Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HapsariMutya - 12 Questions
HapsariMutya - 12 Questions
Uploaded by
hapsari mutya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesThis document summarizes several language teaching methods:
1. The goals of most methods are for students to be able to communicate in the target language. Direct Method and TPR focus on oral communication, while others like CLL also emphasize learning how to learn and take responsibility for their own learning.
2. The roles of teachers and students vary across methods. Some methods view the teacher as the authority and students as followers, while others see teacher and students as partners in the learning process.
3. Key aspects of the methods include how new vocabulary, grammar and structures are introduced - whether inductively or through translation, modeling, conversation practice, or other techniques. Most aim to reduce student stress and encourage persistence
Original Description:
Original Title
HapsariMutya_12 Questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes several language teaching methods:
1. The goals of most methods are for students to be able to communicate in the target language. Direct Method and TPR focus on oral communication, while others like CLL also emphasize learning how to learn and take responsibility for their own learning.
2. The roles of teachers and students vary across methods. Some methods view the teacher as the authority and students as followers, while others see teacher and students as partners in the learning process.
3. Key aspects of the methods include how new vocabulary, grammar and structures are introduced - whether inductively or through translation, modeling, conversation practice, or other techniques. Most aim to reduce student stress and encourage persistence
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesHapsariMutya - 12 Questions
HapsariMutya - 12 Questions
Uploaded by
hapsari mutyaThis document summarizes several language teaching methods:
1. The goals of most methods are for students to be able to communicate in the target language. Direct Method and TPR focus on oral communication, while others like CLL also emphasize learning how to learn and take responsibility for their own learning.
2. The roles of teachers and students vary across methods. Some methods view the teacher as the authority and students as followers, while others see teacher and students as partners in the learning process.
3. Key aspects of the methods include how new vocabulary, grammar and structures are introduced - whether inductively or through translation, modeling, conversation practice, or other techniques. Most aim to reduce student stress and encourage persistence
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
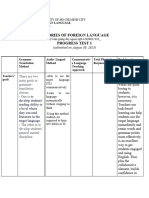
Name : Hapsari Mutya Rini
NIM/Class : 195300063/C-2019
Questions GTM DM ALM Silent Way Desuggestopedia CLL TPR
Teachers who use
CLL want their
students to learn
A TPR was
how to use the
fundamental Teachers who Students should Teachers hope to developed in order to
target language
purpose of use the Direct Teachers want be able to use the accelerate the reduce the stress
communicatively.
1. What are the goals of learning a Method intend their students to language for self- process by which people feel when they
In addition, they
teachers who use this language is to be that students be able to use the expression—to students learn to are studying other
want their students
method? able to read learn how to target language express their use another languages and thereby
to learn about their
literature written communicate communicatively thoughts, language for encourage students to
ow learning, to
in the target in the target . perceptions, and everyday persist in their study
take increasing
language. language. feelings. communication. beyond a beginning
responsibility for
level of proficiency.
it, and to learn how
to learn from one
another.
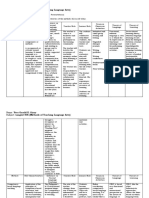
2. What is the role of the The roles are very The teacher and The teacher is The teacher is a The teacher is the The teacher’s The teacher is the
teacher? What is the traditional. The the students are like an orchestra technician or authority in the initial role is director of all student
role of the students? teacher is the more like leader, directing engineer. The classroom. primarily that of a behavior. The
authority in the partners in the and controlling teacher should counselor. It means students are imitators
classroom. The teaching– the language respect the The students will that the teacher of her nonverbal
learning process. behavior of her autonomy of the retain recognizes how model.
students do as she students. learners in their information better threatening a new
says so they can attempts at from someone in learning situation
learn what she Students are relating and whom they have can be for adult
knows. imitators of the interacting with confidence since Learners.
teacher’s model the new they will be
or the tapes she challenges. more responsive to Initially, the
The role of the
students is to
make use of what learners are very
they know, to free dependent upon the
themselves of any her ‘desuggesting’ teacher. It is
obstacles that their limitations recognized,
supplies of
would interfere and suggesting however, that as
model
with giving their how easy it the learners
speakers.
utmost attention to will be for them to continue to study,
the learning task, succeed. they become
and to actively increasingly
engage in independent.
exploring the
language.
