Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsPossible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Uploaded by
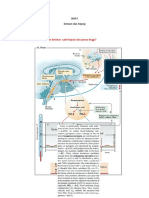
Hyacinth ManoodPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 4444vyuggewdffv PDFDocument1 page4444vyuggewdffv PDFMi-sun ParkNo ratings yet
- RNTCP Training Course For Program Manager Module 1 To 4Document208 pagesRNTCP Training Course For Program Manager Module 1 To 4Ashis DaskanungoNo ratings yet
- ObsGyne MCQ 5Document19 pagesObsGyne MCQ 5salamred100% (2)
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- CNS PathologyDocument10 pagesCNS Pathologysarguss1483% (6)
- PyomeningitisDocument54 pagesPyomeningitisRiya BagdiNo ratings yet
- Seizure Associated With Corona Virus Infection: Meiti Frida PERDOSSI Cabang PadangDocument23 pagesSeizure Associated With Corona Virus Infection: Meiti Frida PERDOSSI Cabang Padangzefri suhendarNo ratings yet
- BoeEoiATKXmvogGcWqYr1601439144 PDFDocument41 pagesBoeEoiATKXmvogGcWqYr1601439144 PDFsrisabrina christiaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Problems During The Covid19 Pandemic - Dr. Zamroni Afif, SP.S (K), M. BiomedDocument21 pagesSleep Problems During The Covid19 Pandemic - Dr. Zamroni Afif, SP.S (K), M. BiomedannnisaNo ratings yet
- PP MorbidityDocument65 pagesPP MorbidityRaymart MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Exámenes Auxiliares: NeurologíaDocument12 pagesExámenes Auxiliares: NeurologíaHugo CardenasNo ratings yet
- Neuro TraumaDocument13 pagesNeuro TraumaFikri IchsanNo ratings yet
- Mengapa Didapatkan Keluhan Sakit Kepala Dan Panas Tinggi?: LBM 5 Demam Dan KejangDocument14 pagesMengapa Didapatkan Keluhan Sakit Kepala Dan Panas Tinggi?: LBM 5 Demam Dan KejangVivie Tirany SoediroNo ratings yet
- UMNLand AHCDocument27 pagesUMNLand AHCdrmamodoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Trauma Medular Dra LucyDocument41 pagesTrauma Medular Dra LucySakuraclowNo ratings yet
- Unconscious and Comatose Patients DR Moses KazevuDocument17 pagesUnconscious and Comatose Patients DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Grand RevalidaDocument342 pagesGrand RevalidaJoeNo ratings yet
- Requirement in PathophysiologyDocument38 pagesRequirement in PathophysiologyckathreenahNo ratings yet
- Neimy Kuliah Cedera OtakDocument45 pagesNeimy Kuliah Cedera OtakCahya RamadhanNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument17 pagesMeningitisKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Monard Et Al-2022-Intensive Care MedicineDocument4 pagesMonard Et Al-2022-Intensive Care MedicinePaulHerreraNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Mental HealthDocument41 pagesInflammation and Mental HealthanindyaguptaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of MENINGITISDocument30 pagesPathogenesis of MENINGITISPrachi TeteNo ratings yet
- CNS Pathology SummaryDocument38 pagesCNS Pathology Summaryimeds100% (2)
- Acute CNS Infections in ChildrenDocument36 pagesAcute CNS Infections in ChildrenS P DigitalNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument15 pagesNeuro NotesClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationShafiq ZahariNo ratings yet
- CNS Demyelinating DisordersDocument8 pagesCNS Demyelinating DisordersRocky BhaiNo ratings yet
- Medicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument4 pagesMedicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromedinakarNo ratings yet
- Meningitis and Fractures Concept MapDocument4 pagesMeningitis and Fractures Concept MapNamayanja SumayiyahNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: Neonates (65)Document5 pagesMeningitis: Neonates (65)Eugina Naiborhu08No ratings yet
- Dugger 2017Document23 pagesDugger 2017andresNo ratings yet
- PHCP - Unit 5 - NEUROLOGIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERDocument10 pagesPHCP - Unit 5 - NEUROLOGIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERDuh realNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitisedrian02No ratings yet
