Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guidelines For The Management of Serotonin Syndrome
Guidelines For The Management of Serotonin Syndrome
Uploaded by
Bianca CaterinalisendraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guidelines For The Management of Serotonin Syndrome
Guidelines For The Management of Serotonin Syndrome
Uploaded by
Bianca CaterinalisendraCopyright:
Available Formats
Guidelines for the management of serotonin syndrome
BACKGROUND
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition associated with increased serotonergic
activity in the central nervous system (CNS). It is seen with therapeutic medication use, inadvertent
interactions between drugs, and intentional self-poisoning. Although classically described as the triad of
mental status changes, autonomic hyperactivity, and neuromuscular abnormalities, serotonin syndrome
is actually a spectrum of clinical findings ranging from benign to lethal.
PRECIPTIANTS
A large number of medications either alone in high dose or in combination can produce serotonin
syndrome.
Antidepressants MAOIs, TCAs, SSRIs, SNRIs, trazodone and mirtazapine.
Opiates Pethidine, fentanyl, buprenorphine, oxycodone, tramadol.
CNS stimulants MDMA, phentermine, amphetamines, sibutramine, methamphetamine, cocaine
Herbs St John's Wort, ginseng, nutmeg
Others Valproate, buspirone, lithium, linezolid, chlorpheniramine, risperidone, olanzapine,
ondansetron, granisetron, metoclopramide.
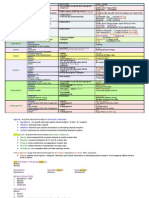
DIAGNOSIS (HUNTER CRITERIA)
Serotonergic agent
ingestion or overdose S
E
R
Yes
O
Spontaneous clonus
T
O
Agitation
No N
OR
Diaphoresis I
Yes OR Yes N
Inducible clonus
or Hypertonia
ocular clonus AND
Pyrexia > 38C S
Y
No No N
Yes Yes
Tremor Hyperreflexia D
R
O
M
No No
E
Not clinically significant serotonin toxicity
CLINICAL FEATURES & TREATMENT
Mild toxicity Moderate toxicity Severe toxicity
Anxiety Temperature 38 – 39.9 C Temperature > 40 C
Restlessness Tachycardia Tachycardia
Palpitations Diaphoresis Diaphoresis
Clonus Hypertension
Hyperreflexia Hyperreflexia
Agitated Hypertonicity
Hallucinations Mental obtundation
Treatment
Oral benzodiazepine Begin cooling measures Aggressive cooling
IV fluids – 1 to 2 litres IV fluids – 1 to 2 litres
IV benzodiazepine (repeat if req) IV benzodiazepine (repeat if req)
Cyproheptadine/chlorpromazine Consider RSI and paralysis
Cyproheptadine
Consider dantrolene
RSI AND SEROTONIN STNDROME
The following points should be considered:
Avoid opiates with intrinsic serotonergic activity
Avoid suxamethonuim due to hyperkalaemia
Rocuronium and atracurium are suitable muscle relaxants
SUPPORTIVE CARE
Supportive acre may be required for:
Pyrexia – cooled IV fluids, Bair Hugger set to ambient, ice packs etc. Paracetemol has no role as the
pyrexia is not hypothalamic in origin.
Hypoglycaemia
Hyperkalaemia
Rhabdomyolysis – consider 1.26% bicarbonate therapy
DRUG TREATMENT IN SEROTONIN SYNDROME
Cyproheptadine – 12mg PO/NG stat then 8mg every 6 hours. This is kept in the emergency pharmacy
room in the ACCU corridor
Chlorpromazine – 25mg IM
Diazepam – 10mg IV. Can be repeated. Large doses may be required.
Dantrolene – 1-2.5mg/kg. Can be repeated up to a maximum of 10mg/kg.