In a beginning
class, which is
what we observed,
Grammar is students typically
New vocabulary Students begin
taught have a
and structural their study of the The course is
Students are inductively; that conversation using Lesson is one of
patterns are language through conducted in a
3. What are some taught to translate is, their native modeling,
presented its basic building classroom that is
from one the students are language. demonstrate.
characteristics of the through blocks, its bright and
language into presented with According to The teacher next
teaching/learning dialogues. The sounds. These are cheerful. Students
another. examples and Curran, there are recombines elements
process? dialogues are introduced select target
Students study they figure out six elements of the commands
learned through through a language names
grammar the rule or necessary for students perform, are
imitation and language-specific and choose new
deductively. generalization nondefensive often humorous.
repetition. sound–color chart. occupations.
from the learning (Security,
examples Aggression,
Attention,
Reflection,
Discrimination).
4. What is the nature of Most of the The initiation of There is student- setting up The teacher Students can learn The teacher interacts
student–teacher interaction in the the interaction to-student situations to ‘force initiates from their with the whole group
classroom is from goes both ways, interaction in awareness,’ interactions with interaction with of students and with
chain drills or
the whole group of
when students listening
students and with
take different attentively to
individuals right
roles in students’ speech,
the teacher to the from teacher to from the beginning each other as well
dialogues, but and silently
students. There is students and of a language as their interaction individual
interaction? What is this interaction is working with
little student from course. Initially, with the teacher. A students. Later on, the
the nature of student– teacher-directed. them on their
initiation and students to the students can spirit of students become more
student interaction? Most of the production
little student– teacher, although only respond cooperation, not verbal and the teacher
interaction is through the
student the latter is often nonverbally or competition, can responds nonverbally.
between teacher use of nonverbal
interaction. teacher-directed. with a few target prevail.
and students and gestures and the
language words
is initiated by the tools he has
they have
teacher. available.
practiced.
The teacher Indirect positive the teacher can
constantly suggestions are help them
There are no There are no Students not be
5. How are the feelings There are no observes the made to enhance overcome negative
principles of the principles of the too rushed either.
of the students dealt principles of the students. Also, students’ self- feelings
method which method that Feelings of success
with? method which students have an confidence and to that might
relate to this relate to this and low anxiety
relate to this area. opportunity to convince them that otherwise block
area. area. facilitate learning.
express success is their learning
how they feel. obtainable. (student security).
6. How is language Literary language Language is The view of Languages of the The culture which Language is for The oral modality is
viewed? How is is considered primarily spoken, language in the world share a students learn communication. primary. Culture is
culture viewed? superior to not written. Audio-Lingual number of concerns the Curran writes that the lifestyle of people
spoken language Method has been features. everyday life of ‘learning is who speak the
and is therefore influenced by However, each people who speak persons,’ meaning language natively.
the language the descriptive language also the language. The that both teacher
students study. linguists. Every has its own unique use of the fine arts and students work
Culture is viewed language is seen reality. is also important in at building trust in
as consisting of as having its own Their culture, as Desuggestopedia one another and the
literature and the unique system. reflected in their classes. learning
fine arts. The own unique world process. Culture is
system view, is an integral part of
comprises inseparable from language learning.
several different
levels:
phonological,
morphological, their language.
and
syntactic.
Since the sounds
are basic to any
Particular grammar
language,
points,
Vocabulary is pronunciation is
Vocabulary and pronunciation
emphasized over Vocabulary is worked on from
grammar are Speaking patterns, and
grammar. The kept to a the
emphasized. communicatively vocabulary are
reading and minimum while beginning. There
Reading and is emphasized. worked with, based
7. What areas of writing exercises the students are is also a focus on
writing are the Students also read on the language the
are based upon mastering the the structures of Vocabulary and
language are primary skills that in the target students have
what the students sound system the language, grammatical
emphasized? What the students work language generated. The
practice orally and grammatical although explicit structures are
language skills are on. There is much (for example, most important
first. patterns. A grammar rules emphasized over
less attention dialogues) and skills are
emphasized? Pronunciation grammatical may never be other language areas.
given to speaking write in it (for understanding and
also receives pattern is not the supplied.
and listening. example, speaking the
attention right same as a Vocabulary is
Pronunciation imaginative language at the
from the sentence. somewhat
receives little, if compositions). beginning, with
beginning restricted at first.
any, attention. reinforcement
of a course. There is no fixed,
through reading
linear, structural
and writing.
syllabus.
