Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Food/Drugs Effect
Drug Food/Drugs Effect
Uploaded by
sadfg asdfg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThis document lists many common drug-drug and drug-food interactions that can affect medication absorption, metabolism, and effectiveness. Some key interactions include antipsychotics and antiparkinsons increasing anticholinergic effects, MAO inhibitors and tyramine-containing foods increasing risk of hypertension, ketoconazole absorption decreasing when taken with antacids, and grapefruit juice reducing metabolism of calcium channel blockers and statins. Proper medication administration and consideration of interactions is important for therapeutic effectiveness and safety.
Original Description:
Original Title
reviewer4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document lists many common drug-drug and drug-food interactions that can affect medication absorption, metabolism, and effectiveness. Some key interactions include antipsychotics and antiparkinsons increasing anticholinergic effects, MAO inhibitors and tyramine-containing foods increasing risk of hypertension, ketoconazole absorption decreasing when taken with antacids, and grapefruit juice reducing metabolism of calcium channel blockers and statins. Proper medication administration and consideration of interactions is important for therapeutic effectiveness and safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesDrug Food/Drugs Effect
Drug Food/Drugs Effect
Uploaded by
sadfg asdfgThis document lists many common drug-drug and drug-food interactions that can affect medication absorption, metabolism, and effectiveness. Some key interactions include antipsychotics and antiparkinsons increasing anticholinergic effects, MAO inhibitors and tyramine-containing foods increasing risk of hypertension, ketoconazole absorption decreasing when taken with antacids, and grapefruit juice reducing metabolism of calcium channel blockers and statins. Proper medication administration and consideration of interactions is important for therapeutic effectiveness and safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
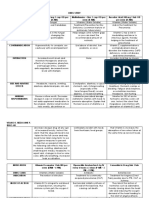
COMMON DRUG-DRUG and DRUG-FOOD INTERACTIONS
Drug Food/Drugs Effect
Antipsychotic + Antiparkinsons Antidepressant there is additive anticholinergic
effect, Anticholinergic effects:
Xerostomia. Constipation
Urinary Retention
Diphenhydramine Chlorphenamine Greater sedative side effect
MAO inhibitor Tyramine containing food Accumulation of Tyramine may
examples: pickled fish, cheddar lead to hypertension
cheese
Probenecid Penicillin Increase serum concentration of
Penicillin derivatives
Calcium Fluoroquinolones Floroquinolones are absorbed
poorly
Ketoconazole Antacid Decrease in absorption and
effectiveness of the antifungal
because Ketoconazole is best
absorbed in an acidic
environment
Bisacodyl Antacid Increase in pH may cause
disintegration of the enteric
coating and may cause gastric
irritation and vomiting
Tetracycline Metals There is low absorption of
Tetracycline due to
complexation
Tetracycline Mg, Al, Fe, Bi, Zn Antibacterial is absorbed poorly
Aluminum Hydroxide Doxycycline Decrease in absorption of
Doxycycline
Tetracycline Milk or Antacid Decrease amount of antibiotics
Doxycycline Iron It should be taken at least an
interval of 3 hours because there
is decrease in absorption of
Doxycycline
Fluoroquinolones Al and Mg Administer 4 hours before or 8
hours after meal
Captopril Food Decrease in the concentration of
captopril,
1 hour before meals
Alendronate and Resodronate Food Reduce bioavailability (use with
plain water only)
Acarbose and Miglitol Food First bite = maximum
effectiveness
Calcium Channel blockers and Grapefruit juice Reduce CYP450 particularly
Statins CYP3A4 therefore increase in
amount of unmetabolized and
increase serum concentration of
statins and calcium channel
blockers
Anticoagulant Antibiotics Increase anticoagulant effect
because of the interference of
Vitamin K production
Acetaminophen Alcohol At a high dose may lead to
COMMON DRUG-DRUG and DRUG-FOOD INTERACTIONS
hepatotoxicity
Disulfiram Warfarin and Phenytoin Enhance the activity of Warfarin
and Phenytoin because of
inhibition of enzyme
Digoxin Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Increase digoxin due to decrease
