00) + (5 – 1)(11.75)]
∴ first term = −45, common difference = 3 2
= RM672.50
(c) Tr 0
a + (r – 1)d 0 S20 – S9 = 20 [2(111.00) + (20 – 1)(11.75)]
(ii)
−45 + (r – 1)(3) 0 2
(r – 1) 45 − 9 [2(111.00) + (9 – 1)(11.75)]
3 2
r 16 = 4 452.50 − 1 422
∴ r = 17 = RM3 030.50
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 2
Additional Mathematics Form 4 Answers
HOTS Challenge
3. …, 71, 84, …
1. 84, 91, 98, …, 252 a = 71, d = 84 – 71 = 13
a = 84, d = 7, Tn = 252
Tn = a + (n − 1)d Tn 71 + 60 1 hour = 60 minutes
252 = 84 + (n – 1)(7) a + (n – 1)d 131
n – 1 = 24 71 + (n – 1)(13) 131
n = 25 n 131 – 71 + 1
13
n 5.615
2. Common difference:
r − q = q − 1 T6 = 71 + (6 – 1)(13)
1 + r = 2q = 136
q = 1 + r The tourist has to wait [136 – (71 + 60)] = 5 minutes.
2
Common ratio:
d.
r + 1 = q
q 1
q2 = r + 1
Bh
q = √
r+1
1 + r = √r+1
2
.
dn
(1 + r)2 = r + 1
4
(1 + r)2 – 4(1 + r) = 0
(1 + r)(1 + r – 4) = 0
S
(1 + r)(r – 3) = 0
r = −1 or 3
gi
∴ r ≠ −1, r = 3
lan
Pe
n
ta
r bi
ne
Pe
3 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- Buff Dudes Mobility Band Workout PlanDocument80 pagesBuff Dudes Mobility Band Workout PlanLeandro Aisa75% (8)
- PTA3 PokedexDocument790 pagesPTA3 PokedexAllan ZistchmelNo ratings yet
- Design A New Style Suspension Linkage and Frame For A Full Suspension Mountain Bike For Banshee BikesDocument52 pagesDesign A New Style Suspension Linkage and Frame For A Full Suspension Mountain Bike For Banshee Bikeskeithmscott100% (3)
- Sequence and SeriesDocument34 pagesSequence and SeriesAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 ProgressionsDocument6 pages12 ProgressionschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Sequence, Series & ProgressionsDocument49 pagesSequence, Series & Progressionsadarshjha1812No ratings yet
- Progression Theory Module-1Document19 pagesProgression Theory Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Jee Mainsample Chapter Maths 11 Sequences and Series PDFDocument44 pagesJee Mainsample Chapter Maths 11 Sequences and Series PDFAditya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Allen: 6. Arithmetic ProgressionDocument3 pagesAllen: 6. Arithmetic ProgressionRitesh MalikNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths N Ch. 2Document5 pages10 Maths N Ch. 2clementjamesmannasNo ratings yet
- ProgressionsDocument8 pagesProgressionsAayush DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Maths Bridge Course Material - 23-24 (16 04 23)Document33 pages3 - Maths Bridge Course Material - 23-24 (16 04 23)Sasi SasiNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics ProgressionDocument23 pages10 Mathematics ProgressionKumarNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression - Short NotesDocument2 pagesArithmetic Progression - Short Noteschanmol12024No ratings yet
- Math - Series & SequencesDocument4 pagesMath - Series & Sequenceshelixate100% (4)
- Series Outline. Subtopic 1 Arithmetic Progressions (A.Ps) : Thiscanbe Writtenas (n+1)Document10 pagesSeries Outline. Subtopic 1 Arithmetic Progressions (A.Ps) : Thiscanbe Writtenas (n+1)Kateu victorNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: Chapter - 4Document13 pagesSequences and Series: Chapter - 4AnupNo ratings yet
- Ntse Mathematics SynopsisDocument32 pagesNtse Mathematics SynopsissrilathaNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: Chapter - 4Document13 pagesSequences and Series: Chapter - 4Ayush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sequence Finite Sequence Infinite Sequence Series: For ExampleDocument2 pagesSequence Finite Sequence Infinite Sequence Series: For ExampleNaresh bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sequences and SeriesDocument40 pagesSequences and SeriesExtra Marks100% (2)
- Mathematics Formulas CompleteDocument28 pagesMathematics Formulas CompleteMark Lester LindoNo ratings yet
- Sequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Document1 pageSequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Jaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionDocument3 pagesArithmetic ProgressionFarhad HossainNo ratings yet
- 0278 MathematicsDocument30 pages0278 MathematicsZarex BorjaNo ratings yet
- 8 Sequences and SeriesDocument37 pages8 Sequences and Seriestusharfiitjee80No ratings yet
- (6665) Sheet 1 Sequence and Series BDocument61 pages(6665) Sheet 1 Sequence and Series BSourabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionsDocument10 pagesArithmetic ProgressionsSiri SBNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series PDFDocument2 pagesSequence and Series PDFscribdNo ratings yet
- 03 Sequence - SeriesDocument19 pages03 Sequence - Seriesabenav05No ratings yet
- 11 - Sequences and Series NotesDocument20 pages11 - Sequences and Series NotesPranab PhagetraNo ratings yet
- 6322deec814cca0018591b2d - ## - Chapter 03 - Sequence and Series - Module PDFDocument39 pages6322deec814cca0018591b2d - ## - Chapter 03 - Sequence and Series - Module PDFAhaan ParasharNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SeriesDocument31 pagesSequence and SeriesSiddhanth VengaliNo ratings yet
- DGT Sequence and SeriesDocument60 pagesDGT Sequence and SeriesRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument8 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets Getmarks ApppranjalpandeyspNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionDocument6 pagesArithmetic ProgressionLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets Quizrrshivam tirmanwarNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series: 1 SequencesDocument7 pagesSequence and Series: 1 SequencesF20BA020Hafsa YounasNo ratings yet
- Progressions A.P, G.PDocument13 pagesProgressions A.P, G.PAnanth SureshNo ratings yet
- Concept Map APDocument1 pageConcept Map APApoorva Eliza JohnNo ratings yet
- 08 Sequence Series Revision Notes QuizrrDocument38 pages08 Sequence Series Revision Notes QuizrrDivyansh KaraokeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1SequenceSeriesiDocument7 pagesWorksheet 1SequenceSeriesiPhysics A1No ratings yet
- SNS SheetsDocument59 pagesSNS SheetsMOHD SARFARAZNo ratings yet
- Class-X Arithmetic ProgressionDocument34 pagesClass-X Arithmetic Progressionchintesh mehtaNo ratings yet
- @StudyTime - Channel Maths-7 PDFDocument8 pages@StudyTime - Channel Maths-7 PDFSipra PaulNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progressons (Part-1)Document16 pagesArithmetic Progressons (Part-1)shambhaviNo ratings yet
- Sequences-Series - Arithmetics and GeometricsDocument10 pagesSequences-Series - Arithmetics and GeometricsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 10.series and SequencesDocument7 pages10.series and SequencesWhatyoudoingNo ratings yet
- Class-X Arithmetic ProgressionDocument34 pagesClass-X Arithmetic ProgressionA. R.S TECHNo ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrShivek SinghalNo ratings yet
- 10 Series and SequencesDocument7 pages10 Series and Sequencespatrick clarkeNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Sequence and SeriesDocument18 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Sequence and SeriesAnweshMishraNo ratings yet
- APGP Series AP GP HP Progressions Handbook by CKDocument31 pagesAPGP Series AP GP HP Progressions Handbook by CKசரவணக்குமார் .பNo ratings yet
- 1979 15erdosDocument19 pages1979 15erdosvahidmesic45No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - SequenceDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 1 - SequenceZuriati SalehaNo ratings yet
- MAA HL Formula Booklet ExamDocument13 pagesMAA HL Formula Booklet Examnathan.kimNo ratings yet
- Sequence & Series (@BrilliantsAcademy)Document37 pagesSequence & Series (@BrilliantsAcademy)AHMMED AHMMEDNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus 86 122 PDFDocument37 pagesPre Calculus 86 122 PDFKheza SuravillaNo ratings yet
- Resource 1109Document2 pagesResource 1109jalpanapaul7430006148No ratings yet
- Harmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)From EverandHarmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)No ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap7Document17 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap7PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap4Document16 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap4PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2Document22 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2PK ChunNo ratings yet
- KSSM 3 in 1 f3 中文参考资料+配版练习 辅助本 ansDocument8 pagesKSSM 3 in 1 f3 中文参考资料+配版练习 辅助本 ansPK ChunNo ratings yet
- 2009 KS3 Maths Level 3-5 Paper 3 Calculator AllowedDocument28 pages2009 KS3 Maths Level 3-5 Paper 3 Calculator AllowedPK ChunNo ratings yet
- KS3 Mathematics SAT 2010 MarkschemeDocument96 pagesKS3 Mathematics SAT 2010 MarkschemePK ChunNo ratings yet
- Rohn #80 290' Guyed - Proposed Antenna - H MODDocument1 pageRohn #80 290' Guyed - Proposed Antenna - H MODJohn Neil MitraNo ratings yet
- AJSSM Children's Readiness For Learning Front Crawl Swimming by B A Blanksby, H E Parker, S Bradley and V OngDocument6 pagesAJSSM Children's Readiness For Learning Front Crawl Swimming by B A Blanksby, H E Parker, S Bradley and V Ongvohm28No ratings yet
- Fallout - Game DesignDocument17 pagesFallout - Game DesignAnonymous HNBHPdSbj100% (1)
- As Ve Sa Su Me Ra Ke: NavamsaDocument1 pageAs Ve Sa Su Me Ra Ke: NavamsaAstroAnudeepNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of RunningDocument19 pagesBiomechanics of RunningJaviera Paz VegaNo ratings yet
- Minor ClassificationDocument28 pagesMinor Classificationnofiya yousufNo ratings yet
- Psoas RehabDocument7 pagesPsoas Rehabmtemei4414No ratings yet
- CD NoDocument2 pagesCD Nohighlander_77No ratings yet
- Character Sheets MoonDocument4 pagesCharacter Sheets MoonGabriel Othero VedolinNo ratings yet
- 30 Natural Ways To Help Treat Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument12 pages30 Natural Ways To Help Treat Polycystic Ovary SyndromeArun AchalamNo ratings yet
- Mazda Bt50 WL C & We C Wiring Diagram f198!30!05l121Document1 pageMazda Bt50 WL C & We C Wiring Diagram f198!30!05l121staff055100% (1)
- Group 10 Steering Valve: 1. StructureDocument2 pagesGroup 10 Steering Valve: 1. StructureالمهندسوليدالطويلNo ratings yet
- 2023 ERCS Finding List A2-5Document4 pages2023 ERCS Finding List A2-5Khine ZinNo ratings yet
- Faction: Steppes TribesDocument5 pagesFaction: Steppes TribesBorchNo ratings yet
- Calgary Barbell 16 Week (Revised) LB + KGsDocument15 pagesCalgary Barbell 16 Week (Revised) LB + KGsMAJ FALLATANo ratings yet
- Rear Axle Shaft DesignDocument11 pagesRear Axle Shaft DesignSandeep Chauhan75% (4)
- Formula R1 Racing - Explosionszeichnungen Und Adapter PDFDocument9 pagesFormula R1 Racing - Explosionszeichnungen Und Adapter PDFIBC_TobiNo ratings yet
- Choose The CORRECT Words Present SimpleDocument2 pagesChoose The CORRECT Words Present SimpleAgustín EchevarríaNo ratings yet
- Codex Imperial Guard FAQ 5th EditionDocument3 pagesCodex Imperial Guard FAQ 5th EditionJohn McLeishNo ratings yet
- 4 Hour BodyDocument536 pages4 Hour BodyHa Ri85% (13)
- Effect of Weight On Stall SpeedDocument2 pagesEffect of Weight On Stall Speedpp2076No ratings yet
- X-Plorers RPG (Illustrated)Document40 pagesX-Plorers RPG (Illustrated)deathbydoughnut100% (1)
- Sargodha 5th Class Result 2014Document396 pagesSargodha 5th Class Result 2014DMO OFFICENo ratings yet
- Assistive DevicesDocument3 pagesAssistive DevicesKarina Bianca ColladoNo ratings yet
- Women's Health Australia - May 2017Document148 pagesWomen's Health Australia - May 2017Lucia Carolina Velasco Lopez100% (2)
- 5.56 NATO Duplication LoadsDocument4 pages5.56 NATO Duplication Loadswatch_sutNo ratings yet
- Ko and Dame Endgames Under Area Scoring: PrefaceDocument64 pagesKo and Dame Endgames Under Area Scoring: PrefaceFrédéric VieiraNo ratings yet