8. What is the role of the The language that The students’ The habits of the Meaning is made Native language Students’ security TPR is usually
students’ native is used in class is native language students’ native clear by focusing translation is used is initially introduced in the
language? mostly the should not be language are the students’ to make the enhanced by using students’ native
students’ native used in the thought to perceptions, not meaning of the their native language. Meaning is
language. classroom. interfere with the by translation. dialogue clear. The language. In a class made clear through
students’ teacher of the teacher also uses where the students body
attempts to target language. the native language speak a variety of movements.
native
languages,
master the target in class when conversations take
language. necessary. place right from
the start in the
target language.
Although no
Evaluation usually Teachers will know
particular mode of
is conducted on immediately whether
Students are The answer to evaluation is
Written tests in students’ normal or not students
asked to use the this question is prescribed in the
which students in-class understand by
language, not to not obvious Although the Community
are asked to performance and observing
demonstrate their because we teacher may never Language Learning
9. How is evaluation translate from not through formal their students’
knowledge about didn’t actually give a formal test, Method, teachers
accomplished? their native tests, which would actions. Formal
the language. observe the he assesses would encourage
language into the threaten the evaluations can be
They are asked to students in this student learning their students to
target language or relaxed atmosphere conducted simply by
do so, using both class taking a all the time. self-evaluate—to
vice versa are considered commanding
oral and written formal test. look at their own
often used. essential for individual students to
skills. learning and to
accelerated perform a series of
become aware of
learning. actions.
their own progress.
Student errors
are to be avoided
The teacher, if at all possible,
employing through the Student errors are Teachers should
the teacher
10. How does the teacher various teacher’s seen as a natural, Errors are work with what the Teachers should be
supplies the
respond to student techniques, tries awareness indispensable part corrected gently, learner has tolerant of them and
students’error
errors? to get students to of where the of the learning with the teacher produced in a only correct major
answer with the
self-correct students will process. using a soft voice. nonthreatening errors.
correct answer.
whenever have difficulty, way.
possible. and restriction of
what they are
taught to say.
11. Who is the initiator? Charles Fries
The German Karl Georgi Lezanov
Charles Berlitz (1945) & Caleb Gattegno Charles Curran James Asher (1977)
Potz (1819-1881) (1978)
Siknner (1957)
12. What learning theory
Behaviorism Behaviorism Behaviorsm Cognitivism Humanism Humanism Behaviorism
is adopted?