Tetracycline) bacterial flora therefore
decrease metabolism of Digoxin
therefore increase in serum
concentration of cardiac
glycoside (bacterial flora of the
intestine contributes to
metabolic process)
ASA Methotrexate Displacement of methotrexate
will increase MTX concentration
or may cause toxicity
Phenytoin Valproic Acid Displacement of Phenytoin will
result to increase in Phenytoin
concentration that may lead to
toxicity
Warfarin Phenobarbital Phenobarbital is an enzyme
inducer thereby increases the
metabolism and result in
decreased pharmacological
effect of Warfarin that may lead
to increase risk of thrombus
Oral contraceptives Phenobarbital, Rifampin Phenobarbital is an enzyme
inducer thereby increases the
metabolism and result in
decreased pharmacological
effect of Oral contraceptives that
may lead to unplanned
pregnancy
Alcohol Disulfiram Inhibits metabolism of alcohol
Cilostazol (anti-thrombotic) Diltiazem Diltiazem will increase the level
of Cilostazol by affecting enzyme
CYP3A4 metabolism
Digoxin Amiodarone increases the blood levels
of digoxin
Aspirin Clopidogrel can cause excessive bleeding
Aspirin Phenytoin, Valproic acid Increase anti- seizure level due
to protein binding displacement
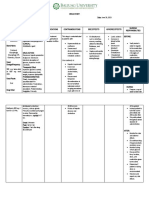
COMMON DRUG-DRUG and DRUG-FOOD INTERACTIONS
Drug Food/Drugs Effect
Ascorbic acid Antacid Ascorbic acid increases levels of
aluminum hydroxide by
enhancing GI absorption.
NSAIDs, including: Diuretics: Furosemide NSAIDS decrease effectiveness
Ibuprofen of diuretics
Naproxen
Acetaminophen Phenytoin May increase risk of
Acetaminophen toxicity
Loperamide Diphenhydramine May increase risk of severe
constipation
Dextromethorphan MAOIs Serotonin syndrome
(sweating, dilated pupils,
hyperthermia etc)
Dextromethorphan Sedatives or tranquilizers Increase sedation
Acetaminophen Aspirin Avoid prolonged concurrent use
of aspirin and acetaminophen, it
may increase risk of analgesis
nephropathy. (additive effects)
OVER THE COUNTER DRUGS
ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS
Drug A Drug B Effect
Metformin Cimetidine May increase Metformin levels
therefore there is a risk of
hypoglycemia
Metformin Glipizide Risk of hypoglycemia, synergistic
effect
Pioglitazone Metformin Decrease levels of both drugs
Metformin Food Reduce absorption of Metformin
Glipizide Metformin May increase risk of
hypoglycemia
Metformin Metoprolol May alter glucose metabolism.
Prolong hypoglycemia and mask
hypoglycemic symptoms.
Glipizide Metoprolol May alter glucose metabolism.
Prolong hypoglycemia and mask
hypoglycemic symptoms.
You might also like
- Nursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesDocument9 pagesNursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesGee Angela ZozobradoNo ratings yet
- Oet Sample SpeakingDocument84 pagesOet Sample Speakingissac jetto100% (5)
- MGH Handbook of Neurology 2ndDocument355 pagesMGH Handbook of Neurology 2nddoctorhousemedNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Prometric Examination PDFDocument155 pagesMCQs For Prometric Examination PDFYacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities in Administering Cardiovascular DrugsDocument76 pagesNursing Responsibilities in Administering Cardiovascular DrugsNikka Moreen Dagdag67% (6)
- Revision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFCattrainuhNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO DRUG INTERACTIONS-PHA 303 - DR Ogunleye - 1Document20 pagesINTRODUCTION TO DRUG INTERACTIONS-PHA 303 - DR Ogunleye - 1Ebenezer SamuelNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNo ratings yet
- 6 Antimicrobial 2Document6 pages6 Antimicrobial 2TMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Drug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheDocument34 pagesDrug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheBhavana GangurdeNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their AntidotesDocument6 pagesCommon Drugs and Their AntidotesShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- Drug Enutrient Interactions in Renal Failure: Raimund HirschbergDocument10 pagesDrug Enutrient Interactions in Renal Failure: Raimund Hirschbergiman prawiraNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument5 pagesAntidoteMaynard ArandaNo ratings yet