Authors - Dr Iain Lang, Dr Chris Lochrin
Publish date – December 2015. Revised -March 2019. Review date 01/04/2022
You might also like
- Chapter 3 - Drug Information ResourcesDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - Drug Information Resourcesreham O100% (1)
- Ten-Star Pharmacist-ConceptDocument45 pagesTen-Star Pharmacist-ConceptJape Garrido100% (2)
- Type Drug ChartDocument3 pagesType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- Nclex MedsssDocument6 pagesNclex MedsssSheryl_13No ratings yet
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialKawe IsamNo ratings yet
- Project RanbaxyDocument25 pagesProject RanbaxyJaimin ModiNo ratings yet
- Dispensing IIDocument6 pagesDispensing IIJvyn GamingNo ratings yet
- Atropine - Symptomatic BradycardiaDocument1 pageAtropine - Symptomatic BradycardiaSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Lipid Profile Normal Values Cardiac Enzyme Normal Values: ECG ChangesDocument3 pagesLipid Profile Normal Values Cardiac Enzyme Normal Values: ECG Changesairnyn_manzo08No ratings yet
- ToxicologyDocument7 pagesToxicologysaadalotaibi31No ratings yet
- Stroke Physician: Clinical Decision FormDocument6 pagesStroke Physician: Clinical Decision FormBaiq PritaNo ratings yet
- Antagonists Erses The Effects of Opioid Analgesics by Binding To The Opioid Receptors in The CNS, and IntravenousDocument3 pagesAntagonists Erses The Effects of Opioid Analgesics by Binding To The Opioid Receptors in The CNS, and IntravenousKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Antihistamines 2019 14 - 08 - 02Document9 pagesAntihistamines 2019 14 - 08 - 02Alexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Cough and Cold PrepDocument3 pagesCough and Cold PrepJOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- Effects: PharmacokineticsDocument7 pagesEffects: PharmacokineticsShiraz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- TryptophanDocument4 pagesTryptophanAmit AnirudhNo ratings yet
- Croup Clinical PathwayDocument8 pagesCroup Clinical PathwayMalak ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Common Abbreviations For The Patient Note USMLE Step 2CSDocument1 pageCommon Abbreviations For The Patient Note USMLE Step 2CSTiondi francisNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Family Practice DiagosesDocument6 pagesTop Ten Family Practice DiagosesKatrina HumphreyNo ratings yet
- Casualty Management PsychiatryDocument11 pagesCasualty Management PsychiatrySandesh VenuNo ratings yet
- Post Anesthesia Care Unit RecordDocument1 pagePost Anesthesia Care Unit RecordDamien Marwein100% (1)
- Drug of ChoiceDocument43 pagesDrug of ChoiceJanna mae PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Medicine HeadacheDocument12 pagesMedicine HeadacheKailash KhatriNo ratings yet
- Medication Worksheet: Citrus College Associate Degree NursingDocument5 pagesMedication Worksheet: Citrus College Associate Degree NursingRhonnie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: o No TX If AsymptomaticDocument3 pagesSinus Bradycardia: o No TX If Asymptomaticelle50% (2)
- ALSANGEDY BULLETS FOR PACES ChoreaDocument2 pagesALSANGEDY BULLETS FOR PACES ChoreasohailsuNo ratings yet
- Merged 2nd ShiftDocument198 pagesMerged 2nd Shiftreag0megaNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument12 pagesAntidepressantsMonica PaulNo ratings yet
- 1030amET PARAGON HF Acc 2020Document22 pages1030amET PARAGON HF Acc 2020Luis Rafael Suárez U.No ratings yet
- 14 Kuliah Kelainan Tiroid Semester 4Document53 pages14 Kuliah Kelainan Tiroid Semester 4hanifah ratna biranaNo ratings yet
- Stress Eco and Eco ReportDocument4 pagesStress Eco and Eco ReportguptarichaandassociatesNo ratings yet
- 02 Pre Anaesthesia Format UroDocument2 pages02 Pre Anaesthesia Format UroVHealthcare SolutionNo ratings yet
- Johns Hopkins PCRDocument1 pageJohns Hopkins PCRdandude505No ratings yet
- Anti HTN DrugsDocument1 pageAnti HTN DrugsDinesh Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensión Ese - Spin - Brochure - Rev. - 03 - LowDocument12 pagesHypertensión Ese - Spin - Brochure - Rev. - 03 - LowVICTOR losanNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Hernia: Case PresentationDocument28 pagesInguinal Hernia: Case Presentationchomz14No ratings yet