You might also like
- Descriptosaurus Supporting Creative Writing For Ages 8 14 Third EditionDocument331 pagesDescriptosaurus Supporting Creative Writing For Ages 8 14 Third EditionJoyce Chan100% (1)
- Action Plan On Reading Intervention For Strugling ReadersDocument3 pagesAction Plan On Reading Intervention For Strugling ReadersJenny Canoneo Getizo100% (1)
- DLL UCSP Aug 29-30Document2 pagesDLL UCSP Aug 29-30Aaron Zephyr100% (6)
- Clinical Field Experience B Schoolwide Budgetary NeedsDocument11 pagesClinical Field Experience B Schoolwide Budgetary Needsapi-520679261100% (1)
- Task 1 Part ADocument3 pagesTask 1 Part Arai hasnainNo ratings yet
- UASDocument7 pagesUASizzati annurNo ratings yet
- 1st Exam - EDENG 1Document3 pages1st Exam - EDENG 1Joy MagbutongNo ratings yet
- Approach ChartDocument5 pagesApproach ChartChagualo Alpargate LuisNo ratings yet
- Tugaskelompok2 EtmDocument5 pagesTugaskelompok2 Etmraudhatul munaNo ratings yet
- LLGDNN111Document6 pagesLLGDNN111Vi Dung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Activity 8Document1 pageActivity 8Mony MaxonNo ratings yet
- Questions The Silent Way Suggestopedia Community Lang Learning Total Physical ResponseDocument3 pagesQuestions The Silent Way Suggestopedia Community Lang Learning Total Physical ResponseNakı Dilber BüyükdağNo ratings yet
- Group FTCDocument12 pagesGroup FTCIsaías CarrascoNo ratings yet
- No. Approach/Method Personal Understanding About The Approach/Method The Implement in Class Techniques Under The Method/approachDocument7 pagesNo. Approach/Method Personal Understanding About The Approach/Method The Implement in Class Techniques Under The Method/approachIraRS 2No ratings yet
- Hapsari - 12 QuestionsUASDocument9 pagesHapsari - 12 QuestionsUAShapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Some Teaching MethodsDocument1 pageSummary of Some Teaching MethodsAsmaNo ratings yet
- Activity Methods - METHODOLOGY IDocument6 pagesActivity Methods - METHODOLOGY IGabby TituañaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Approaches and MethodsDocument9 pagesActivity 1 Approaches and MethodsClarice CalimpongNo ratings yet
- Goals of The Teacher: Grammar-Translation Direct MethodDocument5 pagesGoals of The Teacher: Grammar-Translation Direct MethodJESICAONo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods of English Language Teaching in One LookDocument7 pagesApproaches and Methods of English Language Teaching in One LookNina LynNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Teaching MethodsDocument3 pagesComparision of Teaching Methodsabdul haqNo ratings yet
- Almares - Maria Carmela - Methods of Language Teaching InfographicDocument7 pagesAlmares - Maria Carmela - Methods of Language Teaching Infographicaia.calmaresNo ratings yet
- Assessment GroupingDocument11 pagesAssessment Groupingapi-334275716No ratings yet
- Exploring Methods and Approaches in ELTDocument14 pagesExploring Methods and Approaches in ELTMary Jay Sismar - IsraelNo ratings yet
- METHODS - Language and Arts TeachingDocument25 pagesMETHODS - Language and Arts Teachingmapa.mjjdNo ratings yet
- Adopting Learning Strategies For English Language Acquisition OnDocument14 pagesAdopting Learning Strategies For English Language Acquisition OnRenabeth GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Direct MethodDocument9 pagesDirect MethodIoannes Amare Et ServireNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Teaching GrammarDocument11 pagesApproaches To Teaching Grammarトリガー マグナム100% (2)
- Fundamentos de Educación Pre-Básica T Chart TareaDocument4 pagesFundamentos de Educación Pre-Básica T Chart TareaJennifer SaucedaNo ratings yet
- Activities and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesActivities and-WPS OfficeMa Eloisa Juarez BubosNo ratings yet
- Critical Journal ReviewDocument5 pagesCritical Journal ReviewNurul YuniNo ratings yet
- MethodologiesDocument2 pagesMethodologiesHolly Sheríf-AlsammaniNo ratings yet
- Reading NotesDocument2 pagesReading NotesЕлизавета КонюховаNo ratings yet
- Psycolinguistics Use of LanguageDocument3 pagesPsycolinguistics Use of LanguageShirley MuñozNo ratings yet