- Critical Care Management of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: Dr. Hj. Liliriawati Ananta Kahar, SP - An, KICDocument28 pagesCritical Care Management of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: Dr. Hj. Liliriawati Ananta Kahar, SP - An, KICfirdainiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Cns InfectionDocument18 pagesEmerging Cns InfectionDedy SavradinataNo ratings yet
- Neurocognitive DisordersDocument85 pagesNeurocognitive Disordersadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- LEC 3 - Nerve, Neuromuscular and Muscle Disorders (Dr. Lim) PDFDocument101 pagesLEC 3 - Nerve, Neuromuscular and Muscle Disorders (Dr. Lim) PDFErald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Chediak Higashi Sydrome: Diseases of Immune DysregulationDocument2 pagesChediak Higashi Sydrome: Diseases of Immune DysregulationCarla García TorresNo ratings yet
- ObobDocument1 pageObobNikkie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Classification of NMD PDFDocument6 pagesEpidemiology and Classification of NMD PDFnita prmtasariNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Finaljustineneri324No ratings yet
- HIV-associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSDocument48 pagesHIV-associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSclaudio RivasNo ratings yet
- Fisiología Renal y Equilibrio ElectrolíticoDocument99 pagesFisiología Renal y Equilibrio ElectrolíticofvidalinostrozaNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Finals TheoryDocument27 pagesMedsurg Finals TheoryKAYE PAULINE SERVIDADNo ratings yet
- Synapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 2Document20 pagesSynapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 2bobobNo ratings yet
- Update On MSDocument46 pagesUpdate On MSMahabub Hossain KhanNo ratings yet
- Craig Smith MHS CVHD Seminar Feb 2019 FinalDocument53 pagesCraig Smith MHS CVHD Seminar Feb 2019 Finalp47547nyftNo ratings yet
- Dams - DVT (New)Document48 pagesDams - DVT (New)Msd KishorNo ratings yet
- Therapy of Migraine: An Overview: By-Parul Dixit Iind Trimester, M.Pharm (Pharmacology), SPTM, NmimsDocument29 pagesTherapy of Migraine: An Overview: By-Parul Dixit Iind Trimester, M.Pharm (Pharmacology), SPTM, NmimsParul DixitNo ratings yet
- Sni 13 431Document16 pagesSni 13 431dr.alfredodova19No ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyradiculoneuropathDocument13 pagesChronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathrafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- AAAA2Document142 pagesAAAA2Sruthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- To Neurology: Rini AndrianiDocument46 pagesTo Neurology: Rini Andrianiwaraney palitNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)Document24 pagesLABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)EllenNo ratings yet
- Sazgar CKD and Epilepsy 5 8 2020 v02 WM PWDocument13 pagesSazgar CKD and Epilepsy 5 8 2020 v02 WM PWDita Paramita HaryatiNo ratings yet
- Neurocritico Nuevos ParadigmasDocument16 pagesNeurocritico Nuevos ParadigmasAlessandraCervantesNo ratings yet
- Anti Nmdar EncephalitisDocument2 pagesAnti Nmdar EncephalitisbugogiNo ratings yet
- DEMENTIAAAADocument24 pagesDEMENTIAAAAOreoluwaNo ratings yet
- Intensive Management of Status EpilepticusDocument41 pagesIntensive Management of Status EpilepticussnyNo ratings yet
- 98419-Normal Aging and Brain Athropy - Meike VernooijDocument11 pages98419-Normal Aging and Brain Athropy - Meike Vernooijdrgaganwahi1971No ratings yet
- Hidden Disabilities and Conditions: Creating an Inclusive WorkplaceFrom EverandHidden Disabilities and Conditions: Creating an Inclusive WorkplaceNo ratings yet
- REPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Document126 pagesREPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Yogacharya Dr Ananda Balayogi BhavananiNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument9 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFadikaNo ratings yet
- The Natural Remedy HandbookDocument264 pagesThe Natural Remedy HandbookRoi Trawon100% (2)
- Avipattikar ChurnaDocument3 pagesAvipattikar ChurnadrbhaveshpNo ratings yet
- Daftar Inventaris Alat MedikDocument15 pagesDaftar Inventaris Alat MedikAnggi CimuikNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument126 pagesReferensiFatchul ChoiriNo ratings yet
- Q Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuieDocument6 pagesQ Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuiePhilippus Von HohenheimNo ratings yet
- Welcome To DR SarinDocument12 pagesWelcome To DR SarinDr SarinNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: B260: Fundamentals of NursingDocument31 pagesNutrition: B260: Fundamentals of NursingKACEMNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Resynchronization TherapyDocument3 pagesCardiac Resynchronization TherapyassumptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment / Tugasan NBNS1503 Trauma and Emergency Nursing September Semester 2021Document8 pagesAssignment / Tugasan NBNS1503 Trauma and Emergency Nursing September Semester 2021sitiNo ratings yet
- Group 11Document10 pagesGroup 11revamondalNo ratings yet
- Developmental DefectsDocument16 pagesDevelopmental DefectsdeenmNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Guide 31 Workplace Based AssessmentDocument21 pagesSession 5 Guide 31 Workplace Based AssessmentRiry AmbarsaryNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor and Postpartum CareDocument7 pagesStages of Labor and Postpartum CareAkash SamuelNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Principles of Pharmacology Mid-Term Exam February 24, 2005Document9 pagesAnswer Key: Principles of Pharmacology Mid-Term Exam February 24, 2005Toe PaingNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Consultation SydneyDocument5 pagesAyurveda Consultation SydneyAnand Singh ContentNo ratings yet
- CrohnsDocument19 pagesCrohnsLauren LevyNo ratings yet
- Drug Tariff Workshop 13-14 - StudentDocument10 pagesDrug Tariff Workshop 13-14 - StudentCrystal Sia Yiik SwanNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: PerfusionDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: PerfusionJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Candida Albicans Oral ThrushDocument8 pagesPrevention of Candida Albicans Oral ThrushZkdlin SpaceNo ratings yet
- Review of Aetiology and Management of Testicular Abscess and Case Reports On Testicle Sparing Management of Testicular AbscessDocument5 pagesReview of Aetiology and Management of Testicular Abscess and Case Reports On Testicle Sparing Management of Testicular AbscessBodat BodatsNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- McAndrew, Leske 2019Document17 pagesMcAndrew, Leske 2019Adriana SerratoNo ratings yet
- Borang LohhDocument22 pagesBorang LohhRezki RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Tuarissa Et - Al 2014Document16 pagesTuarissa Et - Al 2014Cho SarangNo ratings yet
- Nursing EssayDocument4 pagesNursing Essayapi-506167521No ratings yet
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Uploaded by
Hyacinth Manood0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Original Description:
For possible mechanism of relationship of mental illness and covid
Original Title
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis for the Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesPossible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Uploaded by
Hyacinth ManoodPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
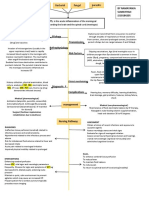
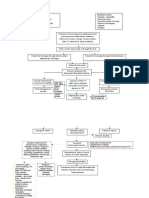
Possible mechanisms of pathogenesis for the neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19.