- Drug InteractionDocument42 pagesDrug InteractionVanita ValluvanNo ratings yet
- Combinations RationaleDocument4 pagesCombinations RationaleAida Tadal GalamayNo ratings yet
- Table of AntidotesDocument5 pagesTable of Antidotesangelotisbe1120No ratings yet
- Food Drug InteractionDocument29 pagesFood Drug InteractionmelodythNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- 5 6339302665821881285Document5 pages5 6339302665821881285Adrija SenNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Prospecto ReliveranDoxiDocument4 pagesProspecto ReliveranDoxiAldana BergesNo ratings yet
- Drug InteractionDocument21 pagesDrug Interactionكسلان اكتب اسميNo ratings yet
- Iron Preparations, Oral (Systemic)Document161 pagesIron Preparations, Oral (Systemic)vellisia secretNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRizza Jane Panit VelascoNo ratings yet
- Table Major Drug Interactions With AntimicrobialsDocument2 pagesTable Major Drug Interactions With AntimicrobialsYasmin ElsobkyNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFhassen zabalaNo ratings yet
- Anti - Diarrheal DrugsDocument5 pagesAnti - Diarrheal DrugsFitri NurullahNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionPiny CesarNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFAmirah AndresNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and AntidotesreynoldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 62 - Important Drug Interactions & Amp Their MechanismsDocument6 pagesChapter 62 - Important Drug Interactions & Amp Their MechanismstetsuroshiroxNo ratings yet
- Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesDrug InteractionsgirlwithbrowneyesNo ratings yet
- Prokinetics and LaxativesDocument2 pagesProkinetics and LaxativesPaul Francis UyNo ratings yet
- DrugsssDocument3 pagesDrugsssLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- m.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Document3 pagesm.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Dasha VeeNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument8 pagesAntidotedeanelaylayNo ratings yet
- Understanding Medical Surgical Nursing - 0833-0833Document1 pageUnderstanding Medical Surgical Nursing - 0833-0833Anas TasyaNo ratings yet
- DRUG INTRACTION (Hospital Pharmacy)Document23 pagesDRUG INTRACTION (Hospital Pharmacy)Alphahin 17No ratings yet
- Treatment of Peptic Ulcer: Dr.M.Purna Chandra Kala Professor DCMS, HydDocument35 pagesTreatment of Peptic Ulcer: Dr.M.Purna Chandra Kala Professor DCMS, HydGodishala Purna ChandrakalaNo ratings yet
- AntigoutDocument21 pagesAntigoutareebwaheedNo ratings yet
- 4853 Medication Worksheet: Student NameDocument8 pages4853 Medication Worksheet: Student Nameapi-546817891No ratings yet
- Ek Ah YG EIA: AlbuminDocument1 pageEk Ah YG EIA: AlbuminRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument1 pageOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (1)
- Drugs Food Drug-Food Interaction WarfarinDocument2 pagesDrugs Food Drug-Food Interaction WarfarinAsri YaniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMajo Coronel100% (1)
- Drugs Causing Lung Fibrosis: Toxin Treatment ParacetamolDocument93 pagesDrugs Causing Lung Fibrosis: Toxin Treatment ParacetamolTanveer SanaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1 Drug ListDocument20 pagesPharmacology Test 1 Drug ListSHRIKANTNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their Antidotes - PDF Version 1Document4 pagesCommon Drugs and Their Antidotes - PDF Version 1Maryam Khushbakhat50% (2)
- Chapter 67 - Important Drug Interactions & Amp Their MechanismsDocument25 pagesChapter 67 - Important Drug Interactions & Amp Their MechanismstetsuroshiroxNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NOt COmpleteDocument6 pagesDrug Study NOt COmpletejiellianemaeNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Fall 2023 Classification of MedicationsDocument6 pagesFall 2023 Classification of Medicationsramyharoon2004No ratings yet
- Drug Interactions in Dentistry: Iyad Abou Rabii DDS, Omfs, Mres, PHDDocument45 pagesDrug Interactions in Dentistry: Iyad Abou Rabii DDS, Omfs, Mres, PHDIyad Abou-Rabii100% (1)