- First Unit: Foreign Language Teaching MethodsDocument8 pagesFirst Unit: Foreign Language Teaching MethodsErika NataliapteNo ratings yet
- Name: Yves Gerald E. Giray Subject: Langlit 806 (Methods of Teaching Language Arts)Document8 pagesName: Yves Gerald E. Giray Subject: Langlit 806 (Methods of Teaching Language Arts)Yves GirayNo ratings yet
- ApproachesDocument2 pagesApproachesJoyce Joyería100% (1)
- Weekly Summary 2 (Presentation)Document26 pagesWeekly Summary 2 (Presentation)Nurmala HendrawatyNo ratings yet
- TableDocument2 pagesTableapi-458681444No ratings yet
- Characteristics and Principles of Communicative Language TeachingDocument1 pageCharacteristics and Principles of Communicative Language TeachingAcro BleedNo ratings yet
- ST - Ainun PratiwiDocument7 pagesST - Ainun PratiwiAinun PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingDocument32 pagesApproaches and Methods in Language TeachingFlorentina HijNo ratings yet
- Grid Methods Approaches Jeff ImbaquingoDocument5 pagesGrid Methods Approaches Jeff ImbaquingoJefferson IsraelNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Activity: History of Language Teaching Processing Time Methods/Approaches Advantages DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesModule 2 Activity: History of Language Teaching Processing Time Methods/Approaches Advantages DisadvantagesFaye Marie DegamoNo ratings yet
- Name: Cristy Ann V. Jayoma Date: July 22, 2021 Course: Educ - 207 Activity 2.1: Discuss The Criticisms Directed Towards GTM: Cite RRL To Support Your AnswerDocument3 pagesName: Cristy Ann V. Jayoma Date: July 22, 2021 Course: Educ - 207 Activity 2.1: Discuss The Criticisms Directed Towards GTM: Cite RRL To Support Your AnswerCristy Ann JayomaNo ratings yet
- ZikraDocument17 pagesZikraZikra MuktiNo ratings yet
- EL107 MIDTERM 2021 - PearlDocument3 pagesEL107 MIDTERM 2021 - PearlMay Pearl BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Teaching Vocabulaty and PronuntionDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Teaching Vocabulaty and PronuntionMarcela SarmientoNo ratings yet
- WPH002 - Ismael - AdditionalDocument7 pagesWPH002 - Ismael - Additionalkristine camachoNo ratings yet
- EXEMPLO Applicationofmemleticsandgrashariechmannlearingstyle-121122004758-Phpapp02 PDFDocument14 pagesEXEMPLO Applicationofmemleticsandgrashariechmannlearingstyle-121122004758-Phpapp02 PDFAmanda MunizNo ratings yet
- Methods and Approaches A ChartDocument3 pagesMethods and Approaches A ChartYasmin BgmNo ratings yet
- Teaching Methods Part 2Document29 pagesTeaching Methods Part 2No Creo Que A NadieNo ratings yet
- Hip Hip HoorayDocument9 pagesHip Hip Hoorayzhallahamed93No ratings yet
- Integrating Macro Skills (DAANOY and PLATON)Document4 pagesIntegrating Macro Skills (DAANOY and PLATON)Random BotNo ratings yet
- Teaching MethodsDocument2 pagesTeaching Methodsphuongquynhdth797No ratings yet
- Method Author Assumptions Methodology Roles Advantages DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesMethod Author Assumptions Methodology Roles Advantages DisadvantagesDenisse Flores MendozaNo ratings yet
- Approach, Method or Technique Targets Strengths Weaknesses ApplicabilityDocument7 pagesApproach, Method or Technique Targets Strengths Weaknesses ApplicabilityJay Rald SinampagaNo ratings yet
- Tefl Mapping 2 0044.tari Yulia Putri Tbi-B 4Document1 pageTefl Mapping 2 0044.tari Yulia Putri Tbi-B 4TariNo ratings yet
- CSTP 4 Walker 4Document7 pagesCSTP 4 Walker 4api-636156921No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document4 pagesLesson 2Lynou ZacalNo ratings yet
- LTM ClassDocument30 pagesLTM ClassJONATHAN BORGESNo ratings yet