- Patient Report Sheet Fall 2023Document1 pagePatient Report Sheet Fall 2023Michelle DuBose AdamsNo ratings yet
- New Drugs 2017Document2 pagesNew Drugs 2017dupuytrenNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation - Carmen PartDocument4 pagesHydrogenation - Carmen Partbeo_bi_1No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Updated Algorithm For SS NMS ACS - DrawioDocument1 pageUpdated Algorithm For SS NMS ACS - DrawiorajvirNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument4 pagesShockKristine Violon SecorinNo ratings yet
- ACS Algorithm 2016 PDFDocument1 pageACS Algorithm 2016 PDFrabin1994No ratings yet
- Disorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NDocument41 pagesDisorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NBharath Kumar PamulapatiNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument29 pagesPsychotropic DrugsBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- ACLS AritmiaDocument18 pagesACLS AritmiaZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument4 pagesOlanzapineKhristle DavidNo ratings yet
- Mock Code Case ScenarioDocument4 pagesMock Code Case ScenarioRosalinda S CambriNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia2010 (2014 - 09 - 24 18 - 08 - 47 UTC)Document181 pagesHyponatremia2010 (2014 - 09 - 24 18 - 08 - 47 UTC)rnsharmasNo ratings yet
- PhychDocument30 pagesPhychRiya JaneNo ratings yet
- ANS DrugsDocument6 pagesANS DrugsRenad AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ni BeshDocument12 pagesDrug Study Ni BeshllianNo ratings yet
- CARBACHOLDocument5 pagesCARBACHOLJan Reginald TaboraNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Hypertension Sci PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithm Hypertension Sci PDFGustavo CabanasNo ratings yet
- DS Male SurgicalDocument6 pagesDS Male SurgicalErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyElva Borlado BilocuraNo ratings yet
- Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument10 pagesMedsurg 8 Cardiovascular MedicationsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- ToxidromesDocument2 pagesToxidromesAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument9 pagesAutonomic DrugscrayonNo ratings yet
- PREM AlgorithmsDocument20 pagesPREM AlgorithmsalexNo ratings yet
- 2 Types of SeizuresDocument1 page2 Types of SeizuresRatu PalarNo ratings yet
- Name of The Disease Defintion/Description of The Disease Name of The Drug Drug Use/IndicationDocument6 pagesName of The Disease Defintion/Description of The Disease Name of The Drug Drug Use/IndicationFrank Jomari MurilloNo ratings yet
- Advance Life Support MaterialDocument2 pagesAdvance Life Support MaterialmayNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument2 pagesPregnancyBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence of Schizophrenia in South Jakarta Administrative CityDocument10 pagesThe Prevalence of Schizophrenia in South Jakarta Administrative CityBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers For Macrosomia Prediction in Pregnancies Affected by DiabetesDocument25 pagesBiomarkers For Macrosomia Prediction in Pregnancies Affected by DiabetesBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Genetic and Neuroimaging CorrelatesDocument16 pagesTreatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Genetic and Neuroimaging CorrelatesBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Ijca 7 2 313 318Document6 pagesIjca 7 2 313 318Bianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Uterine Synechiae and Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument5 pagesUterine Synechiae and Pregnancy ComplicationsBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Resuscitation Interventions For.13Document8 pagesIntrapartum Resuscitation Interventions For.13Bianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Pandemic: What Are The Risks and Challenges For Schizophrenia?Document3 pagesCOVID-19 Pandemic: What Are The Risks and Challenges For Schizophrenia?Bianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Updates and New Options in Advanced Epithelial.14Document14 pagesUpdates and New Options in Advanced Epithelial.14Bianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnoses and Management Strategies in Patients With Schizophrenia and Bipolar DisorderDocument8 pagesDifferential Diagnoses