Mechanism of Details Neuropsychiatric effects
pathogenesis
• Exaggerated immune response • Encephalopathy
Direct injury (Blood • Cytokines increasing blood- • Delirium and acute
circulation) brain-barrier (BBB) confusional state
Koyuncu et al., 2013 Desforges et al.,
( ; permeability
2020
)
Direct injury (Neuronal • Predilection for olfactory • Anosmia
route) epithelium, bulb and vagal • Dysguesia
(Mori, 2015; Bohmwald et al., 2018) centers • Psychiatric disorders
• Anterograde and retrograde
neural proliferation via dynein
and kinesin
• Structural preference for the
forebrain, basal ganglia and
hypothalamus
Hypoxic injury • Impaired pulmonary exchange • Encephalopathy
(Abdennour et al., 2012; Guo et al., and pulmonary oedema can • Somnolence
2020
) cause cerebral hypoxia • Coma
• Cerebral oedema, vasodilation, • Headache
ischaemia and vascular • Confusion
congestion
• Increased intracranial pressure
Dysregulated • Cytokine storm (surge of • Encephalitis
immunomodulation peripheral IL-6,8,10,18, TNF- • MODS
Mechanism of Details Neuropsychiatric effects
pathogenesis
(Fu et al., 2020; Mehta et al., alpha, etc.) • Acute psychosis
2020 Wan et al., 2020
; ) • Systemic Inflammatory • Seizures
Response Syndrome (SIRS)
• Upregulation of
oligodendrocytes and astrocytes
(increased release of IL-15,
TNF-alpha)
• Leaky BBB
• Disturbed neurotransmission
Immune cell • Increased neuro-inflammation • Both acute and chronic
transmigration to CNS • Microglial activation neuropsychiatric effects
(Wohleb et al., 2015; Desforges et al., • Neural and glial cells as latent
2020
) ‘viral-carriers’
ACE-2 and CoV spike • Vascular and endothelial • Cerebro-vascular
protein interaction damage accidents
(Miller and Arnold, 2019; Wrapp et al., • Hyper-coagulability • Pulmonary and cerebral
2020
) • Increased blood-pressure venous
• Microangiopathy thromboembolism
• Risk of chronic
neurodegeneration
Autoimmunity • Molecular mimicry (cross- • Demyelination
(Kim et al., 2017; Rose, 2017) reaction of myelin, glia and • GBS
beta-2 glycoprotein with viral • Neuropathy
epitopes
Mechanism of Details Neuropsychiatric effects
pathogenesis
Miscellaneous • High ‘viral-latency’ in CNS • Persistent or relapsing-
(Reinhold and Rittner, 2017) • Lack of MHC in brain remitting neurological
• Homeostasis of neural issue sequelae
• Reactivation of seizures
• Chronic psychiatric
conditions
You might also like
- 4444vyuggewdffv PDFDocument1 page4444vyuggewdffv PDFMi-sun ParkNo ratings yet
- RNTCP Training Course For Program Manager Module 1 To 4Document208 pagesRNTCP Training Course For Program Manager Module 1 To 4Ashis DaskanungoNo ratings yet
- ObsGyne MCQ 5Document19 pagesObsGyne MCQ 5salamred100% (2)
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- CNS PathologyDocument10 pagesCNS Pathologysarguss1483% (6)
- PyomeningitisDocument54 pagesPyomeningitisRiya BagdiNo ratings yet
- Seizure Associated With Corona Virus Infection: Meiti Frida PERDOSSI Cabang PadangDocument23 pagesSeizure Associated With Corona Virus Infection: Meiti Frida PERDOSSI Cabang Padangzefri suhendarNo ratings yet
- BoeEoiATKXmvogGcWqYr1601439144 PDFDocument41 pagesBoeEoiATKXmvogGcWqYr1601439144 PDFsrisabrina christiaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Problems During The Covid19 Pandemic - Dr. Zamroni Afif, SP.S (K), M. BiomedDocument21 pagesSleep Problems During The Covid19 Pandemic - Dr. Zamroni Afif, SP.S (K), M. BiomedannnisaNo ratings yet
- PP MorbidityDocument65 pagesPP MorbidityRaymart MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Exámenes Auxiliares: NeurologíaDocument12 pagesExámenes Auxiliares: NeurologíaHugo CardenasNo ratings yet
- Neuro TraumaDocument13 pagesNeuro TraumaFikri IchsanNo ratings yet
- Mengapa Didapatkan Keluhan Sakit Kepala Dan Panas Tinggi?: LBM 5 Demam Dan KejangDocument14 pagesMengapa Didapatkan Keluhan Sakit Kepala Dan Panas Tinggi?: LBM 5 Demam Dan KejangVivie Tirany SoediroNo ratings yet
- UMNLand AHCDocument27 pagesUMNLand AHCdrmamodoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Trauma Medular Dra LucyDocument41 pagesTrauma Medular Dra LucySakuraclowNo ratings yet
- Unconscious and Comatose Patients DR Moses KazevuDocument17 pagesUnconscious and Comatose Patients DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Grand RevalidaDocument342 pagesGrand RevalidaJoeNo ratings yet
- Requirement in PathophysiologyDocument38 pagesRequirement in PathophysiologyckathreenahNo ratings yet