- Group 11: Hapsari Mutya Rini (195300063) Sabana Rusdiyanti (195300029) Group Assignment of Direct MethodDocument3 pagesGroup 11: Hapsari Mutya Rini (195300063) Sabana Rusdiyanti (195300029) Group Assignment of Direct Methodhapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Hapsari C19 SentenceUtteranceSenseDocument2 pagesHapsari C19 SentenceUtteranceSensehapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Name: Hapsari Mutya Rini Class: C-19 NIM: 195300063 Language VariationDocument2 pagesName: Hapsari Mutya Rini Class: C-19 NIM: 195300063 Language Variationhapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Hapsari C19 Language VarietiesDocument2 pagesHapsari C19 Language Varietieshapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Hapsari C19 Summary Part 2Document2 pagesHapsari C19 Summary Part 2hapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Practices How To Write CitationsDocument3 pagesPractices How To Write Citationshapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Words and Its Forms: InflectionalDocument4 pagesSummary of Words and Its Forms: Inflectionalhapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Consequences For Not Doing Homework in High SchoolDocument5 pagesConsequences For Not Doing Homework in High Schoolafeusgqqj100% (1)
- Tutoring The Complete GuideDocument68 pagesTutoring The Complete Guideshamila3No ratings yet
- Kces Sip New FormatDocument20 pagesKces Sip New FormatJERALD HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- NITDA Report For IT in Schools Complete Compliance FrameworkDocument30 pagesNITDA Report For IT in Schools Complete Compliance FrameworkGabriel Inya-AghaNo ratings yet
- Lancaster Alex Resume 2020 1Document4 pagesLancaster Alex Resume 2020 1api-496200164No ratings yet
- Iasce Placement ManualDocument22 pagesIasce Placement Manualapi-238991913No ratings yet
- Grad PaperDocument10 pagesGrad Paperapi-675343232No ratings yet
- 2 - Critical Perspectives in English PDFDocument8 pages2 - Critical Perspectives in English PDFNayab AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1 Wednesday 1 Language Awareness Speaking People and CultureDocument1 page1 Wednesday 1 Language Awareness Speaking People and CultureTc NorNo ratings yet
- Finals Quiz Educ 8-Assessment of Student Learning 2Document9 pagesFinals Quiz Educ 8-Assessment of Student Learning 2Settie Ainah Sharief MaruhomNo ratings yet
- ConnectingClassroomstotheCommunity AGuideforCBEDocument196 pagesConnectingClassroomstotheCommunity AGuideforCBEWayaya2009No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Experts and Novice TeacherDocument20 pagesCharacteristics of Experts and Novice TeacherMrdvlvte TwnejmaNo ratings yet
- School Commitment MATATAGDocument46 pagesSchool Commitment MATATAGAlejandro Jr. Ricardo100% (1)
- Principles of Guidance and Values EducationDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Guidance and Values EducationLory Mae Alcosaba0% (1)
- UNIT 1 LESSONS 1-3 Preliminary Concepts, Basic Terminologies and Types of AssessmentDocument40 pagesUNIT 1 LESSONS 1-3 Preliminary Concepts, Basic Terminologies and Types of AssessmentCatherine Calata Dalafu - Tan100% (1)
- Action ResearchDocument2 pagesAction ResearchMARK LLOYD TINAMBACANNo ratings yet
- The Demands of Society From The Teacher As Professional 1Document8 pagesThe Demands of Society From The Teacher As Professional 1Dianne GomeraNo ratings yet
- EDFS 22 LEp 3Document4 pagesEDFS 22 LEp 3John Reign MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Prediger-Neugebauer2021 Article CapturingTeachingPracticesInLaDocument16 pagesPrediger-Neugebauer2021 Article CapturingTeachingPracticesInLaSadrack Luden PagilingNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Field Study 2Document9 pagesReviewer For Field Study 2leonardoalbor05No ratings yet
- Re Lesson Plan Pre-Primary/ PrimaryDocument5 pagesRe Lesson Plan Pre-Primary/ Primaryapi-426749233No ratings yet
- Worksheet Related LiteratureDocument21 pagesWorksheet Related LiteratureR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W6Document6 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W6Rucelle Mae Fernandez ArbolerasNo ratings yet
- Example Staff GuideDocument123 pagesExample Staff GuideAnees AhamedNo ratings yet
- Coyle 2018 PDFDocument12 pagesCoyle 2018 PDFMaria PsaltouNo ratings yet
- Exploring Teachers' Perceptions of OER in Higher Education Institutions: A Case Study of VietnamDocument9 pagesExploring Teachers' Perceptions of OER in Higher Education Institutions: A Case Study of VietnamIjahss JournalNo ratings yet
- The Speech Act of English Teacher in The ClassroomDocument14 pagesThe Speech Act of English Teacher in The ClassroomAshhabulKahfiNo ratings yet