and Management Strategies in Patients With Schizophrenia and Bipolar DisorderBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Epidural For Modified Radical Mastectomy in A High-Risk PatientDocument2 pagesThoracic Epidural For Modified Radical Mastectomy in A High-Risk PatientBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Complex Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Sources ofDocument9 pagesComplex Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Sources ofBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Administration of Epidural Labor Analgesia Is NotDocument6 pagesAdministration of Epidural Labor Analgesia Is NotBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- HK MJ 208944Document3 pagesHK MJ 208944Bianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Anesthesia For Ambulatory SurgeryDocument12 pagesReview Article: Anesthesia For Ambulatory SurgeryBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Anticipated Dif Ficult Airway During Obstetric General Anaesthesia: Narrative Literature Review and Management RecommendationsDocument17 pagesAnticipated Dif Ficult Airway During Obstetric General Anaesthesia: Narrative Literature Review and Management RecommendationsBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- 1 XXX 6Document105 pages1 XXX 6joelrequenaNo ratings yet
- Apixaban Uses, Side Effects & WarningsDocument5 pagesApixaban Uses, Side Effects & WarningspatgarettNo ratings yet
- FTI Consulting GlobalDocument2 pagesFTI Consulting GlobalHatomi ShibataNo ratings yet
- Reinventing Lean Six Sigma For Pharmacuticals IndustryDocument4 pagesReinventing Lean Six Sigma For Pharmacuticals IndustryMohdshariqNo ratings yet
- Voda Idea Breaches Loan Covenants: NPPA Allows 50% Price Hike For Three Key DrugsDocument20 pagesVoda Idea Breaches Loan Covenants: NPPA Allows 50% Price Hike For Three Key DrugsSatish WadawadagiNo ratings yet
- WhodunnitDocument15 pagesWhodunnitapi-328789300No ratings yet
- NAC Medications Chart 2016 A2Document1 pageNAC Medications Chart 2016 A2ayuniNo ratings yet
- CM-1092-01 - Module 07Document38 pagesCM-1092-01 - Module 07Hoa Linh GMPNo ratings yet
- Counter Transfer Vipin MishraDocument6 pagesCounter Transfer Vipin Mishravipin mishraNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustakasyra55No ratings yet
- TiotropiumDocument3 pagesTiotropiumLinto JohnNo ratings yet
- Detection of Vancomycin MIC by Agar Dilution in Clinical IsolateDocument11 pagesDetection of Vancomycin MIC by Agar Dilution in Clinical IsolateVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CST 363 Project Part 2Document9 pagesCST 363 Project Part 2api-479531624No ratings yet
- Jurnal TSF 1 - Pharmacopoeial Standards and Specifications For PDFDocument12 pagesJurnal TSF 1 - Pharmacopoeial Standards and Specifications For PDFAngelia Nuuril FahmiNo ratings yet
- Practice MCQs Sem VII Pharmaceutical Chemistry II CBCS With Answer KeyDocument6 pagesPractice MCQs Sem VII Pharmaceutical Chemistry II CBCS With Answer KeyDaya shankarNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Process of IPCA LABDocument44 pagesRecruitment and Selection Process of IPCA LABAnilGoyal100% (1)
- Preand Post IntegrityDocument29 pagesPreand Post IntegrityJaideep Katarey0% (1)
- Bài Tập Chuỗi Chuyển Hóa Hữu Cơ 1Document10 pagesBài Tập Chuỗi Chuyển Hóa Hữu Cơ 1Phạm HươngNo ratings yet
- MacCallum Russo Practical Considerations in Medical Cannabis Administrat...Document9 pagesMacCallum Russo Practical Considerations in Medical Cannabis Administrat...sl duoNo ratings yet
- 2016 Generic Pharmaceuticals Pricing Antitrust LitigationDocument243 pages2016 Generic Pharmaceuticals Pricing Antitrust LitigationAdam ForgieNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1.3.ophthalmic PreparationsDocument3 pages6.2.1.3.ophthalmic PreparationsRosnita Dewi RNo ratings yet
- Extraction Technologies For Medicinal and Aromatic PlantsDocument266 pagesExtraction Technologies For Medicinal and Aromatic PlantsOscar MirandaNo ratings yet
- Product BrochureDocument20 pagesProduct BrochureSiddhan100% (1)
- Production - Pharma Pathway PDFDocument7 pagesProduction - Pharma Pathway PDFDeepakNo ratings yet
- ZS Case Study Global Biopharma ForecastingDocument2 pagesZS Case Study Global Biopharma ForecastingNour GafarNo ratings yet