- Neimy Kuliah Cedera OtakDocument45 pagesNeimy Kuliah Cedera OtakCahya RamadhanNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument17 pagesMeningitisKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Monard Et Al-2022-Intensive Care MedicineDocument4 pagesMonard Et Al-2022-Intensive Care MedicinePaulHerreraNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Mental HealthDocument41 pagesInflammation and Mental HealthanindyaguptaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of MENINGITISDocument30 pagesPathogenesis of MENINGITISPrachi TeteNo ratings yet
- CNS Pathology SummaryDocument38 pagesCNS Pathology Summaryimeds100% (2)
- Acute CNS Infections in ChildrenDocument36 pagesAcute CNS Infections in ChildrenS P DigitalNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument15 pagesNeuro NotesClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationShafiq ZahariNo ratings yet
- CNS Demyelinating DisordersDocument8 pagesCNS Demyelinating DisordersRocky BhaiNo ratings yet
- Medicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument4 pagesMedicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromedinakarNo ratings yet
- Meningitis and Fractures Concept MapDocument4 pagesMeningitis and Fractures Concept MapNamayanja SumayiyahNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: Neonates (65)Document5 pagesMeningitis: Neonates (65)Eugina Naiborhu08No ratings yet
- Dugger 2017Document23 pagesDugger 2017andresNo ratings yet
- PHCP - Unit 5 - NEUROLOGIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERDocument10 pagesPHCP - Unit 5 - NEUROLOGIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERDuh realNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitisedrian02No ratings yet
- Critical Care Management of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: Dr. Hj. Liliriawati Ananta Kahar, SP - An, KICDocument28 pagesCritical Care Management of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: Dr. Hj. Liliriawati Ananta Kahar, SP - An, KICfirdainiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Cns InfectionDocument18 pagesEmerging Cns InfectionDedy SavradinataNo ratings yet
- Neurocognitive DisordersDocument85 pagesNeurocognitive Disordersadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- LEC 3 - Nerve, Neuromuscular and Muscle Disorders (Dr. Lim) PDFDocument101 pagesLEC 3 - Nerve, Neuromuscular and Muscle Disorders (Dr. Lim) PDFErald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Chediak Higashi Sydrome: Diseases of Immune DysregulationDocument2 pagesChediak Higashi Sydrome: Diseases of Immune DysregulationCarla García TorresNo ratings yet
- ObobDocument1 pageObobNikkie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Classification of NMD PDFDocument6 pagesEpidemiology and Classification of NMD PDFnita prmtasariNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Finaljustineneri324No ratings yet
- HIV-associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSDocument48 pagesHIV-associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSclaudio RivasNo ratings yet
- Fisiología Renal y Equilibrio ElectrolíticoDocument99 pagesFisiología Renal y Equilibrio ElectrolíticofvidalinostrozaNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Finals TheoryDocument27 pagesMedsurg Finals TheoryKAYE PAULINE SERVIDADNo ratings yet
- Synapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 2Document20 pagesSynapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 2bobobNo ratings yet
- Update On MSDocument46 pagesUpdate On MSMahabub Hossain KhanNo ratings yet
- Craig Smith MHS CVHD Seminar Feb 2019 FinalDocument53 pagesCraig Smith MHS CVHD Seminar Feb 2019 Finalp47547nyftNo ratings yet
- Dams - DVT (New)Document48 pagesDams - DVT (New)Msd KishorNo ratings yet
- Therapy of Migraine: An Overview: By-Parul Dixit Iind Trimester, M.Pharm (Pharmacology), SPTM, NmimsDocument29 pagesTherapy of Migraine: An Overview: By-Parul Dixit Iind Trimester, M.Pharm (Pharmacology), SPTM, NmimsParul DixitNo ratings yet
- Sni 13 431Document16 pagesSni 13 431dr.alfredodova19No ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyradiculoneuropathDocument13 pagesChronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathrafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- AAAA2Document142 pagesAAAA2Sruthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- To Neurology: Rini AndrianiDocument46 pagesTo Neurology: Rini Andrianiwaraney palitNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)Document24 pagesLABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)EllenNo ratings yet