- 7 Drug InteractionDocument8 pages7 Drug InteractionShoaib AliNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument19 pagesAsthmaSubhashreeswainNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease by ACC-1Document31 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease by ACC-1Prince PumuloNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Ms. IbaleDocument23 pagesDrugstudy Ms. IbaleNabor, MelagroseNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction: Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument49 pagesPharmacokinetic Drug Interaction: Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraSamuel TanNo ratings yet
- 1-Peptic UlcerDocument12 pages1-Peptic UlcerDAVID ULRICH DALLENo ratings yet
- Interaksi Obat - Farmakologi AfifahDocument42 pagesInteraksi Obat - Farmakologi AfifahShaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (I)Document12 pagesPharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (I)anaNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument15 pagesMetabolismnadila oktaviaNo ratings yet
- Systemic: Gastric Acidity in Water q4h Pregnancy and Lactation Use With Caution in Clients With Renal ImpairmentDocument6 pagesSystemic: Gastric Acidity in Water q4h Pregnancy and Lactation Use With Caution in Clients With Renal ImpairmentVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Sistem Gastrointestinal 1 - FiksDocument77 pagesFarmakologi Sistem Gastrointestinal 1 - FiksINDRINo ratings yet
- Heparin vs. WarfarinDocument1 pageHeparin vs. WarfarinSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Pharmacogenomics: Current Status and Future PerspectivesDocument13 pagesPharmacogenomics: Current Status and Future PerspectivesSergio VillicañaNo ratings yet
- DVT Blok 4.1Document67 pagesDVT Blok 4.1Dz Putra100% (1)
- 18 OctDocument82 pages18 OctAseel AlsheeshNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism in PregnancyDocument10 pagesVenous Thromboembolism in Pregnancydr.diverNo ratings yet
- Practical Tips For Warfarin Dosing and Monitoring PDFDocument11 pagesPractical Tips For Warfarin Dosing and Monitoring PDFNabilah MuhlisNo ratings yet
- Ifferences Between Warfarin and New Oral Anticoagulants in Dental Clinical PracticeDocument6 pagesIfferences Between Warfarin and New Oral Anticoagulants in Dental Clinical PracticeCezara PanainteNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document7 pagesJurnal 1Nur WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Brufen Sustained Release (SR) : Data SheetDocument11 pagesBrufen Sustained Release (SR) : Data SheetPrince Ali100% (1)
- Atrial FibrillationDocument19 pagesAtrial FibrillationAnwari MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal 2Document42 pagesCompetency Appraisal 2Frances Sofia DuranNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Disorders in PregnancyDocument20 pagesCoagulation Disorders in PregnancyHannaTashiaClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management of Warfarin and Antiplatelet TherapyDocument15 pagesPerioperative Management of Warfarin and Antiplatelet TherapyAfin Aslihatul Ummah100% (1)
- 0000Document135 pages0000Lizbeth Mar ToNo ratings yet
- Ati Final PharmDocument54 pagesAti Final PharmJohanna CruzNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Physical Therapists 04-08Document41 pagesPharmacology For Physical Therapists 04-08Johannes Purwanto0% (1)
- Venous DiseaseDocument45 pagesVenous DiseaseNinch Nagac100% (1)
- Nejmcp 2023658Document9 pagesNejmcp 2023658bbraitsilvaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacogenomicsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacogenomicssazaki224No ratings yet
- Efficacy of Feracrylum As Topical Hemostatic Agent in Therapeutically Anticoagulated Patients Undergoing Dental Extraction: A Comparative StudyDocument5 pagesEfficacy of Feracrylum As Topical Hemostatic Agent in Therapeutically Anticoagulated Patients Undergoing Dental Extraction: A Comparative StudyDr.Sudarsan SenNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Haematopoietic System of AnimalsDocument28 pagesDrugs Acting On Haematopoietic System of AnimalsSunil100% (1)
- DVT PreventionDocument8 pagesDVT PreventionRonald ThakorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Case StudyDocument8 pagesNursing Care Case StudyalexNo ratings yet
- Patient Warfarin Education Review 2005Document6 pagesPatient Warfarin Education Review 2005Mano cempakaNo ratings yet