- Sazgar CKD and Epilepsy 5 8 2020 v02 WM PWDocument13 pagesSazgar CKD and Epilepsy 5 8 2020 v02 WM PWDita Paramita HaryatiNo ratings yet
- Neurocritico Nuevos ParadigmasDocument16 pagesNeurocritico Nuevos ParadigmasAlessandraCervantesNo ratings yet
- Anti Nmdar EncephalitisDocument2 pagesAnti Nmdar EncephalitisbugogiNo ratings yet
- DEMENTIAAAADocument24 pagesDEMENTIAAAAOreoluwaNo ratings yet
- Intensive Management of Status EpilepticusDocument41 pagesIntensive Management of Status EpilepticussnyNo ratings yet
- 98419-Normal Aging and Brain Athropy - Meike VernooijDocument11 pages98419-Normal Aging and Brain Athropy - Meike Vernooijdrgaganwahi1971No ratings yet
- Hidden Disabilities and Conditions: Creating an Inclusive WorkplaceFrom EverandHidden Disabilities and Conditions: Creating an Inclusive WorkplaceNo ratings yet
- REPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Document126 pagesREPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Yogacharya Dr Ananda Balayogi BhavananiNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument9 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFadikaNo ratings yet
- The Natural Remedy HandbookDocument264 pagesThe Natural Remedy HandbookRoi Trawon100% (2)
- Avipattikar ChurnaDocument3 pagesAvipattikar ChurnadrbhaveshpNo ratings yet
- Daftar Inventaris Alat MedikDocument15 pagesDaftar Inventaris Alat MedikAnggi CimuikNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument126 pagesReferensiFatchul ChoiriNo ratings yet
- Q Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuieDocument6 pagesQ Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuiePhilippus Von HohenheimNo ratings yet
- Welcome To DR SarinDocument12 pagesWelcome To DR SarinDr SarinNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: B260: Fundamentals of NursingDocument31 pagesNutrition: B260: Fundamentals of NursingKACEMNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Resynchronization TherapyDocument3 pagesCardiac Resynchronization TherapyassumptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment / Tugasan NBNS1503 Trauma and Emergency Nursing September Semester 2021Document8 pagesAssignment / Tugasan NBNS1503 Trauma and Emergency Nursing September Semester 2021sitiNo ratings yet
- Group 11Document10 pagesGroup 11revamondalNo ratings yet
- Developmental DefectsDocument16 pagesDevelopmental DefectsdeenmNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Guide 31 Workplace Based AssessmentDocument21 pagesSession 5 Guide 31 Workplace Based AssessmentRiry AmbarsaryNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor and Postpartum CareDocument7 pagesStages of Labor and Postpartum CareAkash SamuelNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Principles of Pharmacology Mid-Term Exam February 24, 2005Document9 pagesAnswer Key: Principles of Pharmacology Mid-Term Exam February 24, 2005Toe PaingNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Consultation SydneyDocument5 pagesAyurveda Consultation SydneyAnand Singh ContentNo ratings yet
- CrohnsDocument19 pagesCrohnsLauren LevyNo ratings yet
- Drug Tariff Workshop 13-14 - StudentDocument10 pagesDrug Tariff Workshop 13-14 - StudentCrystal Sia Yiik SwanNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: PerfusionDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: PerfusionJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Candida Albicans Oral ThrushDocument8 pagesPrevention of Candida Albicans Oral ThrushZkdlin SpaceNo ratings yet
- Review of Aetiology and Management of Testicular Abscess and Case Reports On Testicle Sparing Management of Testicular AbscessDocument5 pagesReview of Aetiology and Management of Testicular Abscess and Case Reports On Testicle Sparing Management of Testicular AbscessBodat BodatsNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- McAndrew, Leske 2019Document17 pagesMcAndrew, Leske 2019Adriana SerratoNo ratings yet
- Borang LohhDocument22 pagesBorang LohhRezki RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Tuarissa Et - Al 2014Document16 pagesTuarissa Et - Al 2014Cho SarangNo ratings yet
- Nursing EssayDocument4 pagesNursing Essayapi-506167521No ratings yet